Topic 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
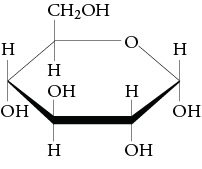
What monosaccharide is this
Alpha- glucose
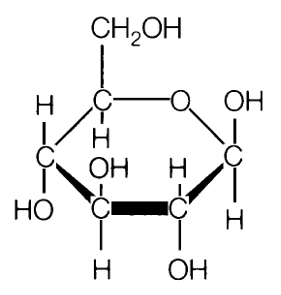
What monosaccharide is this
Beta- glucose
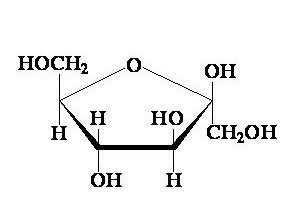
What monosaccharide is this
Fructose
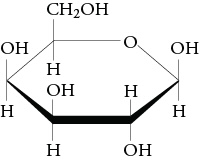
What monosaccharide is this
Beta galactose
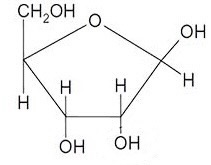
What monosaccharide is this
Ribose
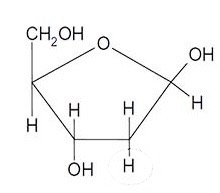
What monosaccharide is this
Deoxyribose
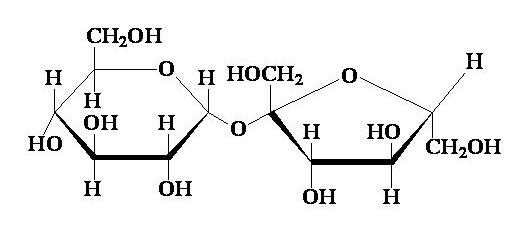
What disaccharide is this
Sucrose
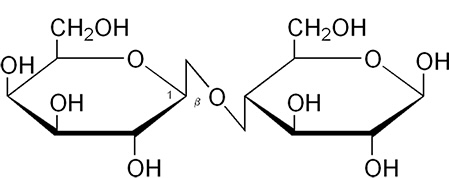
What disaccharide is this
Lactose
What monosaccharides is sucrose composed of?
Fructose and alpha glucose
What bond is shared between the units in a disaccharide
glycosidic bonds
What monosaccharides is lactose composed of?
Beta galactose and glucose
What monosaccharides is maltose composed of?
Glucose and glucose
What are the component of starch
Amylose and Amylopectin
What are polysaccharides with 3-10 monomers called
Oligosaccharides
What are polysaccharides with 11+ monomers known as
True polysaccharides
What types of substances are water soluble
Ionic and polar covalent
General formula of monosaccharides
(CH2O)n
Which monosaccharides and disaccharides are not reducing sugars
Sucrose
Why are mono/disaccharides not good energy storage units
-They are chemically active
-The are water soluble/ affect osmotic potential
Why are polysaccharides good energy storage units
-They form compact molecules
-They’re insoluble
-Chemically inactive
structure of Amylose
-Straight chain of a-glucose monomers
-Consists of only 1-4 glycosidic bonds
-Forms hydrogen bonds, spirals and becomes compact
Structure of Amylopectin
Mix of 1-4 and 1-6 bonds between a-glucose monomers
Structure of glycogen
More 1-6 bonds, more branched, better for animals
Reaction where water is produced as byproduct, and reverse reaction
Condensation, hydrolysis
Bonds between monosaccharides
1-4 or 1-6 glycodidic
Characteristics of fats
-From animals
-Solid at room temperature
Characteristics of lipids
-Liquid at room temp
-From plants
Saturated fatty acids are usually in what form
Solid
Unsaturated fatty acids are usually in what form
Liquid
Structure of triglycerides
A glycerol molecule bonded to the carboxyl groups of 3 fatty acid chains by ester bonds
Differences in atom composition of lipids and carbohydrates
Both have carbon hydrogen and oxygen, lipid have lower oxygen proportions
What can fatty acids vary in
-Chain length
-Being saturated/ unsaturated
What are essential lipids and their importance
The are polyunsaturated lipids, and humans can not produce them themselves
The general formula of saturated fatty acids
CnH2nO2
What common bonds are formed by condensation reactions
-Glycosidic
-Ester
-Peptide
-Phosphodiester
Structure of an amino acid
Amino group (NH3) and Carboxyl group (COOH) and R group attached to a central carbon atom
Primary structure
The sequence of amino acids in a chain
Secondary structure
The arrangement of the chain into 3D structures like a-helixes
Tertiary structure
The further folding of the secondary structure into complex shapes
Quaternary structure
How multiple polypeptide chains fit together
Bonds that influence shapes of proteins
-Hydrogen
-Ionic
-Disulfide
structure of fibrous proteins
Long parallel chains with little/no tertiary structure. They are insoluble and tough
Structure of collagen
Fibrous protein made from 3 alpha helixes arranged in a triple helix
structure of globular proteins
Spherical, with hydrophilic R groups outside and hydrophobic inside
Solubility of globular proteins in water
Insoluble (too large) they form a colloid instead
Structure of conjugated proteins
Have prosthetic groups
Main types of proteins
-Fibrous
-Globular
-Conjugated
What type of protein is haemoglobin
Globular and conjugated
Features of glycoproteins
-Retain more water (therefore more slippery e.g mucus)
-Digested less easily by proteases
How many oxygen molecules and atoms can haemoglobin carry
4 molecules, 8 atoms
Name of the changes in haemoglobin’s affinity after different numbers of molecules have binded
Cooperative binding/ confirmational changes/ The bohr effect
How does haemoglobin buffer blood pH
H+ ions from dissociated carbonic acid (CO2 + H2O) bind to it in so they don’t alter pH
Adaptations of blood in muscle tissues for faster O2 release during respiration
-When partial pressure of CO2 increases, it reduces haemoglobin’s affinity to oxygen so it dissociates faster.
-CO2 also reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into carbonate and H+ ions. These bind to haemoglobin, reducing its affinity as well
Methods of CO2 transfer in blood
-As carbinohaemoglobin
-In blood plasma
-As Hydrogen and carbonate ions
Types of circulation in mamals
-systemic circulation
-pulmonary circulation
Benefits of double circulation
-High concentration gradient for gas exchange
-Oxygenated blood is delivered fast at high pressures
-Deoxygenated blood is at low pressures to prevent damage to lungs and vessels
Specific stages of the cardiac cycle
Atrial systole —> AV valves close —> ventricular systole —> SV valves close —> diastole
Layers of blood vessels
Lumen
Tunica intima (endothelial lining)
Tunica media (Smooth muscle, elastic fibres)
Tunica externa (tough layer of collagen)
Tissue composition of artieries
-Higher proportions of elastic fibres for blood surges and elastic recoil
-Peripheral arteries have less elastic fibre due to lower bp, and more muscle tissue to control blood flow
-All have high collagen
Adaptations of veins
-Larger lumen to carry more blood
-Thin muscle and elastic fibres due to lower bp
-Often in between muscles which push blood through when contracted
-Has valves to prevent backflow
Adaptations of capillaries
-Small lumen lets through only one RBC at a time, more diffusion
-One cell thick walls for short diffusion distance and the ability to branch between cells
Adaptations of erythrocytes
-Bioconcave for larger SA:V
-No nucleus, more space
-A lot of haemoglobin
The blood clotting cascade
Platelets have contact with exposed vessels and activate, releasing:
-Seratonin, causes vasoconstriction
-Thromboplastin
—> has contact with prothrombin in blood stream and catalyses its breakdown to thrombin
—> thrombin catalyses fibrinogen into fibrin
—> fibrin firms a mesh (clot)
Which elements of the clotting cascade are soluble
-Prothrombin
-Fibrinogen
The breakdown of prothrombin requires
Ca 2+ ions
Composition of LDLs
-Less proteins
-More saturated fats
Composition of HDLs
-More proteins
-Unsaturated fats
Role of LDLs and HDLs in atherosclerosis
-HDLs carry cholesterol and deposit it in the liver for removal
-LDLs carry cholesterol and deposit it in plaques
Benefits of antioxidants
They prevent cholesterol in atheromas from oxidising and triggering inflammation
Risks of atheromas
-Reduces elasticity —> high bp, rupturing
-Reducing lumen size —> high bp
A thrombus
A clot attached to the vessel wall
An aneurism
Blood buildup behind a blockage, weakening artery walls. It may split and cause internal bleeding
Possible test for atherosclerosis
Proteins in urine due to high bp in kidney blood
Possible consequences of atherosclerosis
Damage to retina blood vessels —> blindness
Interruption in blood supply to brain causing a stroke
Blockage in coronary arteries causing angina or myocardial infarction
Symptoms of angina
gripping chest pain and breathlessness, stops when exercise is stopped
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
Random severe chest pain, death if not assisted
Diseases with multiple risk factors are
Multifactorial
Studies over a long timeline
Longitudinal studies
Research project on all the data available from a topic
Metadata analysis
Non modifiable risk factors for atherosclerosis
-Age, (vessels become less elastic)
-Gender (oestrogen reduces plaque buildup)
-Genes (e.g. less elastic arteries)
Modifiable risk factors for atherosclerosis
-Smoking (nicotine raises bp + chemicals that damage walls)
-Sedentary lifestyle
-Hypertension
-Obesity which can cause Hbp and diabetes
-Diet and balance of lipids, Vit C deficiency
Assessors of risk
BMI
Waist to hip ratio
Formula for BMI
Mass in Kg/ (height in m)²
Formula for waist to hip ratio
Waist size in cm/ Hip size in cm
Waist to hip ratio expected in healthy men and women
Men - <0.9
Women - <0.85
Test for Vit C
DCPIP, blue oxidising agent, turns colourless when reduced by vit C
How can Vit C conc be calculated
(Volume of standard solution added/ Volume of fruit juice added) x conc standard solution
Treatments for atherosclerosis
Antihypertensives
- Diuretics
- Beta blockers
- Sympathetic nerve inhibitors e.g. ACE inhibitors
Statins
- Plant stanols and sterols
Anticoagulants
Platelet inhibitory drugs
How do diuretics work
Reduce bp by increasing proportion of water in urine, and so decreasing blood volume
How do beta blockers work
They reduce hypertension by blocking the heart’s response to hormones like adrenaline
How do sympathetic nerve inhibitors work
Prevent signals to the arteries for vasoconstriction
How do ACE inhibitors work
They block production of a hormone which causes vasoconstriction
Possible side effects of taking antihypertensives
-Low bp (possible falling in the elderly)
-coughing, swelling, impotence, fatigue ecc.
How do statins work
They block the enzyme that makes cholesterol in the liver, blocking LDL production and inflammation
Benefits of statins as treatment
-Improve other conseguences of high cholesterol levels
-Seemingly effective in all groups of people
-Long lasting effect even after drug is stopped
-Come in plant Stanols and Sterol forms which can be included in diet
Disadvantages of taking statins
-Side effects like nausea, constipation, diarrhoea
-Low chance of fatal muscle inflammation
-Low chance of liver problems, possible failure
-Patients may be less careful in maintaining diet, causing other health problems
How do anticoagulants work
They interfere with the blood clotting cascade
Risks of taking anticoagulants
Internal bleeding could be fatal, they must be controlled very carefully
How do platelet inhibitory drugs work
Reduce clotting by making platelets stick together less
Risks of taking platelet inhibitory drugs
Stomach irritation, major stomach bleeds