ORG BH CH 1- 6 Study Guide for EXAM 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is organizational behavior?
(Chapter 1)
the study of individual and group dynamics within an organization setting
Helps Managers:
PREDICT
MANAGE
Vertical Integration
(Chapter 1)
focuses on the continuum of care to meet the patient's full range of health needs
Horizontal Integration
(Chapter 1)
occurs through mergers, acquisitions, and/or consolidation within one segment of the industry
Virtual Integration
(Chapter 1)
emphasizes coordination of health care services through patient-management agreements, provider incentives, and/or information systems
What is Taylorism (Frederick Taylor)
(Chapter 1)
Believed that efficiency was achieved by creating jobs that economized time, human energy, and productive resources - put in the book The principles of Management
What is the Hawthorne Effect
(Chapter 1)
the bias that occurs when people know that they are being studied (know the 4 studies)
Illumination Experiments
(Chapter 1)
Conducted to determine whether increasing or decreasing lighting would lead to changes in productivity (both groups performed better bc they were being tested)
Relay-Assembly Experiment
(Chapter 1)
Productivity of a segregated group of workers was studied as they were subjected to different working conditions (performance maintained after good conditions were gone)
Bank-Wiring Observation
(Chapter 1)
Paid workers a piecework rate that reflected both group and individual efforts (showed that pay didn't matter)
Interviewing program
(Chapter 1)
Conducted to determine the employees' attitudes toward the company and their jobs
Theory X
(Chapter 1)
Negative/Pessimistic ; people are lazy and managers need to provide money or rewards to motivate them
Theory Y
(Chapter 1)
Positive/Optimistic;
People are motivated by satisfaction and self-esteem achieved from the work they do.
What is diversity?
(Chapter 2)
the full range of human similarities and differences in group affiliation including gender, race, social class, role, age, religion, sexual pref, physical ability, etc
Diversity Management
(Chapter 2)
A strategically driven process whose emphasis is on building skills and creating policies what will address the changing demographics of the workforce
What is cultural competence
(Borkowski CH 2)
The ongoing commitment or institutionalism of appropriate practices and policies for diverse populations
Goals of the commonwealth Fund?
(Borkowski CH 2)
Attempts to eliminate the cultural and linguistic barriers between health care providers and patients through five main goals
Key discoveries from the Kellogg Foundation
(Borkowski CH 2)
1) Racial & ethnic minority professionals are more likely to serve minority and medically under-served communities
2) Minority patients who have a choice are more likely to select providers with the same race/ethnic background
3) Diversity in healthcare training may assist in efforts to improve cross-cultural training
Culturally & Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS)
(Borkowski CH 2)
15 standards under 4 categories:
1) Principal Standard
2) Governance, Leadership, and Workforce
3) Communication & Language assistance
4) Engagement, Continuous Improvement, and Accountability
Alliance for Aging Research (Ageism)
(Borkowski CH 2)
Any attitude, action, or institutional structure, which subordinates a person or group because of age or any assignment of roles in society purely on the basis of age
Primary purpose of the Healthcare Equality Index (HEI)?
(Borkowski CH 2)
Provide equitable, inclusive care to LGBT Americans
4 Criteria:
1) Patient Nondiscrimination
2) Equal Visitation
3) Employment Nondiscrimination
4) Training in LGBT patient centered care
What is diversity management?
(Borkowski CH 2)
a strategically driven process whose emphasis is on building skills and creating policies that will address the changing demographics of the workforce and patient population
Healthcare Leadership Minority Composition
(Borkowski CH 2)
Minorities comprised of:
1) 14% - hospital board members
2) 12% - executive leadership positions
3) 17% - first/mid-level management
What is an "attitude"?
(Borkowski CH 3)
A mental or neural state of readiness, organized through experience, exerting a directive or dynamic influence on the individual's response to all objects and situations to which it is related
Typically invoked when we are "attempting" to explain behavior (e.g. positive vs negative attitude toward work, etc.)
How do you change attitudes?
(Borkowski CH 3)
Must address both cognitive and emotional components.
What are the three components on attitudes
(Borkowski CH 3)
1) Actions
2) Feelings
3) Beliefs
Cognitive Dissonance
(Borkowski CH 3)
A conflict between a person's attitude and their behavior (Alfred Adler)
Managing Cognitive Dissonance
(Borkowski CH 3)
1) Proactively attempt to re-balance feelings
2) Eliminate personal responsibility or control over the act or decision (washing your hands of it)
3) Denying, distorting or "selectively" forgetting information
4) Minimizing the importance of the issue, decision or act
5) Selecting new information that is consistent with an attitude or behavior
Forming Attitudes
(Borkowski CH 3)
The result of learning, modeling others' actions/attitudes, and experiences
Measuring Attitudes
(Borkowski CH 3)
Command Climate Surveys, Employee Satisfaction
What is perception?
(Borkowski CH 3)
The process by which organisms interpret and organize sensation to produce a meaningful expeirence of the world.
Four stages of perception
(Borkowski CH 3)
Stimulation
Registration
Organization
Interpretation
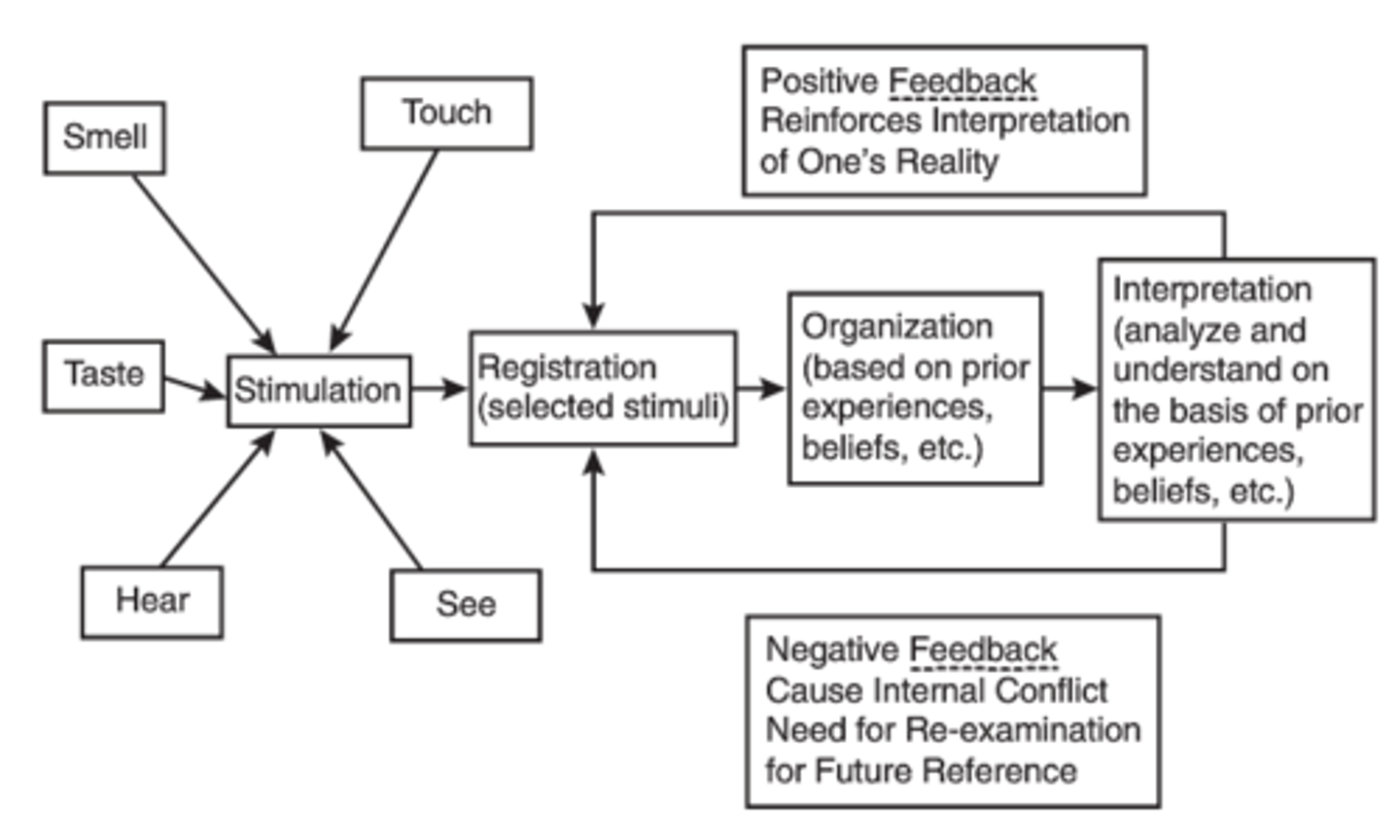
Type of perception:
(Borkowski CH 3)
1) Perceptual vigilance: selecting stimuli that satisfies immediate needs
2) Perceptual defense: disregard stimuli that may cause anxiety
3) Selective perception: limiting the processing of stimuli based on beliefs, attitudes, etc
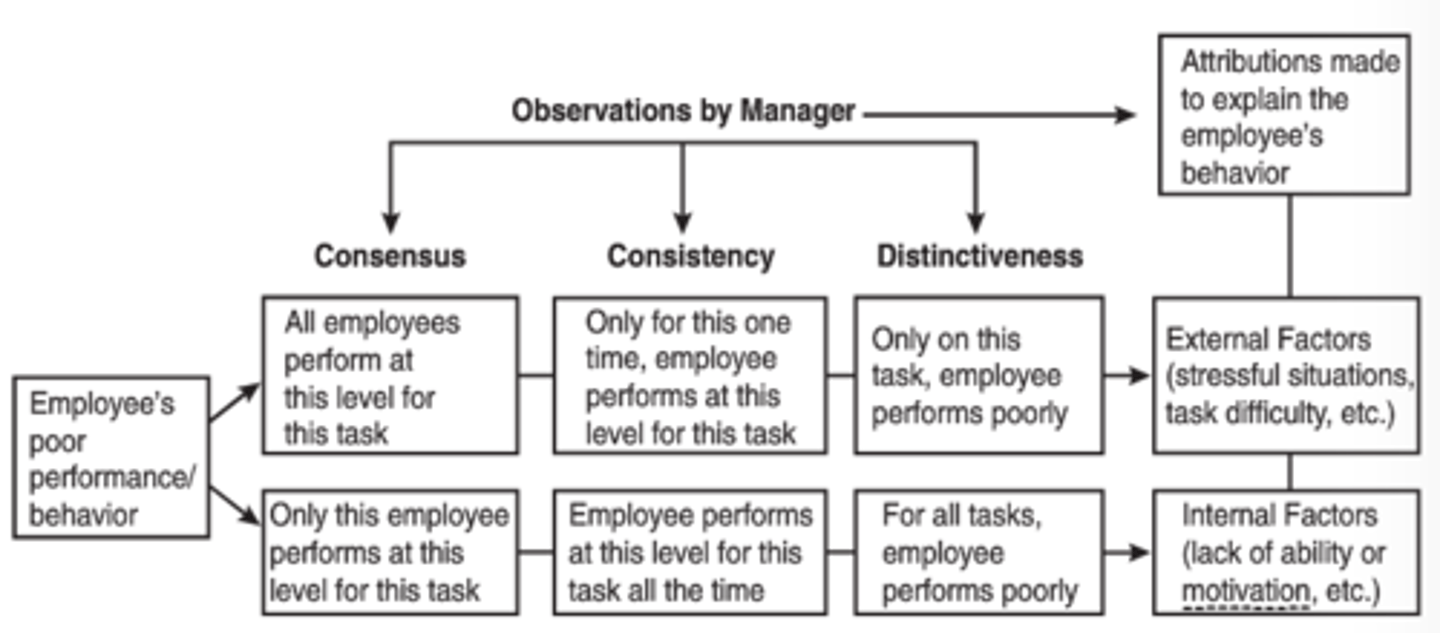
What is attribution theory?
(Borkowski CH 3)
Concept from social psychology that allows people to offer explanation for why things happen and is more concerned with the individual's cognitive perception than the reality of events.
Attribution Theory Model
(Borkowski CH 3)
How managers' perceive the actions of their subordinates.
Manager Observations:
-Consensus
-Consistency
-Distinctiveness
What is social perception
(Borkowski CH 3)
how an individual "sees" others and how others perceive an individual
Halo / Horn effect
(Borkowski CH 3)
judging someone based on a single characteristic
Contrast Effects
(Borkowski CH 3)
relate to an individual's evaluation of another person's characteristics who rank higher or lower than them
What is projection?
(Borkowski CH 3)
the attribution of one's own attitudes and beliefs onto others
Stereotyping
(Borkowski CH 3)
a conventional image applied to whole groups of people, and the treatment of groups according to a fixed set of generalized traits or characteristics.
What is the Pygmalion effect
(Borkowski CH 3)
Self-fulfilling prophecy; describes a person' behavior that is consistent with another individual's perception whether or not it is accurate.
Impression Management
(Borkowski CH 3)
a broad phenomenon in which we try to influence the perceptions and behaviors of others by controlling the information they receive
Goals of Employee Selection
(Borkowski CH 3)
1) Idenitfy the knowledge, skills, abilities, and qualities necessary to perform a job well
2) Design tests to measure applicants levels
3) Administer and score the tests
4) Determine the applicants most suitable for the position
Describe the communication process
(Borkowski CH 4)
S - Sender
M - Message
C - Channel (method)
R - Receiver
Effective commo occurs only when the message received is the same as the one intended
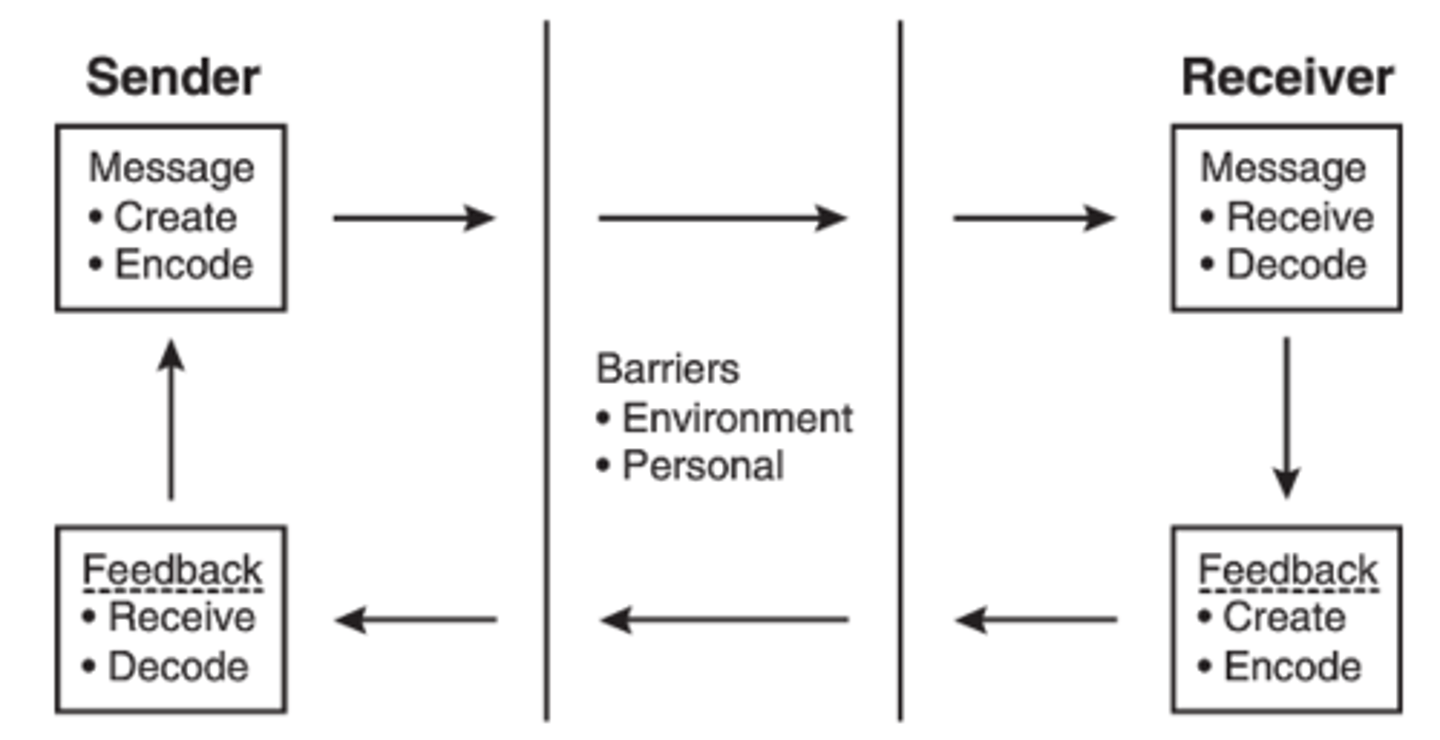
Barriers to communication
(Borkowski CH 4)
Environmental - time, heirarchy, philosophy, power, etc
Personal - beliefs, values, prejudices, jealousy, fear, etc
Types of Feedback
(Borkowski CH 4)
1) Descriptive: identifies or describes how a person communicates
2) Evaluative: provides an assessment of the person who communicates
3) Prescriptive: Provides advice about how one should behave or communicate
Four levels of feedback
(Borkowski CH 4)
Task or Procedural Feedback
Relational Feedback
Individual Feedback
Group Feedback
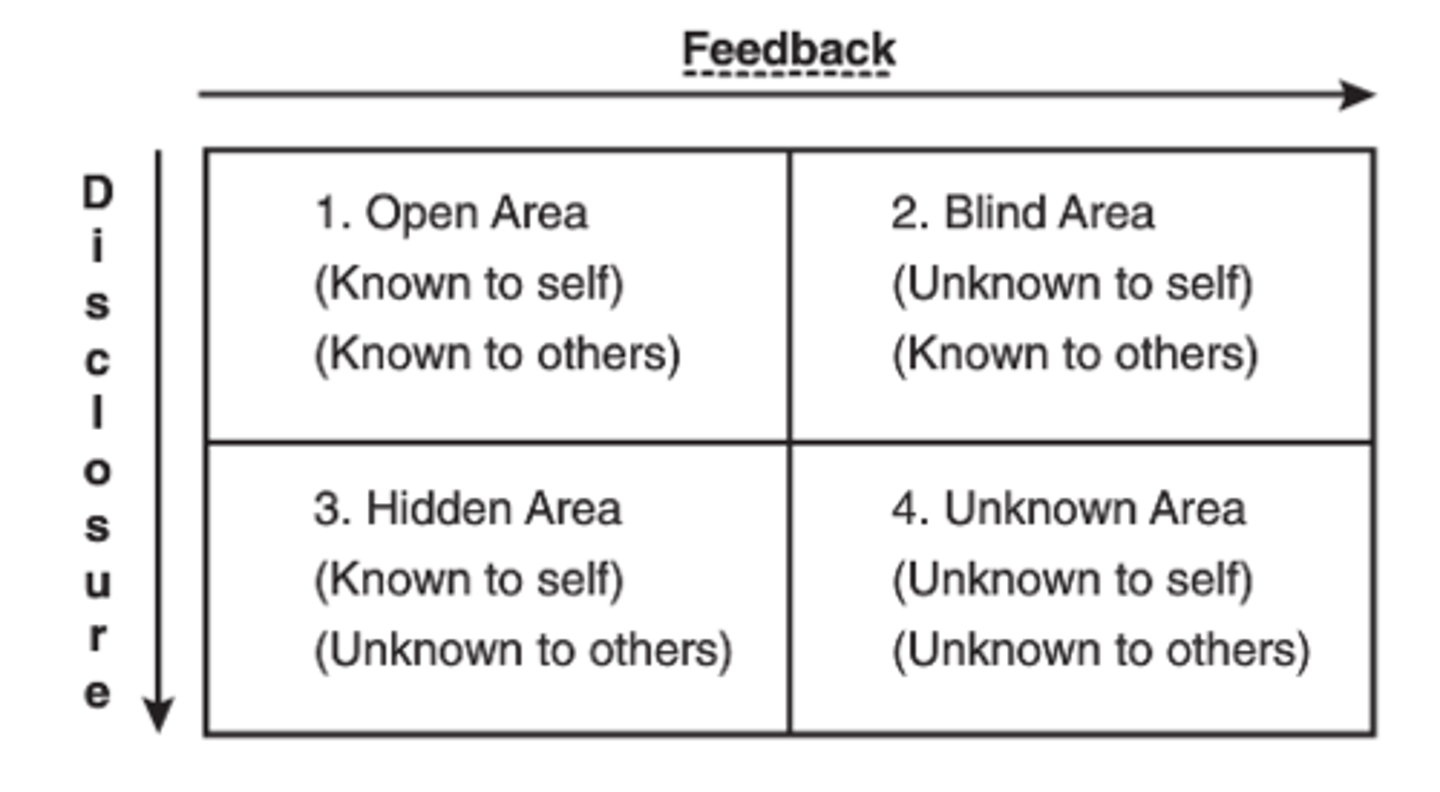
Key concepts of the Johari Window
(Borkowski CH 4)
1) you can build trust with others by disclosing information about yourself
2) with the help of feedback from others, you can learn more about yourself
Four basic forms of non-verbal communication
(Borkowski CH 4)
Mehrabian - very little of a message is conveyed in words - 55%
Four Basic Forms:
1) Proxemics - proximity
2) Kinesics - body language
3) Facial/eye Behavior
4) Paralangauge - voice quality/tone
Strategic Communication
(Borkowski CH 4)
Intentional process of presenting ideas in a clear, concise, and persuasive way
Two types of communciation networks
(Borkowski CH 4)
Centralized: Chain, Y, Circle, Wheel
Decentralized: Terrorist Cell
What is motivation?
(Borkowski CH 5)
The psychological process through which unsatisfied needs or wants lead to drives that are aimed at goals or incentives.
Two broad categories of motivation
(Borkowski CH 5)
Content Theories (what drives them)
Process Theories (How are they energized, sustained, stopped)
Mazlow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory
(Borkowski CH 5)
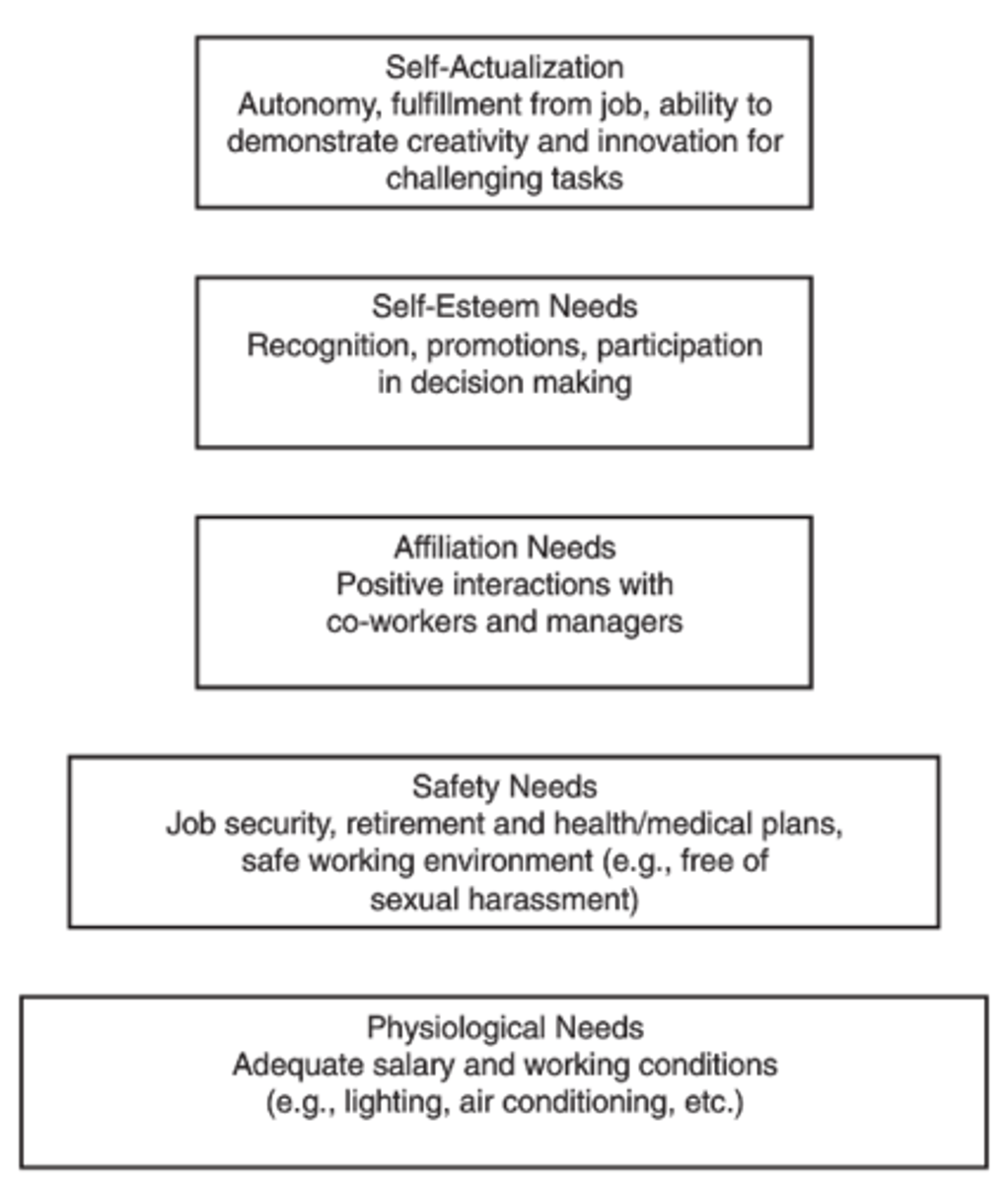
Alderfer's ERG Theory
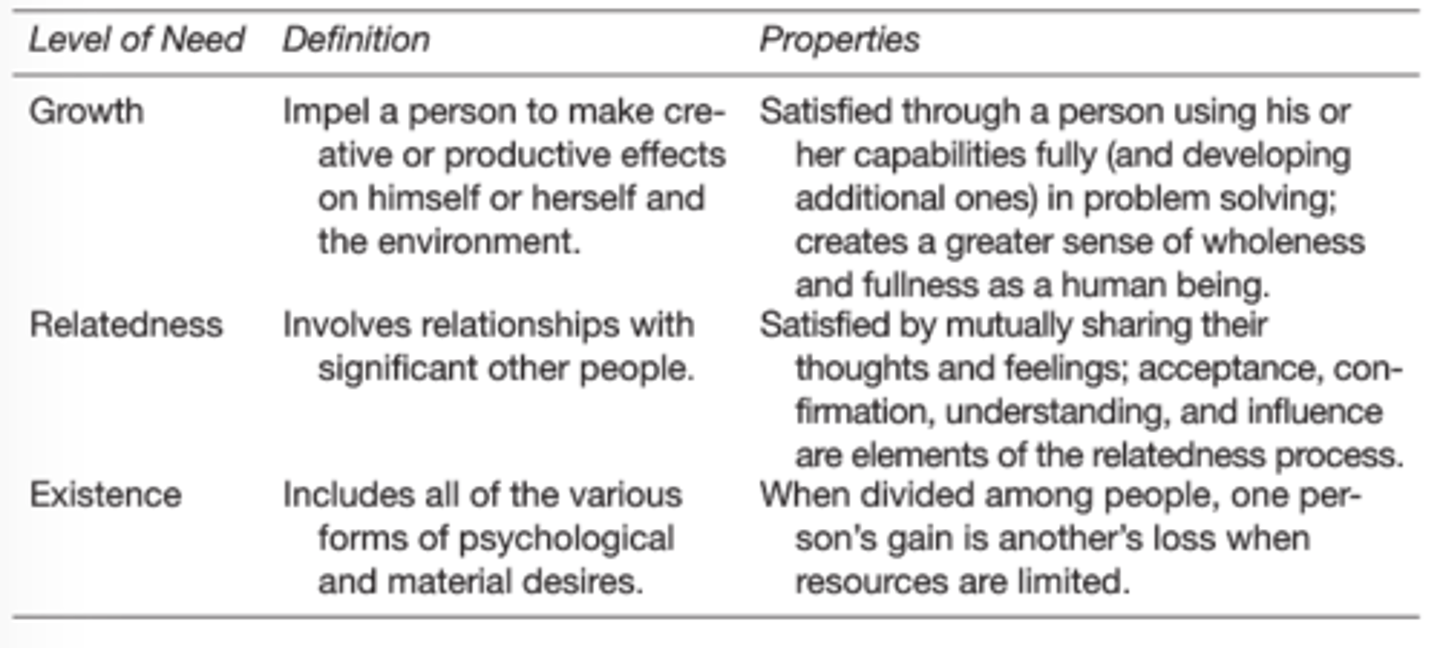
(Borkowski CH 5)
Differs by:
1) Allowing flexibility between needs
2) Accounts for differences in cultures
3) Frustration-Regression
---individual may regress to lower needs if they are frustrated with barriers at higher needs
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
(Borkowski CH 5)
People have two types of needs:
1) Avoidance of unpleasantness
2) Personal Growth
Motivators and Hygiene Factors
Opposite of dissatisfaction is no dissatisfaction not satisfaction (vice versa)
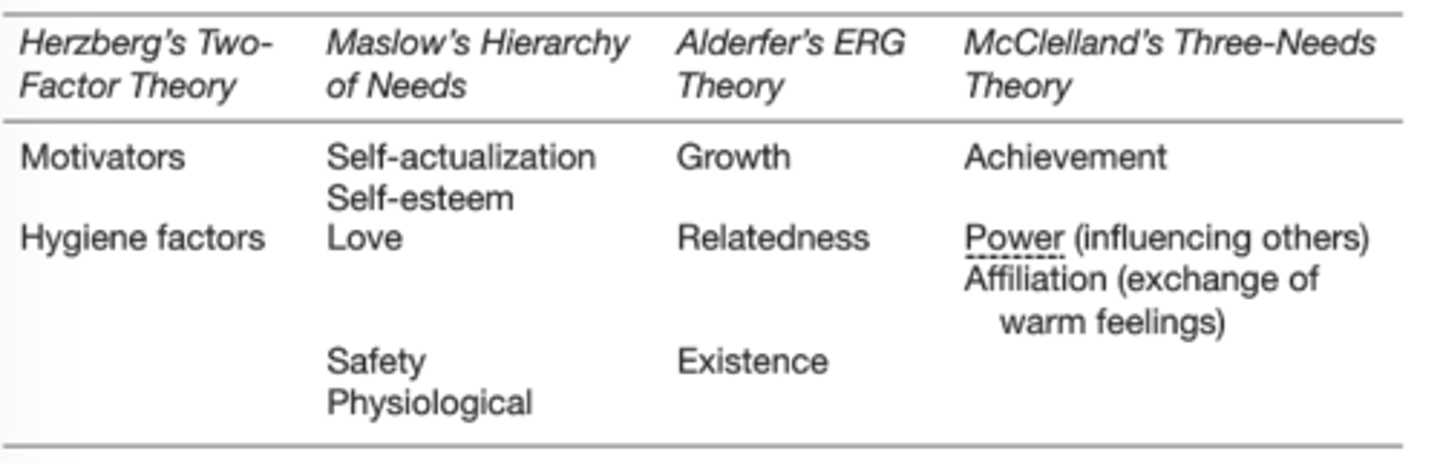
McClelland's Three-Needs Theory
(Borkowski CH 5)
Three needs:
1) Achievement
2) Power (influencing others)
3) Affiliation (exchange of warm feelings)
Comparison between models
(Borkowski CH 5)
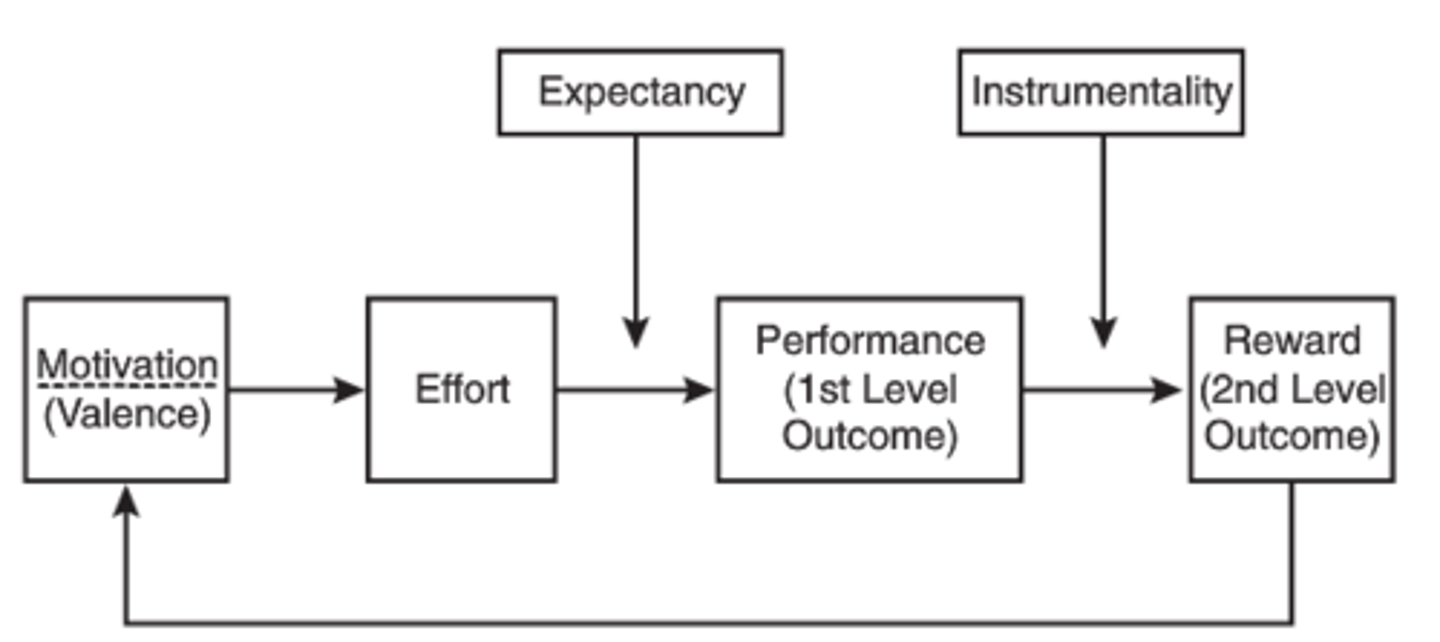
Victor Vroom's Expectancy (VIE) Theory
(Borkowski CH 6)
1) Valence - Strength for a certain outcome
2) Instrumentality - Perception that performance is related to the desired outcome
3) Expectancy - Perception that effort will positively influence performance
Newsome's 9Cs
(Borkowski CH 6)
Challenge
Criteria
Compensation
Capability
Confidence
Credibility
Consistency
Cost
Communication
Adam's Equity Theory
(Borkowski CH 6)
Proposes that person evaluates their outcomes and inputs by comparing them to those of others (think chips ahoy scenario)
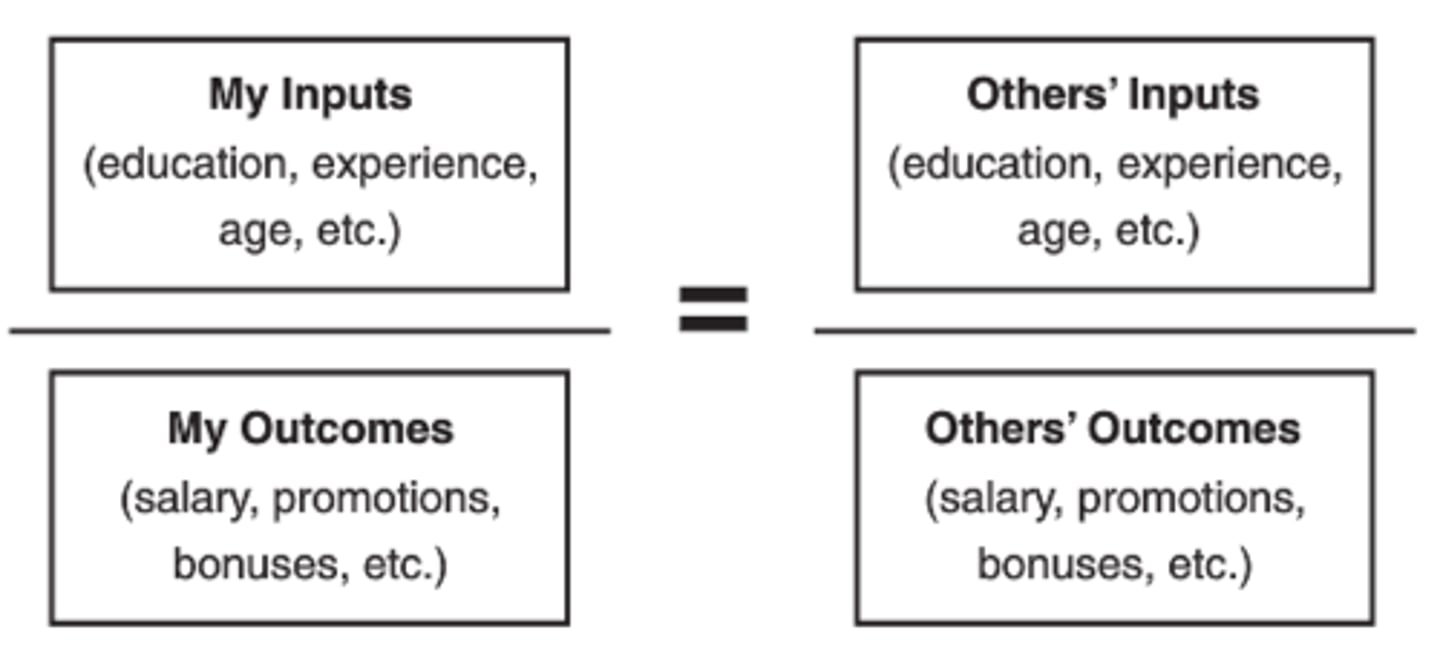
6 coping methods in equity theory
(Borkowski CH 6)
1) Altering Inputs - reduce productivity
2) Altering Outcomes - get a pay raise
3) Cognitively distorting Inputs or Outcomes (self) - I work harder then them
4) Leaving the Field - quit
5) Distorting the Inputs or Outcomes of the Comparison Other - their job is easy and routine
6) Changing the Comparison Other - find someone more like me
Porter and Lawler's Satisfaction-Performance Theory
(Borkowski CH 6)
Effort and performance are driven by satisfaction derived from both intrinsic and extrinsic rewards
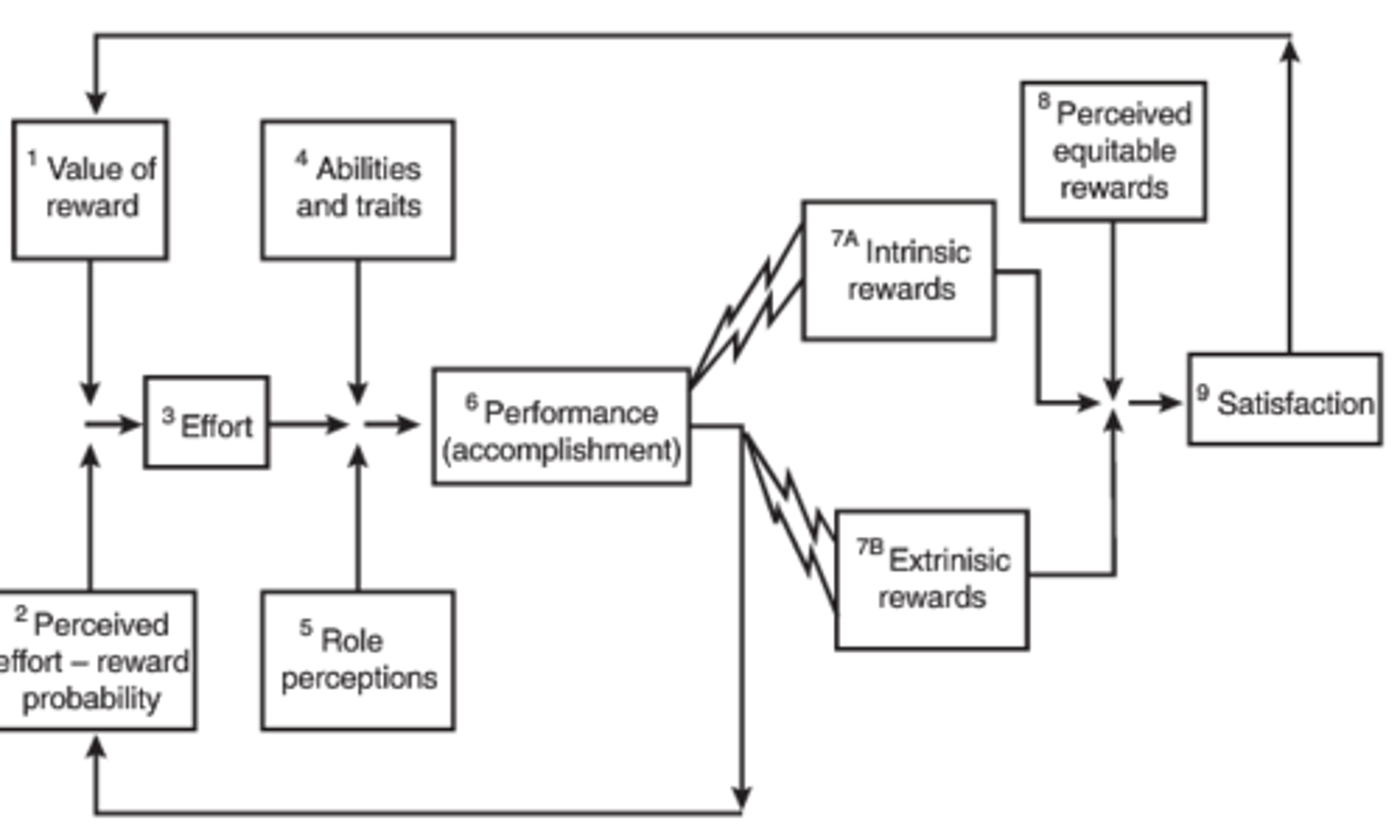
Latham and Locke's Goal-Setting Theory
(Borkowski CH 6)
Specific goals outperform "do your best"
3 Steps:
1) Setting the goal (specific and measurable)
2) Obtaining goal commitment
3) Providing Support Elements (adequate resources)
Skinner's Reinforcement Theory
(Borkowski CH 6)
Behavior can be redirected if it is associated with positive rewards (operant conditioning)
-More likely to repeated if outcome is good, less likely if outcome is bad (positive/negative reinforcement)