WEEK 13 - Alcohol and Phenols
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Alcohols
• Characterized by one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon chain
alkyl group
In common names, the separate word “alcohol” is placed after the name of the?
MONOhydric
what kind of classification
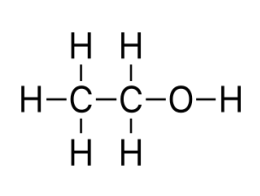
Dihydric
what kind of classification
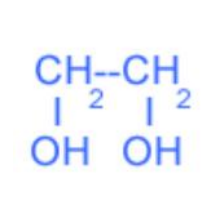
TRihydric
what kind of classification
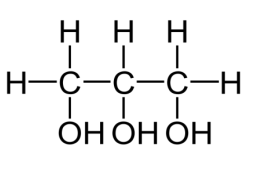
Allylic carbon atom
what kind of CARBON ATOM
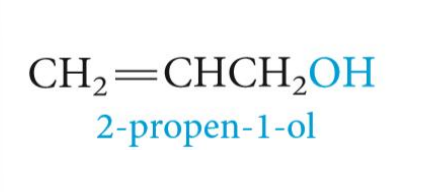
Benzylic carbon atom
what kind of CARBON ATOM
colorless liquids at room temperature.
Most of the common alcohols are
4-10
Higher alcohols containing HOW MANY atoms
viscous or oily
heavy fruity odors
Higher alcohols (4-10) somewhat?
12
Highly branched alcohols containing more than HOW MANY carbon atoms are solids at room temperature.
solids at room temperature.
highly branched alcohols containing more than 12 carbon atoms are?
hydrophilic (“water-loving”)
hydroxyl group is referred to as a
Methanol
ethanol
n-propyl alcohol
isopropyl
alcohol are all miscible with water.
less water-soluble
Alcohols with higher molecular weights tend to be
4
lower alcohols with UP to HOW MANY carbon atoms
Methanol
Very soluble in water
Butanol
Slightly soluble in water
Octanol
Insoluble in water
wood by distillation
Methanol was at one time produced from?
wood alcohol
Methanol sometimes called?
carbon monoxide
hydrogen
Methanol is manufactured from
Methanol
produce formaldehyde and other chemicals, but some is used as a solvent and as an antifreeze.
Formaldehyde
Methanol Oxidized what?
Opsin
Formaldehyde bind to?
rhodopsin,
formaldehyde, which binds to opsin, preventing formation of?
rhodopsin
the light-sensitive pigment neededforvision.
Methanol
highly toxic and can cause permanent blindness
Mild CNS depression
Cinical Effects of Methanol Intoxication:
Early CNS
Vertigo
lethargy
coma,
Parkinson-like syndrome
putamen necrosis
Hemorrhage
Clinical Effects of Methanol Intoxication:
Late CNS
Photophobia
retinal edema
blindness
Clinical Effects of Methanol Intoxication:
Late VISION
Abdominal pain
pancreatitis
Clinical Effects of Methanol Intoxication:
Late GI
AKI (rare)
Clinical Effects of Methanol Intoxication:
Late KIDNEY
Ethanol
used fermentation to make
Yeast
Fermantation catalyst
acid-catalyzed hydration of ethylene
Beside fermentation ETHANOL manufactured by the
Sulfuric acid
acid-catalyzed hydration of ethylene CATALYST
Ethanol
used as a solvent, as a topical antiseptic (for example, when drawing blood).
Ethanol
It also can be used as a fuel, often as a blend with gasoline.
80-300mg/dL
Loss of balance and speech, amnesia
300-400mg/dL
N/V, loss of consciousness
400-600mg/dL
Loss of protective reflexes
600mg/dL
Spontaneous respiration
CV problems
death
2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol)
is manufactured commercially by the acid-catalyzed hydration of propene.
It is the main component of rubbing alcohol and is used in many household and personal care products.
ethylene glycol
refers literally to “the glycol made from ethylene.”
Ethylene glycol
commonly used as automotive antifreeze and as an ingredient in hydraulic fluids, printing inks, and paint solvents
Glycerol
is a sweet syrupy substance with three alcohol hydroxyl groups.
was first obtained as a by-product of soap manufacture.
Dehydration
Oxidation
Substitution
Esterification
Chemical Reaction in ALCOHOL
ketones
aldehydes
carboxylic acids.
Alcohols may be oxidized to give
phenol
In 1865 the British surgeon Joseph Lister used as an antiseptic to sterilize his operating field.
1865
In WHAT YEAR British surgeon Joseph Lister used phenol as an antiseptic to sterilize his operating field.
Joseph Lister
WHO IS THE British surgeon THAT used phenol as an antiseptic to sterilize his operating field.
Phenol
Joseph Lister used WHAT as an antiseptic to sterilize his operating field.