APHUG Unit 5
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:30 AM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
Agriculture
Process by which humans alter the landscape in order to raise crop and raise livestock for consumption and trade.
2
New cards
Climate
Long-term weather patterns in a region
3
New cards
Subsistence Agriculture
Primary goal: Grow enough food/raise enough livestock to meet immediate needs of farmer and family.
Secondary goal: Sell/trade any surplus for income/goods
Most subsistence farmers live in less-developed regions and have small farmers with less than 2 acres. Hard to grow extra food to sell/trade w/ limited land and agricultural tech costs.
Secondary goal: Sell/trade any surplus for income/goods
Most subsistence farmers live in less-developed regions and have small farmers with less than 2 acres. Hard to grow extra food to sell/trade w/ limited land and agricultural tech costs.
4
New cards
Commercial Agriculture
Primary goal: Grow enough food/raise enough livestock to sell for profit
Exists in all countries, more common in developed countries but increasing in semi-periphery countries like China, Mexico, and Brazil.
Exists in all countries, more common in developed countries but increasing in semi-periphery countries like China, Mexico, and Brazil.
5
New cards
Intensive Agriculture
Farmers/ranchers use large amounts of inputs(energy, fertilizers, labor, machines) to maximize yields.
6
New cards
Extensive Agriculture
Use fewer amounts of inputs and usually have less yields.
7
New cards
Capital
Money invested in land, equipment, and machines
8
New cards
Intensive Commercial Agriculture
Large amount of input with goal of selling for profit.
\
Almost always capital intensive, can be labor intensive.
Ex. Market Gardening, plantations, large scale mixed crop and livestock systems.
\
Labor and capital intensive, high crop and livestock productivity.
Global: core, semi-periphery, periphery
Regional: near transport access to urban and global markets
\
Almost always capital intensive, can be labor intensive.
Ex. Market Gardening, plantations, large scale mixed crop and livestock systems.
\
Labor and capital intensive, high crop and livestock productivity.
Global: core, semi-periphery, periphery
Regional: near transport access to urban and global markets
9
New cards
Intensive Subsistence Agriculture
Large amount of inputs with goal of meeting needs of farmer and family.
\
Often labor and animal intensive.
\
Labor intensive, not capital intensive, and low crop and livestock productivity
Global: primarily periphery and semi-periphery
Regional: usually near towns and cities with access to local markets
\
Often labor and animal intensive.
\
Labor intensive, not capital intensive, and low crop and livestock productivity
Global: primarily periphery and semi-periphery
Regional: usually near towns and cities with access to local markets
10
New cards
Extensive Commercial Agriculture
Uses low input of resources but has goal of selling product for profit. Ranching is most common form. Western regions of the US and Canada, Argentina, New Zealand, and Australia.
\
Capital intensive, not labor intensive, high crop productivity and low livestock productivity
Global: core, semi-periphery, periphery
Regional: transport access to processing and local, regional, and global markets
\
Capital intensive, not labor intensive, high crop productivity and low livestock productivity
Global: core, semi-periphery, periphery
Regional: transport access to processing and local, regional, and global markets
11
New cards
Extensive Subsistence Agriculture
Few inputs used with goal of meeting needs of farmer and family.
\
Often in areas w/ climactic extremes like tropics, semi-arid, or arid regions. Ex. Nomadic herding and shifting cultivation
\
Labor intensive, not capital intensive, and low crop and livestock production.
\
Often in areas w/ climactic extremes like tropics, semi-arid, or arid regions. Ex. Nomadic herding and shifting cultivation
\
Labor intensive, not capital intensive, and low crop and livestock production.
12
New cards
Pastoral Nomadism
Subsistence extensive agriculture practiced in arid and semi-arid climates. Herds are moved to different pastures within their territory and often trade meat for crops w/ nearby subsistence farmers.
\
Different regions = different animals→ depends on culture and climate
\
Cattle, camels, reindeer, goats, yaks, sheep, horses: provide meat for food and hides for clothing and shelter.
\
South Central and East Asia— cattle→ adat to hot climate
Middle East desert area— camels→ survive long w/o water
Siberia— reindeer→ thrive in cold
\
Different regions = different animals→ depends on culture and climate
\
Cattle, camels, reindeer, goats, yaks, sheep, horses: provide meat for food and hides for clothing and shelter.
\
South Central and East Asia— cattle→ adat to hot climate
Middle East desert area— camels→ survive long w/o water
Siberia— reindeer→ thrive in cold
13
New cards
Shifting Cultivation
Subsistence extensive farming, grows crops on land for year or 2 then move to new field when fertility is lost.
\
Not crop rotation: Involves using new fields while in crop rotation, crops are changed
\
Not crop rotation: Involves using new fields while in crop rotation, crops are changed
14
New cards
Plantation
Large commercial farm specializing in a single crop
15
New cards
Mixed crop and livestock farming
Large scale, intensive commercial integrated system demonstrating interdependence between crops and animals. Majority of crops are grains that are eaten by livestock to fatten cattle for slaughter or feed dairy cows. Animal manure is used for crop fertilizer.
\
Common in developed regions. Canada, Midwestern US(often grow corn and soybeans), Northern Europe
\
Common in developed regions. Canada, Midwestern US(often grow corn and soybeans), Northern Europe
16
New cards
Grain farming
In regions too dry for mixed crop agriculture.
World’s top wheat producers: China, India, Russia, and US
\
Two types:
Spring wheat: Planted early spring, harvested early autumn. Grown in colder regions(Canada, Montana, Dakotas)
Winter wheat: Planted fall, harvested early summer. Grown in warmer regions(Europe, Kansas, Oklahoma)
World’s top wheat producers: China, India, Russia, and US
\
Two types:
Spring wheat: Planted early spring, harvested early autumn. Grown in colder regions(Canada, Montana, Dakotas)
Winter wheat: Planted fall, harvested early summer. Grown in warmer regions(Europe, Kansas, Oklahoma)
17
New cards
Commercial Gardening
Intensive farming also known as truck farming(traditionally was driven to local urban markets and sold, now trucks are refrigerated, farmers can sell products to distant markets). Farming for profit.
Typical fruits/vegetables grown in US:
Lettuce, apples, broccoli, oranges, tomatoes.
Where:
California, Arizona, SE states. (Winter: imported from Mexico and Chile).
Typical fruits/vegetables grown in US:
Lettuce, apples, broccoli, oranges, tomatoes.
Where:
California, Arizona, SE states. (Winter: imported from Mexico and Chile).
18
New cards
Dairy farming
(Definition from Quizlet(not in book)) An agricultural activity involving the raising of livestock, most commonly cows and goats, for dairy products such as milk, cheese, and butter.
\
Large corporate dairy operations replace smaller family owned farms. This→ less farms but more production.
\
Most dairy farms are near urban centers and transportation corridors. Increasing in Argentina and Brazil, demand increased faster than pressure for consolidation. W/ economic growth and higher incomes = # of dairy farms increased.
\
Large corporate dairy operations replace smaller family owned farms. This→ less farms but more production.
\
Most dairy farms are near urban centers and transportation corridors. Increasing in Argentina and Brazil, demand increased faster than pressure for consolidation. W/ economic growth and higher incomes = # of dairy farms increased.
19
New cards
Milk Shed
Geographic distance that milk is delivered.
20
New cards
Mediterranean Agriculture
Climate must be: hot, dry summers, mild winters, narrow valleys, often some irrigation. Southern Europe, SW Africa, SW Asia, SW Australia, California, Central Chile.
Common crops: figs, dates, olives, grapes
Common crops: figs, dates, olives, grapes
21
New cards
Transhumance
Seasonal herding of animals from higher elevations in the summer to lower elevations and valleys in the winter. (Because of rugged terrain, goats and sheep are principal livestock).
22
New cards
Livestock Ranching
Commercial grazing of animals confined to a specific area. Found in areas too dry to grow crops in large quantities.
Most commonly: Western US; pampas of Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay; parts of Spain and Portugal; China; and Central Australia.
Most commonly: Western US; pampas of Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay; parts of Spain and Portugal; China; and Central Australia.
23
New cards
Clustered/Nucleated Settlements
Had groups of houses located near each other in a village and fostered stronger sense of place and shard services. Common through history.
24
New cards
Dispersed Settlements
Farmers lived in houses spread throughout the countryside. Encourage individual self-sufficiency but make shared service hard. These occur more in areas with rugged/challenging environments like limited water/poor soil.
25
New cards
Linear Settlement
Buildings/human activities organized near body of water or along a transportation route.
26
New cards
Metes and Bounds
System describing plot boundaries in England.
Metes—used for short distances and referred to features of specific places.
Bounds—covered bigger areas and based on larger features(streams, roads)
Also used by English colonizers in America.
Metes—used for short distances and referred to features of specific places.
Bounds—covered bigger areas and based on larger features(streams, roads)
Also used by English colonizers in America.
27
New cards
Public Land Survey Systems(Township and Range System)
Made rectangular plots of consistent size.
Township: Areas 6 miles long and wide
Section: Each square mile, 640 acres. Can be divided.
Common in most land west of the Appalachian Mountains, often squares/rectangles.
Township: Areas 6 miles long and wide
Section: Each square mile, 640 acres. Can be divided.
Common in most land west of the Appalachian Mountains, often squares/rectangles.
28
New cards
French Long-lot System
System where farms were long, thin sections of land that ran perpendicular to a river. In North America: found in Quebec and Louisiana.
29
New cards
First(Neolithic) Agricultural Revolution
Origin of farming. Marked by domestication of plants and animals. Most farming here— subsistence. Simple tools and labor.
30
New cards
Hunters and Gatherers
Before agriculture, we lived like this for tens of thousands of years.
Lived in small, mobile groups(30–50 people) who could move easily in search of food. Survived by living in low population density regions.
Larger groups would’ve surpassed the carrying capacity of the regions.
Lived in small, mobile groups(30–50 people) who could move easily in search of food. Survived by living in low population density regions.
Larger groups would’ve surpassed the carrying capacity of the regions.
31
New cards
Animal Domestication
Hunters in central Asia first to do this w/ dogs and horses(food, protection, work, transportation)
SW Asia: Goats, pigs, sheep, cattle
After SW Asia: Cats, horses, camels, donkeys, llamas
SW Asia: Goats, pigs, sheep, cattle
After SW Asia: Cats, horses, camels, donkeys, llamas
32
New cards
Plant Domestication
Probably started after domesticating animals.
First used(before seed planting): vegetative planting: Using parts of the stems/roots of existing plants to grow others
First used(before seed planting): vegetative planting: Using parts of the stems/roots of existing plants to grow others
33
New cards
Major Agricultural Hearths
SW Asia, East Asia, South Asia, Africa, and the Americas
Characteristics: High biodiversity on edge of forest, available fresh water, fertile soil, moderate climates, skilled residents
Characteristics: High biodiversity on edge of forest, available fresh water, fertile soil, moderate climates, skilled residents
34
New cards
Independent Innovation
When crops and animals were domesticated in multiple regions w/ seemingly no interaction
Ex. Wheat→ SW Asia, East Asia, and South Asia
Pigs→ SW Asia, SE Asia, and South Asia
Ex. Wheat→ SW Asia, East Asia, and South Asia
Pigs→ SW Asia, SE Asia, and South Asia
35
New cards
Columbian Exchange
Global movement of plants and animals between Afro-Eurasia and the Americas
36
New cards
Second Agricultural Revolution
Based on innovation and science to meet increasing global demand for food.
Began 1700s. Used Industrial Revolution to increase food supplies and support pop. growth.
Agriculture benefitted from mechanization and increased knowledge of fertilizers, soil, and selective breeding practices for plants and animals.
Began 1700s. Used Industrial Revolution to increase food supplies and support pop. growth.
Agriculture benefitted from mechanization and increased knowledge of fertilizers, soil, and selective breeding practices for plants and animals.
37
New cards
Enclosure Movement
Series of laws by British gov—lets landowners buy land and enclose it for own use. Before: common land shared.
Cons: Many farmers forced off their land and lost traditional way of life
Cons: Many farmers forced off their land and lost traditional way of life
38
New cards
2nd Revolution Advances
\-Iron/steel plow(1819)
\-Mechanized Seed Drilling(18th century)
McCormick Reaper/Harvester(1831)
\-Grain Elevator(1849)
\-Barbed Wire(1870s)
\-Mixed nitrogen and nitric acid fertilizer(1903)
\-Mechanized Seed Drilling(18th century)
McCormick Reaper/Harvester(1831)
\-Grain Elevator(1849)
\-Barbed Wire(1870s)
\-Mixed nitrogen and nitric acid fertilizer(1903)
39
New cards
Crop Rotation
Technique of planting different crops in a specific sequence on the same plot of land in order to restore nutrients back into the soil(grains take nitrogen out of soil, alfalfa puts it in). A fallow period(ground left unseeded) is also common.
40
New cards
Irrigation
Process of applying controlled amounts of water to crops using canals, pipes, sprinkler systems, or other human made resources
41
New cards
2nd Revolution's impact on demographics
1920 US Census showed for the first time in the country’s history that more people lived in urban areas than rural areas.
42
New cards
Third Agricultural Revolution
Born mid-20th century from science, research, and technology.
Expanded mechanization of farming, developed new global agricultural systems, and used scientific and information tech to further previous advances in agricultural production.
Expanded mechanization of farming, developed new global agricultural systems, and used scientific and information tech to further previous advances in agricultural production.
43
New cards
Green Revolution
Advances in plant biology of the mid-20th century
44
New cards
Impact of Norman Borlaug
“Father of the Green Rev.“ laid foundation for scientifically increasing the food supply to meet the demands of ever increasing global pop. Developed higher-yield, more disease-resistant, and faster growing varieties of grain: most important contribution.
Turned Mexico from wheat importing country to one that was self-sufficient and even had wheat surplus.
Turned Mexico from wheat importing country to one that was self-sufficient and even had wheat surplus.
45
New cards
(Seed) Hybridization
Process of breeding 2 plants w/ desirable characteristics to make 1 seed w/ both characteristics.
For 100s of years, we created plant hybrids from local varieties available. GR scientists focused on grains. Much wider range of plants.
\
Ex. 1960s→ new strain of rice made(Long grain from Indonesia w/ dense grain dwarf rice from Taiwan→ rice grain both longer and denser)
For 100s of years, we created plant hybrids from local varieties available. GR scientists focused on grains. Much wider range of plants.
\
Ex. 1960s→ new strain of rice made(Long grain from Indonesia w/ dense grain dwarf rice from Taiwan→ rice grain both longer and denser)
46
New cards
Machinery’s impact on the Green Rev.
Tractors, tiller, broadcast seeders, and grain carts were introduced to countries of the developing world
47
New cards
Genetically Modified Organisms(GMOs)
Process where humans use engineering techniques to change a seed’s DNA. Developed to increase yields, resist diseases, and withstand chemicals used to kill weeds and pests.
48
New cards
Positive impacts of the Green Rev.
More food = reduced hunger, lower death rates, and growing pop in many parts of the developing world.
Good especially in Latin America, East Asia, and SE Asia
More crops = less hunger, 80% developing world pop→ adequate diet
Good especially in Latin America, East Asia, and SE Asia
More crops = less hunger, 80% developing world pop→ adequate diet
49
New cards
Negative impacts of the Green Rev.
Crop yields increased at expense of natural environment
Some say GR was not sustainable system
Chemicals introduced = potentially hazardous runoff into streams, rivers, and lakes, which posed serious consequences to the local ecosystems, habitats, and communities.
Hazards ex. Polluted drinking water, species extinction, and health issues
Also, air, sound, and water pollution from machines→ require fossil fuels
Some say GR was not sustainable system
Chemicals introduced = potentially hazardous runoff into streams, rivers, and lakes, which posed serious consequences to the local ecosystems, habitats, and communities.
Hazards ex. Polluted drinking water, species extinction, and health issues
Also, air, sound, and water pollution from machines→ require fossil fuels
50
New cards
Green Rev. impact on gender roles
Men usually dominate socially, politically, and economically based on societies’ traditional beliefs, though much of farming labor is by women
Men owned the land, had access to financial resources, and were educated on newer methods of farming, while women were often excluded from these opportunities
Men owned the land, had access to financial resources, and were educated on newer methods of farming, while women were often excluded from these opportunities
51
New cards
Why didn’t the GR help Africa?
* Has great diversity of climate and soils than other places. So development of right fertilizers = expensive
* Many regions w/ harsh environmental conditions. Insects, plants, and viral strains proved to be very difficult w/ GR researchers and their tech.
* Large and lacks well developed transportation infrastructure, so cost of investment in research, development, and transportation were very high.
* Staple crops like sorghum, millet, cassava, yams, cowpeas, and peanuts were not always include in research for seed-hybridization programs
* Many regions w/ harsh environmental conditions. Insects, plants, and viral strains proved to be very difficult w/ GR researchers and their tech.
* Large and lacks well developed transportation infrastructure, so cost of investment in research, development, and transportation were very high.
* Staple crops like sorghum, millet, cassava, yams, cowpeas, and peanuts were not always include in research for seed-hybridization programs
52
New cards
Bid-rent Theory
Geographers use when discussing land costs for different types of agricultural activities. Distance decay w/ proximity to an urban center→ refers to changing value and demand for land as the distance from the market increases(used to determine what type of agriculture is located in each (VT) zone)
53
New cards
Capital Intensive
Lots of money invested. Ex. Expensive machinery
54
New cards
Labor Intensive
Heavy labor needed
55
New cards
Factory Farming
Capital-intensive livestock operation in which many animals are kept in close quarters, and bred and fed in a controlled environment
56
New cards
Aquaculture(aquafarming)
Intensive farming. Rather than raising typical farm animals in close quarters with a controlled environment, fish, shellfish, or water plants are raised in netted areas in the sea, tanks, or other bodies of water.
57
New cards
Double cropping
Planting and harvesting 2 or 3 times a year on same piece of land
58
New cards
Intercropping/multi-cropping
2 or more crops grown simultaneously on same field
59
New cards
Monoculture/monocropping
Only 1 crop/1 type of animal raised per season on a piece of land.
60
New cards
Feedlots(CAFOs)
Confined spaces where cattle and hogs have limited movement. Bigger in shorter time because of this. Maxes use of space = maxes profit.
CAFOs = Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations
CAFOs = Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations
61
New cards
Agribusiness
Used to refer to economic activities derived from or connected to farm products. In other words, crop production, as well as crop processing, transportation and distribution.
\
(Definition online, no direct definition in textbook)
\
(Definition online, no direct definition in textbook)
62
New cards
Transnational Corporations
Corporations that operate in many countries
63
New cards
Vertical Integration
Ownership in other businesses involved in the steps of producing a particular good.
64
New cards
Economies of Scale
Increase in efficiency to lower the per-unit production cost, resulting in greater profits. Ex. Grain farmer adds land, more efficient w/o new equipment
65
New cards
Commodity Chain
Process used by corporations to gather resources, transform them into goods, and transport them to consumers.
66
New cards
Cool Chains
Transportation networks that keep food cool throughout a trip.
67
New cards
Location Theory
Key component of econ. geography, deals w/ why people choose certain locations for various econ. activity.
68
New cards
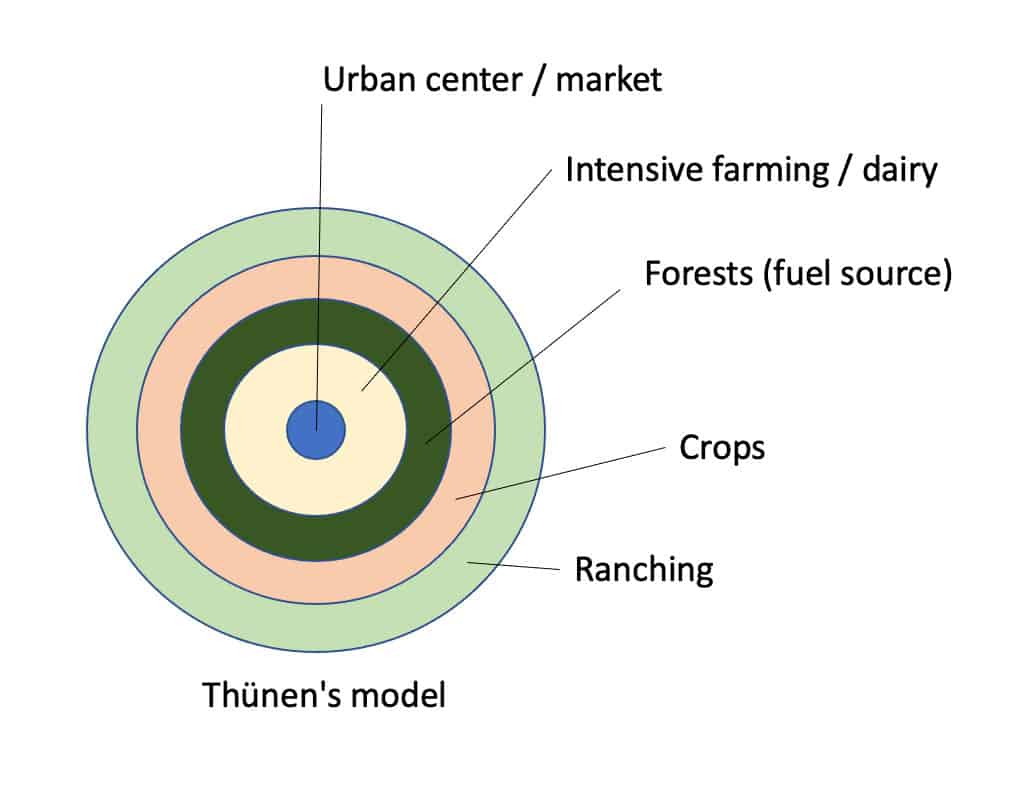
Von Thunen Model
\-Urban Center
\-Ring one: Intensive & Dairy(fruits, vegetables, etc.)(Spoil, land near city = more expensive so = intensive)
\-Ring two: Timber(Fuel source, hard to transport at the time, heavy)
\-Ring three: Grains(more preservable, land is cheaper, you can do more with big land)
\-Ring four: Ranching/livestock(grain right next to it can be used, again, land cheaper, can be transported)
\-Ring one: Intensive & Dairy(fruits, vegetables, etc.)(Spoil, land near city = more expensive so = intensive)
\-Ring two: Timber(Fuel source, hard to transport at the time, heavy)
\-Ring three: Grains(more preservable, land is cheaper, you can do more with big land)
\-Ring four: Ranching/livestock(grain right next to it can be used, again, land cheaper, can be transported)
69
New cards
Bid-rent Curve
Used to determine starting position for each land use relative to the market as well as when each land use would end.
70
New cards
Comparative Advantage
Naturally occurring beneficial conditions
71
New cards
Free Market Economy
Supply and demand, rather than gov. policy, determines the outcome of competition for land. (Farmer w/ biggest profit pays most)
72
New cards
Von Thunen’s Model Assumptions
\-Land was an isotropic plain(flat, featureless, similar climate and fertility throughout)
\-There’s one primary market
\-Transportation would stay the same(became outdated, refrigeration, wood was exchanged for others as fuel source)
\-There’s one primary market
\-Transportation would stay the same(became outdated, refrigeration, wood was exchanged for others as fuel source)
73
New cards
5 Criticisms of Von Thunen Model
1. Farming is an economic activity(gov. policies can interfere w/ free market econ. & affect farmers’ decisions)
2. Farmers where in business to make a profit(subsistence)
3. One market where they sold(modern agriculture has multiple)
4. One transportation system(Many advances in transport change distance considerations for farmers)
5. Market was situated in center of isotropic plain(differences in land formation, soil fertility, and climate exist, isotropic plains are uncommon).
74
New cards
Supply Chains
All steps required to get a product/service to customers
75
New cards
Interdependence
Connections among regions of the world
76
New cards
Luxury Crops
Not essential to human survival but have a high profit margin
77
New cards
Ways Rich countries exploit poor
Transnational companies that own plantations provide the capital necessary to develop and run the plantations, taking advantage of the cheap land and labor and favorable climate.
Sometimes also take advantage of weak labor and environmental laws which lets them reduce costs and increase profits.
Sometimes also take advantage of weak labor and environmental laws which lets them reduce costs and increase profits.
78
New cards
Neocolonialism
Use of econ. political, and social pressures to control former colonies
79
New cards
Fair Trade
Doing something about the disparity between the high incomes of those in developed countries who manage trade and the low incomes of the producers in the developing countries.
80
New cards
Fair Trade Movement Principles(5)
\-Direct trade to eliminate the intermediary. Transactions directly between the producer and the importer ensure more money to producer
\-Fair price paid to workers and farmers
\-Decent conditions for laborers, safe working environment and no child/forced labor
\-Environmental sustainability that required farmer to use environmentally safe practices and prohibited GMOs
\-Respect for local culture through shared agricultural techniques w/ farmers.
\-Fair price paid to workers and farmers
\-Decent conditions for laborers, safe working environment and no child/forced labor
\-Environmental sustainability that required farmer to use environmentally safe practices and prohibited GMOs
\-Respect for local culture through shared agricultural techniques w/ farmers.
81
New cards
Subsidies
Public financial support(to farmers to safeguard food production)
82
New cards
Infrastructure
Roads, bridges, tunnels, ports, electrical grids, sewers, telecommunications, etc. of a country. Critical to make products.
83
New cards
Ghana’s Vision 2020
Focused on rapid econ. growth. Attempted to do this w/ improvements like modernizing agricultural inputs, increasing private investment, and developing transportation infrastructure. To raise income and better living conditions.
84
New cards
Land cover changes
Study of how land is used and the impact of changing how land is used. (Geographers are particularly interested in loss of natural land areas to agriculture loss of agricultural land to urban area explanation)
85
New cards
Farming pollution
Most intensive forms of agriculture→ usually responsible for worst agricultural pollution. Chemical fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides, and herbicides
86
New cards
Desertification
Alteration of the natural vegetation in arid areas causes fertile land to become infertile.
87
New cards
Salinization
Occurs when salts from water used by plants remain in the soil. Lowers plant’s ability to uptake water and nutrients. This = lower yields and may make soil useless. Evaporation also leaves salt behind so excess water = increase salinization.
Improper use of irrigation/water high in salt content can lead to it.
Improper use of irrigation/water high in salt content can lead to it.
88
New cards
Conservation
Goal: to counter the damaging effects of destroying the natural landscape, and the various flora and fauna that inhabit it, through the expansion and development of farmland
\-Reduce use of agricultural chemicals
\-Monitoring irrigation usage
\-Using more natural pest control solutions
\-Growing crops organically
\-Reduce use of agricultural chemicals
\-Monitoring irrigation usage
\-Using more natural pest control solutions
\-Growing crops organically
89
New cards
Terrace Farming
Farmers build series of steps into the side of a hill. Creates flat surfaces. One of earliest human alterations to landscape.
90
New cards
Irrigation
Process of applying controlled amounts of water to crops using dams, canals, pipes, sprinkler systems, or other manufactured devices rather than just relying on rainfall.
91
New cards
Aral Sea— problems with irrigation
Tried to divert water from rivers that flowed into the Aral Sea to increase cotton production in the region. Reduced to 10% of its former size
92
New cards
Deforestation
Removal of large tracts of forest
93
New cards
Slash and Burn Agriculture
Type of shifting cultivation, all vegetation in an area of forest→ cut down and burned. Ash gives nutrients to soil and land is farmed on for few years before soil is depleted and plot is abandoned. Returns to natural as farmers move on.
94
New cards
Changing Diets
People in semi-periphery countries starting to see improved standards of living start to want a more western diet w/ meat, dairy, and processed and convenience foods. Pressure on livestock which can be unreliable since its animals. Farmers also feed 35% of world’s crop to livestock which leaves less crops for humans to consume.
95
New cards
Roles of women in agriculture
Play important role in agriculture especially in periphery and semi-periphery countries. Feminization of agriculture has led international aid agencies to recognize that agricultural education and training, and more financial assistance, should be extended to women.
96
New cards
Challenges of GMOs
\-GMO seeds too expensive
\-Ones resistant to pests and herbicides might = superweeds/superpests, potential long term risks to consumers
\-Ones resistant to pests and herbicides might = superweeds/superpests, potential long term risks to consumers
97
New cards
Blue Revolution
Aquaculture becoming the fastest growing form of food production on the planet. Now responsible for around 50% of world’s seafood.
98
New cards
Challenges to aquaculture
\-High fish density in enclosures = diseases and parasites thrive and spread easily
\-Parasites and diseases can spread from fish in enclosures to nearby wild stock.
\-Chemicals and antibiotics used to counter parasites and diseases can damage the ecosystem around the enclosures
\-Fish can escape and breed or compete with native stocks of fish.
\-Parasites and diseases can spread from fish in enclosures to nearby wild stock.
\-Chemicals and antibiotics used to counter parasites and diseases can damage the ecosystem around the enclosures
\-Fish can escape and breed or compete with native stocks of fish.
99
New cards
Environmental challenges
\-Agricultural chemicals and fossil fuels
\-Depletion of water supplies
\-Loss of biodiversity
\-Soil degradation and erosion
\-Sustainability
\-Depletion of water supplies
\-Loss of biodiversity
\-Soil degradation and erosion
\-Sustainability
100
New cards
Overgrazing
Animals graze to the point that grasslands are damaged to the extent that vegetation won’t refresh itself. When the density of animals is greater than even expansive grasslands can support