Water Movement by Osmosis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Define osmosis.
The movement of water by diffusion across a membrane without using energy.
In which direction do water molecules move during osmosis?
From low solute concentration to high solute concentration.
When does osmosis stop?
When equilibrium is reached between the two sides.
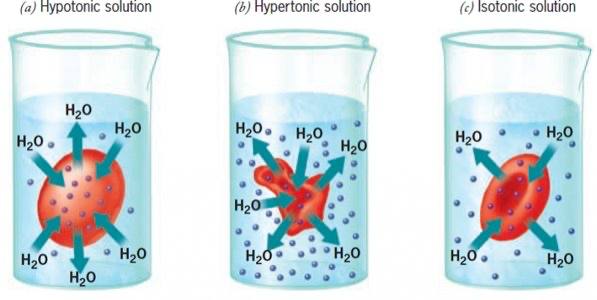
List the three types of solutions based on solute concentration.
Hypertonic, Hypotonic, Isotonic.
Define osmolarity.
A measure of solute concentration, expressed as osmoles of solute per litre of solution (osmol/L).
Define hypotonic solution.
A solution with lower solute concentration and higher water potential than the cell.
What happens to water movement in a hypotonic solution?
Water moves into the cell from the surrounding solution.
Effect of a hypotonic solution on animal cells.
Cells swell and may lyse (burst) due to lack of a cell wall.
Effect of a hypotonic solution on plant cells.
Cells become turgid due to water entering the central vacuole.
Define hypertonic solution.
A solution with higher solute concentration and lower water potential than the cell.
What happens to water movement in a hypertonic solution?
Water moves out of the cell into the surrounding solution.
Effect of a hypertonic solution on animal cells.
Cells crenate (shrivel) as water leaves.
Effect of a hypertonic solution on plant cells.
Cells become plasmolysed as the membrane pulls away from the wall.
Define isotonic solution.
A solution with equal solute concentration to the cell’s internal environment.
What happens to water movement in an isotonic solution?
Equal volumes of water enter and leave the cell.
Osmosis in Plants - Hypertonic
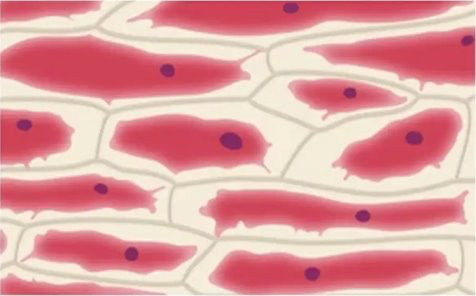
Osmosis in Plants - Hypotonic
Cells are flaccid as there is no net water movement.
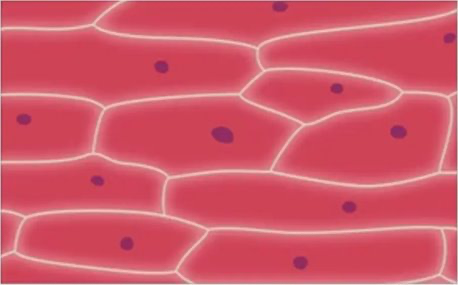
Osmosis in Animals - Hypertonic
Osmosis in Animals - Hypotonic
Osmosis in Animals - Isotonic