BPSC104 Class 12
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Plant hormones are also called plant ____?
growth regulators
Plant hormones can either ____ or _____ a process
promote; inhibit
Depends on:
Process
Hormone
if same plant hormone, can produce a different response in different tissues or at different times
Plant hormones rare act ____
alone
Hormones:
Hormones that activate the synthesis or other hormones
Hormones that oppose the activity of another hormone
Most hormones:
Usually a combination of specific hormones produces a response
3 Major steps to a plant/animal to stimulus
Perception
Transduction
Response
Perception
Step 1 of plant or animal responding to stimulus
Sensing the stimulus
Transduction
Step 2 to a plant or animal responding to a stimulus
Changing the stimulus to a form that can be communicated to other cells and parts of the plant
A hormone or other signaling molecule moves through vasculature or from cell to cell
Response
Step 3 to plant or animal responding to stimulus
Change in:
Growth
Morphology
Physiology (resulting in gene expression)
The 3 steps to plants and animals reacting to a stimulus (at the cellular level)
Perception / Reception
Transduction
Response/Induction
Signals are transmitted across ____
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Perception/ Reception
Step 1 to plant or animal responding to stimulus at cell lvl
Receptor molecule detects stimulus in the cell membrane
Transduction
Step 2 to plant or animal responding to stimulus at cell lvl
Receptor transfers the signal to a secondary messenger within the cell
Response/induction
Step 3 to plant or animal responding to stimulus at cell lvl
Secondary messengers direct a change in gene expression that will then produce a change in cell function
(Major) Plant hormones
Auxin
Cytokinin
Ethylene
Abscisic acid
Gibberellins
And others
Auxin (IAA)
Apical dominance
Adventitious rooting
Tropic responses
Cytokinin
cell division
Shoot production in tissue culture
Delay or leaf senescence
Gibberellin (GA)
Stem elongation
Release from seed dormancy
Stimulation of flowering
Abscisic acid
Stomatal closure
Stress resistance
Induction of dormancy of seeds and buds in certain gas
Ethylene (gas)
Abscission (leaves and fruits)
Fruit ripening
Phototropism (plant response)
growth of the shoots toward light (bending toward light)
Influence is produced in the shoot tip and transmitted down the stem
(darwin decided that the influence was in the shoot tip)
If light comes from the top, there is no influence
If light comes on the shady side: it will promote these cells to elongate,
longitudinal elongation (leads to bending to light)
differential cell elongation - these cell are elongating these cells are not

Gravitropism
shoot will elongate and respond to gravity and shoot will go upwards

Phototropism
on the shaded side
Negative gravitropism
cell elongation and allow shoot to move upward
Think:
hormone can have different responses depending on different tissues
Auxin
Synthesized in baby leaves, young primordia
Developing seeds and roots
Auxin functions in ____
Tropisms
Apical dominance
Vascular tissue differentation
Inhibittion of leaf and fruit abscission
Phyllotaxis (does it attach opp or same, 2 leaves per node etc.)
Lateral root development
Many developmental processes in roots and shoots

What happens to the plant if the apical bud is removed?
The source of auxin is removed, axillary buds are no longer repressed
(If removed, axillary buds are now giving rise to new shoots)
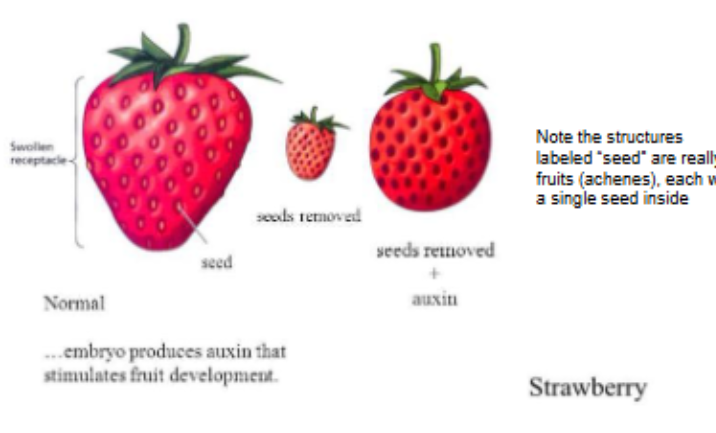
Auxin promotes ___ development
Fleshy fruit
Baspiteal
Polar transport is always this
can mean both directions
away from shoot tip (down)
away from root tip (upward)
Nonpolar or acropetal (base of tip) transport
can also occur
Cytokinin
work together to promote plant growth in tissue culture
Callus - forms when a piece of plant tissue is placed on culture media (mass of undifferenitated cells)
Callus
groups of undifferentiated cells
ready to be differentiated
Can be induced to form roots and/or shoots
New plants are clones of the original
Auxin promotes cell ___ and __ formation in tissue culture
Elongation; root;
Cytokinins promote ___ and ___ formation in tissue culture
cell division; shoot
Ratio of auxin:cytokinin (determine fate of callus)
determines root vs shoot formation in tissue culture (determine fate of callus - undiff cells)
High auxin/cytokinin = root formation
High cytokinin/auxin - shoot fomration
Balanced = undifferentiated (callus) proliferation
Ethylene background information
Promotes growth of most tissues
Inhibits cell elongation
Promotes fruit maturation
Promotes senescence and abscission (elongation)
Can inhibit OR promote cell division
Synthesized in response to stress or damage
Ethylene (inhibits vertical cell elongation) causes
Triple response - seedlings grown in the dark show this in response to ethylene
Causes:
Decreased vertical growth (shorter)
Increased lateral growth (wider)
Horizontal growth (curve)
Takeaway: Short, thicker, curved helps to protect shoots pushing through the soil to get light after germination
Ethylene in promoting fruit ripening
Climacteric fruits ripen rapidly
Cellular respiration - increases dramatically
Banana, tomato, avocado
Spike in ethylene production - precedes ripening and induces the increase of respiration
Continue to ripen after harvest (climatic fruits)
Ethylene promotes ripening of some fruits
Important for agriculture and economics
these fruits can continue to produce ethylene as they ripen
Reduced ethylene production or sensitivity
facilitates food storage and transport
Inhibiting ethylene synthesis can prolong the storage life of fruits and vegetables
Abscisic acid (ABA)
slowing things down
Involved in prventing seed germination
root to shoot signaling
Response to drought stress, stomatal closure
No direct role in abscission
(Synthesized in mature leaves roots)
Dormin - growth inhibitor found in dormant buds
Abscisin - an accelerator of leaf and fruit abscission
ABA levels
correlated to seed quiescence and dormancy
Aba required to maintain dormancy/quiescence
Decreasing ABA levels = breaking dormancy
Mutant seeds - insensitive to ABA germinate within the fruit
Turogor pressure
mediated by the vacuole
Gibberellins
Induces seed germination (opposing ABA)
promotes stem elongation
Stimulates cell division and cell elongation
Can stimulate flowering
Over 136 giberellins
Produced in seeds and young tissues
Found throughout the plant body
How are giberellins important in seed germination
(giberellins important in seeds accessing the endosperm and starch in that endosperm)
Giberellins have ___ and ___ uses
Agricultural; commercial
Mutants that cannot produce of perceive Giberellins are
Dwarfed
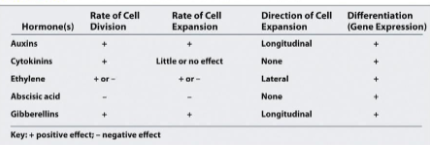
How do hormones work?
Absisic acid is a down regulat or of the genes expression those genes are involved in
Giberellins are up regulators
Photo
light, daylength
Morphogenic
changing growth pattern of entire plant
Morphogenesis — response to stimulus by changing the growth pattern
Nastic (nasty)
Response to stimulus
Not specifically towards or away from stimulus
Tropic (tropism)
Response to stimulus by growing towards or away from the stimulus
Gravi
gravity, weight
Thigmo
touch (harmful or helpful)
Thermo
temperature (cold or hot)
Chemo
Chemicals
Hydro
water (prescence or absence)
thigmomorphogenesis
thigmo - touch
morphogenic - morphogenesis (plant growth)
Phototropisms
can be positive or negative
Positive - toward light
negative - away from
towards or away from light
Gravitropic responses
Starch-stratolith hypothesis*
Statoliths
Statoliths
amyloplasts (starch-filled plastids) within gravity-sensing cells
In stems:
In cells surrounding the vascular tissues
In roots:
In columella cells (Stratocytes) of the root cap
Sedimentation of stratoliths
perceives gravity
Stratolith sedimentation induces differential auxin levels in the root elongation zone
Auxin moves cell to cell (polar auxin transport)
Higher auxin levels on lower side inhibits elongation
Response in roots is opposite to that inshoots
Thigmotropic responses
shown in both tendrils and roots
Cells on the side opposite the touch stimulus elongate
Tendrils wraps - around the object it has touched
Roots grow around rocks and other obstacles
Likely at least partially auxin mediated, but unclear for now