BIOLOGY - digestion, respiration, transportation (human+plant)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Macromolecules are
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of many repeating units, that are linked together through covalent bonds.
Macromolecule types
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Macromolecule function
depends on the properties of functional groups. Each group has specific properties, such as polarity.
-A single macromolecule may contain many different functional groups.
stages of digestion
ingestion, digestion, absorption, compaction, defecation
mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
mechanical vs chemical digestion
Mechanical- broken down by moving, pushing, churning, breaking
Chemcial- uses chemicals and enzymes to break down food
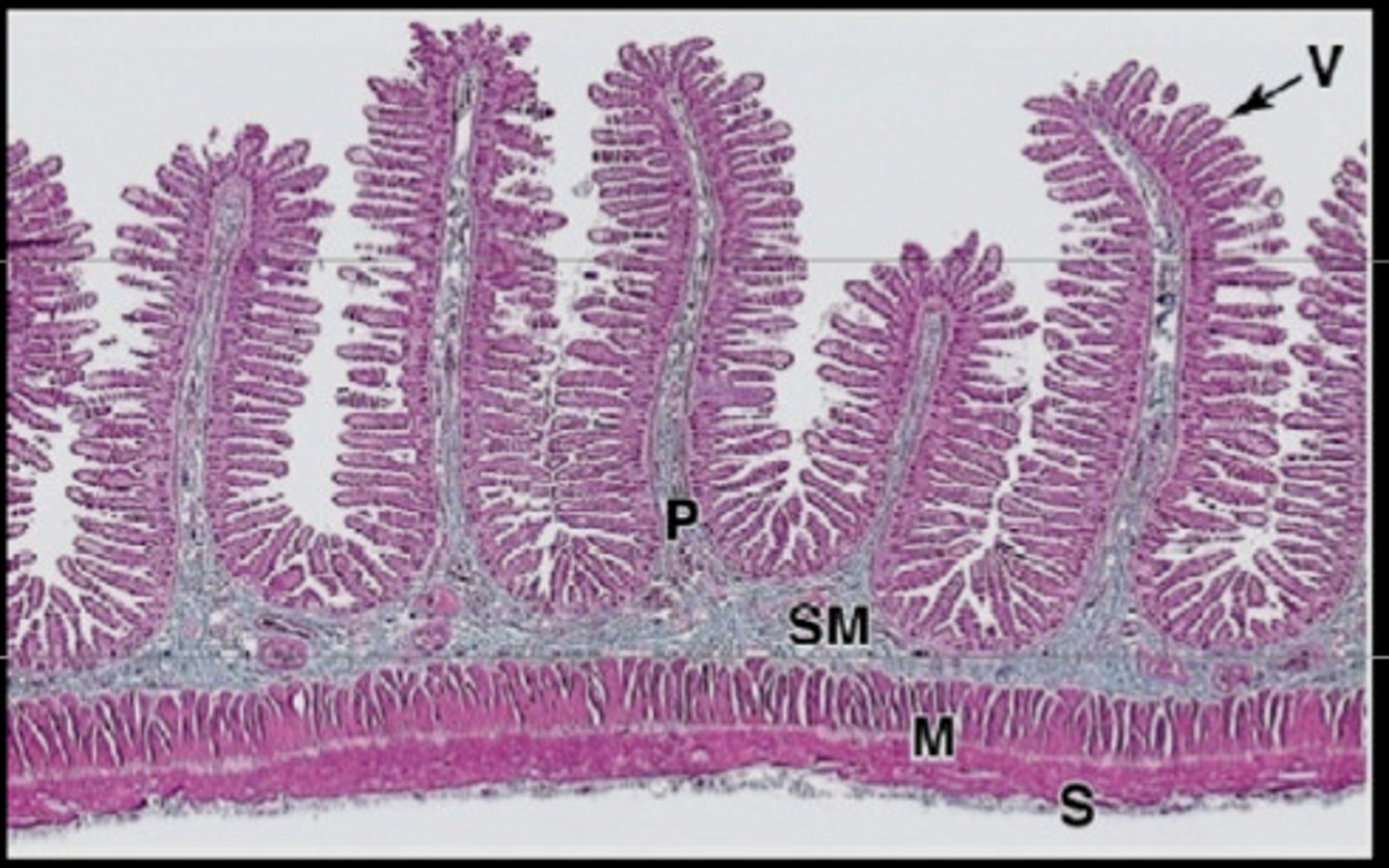
Absorption (*villi in small intestine)
The microvilli are covered in a specialized membrane that allows for the efficient uptake of nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The absorbed nutrients are then transported to the bloodstream and distributed to various parts of the body for use in metabolic processes.
Breathing vs Respiration
breathing = inhaling and exhaling air
respiration = chemical exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
order of respiratory system
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
Alveolus is what?
the place where gas exchange takes place
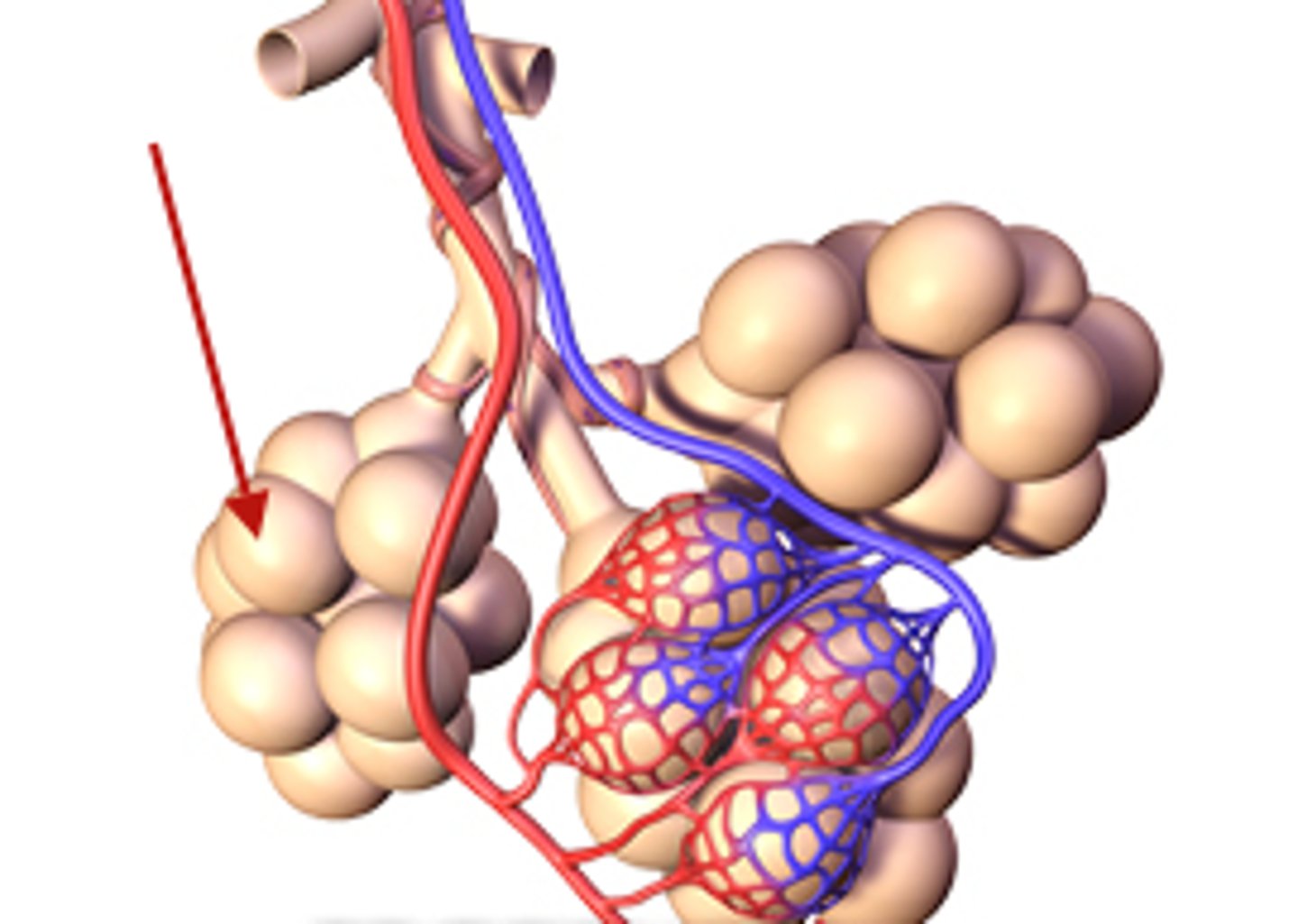
anaerobic vs aerobic respiration
aerobic: occurs when enough oxygen reaches cells to support their energy needs
Anaerobic: occurs when the demand for oxygen is greater than the body's ability to deliver it
arteries, viens, capillaries function
three types of blood vessels
A = away! arteries transport blood away from the heart around the body
V= veins do the opposite they transport blood towards the heart
C= these are the small vessels that bring the blood into every part of you body
arteries, viens, capillaries structure
A= must handle high pressure (aorta has the highest pressure)
have a small lumen
V= low blood pressure
have a big lumen and a thinner outer wall/muscle wall
C= very slow = very low blood pressure
very small lumen 1 cell thick outer wall
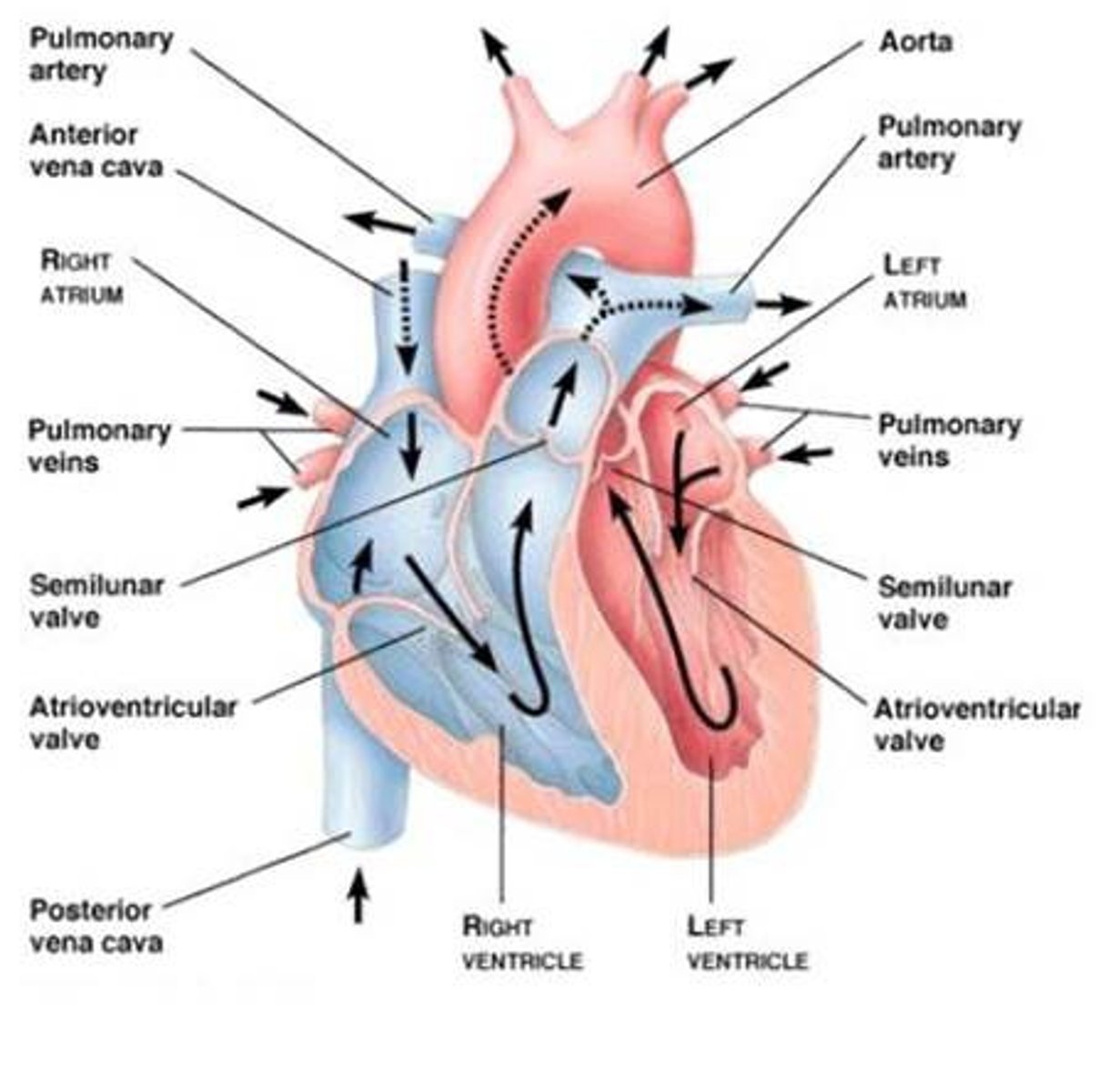
Path of blood through the heart
Right Atrium --> AV valve --> Right Ventricle --> semi lunar valves --> pulmonary artery --> lungs --> pulmonary vein --> Left Atrium --> AV valve --> Left Ventricle --> semi lunar valves --> Aorta ====== ALL AROUND THE BODY and back again
what does blood contain?
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
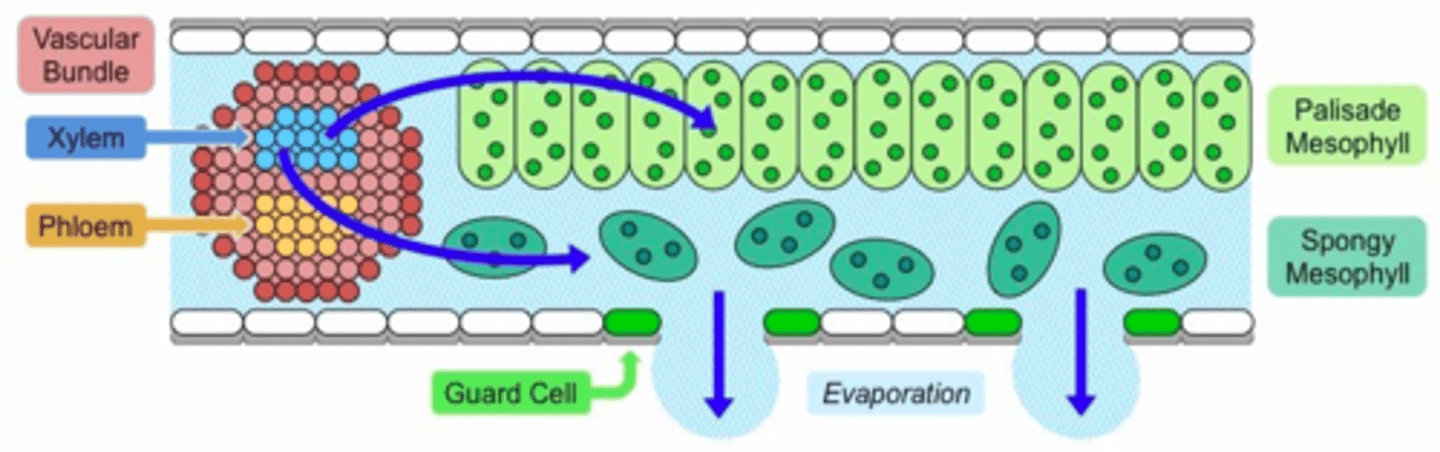
What is traspiration?
Evaporation of water from plants through the stomata
how does transpiration work?
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the air through tiny openings on their leaves called stomata, which helps regulate their temperature and maintain water balance.
if/when a plant finds itself in drought it will close off the stomata to preserve water but in that process it closes off its only means to Co2 which causes the plant to be unable to perform photosynthesis (it dies)
Photosynthesis
HO2 (soli [osmosis]) + Co2 (air [stomata])+ sun
= O2 (released through stomata) + Glucose (used by plant)
![<p>HO2 (soli [osmosis]) + Co2 (air [stomata])+ sun <br>= O2 (released through stomata) + Glucose (used by plant)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f5c09f6b-f564-4bc1-999a-c181c9248506.jpg)
What is xylem?
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
What is phloem?
the vascular tissue in plants that conducts sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves.
What is mesophyll?
the green tissue in the interior of the leaf
What is osmosis?
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Enzymes are
proteins that function as catalysts
examples of enzymes
catalase, lactoase, lipase, protease, maltase, sucrase, pepsin (Most end in -ase)