Digestive System - Chapter 25 Review
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of practice flashcards covering the key concepts from the digestive system lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What are the five stages of digestion?
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Compaction, and Defecation.
What role does the digestive system play according to the notes?
It acts as a disassembly line to digest nutrients into usable forms and absorb them for distribution to tissues.
What is gastroenterology?
The study of the digestive tract and the diagnosis and treatment of its disorders.
What is mechanical digestion?
The physical breakdown of food into smaller particles, including mastication and churning.
What is chemical digestion?
A series of hydrolysis reactions that break dietary macromolecules into monomers, carried out by enzymes from salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine.
What are the end products of carbohydrate digestion?
Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose) after breakdown of polysaccharides.
Which nutrients can be absorbed directly in ingested food (without further digestion)?
Vitamins, amino acids, minerals, cholesterol, and water.
What are the main layers of the digestive tract wall from inner to outer?
Mucosa (including epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosae), Submucosa, Muscularis externa (inner circular, outer longitudinal), Serosa.
What attaches the stomach to the liver?
Lesser omentum.
What covers the intestines like an apron?
Greater omentum.
What holds the small intestine in place and contains many blood vessels?
Mesentery.
What anchors the colon to the body wall?
Mesocolon.
Which enzyme begins carbohydrate digestion in the mouth?
Salivary amylase.
Which enzymes digest fats in the mouth and stomach?
Lingual lipase (mouth) and gastric lipase (stomach).
What components are found in saliva?
Salivary amylase, lingual lipase, mucus, lysozyme, IgA, electrolytes, and a pH of 6.8–7.0.
What is the function of the pharynx and the esophagus in digestion?
is a muscular funnel; the esophagus is a straight muscular tube that transports food to the stomach (via swallowing) and includes the lower esophageal sphincter.
What is chyme?
A soupy or pasty mixture of semi-digested food in the stomach.
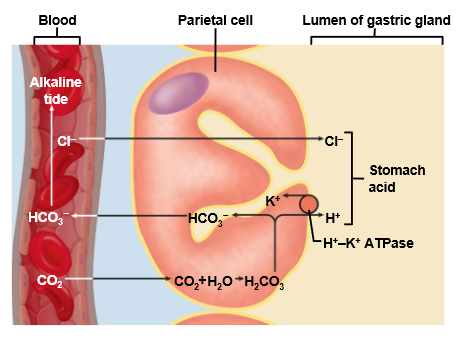
What is gastric juice composed of, and how much is produced daily?
Water, hydrochloric acid (HCl), and pepsin; about 2–3 liters per day.
How low can gastric juice pH drop?
As low as pH 0.8.
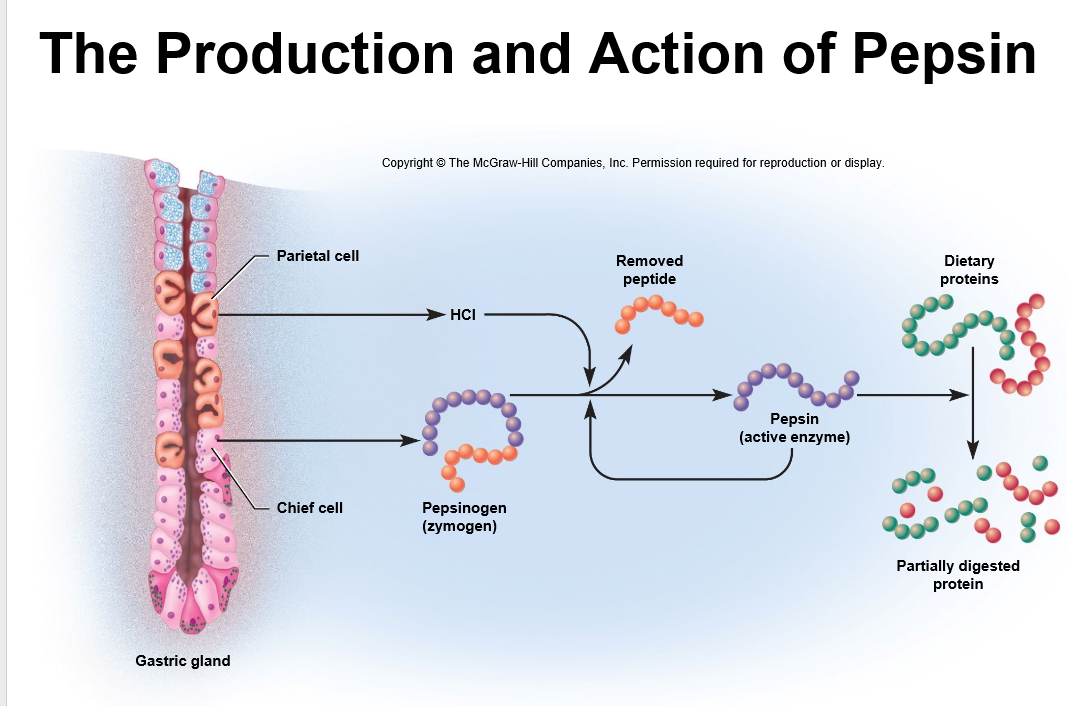
Which cells secrete pepsinogen?
Chief cells.
What is the cephalic phase of gastric regulation?
Triggered by the sight, smell, taste, or thought of food, it prepares the stomach for digestion by increasing gastric secretion and motility via vagal reflexes.
What activates pepsinogen to pepsin?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) that is secreted by parietal cells in the stomach.
What is the cause and management of peptic ulcers as noted?
Gastritis leading to ulcers; most ulcers are caused by Helicobacter pylori and are treated with antibiotics (and Pepto-Bismol).
What is the gastric phase of gastric regulation?
when food enters the stomach, stimulated by distension, pH changes, and undigested proteins, further boosting gastric secretion and motility via reflexes and gastrin release.
What regulates gastric function during the intestinal phase?
Enterogastric reflex; secretin and CCK inhibit gastric secretion and motility.
What is the intestinal phase of gastric regulation?
Starts when chyme enters the duodenum. It initially stimulates but then primarily inhibits gastric activity via the enterogastric reflex and hormones (secretin, CCK) to control chyme flow.
What is the liver’s primary digestive role?
Secretes bile, aiding digestion, detoxification, stores glycogen and certain vitamins or minerals, produces cholesterol and triglycerides, and urea.
Where is bile stored and concentrated?
In the gallbladder.
Which ducts carry bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum?
Common hepatic duct, cystic duct (from the gallbladder) combine to form the bile duct.
What are the five stages of digestion?
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Compaction, and Defecation.
What are the main pancreatic enzymes involved in digestion?
Trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase (proteases); pancreatic amylase; pancreatic lipase; ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease.
What are the three regions of the small intestine?
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum.
How is the inner surface area of the small intestine greatly increased?
Circular folds (plicae circulares), villi, and microvilli (brush border).
What is the role of lacteals in the villi?
are lymphatic vessels that absorb dietary fats.
What are goblet cells and Paneth cells known for in the small intestine?
secrete mucus; and secrete antimicrobial agents.
What enzymes digest carbohydrates in the small intestine’s brush border?
Maltase, sucrase, and lactase (in addition to pancreatic amylase in the lumen).
What happens in lactose intolerance?
Lactose passes undigested into the colon, increasing osmolarity and causing water retention and diarrhea; dairy lactose can be mitigated by bacteria in yogurt/cheese.
Where does protein digestion begin and what enzyme initiates it?
In the stomach with pepsin (active in low pH) initiated by pepsinogen from chief cells; pepsin digests 10–15% of dietary protein.
What are the small intestinal proteases that finish protein digestion?
Trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase, and dipeptidase.
How are lipids digested and absorbed?
Lipases (lingual, gastric, pancreatic) hydrolyze triglycerides to free fatty acids and monoglycerides; most are absorbed via lymphatics; bile acids and micelles emulsify fats.
What are micelles and what is their role in fat absorption?
emulsified droplets that transport lipids to the absorptive surface for uptake.
Which vitamins are fat-soluble and how are they absorbed?
Vitamins A, D, E, and K; absorbed with lipids.
What is the role of water in digestion and what conditions affect it?
most is absorbed in the small intestine; diarrhea and constipation relate to its absorption in the large intestine.
What are the major sections of the large intestine?
Cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal.
How is defecation neurally controlled?
Stretch receptors in the rectum trigger a spinal reflex causing rectal contraction and internal anal sphincter relaxation; the external anal sphincter is controlled voluntarily, and defecation occurs when it relaxes.
what is the bodys largest gland
the liver
what nervous system class works on the stomach
parasympathetic nervous system acts on the stomach to stimulate digestion, sympathetic for inhibiting peristalsis
sympathetic on the stomach
slows down digestion and inhibits peristalsis.
What are the pancreas’s endocrine roles?
islets secrete insulin and glucagon
what are the pancreases exocrine roles?
acinar cells secrete pancreatic juice with digestive enzymes.
endocrine means
related to hormone secretion into the bloodstream.
exocrine means
related to secretion through ducts.
mucous cells
Secrete mucus and predominate in the cardiac part and pylorus
regenerative cells
Divide rapidly and provide a continuous supply of new cells
parietal cells
Secrete hydrochloric acid, intrinsic factor, and ghrelin (necessary for vitamin B12 absoption)
chief cells
Secrete the digestive enzymes gastric lipase and pepsinogen
enteroendocrine cells
secrete hormones and paracrine messengers
zymogen
an inactive/pro-enzyme that is only activated after it has been secreted and had some of its amino acids cleaved
within the presence of HCl, what becomes the active form of this enzyme?
Pepsinogen becomes pepsin
trypsinogen turns into what
trypsin after contacting intestinal enzyme enteropeptidase
hepatic triad
made up of branch of the hepatic portal vein, a branch of the hepatic artery, and a bile duct
process of segmentation
consists of muscular contractions that knead and churn the contents
contact digestion
is when enzymes on the brush border of the intestinal mucosa break down nutrients for absorption.
peristalsis
as segmentation decreases, this begins in the duodenum
migrating motor complex
successive peristaltic waves of contraction overlap with each other
gastroileal reflex
enhances segmentation in the ileum relaxing ileal papilla
relaxation of ileal papilla
allows for contents in the ileum to enter cecum
once in the stomach, what hydrolyzes peptide bonds?
pepsin
what of the small intestine will finish the breakdown and absorption of proteins
the brush boarder
the process of starch digestion begins where with amylase?
in the mouth
what does amylase digest starch into first, these are 8 glucose residues long.
Oligosaccharides
what do oligosaccharides get catabolized into?
maltose, a disaccharide
what is maltose converted into which then gets absorbed by the small intestine?
glucose
what is the outermost layer of the digestive tract wall?
serosa
what is the enteric plexus?
network of nerves that regulate digestive motility, secretion, and blood flow
what organ is behind the greater curvature of the stomach and acts as both endocrine and exocrine gland?
the pancreas
what are the 3 segments of the small intestine?
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
what does the small intestine and stomach have in common?
mucus-secreting cells
what is mass movement?
peristaltic movement of colonic contents triggered by gastrocolic reflex 1-3 times per day
what stimulates mass movements in the colon?
food in the stomach, and chyme in the duodenum
defecation is stimulated by
parasympathetic and local reflexes
the muscularis externa
layer responsible for motility that propels food and residue through digestive tract
what regulates digestive tract motility, secretion and blood flow with its neurons in the submucosa and muscularis externa
enteric plexus
where does carbohydrate digestion begin
in the mouth with saliva
where does protein digestion begin
in the stomach with pepsin
pyloric sphincter
regulates the flow of contents from the stomach to the duodenum
enterogastric reflex serves to
inhibit gastric motility when there is chyme in the small intestine
bile salts
components contributes to digestion by means of emulsification of lipids
pancreatic enzymes are secreted in response to a hormone called _?
cholecystokinin (CCK)
A sodium bicarbonate solution is secreted in response to a hormone called __________?
secretin
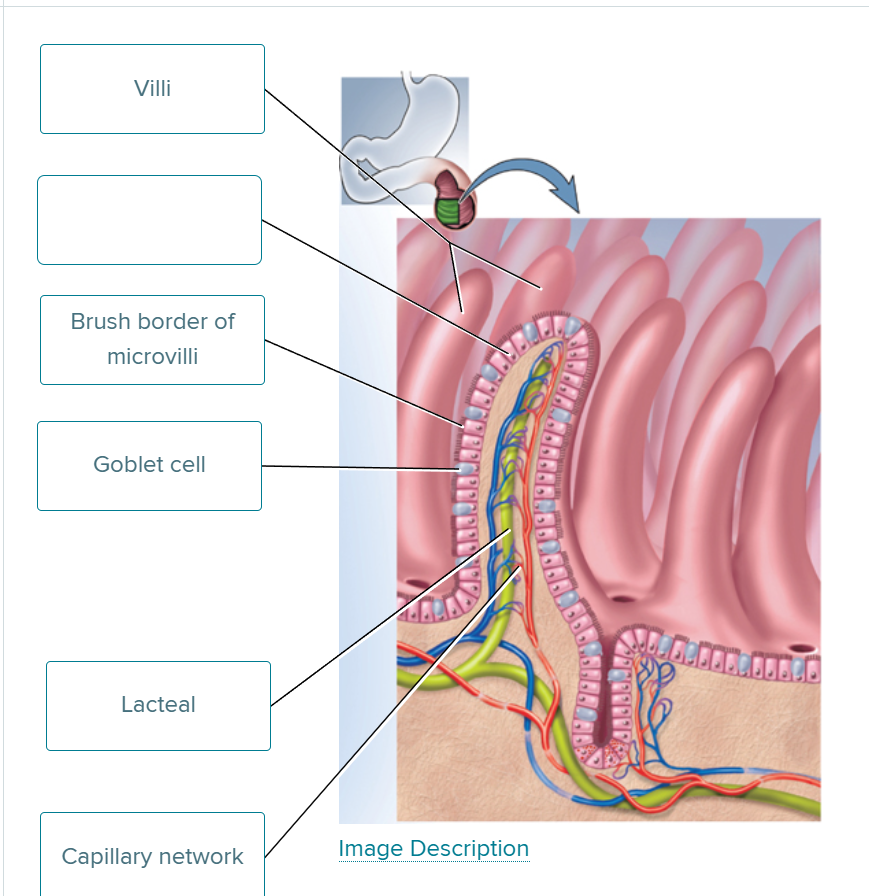
fill in the blank
absorptive cell
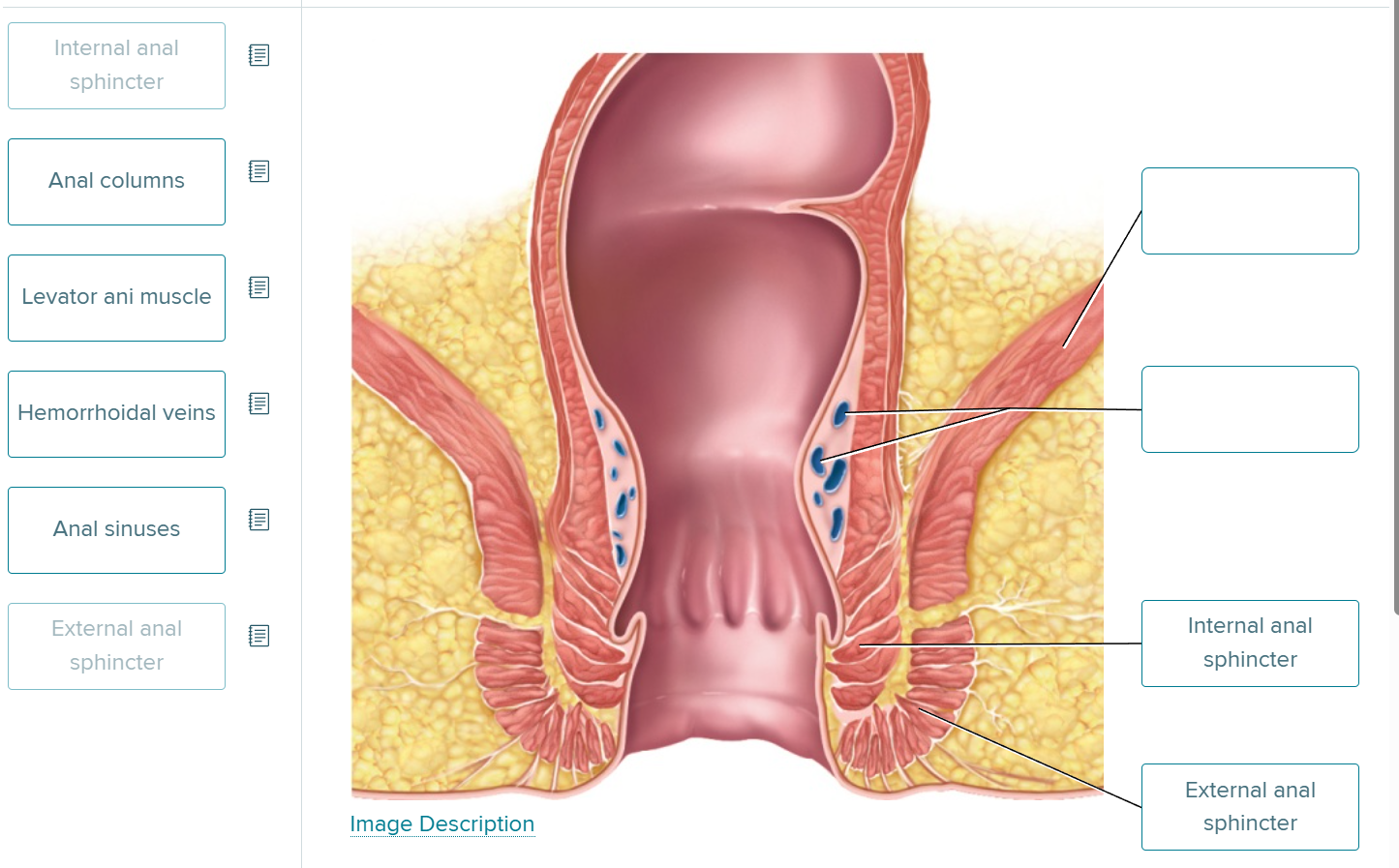
label the blue bean shaped figures
hemorrhoidal veins