Aca Deca 2022-23 Science
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:17 AM on 11/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
-Electrically neutral
-Same number of protons and electrons
-number of protons defines its element
-Same number of protons and electrons
-number of protons defines its element
Atom
2
New cards
-Electrically charged
-Different number of protons and electrons
-May contain one or more atoms
-Different number of protons and electrons
-May contain one or more atoms
Ion
3
New cards
Atoms
smallest distinct particles that make up matter
4
New cards
What does the internal structure of an atom determine in an element?
The element's chemical behavior
5
New cards
What is the structure of an atom?
There is a nucleus made up of protons(+) and neutrons(no charge) surrounded by a cloud or ring of electrons(-). In a neutral charged atom, there is one proton for every electron.
6
New cards
How are ions formed?
atoms can lose or gain one or more electrons to form, respectively, positive or negative ions.
7
New cards
Mass spectrometers
-instrument that determines the relative mass of a single atom
-are able to separate and measure atoms and compounds because moving charged species (ions) of different mass (and energy) are affected differently by magnetic or electric fields
-are able to separate and measure atoms and compounds because moving charged species (ions) of different mass (and energy) are affected differently by magnetic or electric fields
8
New cards
Three basic components of a mass spectrometer
1. An ion source where compounds or atoms are converted into (usually positive) ions;
2. A mass analyzer where the ions are accelerated in magnetic fields and take different pathways;
3. A detector that measures the number of ions of each mass that are present.
2. A mass analyzer where the ions are accelerated in magnetic fields and take different pathways;
3. A detector that measures the number of ions of each mass that are present.
9
New cards
Mass spectrometer used in airports
a straight pathway used with a cycling magnetic field
10
New cards
Which Greek philosopher proposed the concept of atomism?
Leucippus
11
New cards
John Dalton
English chemist, meteorologist, and physicist who developed the atomic theory of matter in the 19th century
12
New cards
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures of all the gases in the mixture, (Ptotal = Pa + Pb)
13
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
the law that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical and physical changes, mass of reactants is equal to the mass of the products
14
New cards
Who proposed the law of conservation of mass?
Antoine Lavoisier (1789)
15
New cards
law of definite proportions
a substance is always composed of the same proportion of each element.
16
New cards
Who proposed the law of definite proportions?
Joseph Proust (1799)
17
New cards
Dalton's Law of Multiple Proportions
if two elements combine to form more than one compound, the ratios of their masses are whole numbers that are determined by the atomic weights of the elements involved.
18
New cards
When did Dalton publish "A New System of Chemical Philosophy"
1808
19
New cards
A New System of Chemical Philosophy
Published in 1808 by John Dalton; included Dalton's basic atomic principles
20
New cards
Dalton's major conclusions on atomic behavior
-All matter is composed of very small, indivisible particles called atoms.
-Atoms of the same element have the same properties (size, mass, etc.) while atoms of different elements will have different properties (e.g., hydrogen has different properties than lead).
-Atoms cannot be divided any further and cannot be created or destroyed.
-Atoms of different elements can combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds.
-Chemical reactions can cause atoms to combine, separate, and rearrange.
-Atoms of the same element have the same properties (size, mass, etc.) while atoms of different elements will have different properties (e.g., hydrogen has different properties than lead).
-Atoms cannot be divided any further and cannot be created or destroyed.
-Atoms of different elements can combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds.
-Chemical reactions can cause atoms to combine, separate, and rearrange.
21
New cards
Which element does not contain any neutrons?
Hydrogen
22
New cards
What is the atomic number?
the number of protons in an atom
23
New cards
How do you find the mass number
the number of protons plus the number of neutrons
24
New cards
in (A/Z)X, What does the A represent?
The Mass Number
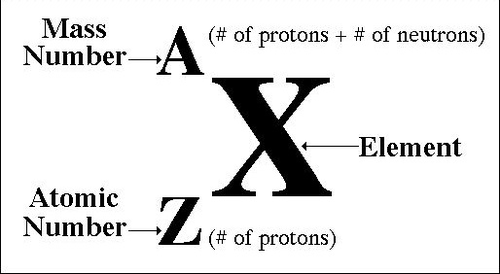
25
New cards
in (A/Z)X, What does the X represent?
The Element
26
New cards
in (A/Z)X, What does the Z represent?
The Atomic Number
27
New cards
What never changes in an element?
number of protons (atomic number)
28
New cards
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
29
New cards
What is a nuclide?
Any arrangement of protons and/or neutrons forming a nucleus
30
New cards
What indicates the number of neutrons
The mass number minus the number of protons will indicate the number of neutrons
31
New cards
radioactive atoms
atoms that are unstable and decay over time
32
New cards
Deuterium
-An isotope of hydrogen with one proton and one neutron in the nucleus having an atomic weight of 2.014
-all forms of compounds containing hydrogen, such as water, contain small amounts of deuterium
-all forms of compounds containing hydrogen, such as water, contain small amounts of deuterium
33
New cards
atoms of deuterium per 6500 hydrogen atoms
1 atom of deuterium for every 6,500 atoms of hydrogen.
34
New cards
What is deuterium used for?
deuterium can be used as a "tracer" to find out how chemical reactions of hydrogen occur.
35
New cards
What is the most common nuclide used in fusion reactors?
Deuterium
36
New cards
What is the half-life of carbon-14?
5730 years
37
New cards
Why is carbon-14 radioactive?
Number of neutrons is increased to 8
*Unequal balance of protons and neutrons* is what makes something radioactive
*It is unstable
*Unequal balance of protons and neutrons* is what makes something radioactive
*It is unstable
38
New cards
What is carbon-14 useful for
the dating of materials containing carbon, such as wood or bones.
39
New cards
What is the half life of cobalt
5.3 years
40
New cards
What do you need to know to calculate the weighted average atomic mass of an element?
You need to know the mass and abundance of each isotope
41
New cards
How do you determine an electrons energy levels in an atom?
Exciting the electron;
-heated strongly
-raised to a higher energy level
-heated strongly
-raised to a higher energy level
42
New cards
What is it called when the absorbed or emitted photons are examined for their energy?
absorption spectrum or emission spectrum
43
New cards
Who established the Bohr model of an atom
Danish physicist Niels Bohr
44
New cards
What is the quantum mechanical model?
-electrons are not at exact distances or fixed locations and do not rotate in orbits.
-It determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus
-It determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus
45
New cards
The Davisson-Germer experiment showed...
The wave properties of electrons where electrons scattered at preferred angles from a nickel crystal
46
New cards
What is an orbital?
A region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found.
47
New cards
What is the periodic table?
an arrangement of stable atoms according to their electronic orbital structure.
48
New cards
How are elements arranged on the periodic table?
by increasing atomic number
49
New cards
What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called?
periods
50
New cards
What are the vertical columns on the periodic table called?
groups
51
New cards
How many "A" groups are there on the periodic table
8
52
New cards
How many "B" groups are there on the periodic table
10
53
New cards
What are the "A" groups on the periodic table?
The main groups,
-elements within the A groups all have the same amount of valence electrons
-elements within the A groups all have the same amount of valence electrons
54
New cards
What does the position of an element on the periodic table allow one to predict?
The element's properties
55
New cards
Electronegativity
a measure of one atom's attraction of electrons from an adjacent atom to which it is chemically bonded.
56
New cards
Who devised the method of arriving at a single numerical value for relative electronegativity? What is the method referred to as?
Linus Pauling, Pauling electronegativity
57
New cards
What is the atomic radius?
a measure of atomic size
58
New cards
What does the atomic radius do?
decrease from left to right across a period and increases down a group of the period table
59
New cards
Define ionization energy
the energy required to entirely remove an outer electron from an atom
60
New cards
the term applied to an atom as a measure of the fact that most neutral atoms still exhibit a small attraction for an electron
Electron affinity
61
New cards
What is an ionic bond?
A chemical bond that's formed when an atom transfers and electron to another Atom
62
New cards
What is a covalent bond?
A chemical bond formed when two or atoms share electrons.
63
New cards
What is a dipole moment?
a measure of the separation of two opposite electrical charges
64
New cards
When do dipole moments occur?
in molecules that have a positive end and a negative end and provide a measure of the molecule's polarity
65
New cards
A molecule is a...
group of atoms held together in a constant ratio by strong covalent bonds
66
New cards
What is a "cluster" of elements called
a compound
67
New cards
Electrostatic forces
- force of attraction between opposite charges, AND
- force of repulsion between the same charges
- force of repulsion between the same charges
68
New cards
intERmolecular forces
exist BETWEEN molecules
69
New cards
intRAmolecular forces
bond atoms together WITHIN a molecule
70
New cards
What is metallic bonding?
the chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding "sea" of electrons
71
New cards
When more than one element is present in a metal, the metal is call a/an...
alloy
72
New cards
Brass is made from
copper and zinc
73
New cards
These are classified as ionic, covalent, or metallic bonds.
Intramolecular Forces
74
New cards
Intermolecular forces are ________ than intramolecular forces
weaker forces of attraction
75
New cards
What are intermolecular forces responsible for
causing a clustering effect in liquids and solids
76
New cards
the name given to an intermolecular force first recognized by Johannes van der Waals
Van der Waals force
77
New cards
Molecules are said to be ___________ if a permanent distance can be measured between the center of positive charge and the center of negative charge
polar molecules
78
New cards
What is another name for a polar molecule
dipole moment
79
New cards
Lavoisier discovered that air was composed primarily of
O2 and N2
80
New cards
the process when electron orbitals like s and p mix together to form new orbitals such as sp
hybridization
81
New cards
What is the ratio of hydrogen to fluorine to form the compound HF
1:19
82
New cards
amu stands for
atomic mass unit
83
New cards
London dispersion forces
the intermolecular attraction resulting from the uneven distribution of electrons and the creation of temporary dipoles
84
New cards
london dispersion forces were discovered by
Fritz London
85
New cards
Cavendish referred to hydrogen as
"flammable air"
86
New cards
Antoine Lavoisier named the "flammable air"
hydrogène.
87
New cards
What did Cavendish confirm in 1781?
burning hydrogen produced water
88
New cards
Who took note that flammable gas was produced when iron was dissolved in acid
Robert Boyle
89
New cards
VSEPR stands for
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
90
New cards
On august 27, 1783, Roberts and Charles launched...
the first hydrogen-powered balloon
91
New cards
The flight of the first hydrogen-powered balloon lasted about
45 minutes
92
New cards
What were hydrogen balloons referred to after Charles could no longer ride in the balloons
Charlière
93
New cards
Charles' Law
V1/T1=V2/T2
94
New cards
What does Charles' Law state
As temperature increases, volume increases and as temperature decreases, volume decreases
95
New cards
KMT
kinetic molecular theory
96
New cards
Avogadro's Law
V1/n1=V2/n2
97
New cards
What does Avogadro's Law state?
no matter the nature of the gas, at a given temperature, pressure, and volume, there would be the same number of molecules
98
New cards
what is the formula of force
Force = mu^2/ℓ
99
New cards
what is a mole
the standard international base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
100
New cards
Avogadro's number
6.02 x 10^23