Chemistry: physical chl
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Metal + steam →
Metal oxide + hydrogen
Give a commercial use of a group 2 compound (2 examples)
Mg(OH)2 is used as an antacid to neutralise excess stomach acid
Ca(OH)2 is used in agriculture to neutralise excess acid in soil
Other than Mg(OH)2,what compound is used as an antacid?
CaCO3
Explain why it is difficult to predict whether MgF2 or MgI2 will have more or less exothermic enthalpy change of solution
Ionic radius increases down the group so F- is smaller than I-
Lattice enthalpy for MgI2 is less exothermic than for MgF2
I- has less attraction for H2O than F- so Hydration enthalpy is less exothermic for MgI2
Difficult to predict whether lattice enthalpy or hydration enthalpy has a bigger effect
Entropy definition
A measure of the dispersal of energy in a system which is greater when the system is more disordered
Why is a buffer solution formed from acid and base?
The acid is partially neutralised and forms conjugate base (salt of weak acid - give example!)
When a solid ionic lattice is dissolved in solution, what happens to entropy?
Entropy increases as ions are more disordered
Equation used to calculate entropy change

What are the limitations of feasibility predictions made using gibbs’ free energy equation?
Activation energy may be too high
Rate of reaction may be too slow
Oxidising agent
A species that is reduced in a reaction and causes another species to be oxidised
Standard conditions for gas pressure
1 atm (100 kPa)
Standard hydrogen half cell
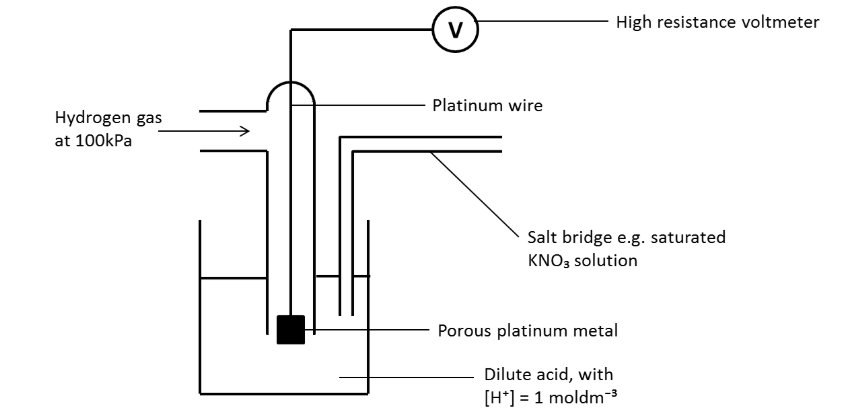
How to make a simple salt bridge?
Filter paper dissolved in aqueous solution of potassium or ammonium nitrate
Which states can be used in heterogeneous Kc?
aq only
Precipitation reaction adding NH3 dropwise (reaction with water)
NH3 + H2O → NH4++ OH-
Blood buffer (carbonic acid)
H++ CO3- → CO2 + H2O
Equivalence point
The point in the titration when the volume of one solution has reacted exactly with the volume of the 2nd solution ([OH-]=[H+])
How to select an indicator for titration
The pH range of the indicator coincides with the vertical section
End point
pH at which there are equal concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base ([HA]=[A-])
Conjugate acid-base pair
Two species that transform into each other by gain or loss of a proton
Limitations of Ka
Stronger weak acids have more dissociation of HA and [H+] becomes significant and sig diff. between HA and H+ (if Ka > 10-²)
Weaker weak acids are not valid for approximation [H+] ~ [A-], if pH > 6, the dissociation of water becomes significant
Lattice enthalpy
Enthalpy change the accompanies the formation of 1 mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions in their standard states
Lattice enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from it elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Lattice enthalpy of solution
Enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is dissolved in water under standard conditions
First ionisation energy
Energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions
Enthalpy change of hydration
Enthalpy change when one mole of isolated gaseous ions is dissolves in water forming one mole of aqueous ions under standard conditions
Comparing lattice enthalpies of MgS and Na2O (ICSAE)
Mg2+ ion has a greater charge than Na+ ion and Mg2+ is also smaller
The O2- ion is smaller than the S- ion
Mg2+ attracts negative ions more strongly than Na+ however O2- attracts positive ions more strongly than S2-
It is hard to predict which lattice enthalpy is the most exothermic
Compare hydration enthalpy of Cl- and O2- (ICSAE)
O2- has a greater charge than Cl- and it is smaller
There is a greater attraction between O2- ions and H2O molecules than between Cl- ions
O2- has a more exothermic hydration enthalpy
What units is temperature in for Q=mcΔT?
Degrees C
How does dative covalent bonds differ in bond enthalpy from covalent bonds?
Not at all - they have the same bond enthalpies!