PBSI 302 Exam 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is a survey/poll?
a method of posing questions to people on the phone, in personal interviews, on written questionnaires, or online
"What can we do to improve this product?" is an example of what type of question format?
open-ended
"Which flavor do you prefer: chocolate or vanilla?" is an example of what type of question format?
Forced-choice
"On a scale of 1-5, 1 being strongly dissatisfied & 5 being strongly satisfied, how pleased are you with your job?" is an example of what type of question format?
Likert
"On a scale of 1-5, 1 being disgusting & 5 being amazing, how good is the food?" is an example of what type of question format?
Semantic
How do you differentiate between semantic and Likert questions?
- Likert measures a person's level of agreeableness by asking respondents to agree or disagree with a statement.
- Semantic measures the participant's attitude toward the object or concept on a continuum between the two adjectives by Asking respondents to rate an object or concept on a scale between two opposing adjectives.
"How much did you enjoy our fantastic event?" is an example of what type of ill-worded question?
Leading
- these types of questions have wording that LEAD people to a certain response
"Do you want coffee and breakfast?" is an example of what type of ill-worded question?
Double-barreled
- Complicated, asking two questions at a time
"Was the facility not unclean?" is an example of what type of ill-worded question?
Negatively worded
-contain negative phrasing or double-negative
"what is the most important problem facing the nation?" followed by a question about the president's job performance is an example of what type of ill-worded question?
Question order
- the earlier question can change the way respondents understand and answer later questions
Consistently choosing "agree" to every question on a survey, even if they don't truly agree with the statement, is an example of what type of response?
Response sets
Allows answering positively or "yes" is an example of what type of response?
acquiescence
Always responding "i don't know" or neutrally is an example of what type of response?
Fence sitting
- avoiding picking a side
Giving answers that make the participant look better than they really are is an example of what type of response?
Socially desirable/faking good
Giving answers that make them look worse than they are is an example of what type of response?
Faking bad
T/F: self-reporting are often inaccurate because there are limits to what people know about themselves
True
T/F: observations are better than self-report because they are not subject to memory failure, influenced by how a question is asked, social desirability and shortcuts.
True
when an observer sees what they want to see, this is called?
Observer bias
How do you fix observer bias?
- multiple trained observers
- codebook
Clever Hans (the horse) was able to do math by reading the body language of its owner for when it got close to the correct answer. how is the horse affecting the construct validity of observations?
Observer effect
- the horse is showing the owner what it wants to see
How do you fix masked/ blind bias?
-observers don't know which condition the participant has been assigned
- observer is not aware of what the study is about
The principal comes into the classroom to observe the classroom and students. When they come in, the students are on their best behavior. The presence of the principal affects what part of construct validity in observations?
Reactivity
- when participants react to being observed
How to fix reactivity?
- blend in
- wait it out
- measure behavior results (alcohol containers in the trash)
What is external validity?
whether the sample used in the study is adequate to represent the unstudied population
ALL the freshman at TAMU is an example of what?
Population
-entire set of people or things you are interested in
100 freshman currently enrolled at TAMU is an example of what?
Sample
- smaller set of people or things taken from the population
If you were to sample every freshman currently enrolled at TAMU then you are conducting a what?
Census
which sampling strategy involves using a random method so that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected?
Random sampling
Which assignment strategy is only used in experimental designs to assign participants to random groups?
Random assignment
___ is when not all members of a population have an equal probability of being included in the sample
Biased/ unrepresentative
____ is when all members of the population have an equal probability of being included in the sample
Unbiased/ representative
What type of sampling includes only those who are easy to contact?
convenience
what type of sampling includes only those who volunteer?
self-selection
What type of sampling involves putting every individual from your population of interest in a pool and then randomly selecting a predetermined number of individuals to include in your sample?
Simple Random Sampling
Which type of sampling involves populations being separated into groups, then one group is randomly selected and all participants in that group are used?
clustered
Which type of sampling involves populations being separated into groups, then one group is randomly selected and then everyone in that group is randomly sampled?
Multistage
Which type of sampling involves a multistage technique in which the researcher selects specific demographic categories and then randomly selects individuals from each category?
Stratified random sampling
___ is a variation of stratified random sampling in which a researcher over-represents one or more groups
Oversampling
Which type of sampling involves using a computer or a random number table to randomly select a starting point and an interval?
systemic sampling
When you want to study certain kinds of people and you only recruit those types of participants is called?
purposive sampling
When participants are asked to recommend other participants for the study, it is called?
Snowball sampling
when you identify a subset of the population set a target number for each category in the sample, and use nonrandom sampling until the targets are filled?
Quota sampling
what type of correlation involves exactly two measured variables in the same group of people?
Bivariate correlation
How should you graph an association when one variable is categorical?
Scatterplot or bar graph
How well was each variable measured? Does the measure have good reliability? Is it measuring what it's intended to measure?
These questions all measure what?
Construct validity of each variable
How well does the data support the conclusion?
This question is an example of what?
statistical validity
- How strong is the relationship? (effect size)
- How precise is the estimate?
- Has it been replicated?
- Could outliers be affecting the association?
- Is there a restriction of range?
- Is the association curvilinear?
___ describes the strength of an association
effect size
___ refers to the conclusion researchers make regarding how probable it is they would get a correlation of that size by chance, assuming that there is not a correlation in the real world
Statistical significance
___ provides info about statistical significance by evaluating the probability that the difference between groups in the sample came from a population where there are no differences between the group
Probability estimate (p-value)
An extreme score that lies far away from the rest of the scores is an?
outlier
When there is not a full range of scores on one of the variables in an association in a correlation study it is known as a?
restriction of range
When the correlation coefficient is zero or close to zero but the relationship between the two variables isn't a straight line is called?
Curvilinear association
__ is an association between the cause variable (A) and the effects variable (B)
Covariance
Deep talk is positively associated with well-being
When the causal variable (A) occurs before the effects variable (B) it is called?
Temporal precedence (directionality problem)
Deep-talk and well-being were measured at the same time
___ is when another variable (C) might be causing the relationship between variables A & B
Internal validity (Third-variable problem)
The association between deep talk and well-being could be attributed to some third variable
How well the data represents the general population is known as?
External validity
- SIze of sample does not matter as much as How sample was selected
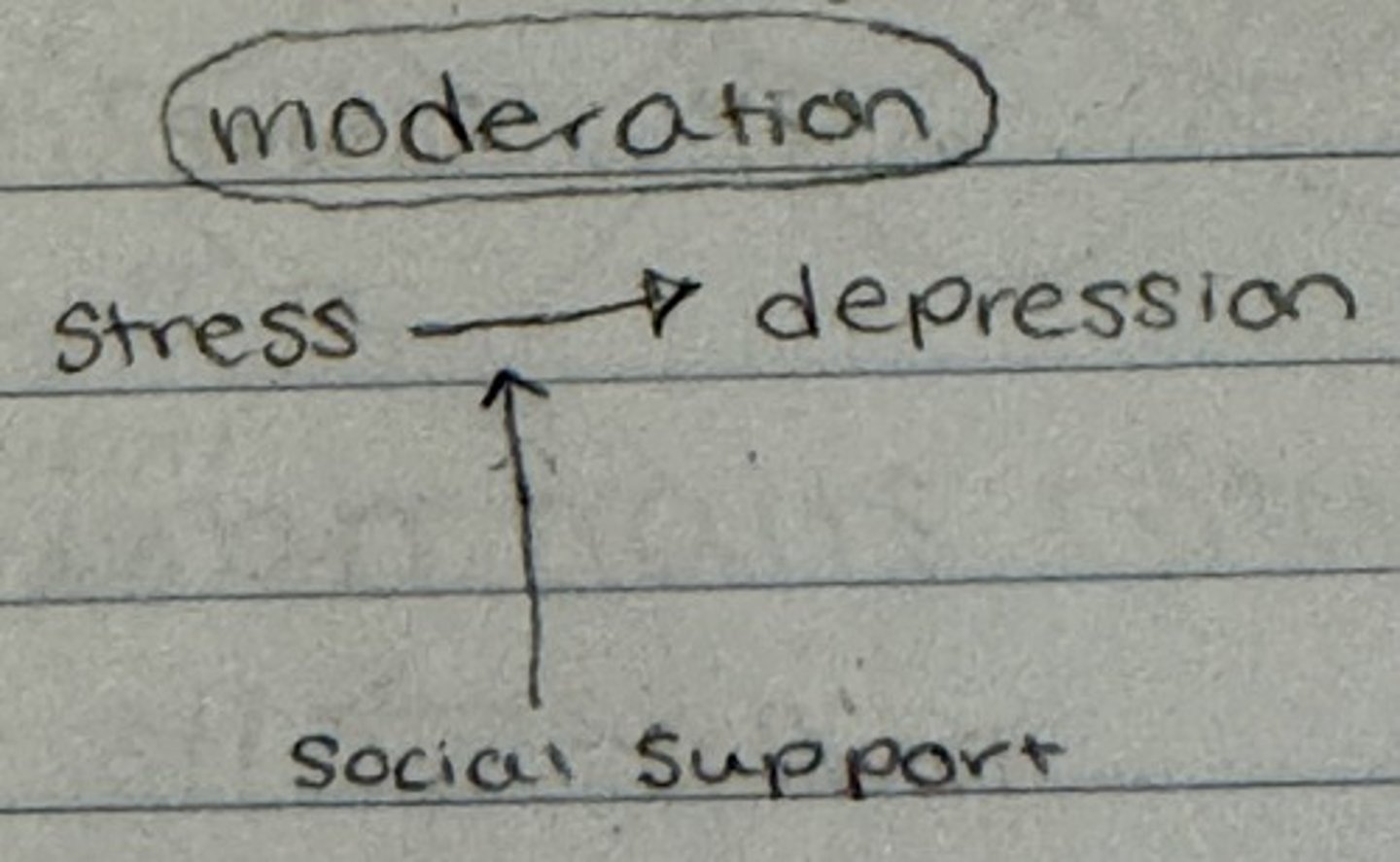
When the relationship between two variables changes depending on the level of another variable, the other variable is called a ___?
Moderator
_____ designs involve more than two measured variables
multivariate
- they get us closer to causality the bivariate
___ ___ can provide evidence for temporal precedence by measuring the same variables in the same people at several different times
longitudinal design
____ ____ is whether two variables measured at the same time point are correlated
Cross-sectional correlations
___ is the correlation of each variable with itself, measured on two different occasions
autocorrelations
the correlation of the degree to which an earlier measure of one variable is associated with a later measure of the other variable is known as?
Cross-lag correlations
T/F: longitudinal designs do rule out third-variable explanations
False, they do not
__ __ helps address questions of internal validity by ruling out some third variable
Multiple regression
Measuring more than two variables
Other variables might play into why higher amounts of sex on TV were associated with a higher risk of pregnancy
Regression results indicate if a third variable affects the relationship (controlling for; beta)
If you control for age will teens who watch higher amounts of sex on TV still be associated with a higher risk of pregnancy?
Adding more predictors to a regression
In the pregnancy example, we only examined age as a possible third variable. Could there be others?
You can detect if a multiple regression has been used if a journalist uses one of these phrases....
"controlled/ controlling for"
"taking into account"
"correcting for"
"adjusting for"
T/F: Multiple regression does not establish causation
true
___ is the degree to which a scientific theory provides the simplest explanation of some phenomenon
Parsimony
a pattern of results best explained by a single parsimonious causal theory
Pattern and parsimony
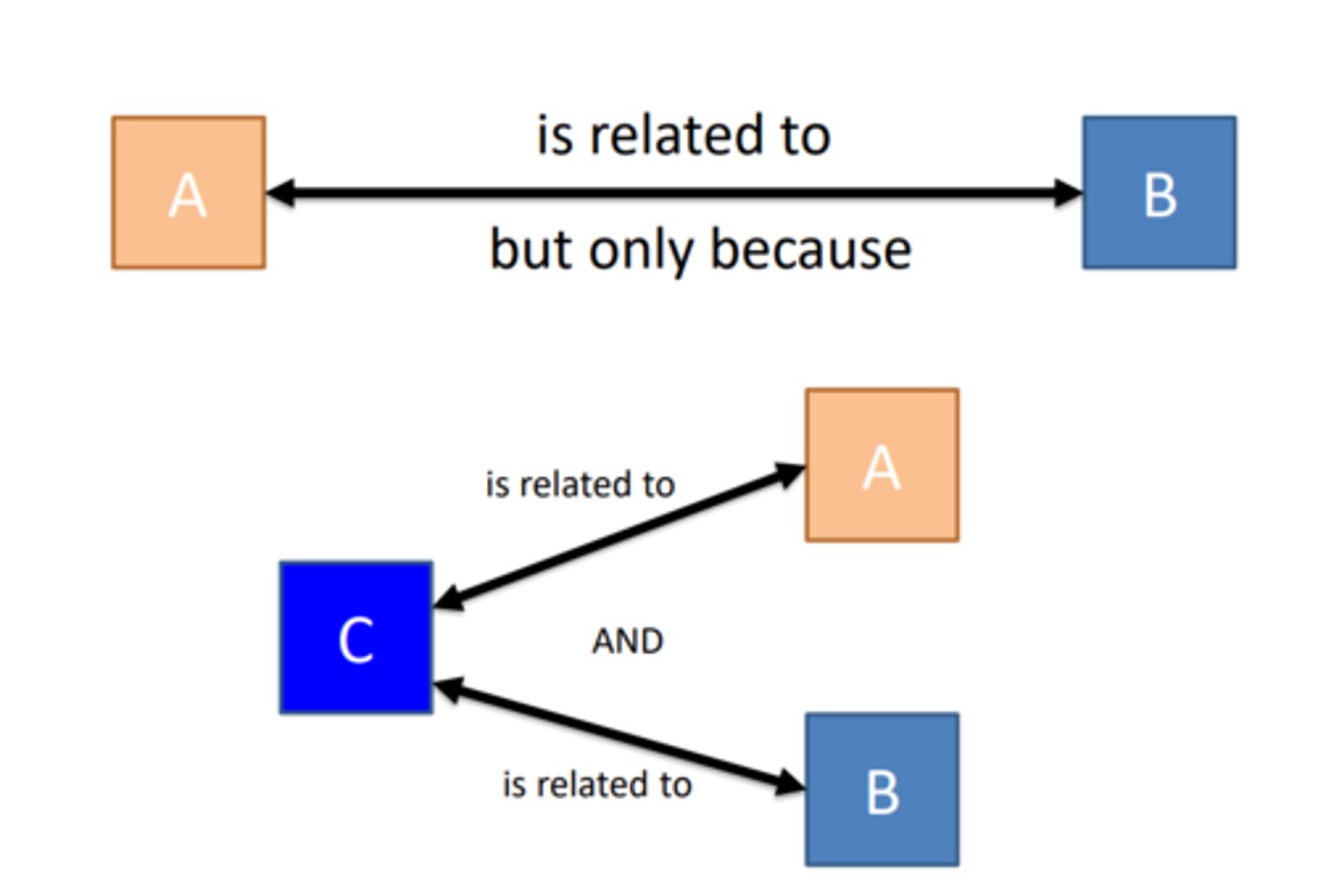
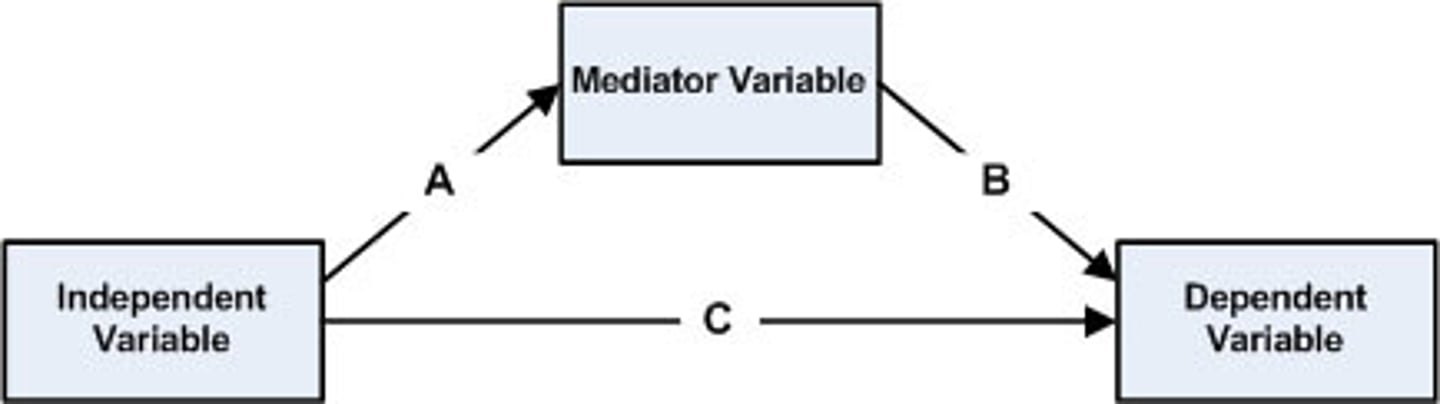
___ assesses why are these two variables related
Mediation
Are there certain groups or situations for which the two variables are more strongly related?
Moderation
Two variables are correlated, but only because they are both linked to a third variable
Third- variable problem