1.8 Acids, bases and salts 🧑🔬
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Chemistry Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Indicator
chemical that gives colour change in acidic, alkaline and neutral solutions
Examples of indicators
red/ blue litmus paper, phenolphthalein and methyl orange
Using litmus paper
use both to confirm if solution is neutral or acid/ alkali
Litmus paper results
Indicator | Acidic solution | Neutral solution | Alkaline solution |
|---|---|---|---|
Red litmus paper | red | red | blue |
Blue litmus paper | red | blue | blue |
Phenolphthalein results
Indicator | Acidic solution | Neutral solution | Alkaline solution |
|---|---|---|---|
Phenolphthalein | colourless | colourless | pink |
Methyl orange results
Indicator | Acidic solution | Neutral solution | Alkaline solution |
|---|---|---|---|
Methyl orange | red | orange | yellow |
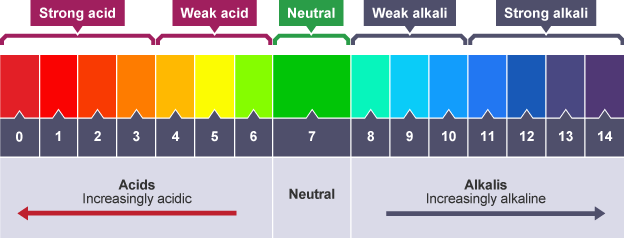
pH scale
gives a measure of the strength of an acid or alkali
Interpreting pH scale
0 – 2: strong acid
3 – 6: weak acid
7: neutral
8 – 11: weak alkali
12 – 14: strong alkali
pH meter
electronic device that measures pH and gives more accurate result
Acid
substance that dissolves in water to produce hydrogen ions, H+(aq)
Higher concentration of hydrogen ions
lower pH so stronger acid
Alkali
a soluble base, dissolves in water to produce hydroxide ions, OH-(aq)
Strength of acids and alkalis
determined by how much they ionise in water, splitting into separate ions
Strong acid/ alkali
ionise completely in water giving high concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions
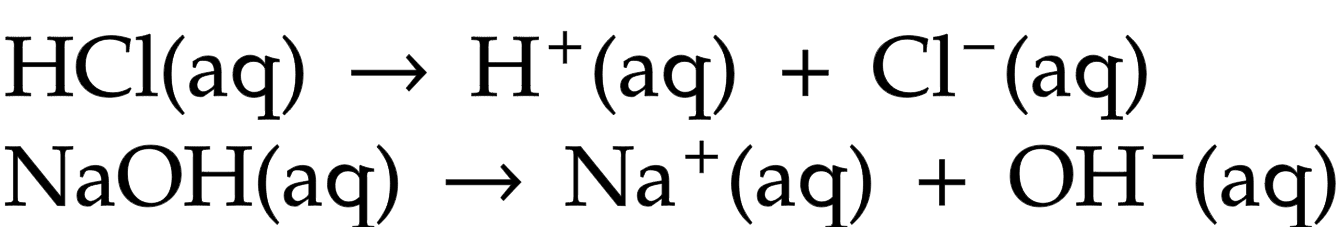
Examples of strong acids
hydrochloric acid (HCl)
sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
nitric acid (HNO3)
Examples of strong alkalis
sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
potassium hydroxide (KOH)
Weak acid/ alkali
ionise partially in water giving lower concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions and is reversible (⇌)
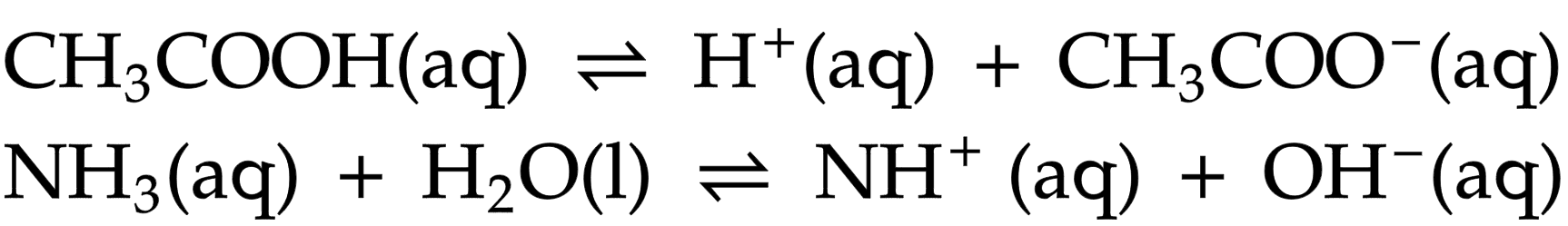
Examples of weak acids
ethanoic acid (CH3COOH)
carbonic acid (H2CO3)
Examples of weak alkalis
ammonia (NH3)
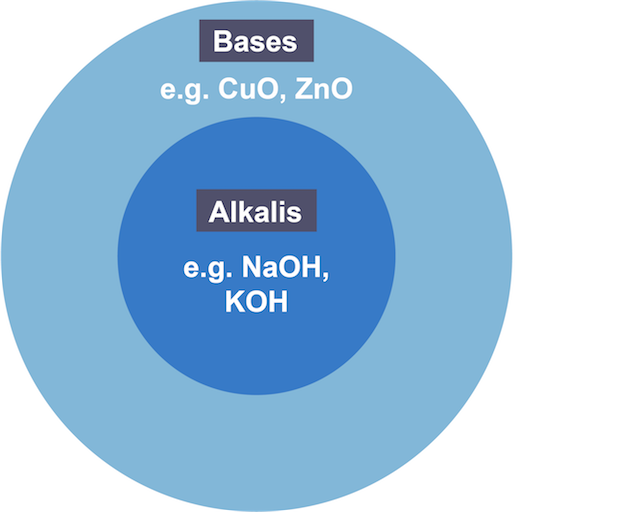
Base
substance that reacts with acid to produce a salt and water
Difference between alkali and base
alkalis are bases that dissolve in water
Concentration (mol/ dm3)
measurement of the amount of acid/ alkali dissolved in solution
Measuring concentration
mol/ dm3
Concentrated acid/ alkali
contains large number of particles dissolved per unit volume so is stronger
Dilute acid/ alkali
contains small number of particles dissolved per unit volume so is weaker
Neutralisation
reaction between an acid and an alkali producing a salt and water
Ionic equation for neutralisation
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
Temperature of neutralisation
exothermic reaction, maximum temperature reached when acid solution is completely neutralised by alkali
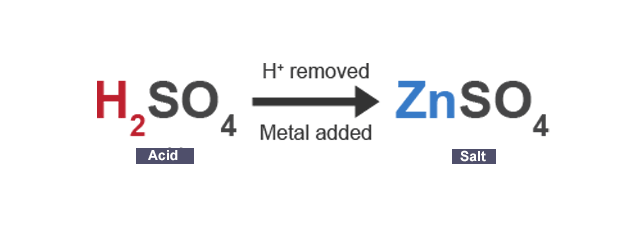
Salt
compound formed when some or all hydrogen ions in acid are replaced by metal ions (or ammonium ions)
Names of salts
first word is the metal and second is type of salt
Hydrochloric acid as salt
Chloride
Sulfuric acid as salt
Sulfate
Nitric acid as salt
Nitrate
Why add excess insoluble solid
ensures all the acid is converted to salt and can be removed via filtration
When do we prepare salts using excess insoluble solid
most Group 2, aluminium and transition metal salts
When do we prepare salts using acids and alkalis
sodium, potassium and ammonium salts
How to dry crystals
place in desiccator/ low temperature oven or between two sheets of filter paper
Observations in acid reactions
when gas is produced, observations are ‘bubbles’ or ‘fizzing’
if solid reacts observation is ‘solid disappears and solution is produced’
most are exothermic except copper(II) oxide and sodium hydrogencarbonate
Colour of iron(II) salts in solution
green solution
Group 1, 2, aluminium and zinc compounds
white solids that dissolve in water to give colourless solutions
Acid + metal
→ salt + hydrogen
Test for hydrogen
apply lighted splint and popping sound results if present
Acid + metal carbonate (or hydrogencarbonate)
→ salt + water + carbon dioxide
Test for carbon dioxide
bubble gas into colourless limewater will change from colourless to milky if present
Limewater
calcium hydroxide solution
Acid + ammonia
→ ammonium salt

Corrosive
burns and destroys living tissue e.g concentrated acid

Explosive
explodes if exposed to flame, heat or knocked e.g potassium

Flammable
catches fire easily when in contact with air e.g ethanol

Toxic
can kill by poisoning e.g weed-killer or cyanide

Caution
may be harmful or an irritant e.g dilute sodium hydroxide
Risk assesssment
PPE should be worn when handling any harmful substance
contact should be minimised and use of fume cupboard with toxic substances
make sure there are no naked flames when using flammable substances (safety flame)
care should be taken when labelled ‘caution’ to avoid spills