Comprehensive NSAIDs and Acetaminophen: Pharmacology, Uses, and Side Effects
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
A class of drugs that are commonly used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever.

Aspirin
The prototype drug for NSAIDs, known for its analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Non-Selective COX Inhibitors
NSAIDs that inhibit both COX1 and COX2 enzymes, with a greater effect on COX1.
Irreversible COX Inhibitors
NSAIDs that permanently inhibit COX enzymes.
Reversible COX Inhibitors
NSAIDs that temporarily inhibit COX enzymes.
Diclofenac
An example of a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Piroxicam
An example of a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Mefenamic acid
An example of a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Sulindac
An indole derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Ketorolac
An indole derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Indomethacin
An indole derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Aspirin/Acetyl Salicylic Acid (ASA)
A salicylic acid derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Ibuprofen
A propionic acid derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Flurbiprofen
A propionic acid derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Ketoprofen
A propionic acid derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Naproxen
A propionic acid derivative that acts as a non-selective COX inhibitor.
Selective COX2 Inhibitors (coxibs)
NSAIDs that preferentially inhibit COX2 over COX1.
Meloxicam
A preferential COX2 inhibitor.
Celecoxib
A selective COX2 inhibitor.
Etoricoxib
A selective COX2 inhibitor.
Rofecoxib
A selective COX2 inhibitor that has been withdrawn from the market.
Valdecoxib
A selective COX2 inhibitor that has been withdrawn from the market.
Acetaminophen
A drug that acts as an analgesic and antipyretic but is not a traditional NSAID.

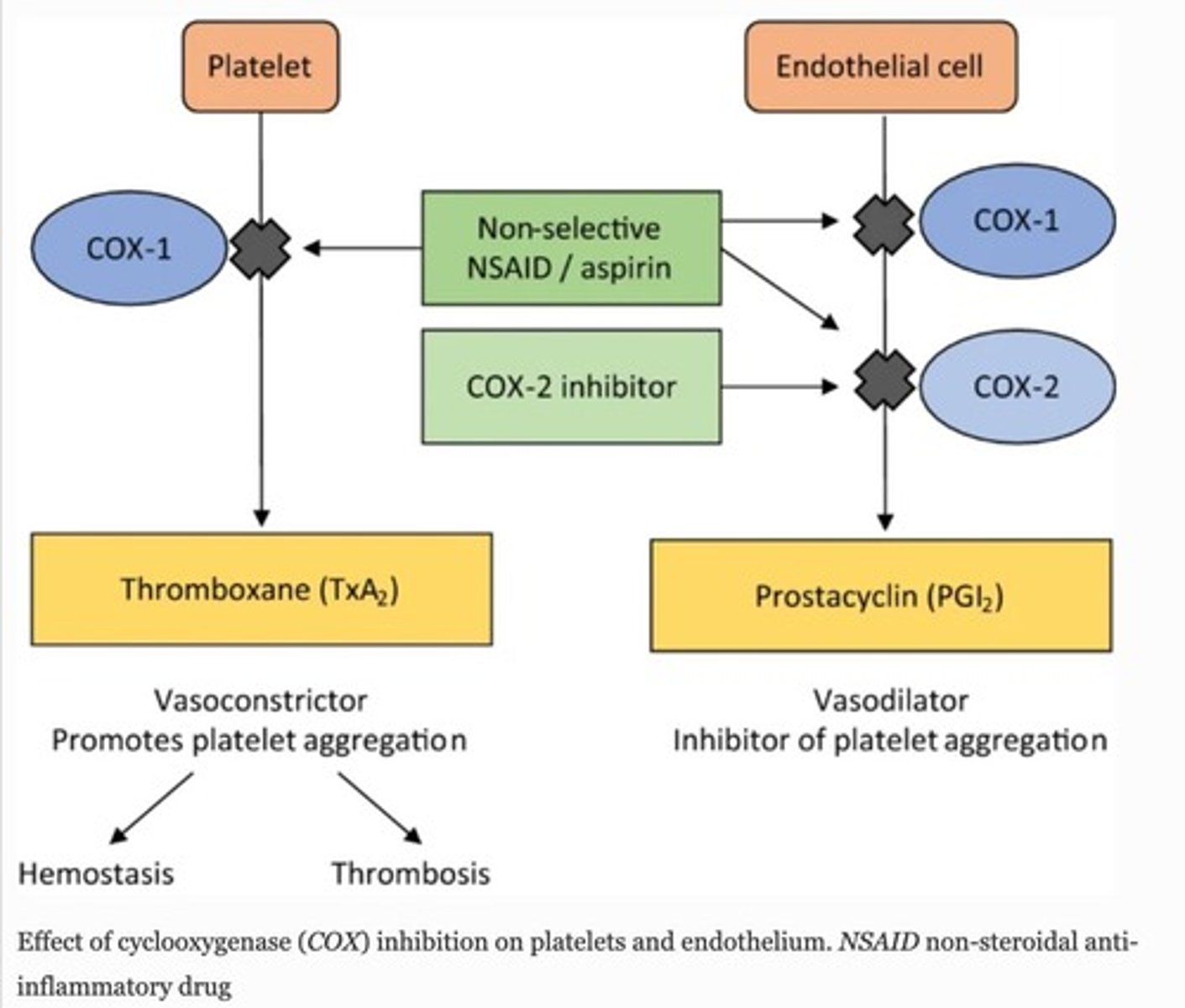
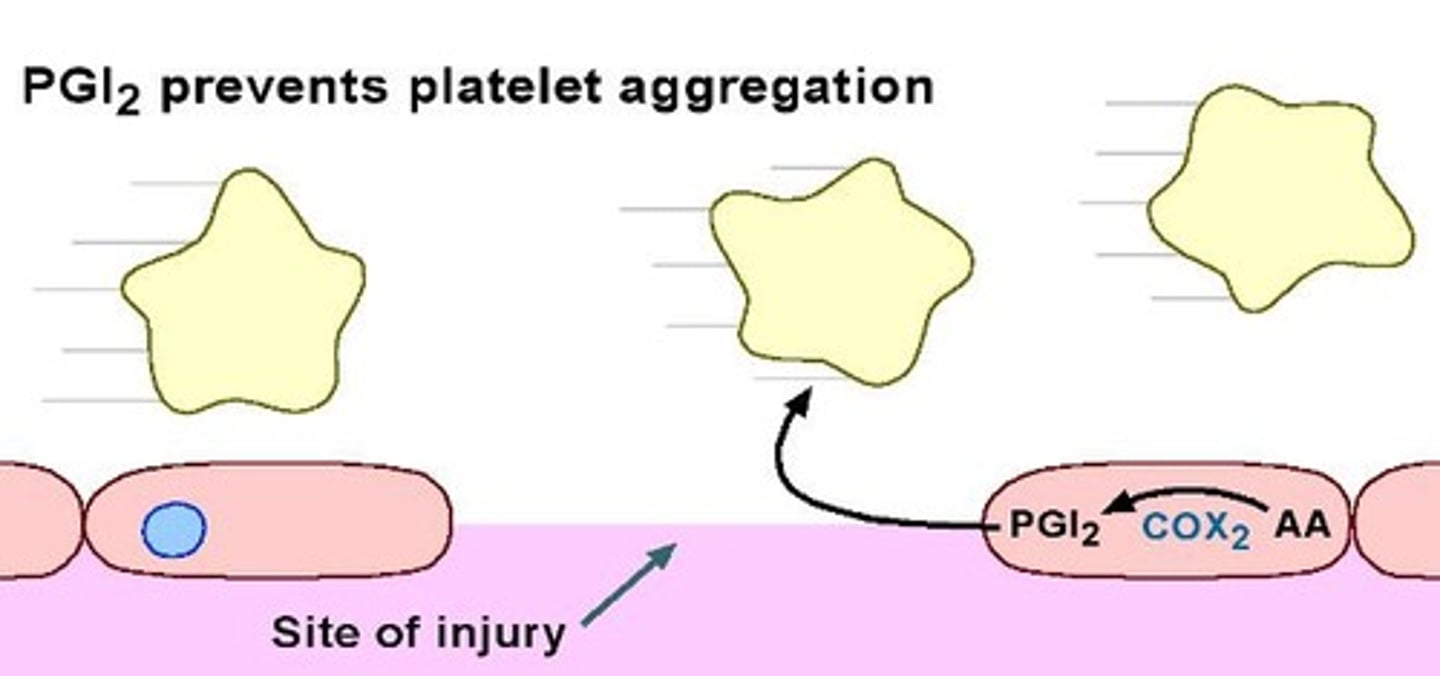
PGI2
Prostaglandin I2 that acts on the hypothalamus to cause fever.
PGE2
Prostaglandin E2 that acts on the hypothalamus to cause fever.
COX1
Constitutive enzyme that is always present in most cells.
COX2
Inducible enzyme that is induced by inflammation in cells.
Ductus arteriosus
A fetal blood vessel that PGE1 maintains patency of during fetal life.
PGE1
Prostaglandin E1 that maintains the patency of the ductus arteriosus in fetal life.
PGF2α
Prostaglandin F2 alpha that initiates and stimulates labor.
LTC4
Leukotriene C4 that causes allergic bronchospasm.
LTD4
Leukotriene D4 that causes allergic bronchospasm.
LTE4
Leukotriene E4 that causes allergic bronchospasm.
NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that inhibit COX enzyme pathway.
Analgesic
Pain relief effect caused by NSAIDs.
Anti-pyretic
Fever relief effect caused by NSAIDs.
Anti-inflammatory effects
Effects of NSAIDs that reduce inflammation.
GI side effects
Gastrointestinal side effects caused by NSAIDs.

Renal side effects
Renal side effects caused by NSAIDs.
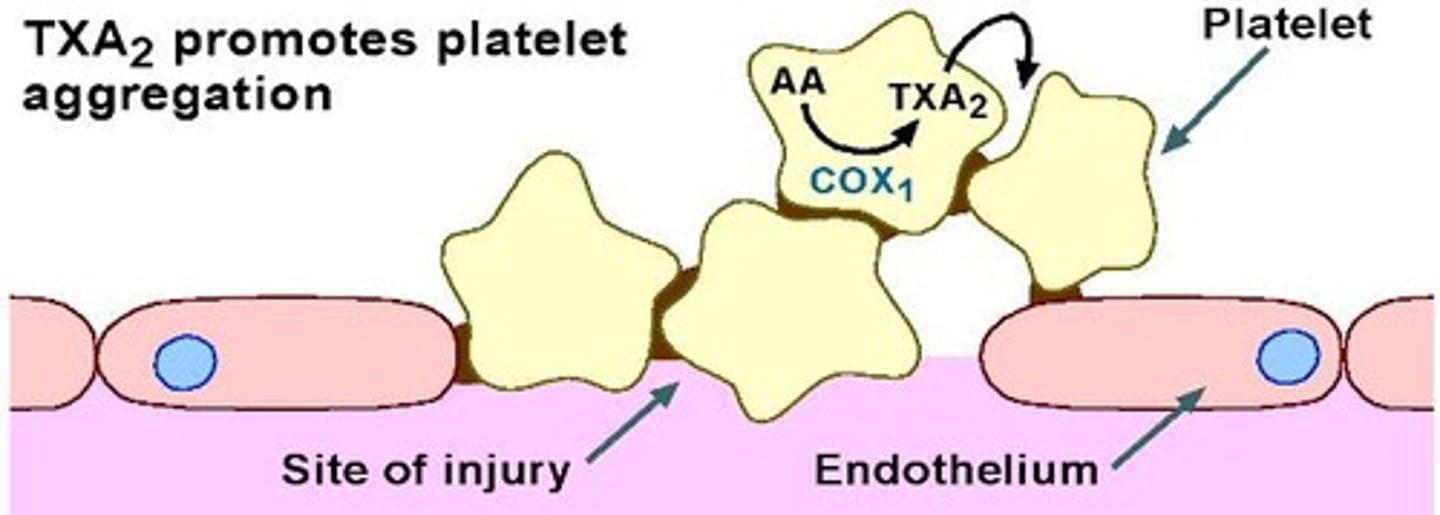
TXA2
Thromboxane A2 that mediates platelet aggregation.
Prothrombotic events
Significant increase in events like heart attacks and strokes caused by COX2 inhibitors.
Urate excretion
Dose dependent effect of aspirin where low doses cause retention and high doses cause excretion.
GIT effects
Gastrointestinal effects of NSAIDs including irritation of GI mucosa and gastric erosion.
Hypersensitivity
Reactions in susceptible individuals due to inhibition of COX pathway.
Respiration effects
Dose dependent effects of NSAIDs on respiration, including stimulation and depression.
Parturition
Delay or retard labor by inhibition of PG synthesis.
Renal effects
Significant effects of NSAIDs in cases of CHF, hypovolemia, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease.
Analgesic nephropathy
Chronic consumption of NSAIDs leading to renal damage.
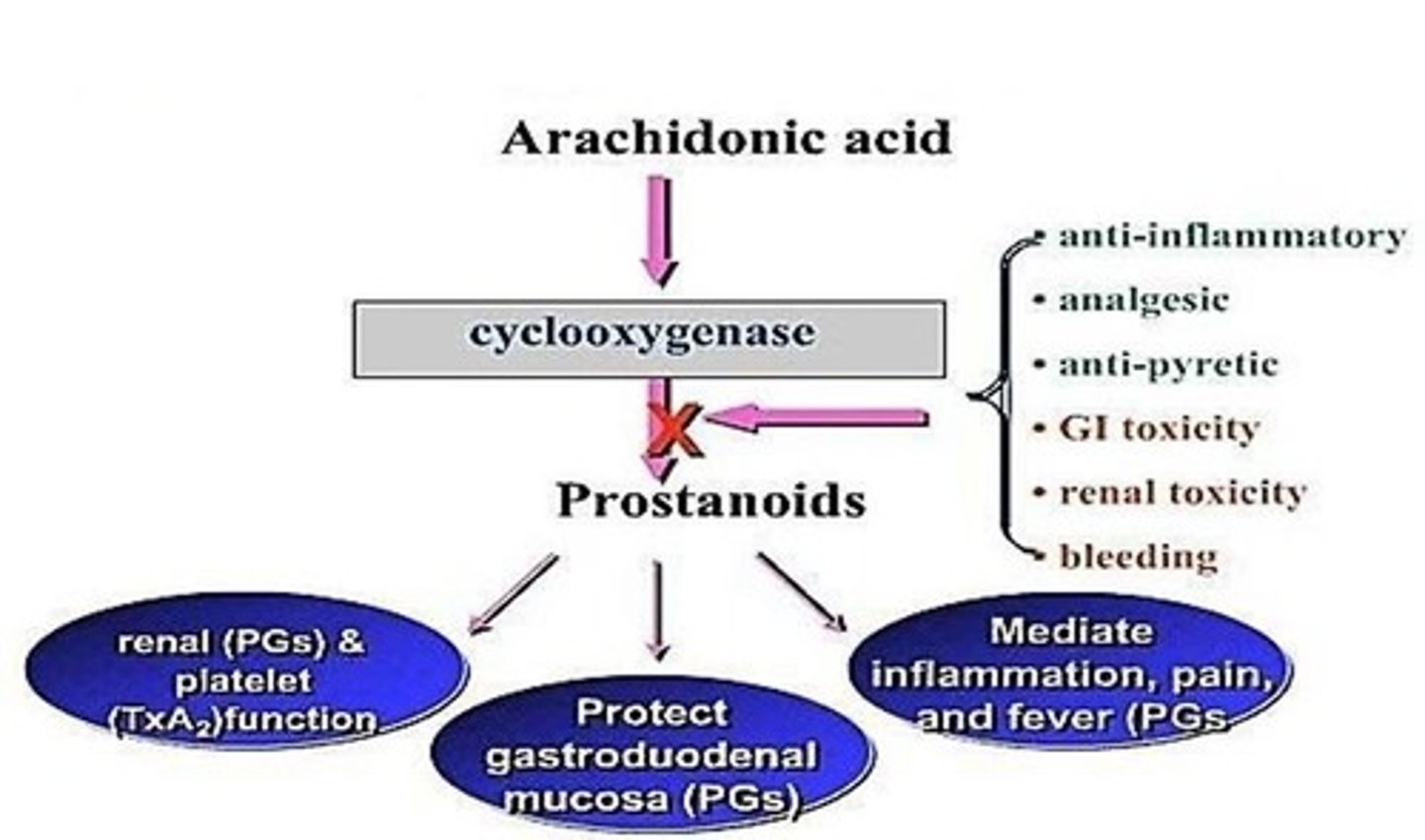
Prostaglandin Synthesis Inhibition
Effects of inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis that can have both beneficial and toxic effects.
Nephropathy
↓ renal blood flow, Na+ and H2O retention, renal papillary necrosis
Pharmacokinetics of NSAIDs
Weak acids; all except nabumetone are weak acids; nabumetone is a ketone converted to a weak acid to become active.
Absorption of NSAIDs
Absorbed from the stomach and small intestines.
Metabolism of NSAIDs
Most NSAIDs are metabolized by CYP3A and CYP2C, then undergo glucuronidation prior to renal elimination.
Protein Binding of NSAIDs
NSAIDs are highly protein bound, most >90%.
Kinetics of NSAIDs
First order to zero order kinetics from therapeutic to toxic dose.
Common Therapeutic Uses of NSAIDs
Pain: headache, injury, arthritis, backache, tooth ache, myalgia, joint pains; Fever: effective in fever of inflammatory/infectious origin; Inflammation: injury, arthritis, acute rheumatic fever, post surgical; Menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea): pain and muscle contraction.
Aspirin Low Dose Use
Low dose → antiplatelet; prevent heart attacks and stroke.
Acetaminophen Uses
Pain: headache, injury (no effect on inflammation due to injury), osteoarthritis pain; Fever.
Less Common Therapeutic Uses of NSAIDs
Low dose aspirin reduces the risk of pre-eclampsia, familial colonic polyposis and colorectal cancer, Alzheimer's disease; high dose ibuprofen slows decline of lung function in cystic fibrosis; can help closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus; treats niacin induced cutaneous flush and pruritus; can arrest premature labor (<32 weeks).
Methylsalicylate
Also known as oil of wintergreen; external use as counter irritant in balms.
Salicylic Acid
Keratolytic agent used for local treatment of corns/warts.
Sulfasalazine
Used in inflammatory bowel disease for local intestinal anti-inflammatory effects and in rheumatoid arthritis.
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs on GI
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, gastric erosions and peptic ulcers, occult blood in stool.
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs on CNS
Dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, headache, tinnitus and rarely aseptic meningitis.
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs on CVS
Fluid retention, hypertension, edema, and rarely myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure (CHF).
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs on Blood
Aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia - these are rare.
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs on Hepatic
↑ transaminases, liver failure (rare).
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs on Renal
Na+ and water retention, CRF, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis.
Hypersensitivity Reactions to NSAIDs
Rashes, pruritis, asthma, nasal polyps (Aspirin Exacerbated Respiratory Disease).
Hypertension due to NSAIDs
Prostaglandins produced by COX pathway cause vasodilation, increased renal perfusion, diuresis, natriuresis; NSAIDs can cause renal ischemia and renal failure, Na+ and H2O retention, worsening hypertension.
Black Box Warnings on NSAIDs
Warnings regarding serious cardiovascular and gastrointestinal risks.
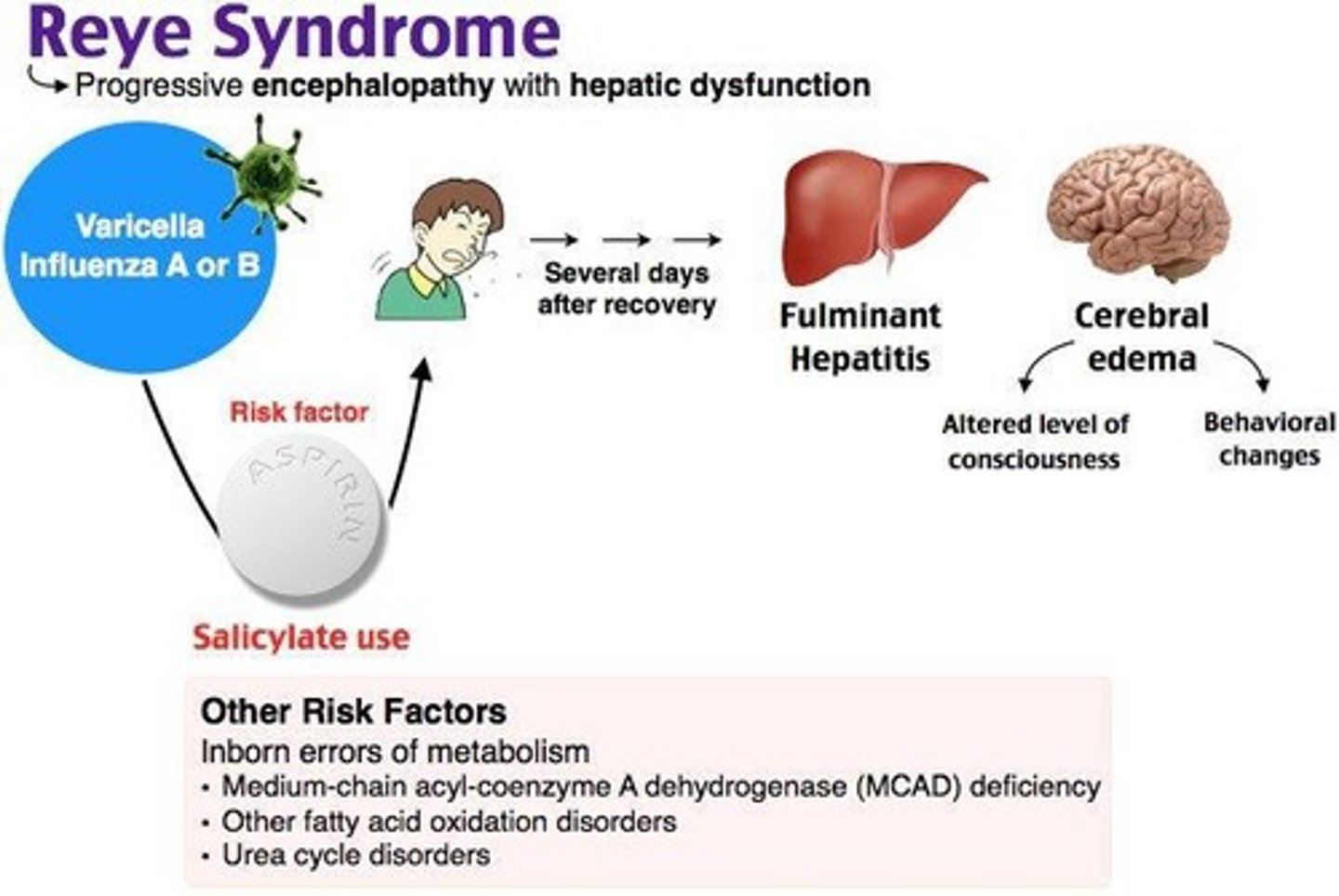
Reye's Syndrome
Rare and fatal disorder seen in children treated with aspirin for flu and VZV, characterized by hepatic damage and encephalopathy.
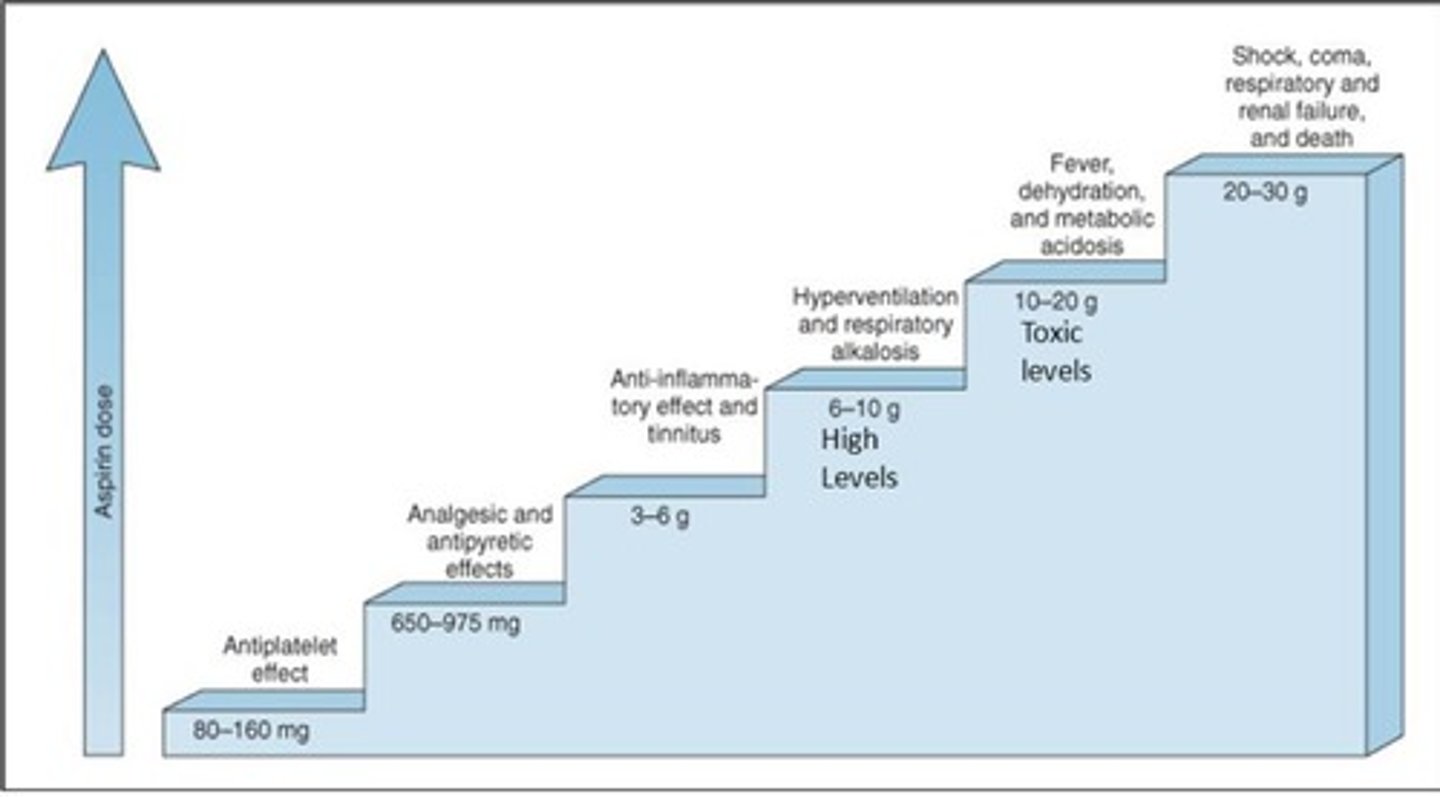
Acute Salicylate Poisoning: Clinical Features
Includes vomiting, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, restlessness, delirium, hallucinations, tinnitus, hyperventilation, respiratory alkalosis, hyperpyrexia, metabolic acidosis, convulsions, coma, and death due to CV collapse, respiratory/renal failure.
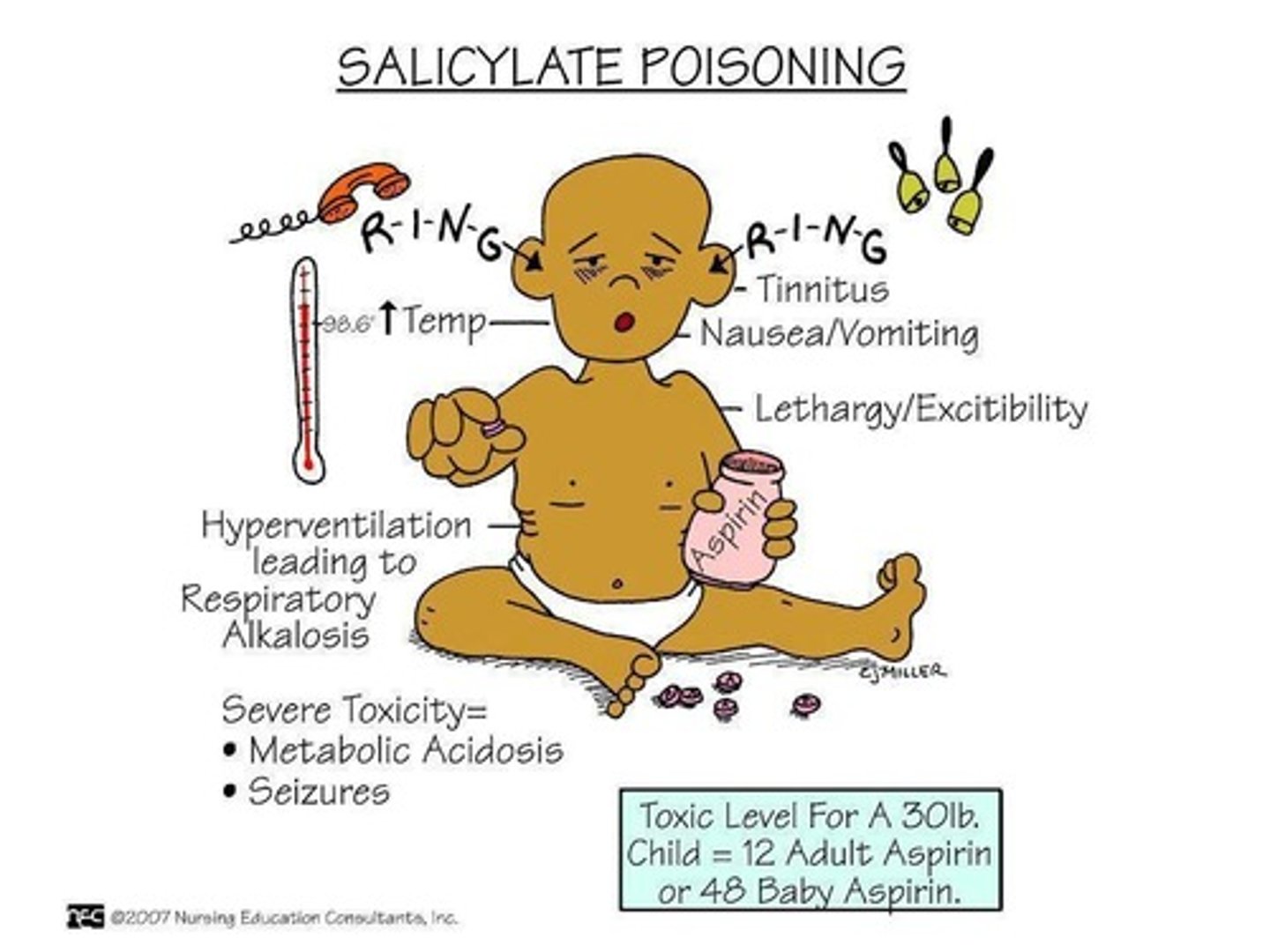
Acute Salicylate Poisoning: Treatment
Involves external cooling, IV fluids with Na+, K+, HCO3-, intense monitoring, gastric lavage, forced alkaline diuresis with NaHCO3, and hemodialysis.
TXA2 formation
Occurs via COX1.
PGI2 formation
Occurs via COX2 in platelets.
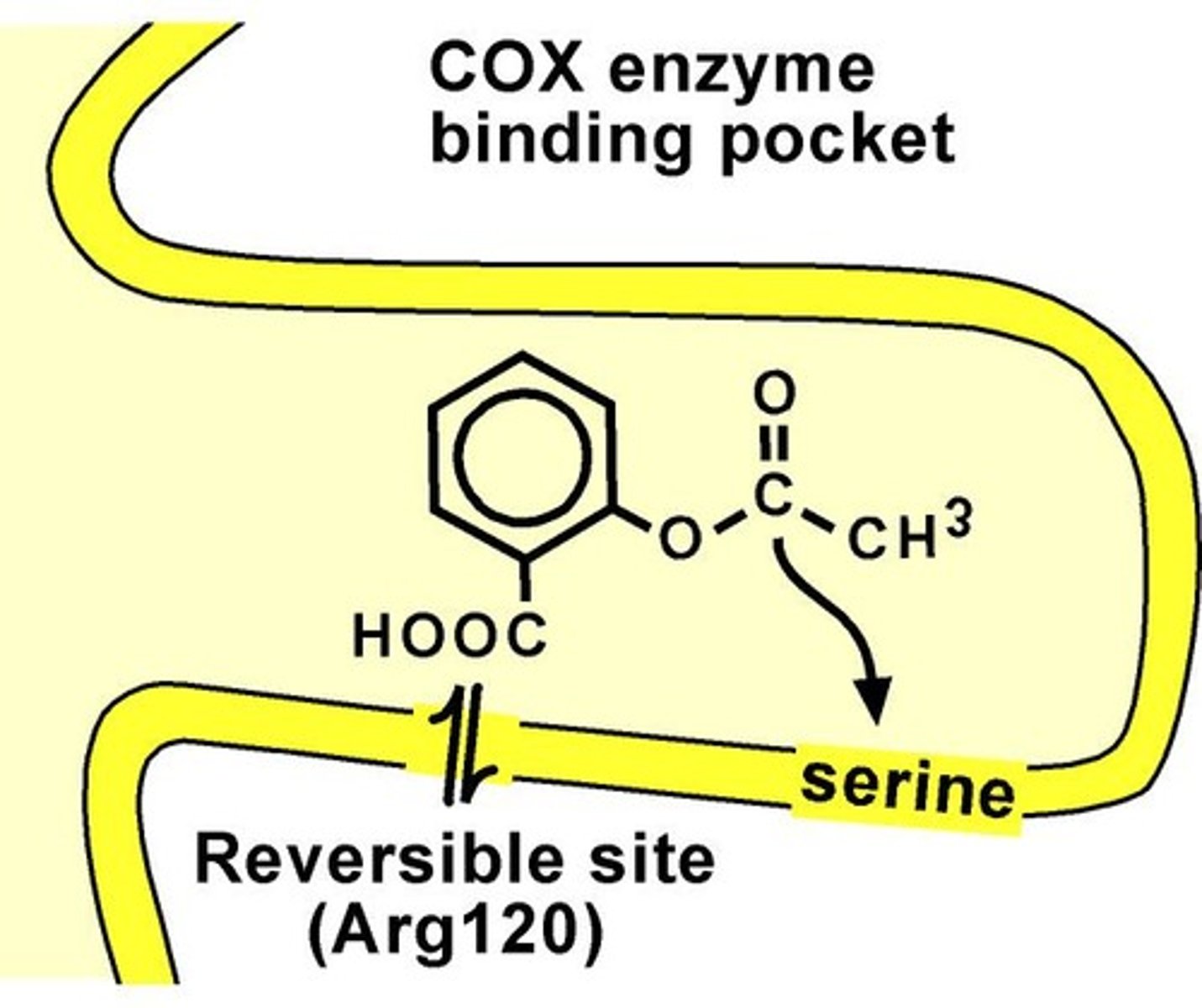
Aspirin mechanism of action
Irreversibly inhibits COX1/2 via covalent acetylation of a serine.
Low dose aspirin
(< 300 mg/day) primarily irreversibly inhibits COX1 on platelets, reducing clotting.
Aspirin prophylactic use
Used as an antiplatelet (anti-thrombogenic) drug.
Aspirin duration of action
Long duration (7-10 days) since new platelets must be formed.
Higher dose aspirin effect
At larger doses, COX selectivity is lost, but reduced clotting (anti-platelet) remains the net effect.
Bleeding risk with aspirin
Potential side effect when used at higher doses (e.g., anti-inflammatory doses) as it inhibits COX1 > COX2.
Co-administration of NSAIDs with Aspirin
Leads to loss of its anti-platelet/cardioprotective effects.
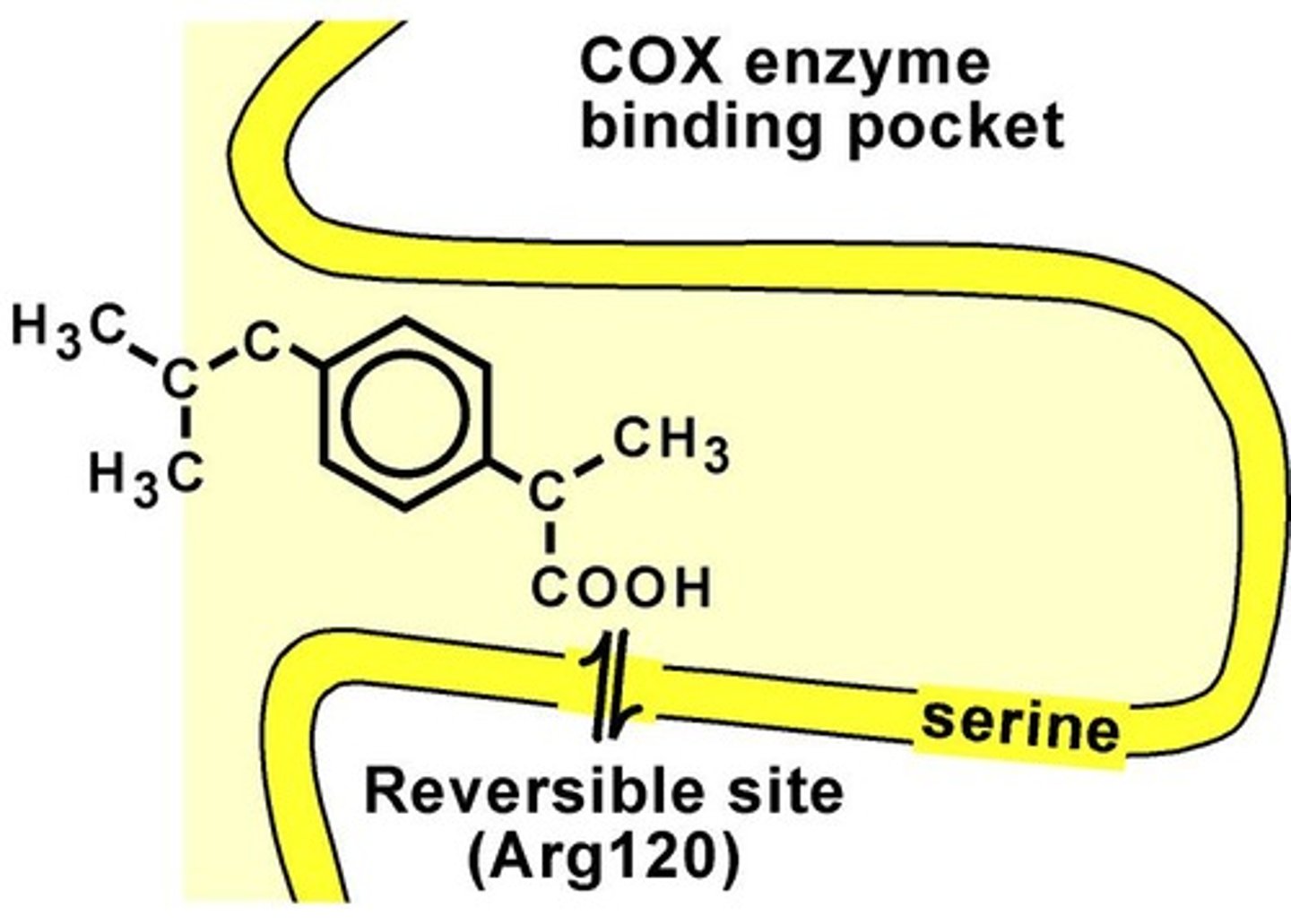
Other NSAIDs competition
May compete for binding sites on COX-1, preventing aspirin from reaching the serine molecule.
NSAIDs precautions
Should be stopped a week before elective surgery; prolongs bleeding time.
G6PD deficiency
Can cause hemolysis.
Pregnancy and NSAIDs
Risk if taken at or near term.
Peptic ulcer/GI bleeds
Contraindication for NSAIDs.
Chronic liver disease
Contraindication for NSAIDs.
Congestive heart failure
Contraindication for NSAIDs.
Diabetes
Precaution when using NSAIDs.
Aspirin in children
Should not be used in children suffering from chicken pox or influenza.
Acetaminophen mechanism of action
Inhibits PG synthesis when arachidonic acid levels are low; a weak inhibitor of COX1 and COX2 (COX2 > COX1).
Acetaminophen therapeutic uses
Effective analgesic for mild to moderate pain; minimal anti-inflammatory activity.
Reduces/relieves fever
A primary therapeutic use of acetaminophen.
In combination with opioids
Acetaminophen is used to decrease the opioid requirement.
In combination with NSAIDs
Acetaminophen is used to increase the effectiveness of NSAIDs.
Preferred analgesic for patients allergic to aspirin
Acetaminophen is recommended for patients who have an allergy to aspirin.
Preferred analgesic for patients with bronchial asthma
Acetaminophen is suitable for patients suffering from bronchial asthma.
Preferred analgesic for patients with bleeding disorders
Acetaminophen is safe for patients who have bleeding disorders.