Chapter 18: (ONLY) Eyes
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Name the 7 Structures of the Lacrimal Apparatus.
Lacrimal Gland
Lacrimal Ducts
Lacrimal Punctum
Superior Lacrimal Canaliculi
Inferior Lacrimal Canaliculi
Lacrimal Sac
Nasolacrimal Duct
The “Nasolacrimal Duct” DRAINS INTO the ___1.____.
nose
Define “Conjunctiva”.
A CLEAR mucous membrane found on the INNER SURFACE of the eyelid and the WHITE PART of the eye.
Identify the 2 Function of the Conjunctiva.
Helps LUBRICATE the eye by PRODUCING mucus and a small amount of tears (less than the lacrimal gland).
Forms a BARRIER to HELP PREVENT microbial entry INTO the eye.
Which Structure of the Eye, DOES NOT Have a “Conjunctiva”?
The cornea.
Define “Conjunctivitis”.
INFLAMMATION of the conjunctiva.
Name the 3 Layers of the Eye.
Fibrous Tunic.
Vascular Tunic.
Neural Tunic.
Identify and Define the purple label.
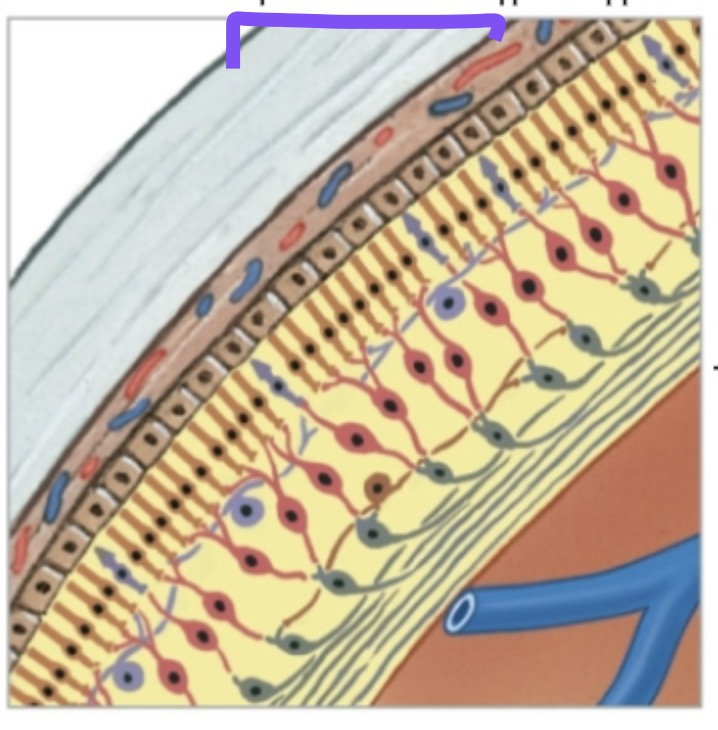
Fibrous Tunic (Sclera).
Identify and Define the purple label.
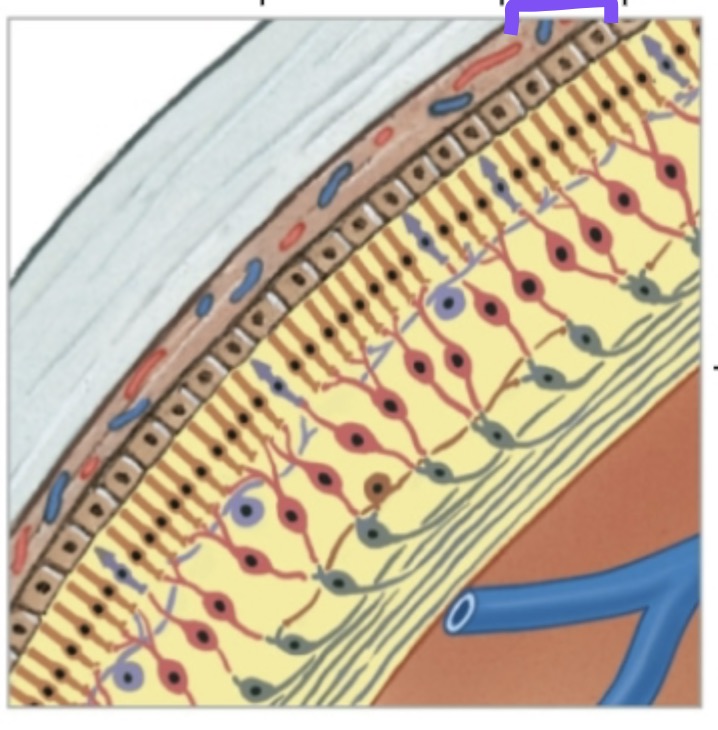
Vascular Tunic (Choroid).
Identify and Define the purple label.
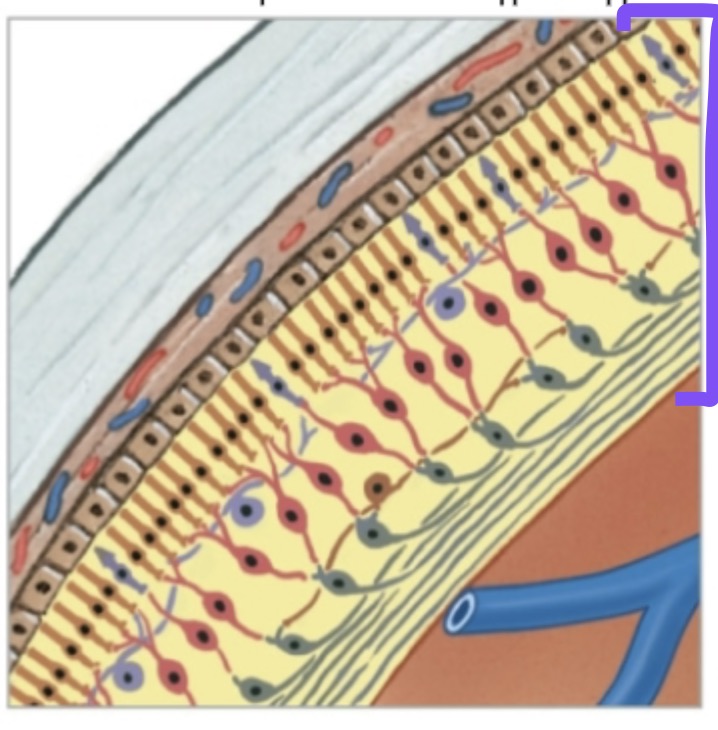
Neural Tunic (Retina).
Name the 2 Structures of the Fibrous Tunic.
Sclera
Cornea
Identify and Define the purple label.
Sclera.
The white of the eyes; becomes more THICKER behind the eyes.
What is the “Sclera” COMPOSED OF?
Collagen and Elastic Fibers.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Cornea.
Made of TRANSPARENT COLLAGEN in regular sheets (alike pages in a book); CONTAINS many PAIN RECEPTORS.
Is the Cornea, “AVASCULAR”?
The cornea is AVASCULAR because it receives oxygen VIA diffusion from air & nutrients FROMAQUEOUS HUMOR in the anterior chamber.
What is the Cornea HIGH CAPACITY for?
Regeneration.
Name the 3 Structures of the Vascular Tunic.
Iris.
Choroid
Ciliary Body
Identify and Define the purple label.
Iris.
(look @ video)
Name the 3 Structures of the Iris.
Pupillary Sphincter Muscle
Pupillary Dilating Muscles
Pigmented Epithium
What 2 Types of Muscle does the Iris Contain?
2 Layers of SMOOTH MUSCLE:
Pupillary Sphincter Muscle
Pupillary Dilating Muscles
Identify and Define the purple label.
Pupillary Sphincter Muscle.
CIRCULARALY ARRANGED the iris.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Pupillary Dilating Muscle.
RADIATING the iris.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Pigmented Epithium.
Various amounts of MELANIN and depth account for EYE COLOR.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Choroid.
MIDDLE layer, pigmented and vascularized.
Identify the Function of “Choroid”.
PROVIDES blood supply TO nourish other layers of the eye.
What does the “Choroid” CONTAIN?
Lymphatics.
In Animals, what Structure REFLECTS LIGHT?
“Tapetum Lucidum”.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Ciliary Body.
Has a RING of tissue that ENCIRCLES the lens.
Identify the Function of the “Ciliary Body”.
CONTROLS the shape of the lens for FOCUSING.
What Type of Muscle Does the “Ciliary Body” Contain?
SMOOTH MUSCLE:
“Ciliary Muscle”.
Name the 2 Structures of the “Ciliary Body” that ANCHORS TO THE LENS.
Ciliary Muscle (Smooth Muscle)
Suspensory Ligaments
Identify the 3 Structures of the Neural Tunic.
Retina
Macula Lutea
Optic Disc
Identify and Define the purple label.
Retina.
INNERMOST layer of the eye.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Ora Serrata.
The line that SEPARATES the retina FROM the ciliary body.
Name the 2 Layers of the Retina.
Outer Pigmented Layer
Thick Neural Layer
The “Outer Pigmented Layer” contains _____1.______.
melanocytes
Name the 3 Types of Neurons of the “Thick Neural Layer”.
Photoreceptors
Bipolar Cells
Ganglion Cells
Name the 2 Structures of the Photoreceptors.
Rods
Cones
Define “Rods”.
Important for PERIPHERAL vision and DETECTING motion.
What are “Rods” Sensitive to?
Rods are very sensitive to LIGHT so they function in NIGHT VISION.
What Colors do “Rods” Detects?
Detects LIGHT/DARK and SHADES of GRAY.
Define “Cones”.
To see bright colors, it requires BRIGHT LIGHT.
What Colors do “Rods” Detects?
Detects BLUE, RED, and GREEN.
Identify the purple label.
Bipolar Cells.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Ganglion Cells.
CONVERGE to FORM the “Optic Nerve”.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Macula Lutea.
"YELLOW SPOT".
Identify and Define the purple label.
Fovea Centralis.
Located at the CENTER of the “Macula Lutea” which ONLY CONTAINS CONES.
The “Fovea” is the point of ____1.____ ___1.____ ___1.____—where LIGHT is ____2.____ when you look ____3.____ at something.
sharpest visual acuity
focused
directly
What is NOT FOUND in the “Fovea Centralis”?
Rods.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Optic Disc.
Area where the Optic Nerve, Artery, and Vein PASS THROUGH the Retina.
The “Optic Disc” is also known as the ____1.____ ___1.____ because it DOES NOT CONTAIN ______2.________.
blind spot
photoreceptors
Identify and Define the purple label.
Anterior Cavity.
Is FILLED with “Aqueous Humor”.
Define “Aqueous Humor”.
FILLED with CLEAR & WATERY FLUID.
Define the 2 Function of the “Aqueous Humor”.
Maintains CONSTANT intraocular pressure by BALANCING its production and drainage.
NOURISHES the cornea and lens.
Are the “Cornea” & “Lens” AVASCULAR?
Yes, both the “cornea” and “lens” are AVASCULAR.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Anterior Chamber.
Located in FRONT OF the iris.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Posterior Chamber.
Located BETWEEN the iris & lens.
Describe the Flow of “Aqueous Humor”.
The Ciliary Body CREATES Aqueous Humor, which FLOWS INTO the Anterior Chamber THROUGH the Pupil. Aqueous Humor DRAINS INTO the Canal of Schlemm.
Define “Glaucoma”.
IMPROPER DRAINAGE of aqueous humor can lead to intraocular PRESSURE BUILD UP & COMPRESSES the delicate blood vessels serving the retina.
Describe the Side Effect of “Glaucoma”.
This can cause NEURON DEATH, vision LOSS or BLINDESS.
Describe the Function of the “Lens” of “Posterior Cavity”.
SEPARATES the Eye into anterior and posterior COMPARTMENTS.
Define “Viterous Humor”.
A CLEAR, GELATINOUS material FOUND (FILLED) inside the Posterior Cavity.
What HELPS the “Posterior Cavity” MAINTAINS its Eye-Shape?
Vitreous Humor helps maintain the shape of the eye and holds the retina in place.
The “Retina” is NOT Firmly ATTACTHED TO the ___1.____ ____1._____.
UNDERLYING choroid.
Define “Retinal Detachment “.
Because of the Retina’s LOOSE ATTACHMENT, it can lead to VISION PROBLEMS OR LOSS if not treated promptly.
Identify and Define the purple label.
Lens.
Thick, transparent, and BIOCONVEX.
“Lens” are “bioconvex” what does that mean?
Biconvex means curved outward on both sides, like the shape of a lens that bulges out in the middle on both the front and back.
The “Lens” are COMPOSED OF _____1.______ ____1._____ of cells that becomes ___2.____.
concentric layers
fibers
The “FIBERS of Concentric Layers of Cells” are _____1.______ FOLDED in such a way that they become ______2.________.
proteins
transparent
The “FIBERS of Concentric Layers of Cells” are _____1.______ THROUGHOUT LIFE that the “Lens” ______2._______ WITH AGE.
added
thicken
What happens when the “Lens” THICKEN WITH AGE?
The Lens becomes DENSER, MORE CONVEX, and LESS ELASTIC.
What are the results when the “Lens” THICKEN WITH AGE?
As a result, the ability to focus DIMINISHES IN OLD AGE.
In order, describe the “Vision Pathway”.
Optic Nerve → Optic Chiasm → Optic Tract → Optic Radiations → Occipital Lobe.
What 3 other “Fibers” does the “Vision Pathway FIBERS” SYNAPSE WITH?
The Thalamus.
The Hypothalamus.
The Pineal Gland.
What does the “Cells at the Thalamus” FORMS to REACH the “Occipital Cortex”.
The “Optic Radiations”.
What other “Fibers” from the “Optic Tract” SYNAPSE AT?
The “Superior Coolliculus of the Midbrain”.