14 Alcohols
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
features of a homologous series
each successive member differs by a CH2 group
similar chemical properties and gradually changing physical properties
same general formula and functional group
functional grp of alcohols
-OH
how can ethanol be formed from ethene
when reacted with steam H2O(g), 300C, acid catalyst H3PO4, 60-70atm
what priority does -OH have in naming
highest priority so far - needs to have the smallest number
alkenes C=C
halogens
alkyl = lowest
what is methanol used for
a high performance fuel due to efficient combustion
starting material in many industrial syntheses
can be converted into polymers, paints, solvents, adhesives and other useful products
what is ethanol used for
alcoholic drinks
a fuel, solvent or feedstock (raw material)
where are the polar bonds on alcohols
on the OH group
Oδ-
Hδ+
miscible def
does a liquid mix with water
are alcohols miscible w water
yes
like dissolves like
alcohols are polar
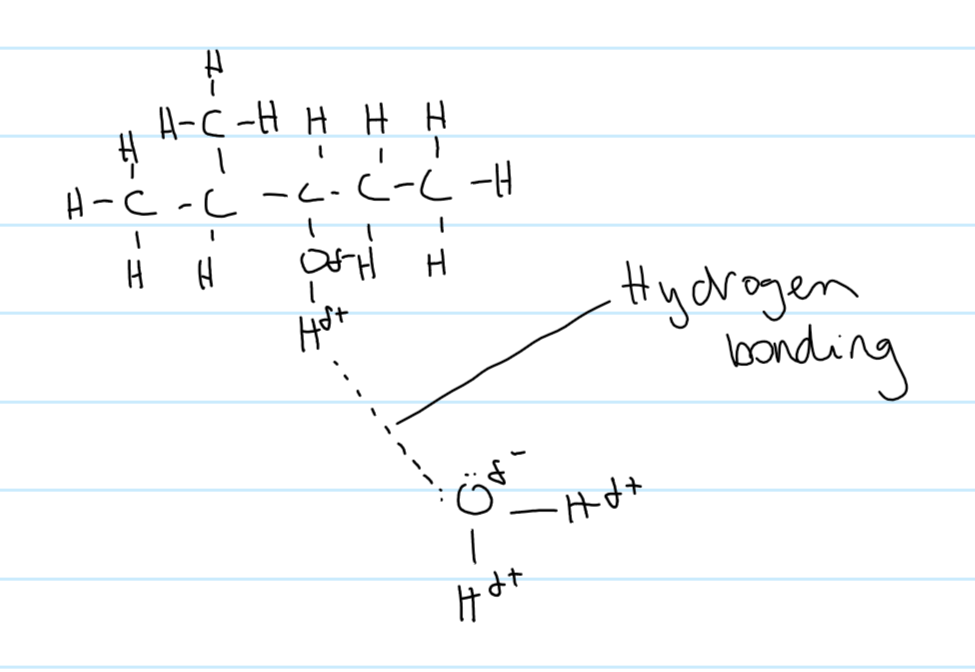
diagram of hydrogen bonding between ethanol molecule and water
how does solubility change as hydrocarbon chain increases
the larger the chain the more LF
greater IMF
harder to pull molecules apart to dissolve
solubility decreases as hydrocarbon chain gets longer
influence of the OH group decreases as the chain length increases, not as energetically favourable
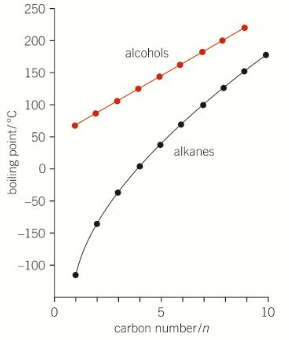
why does methanol have a higher bpt than methane
methanol has hydrogen bonding between molecules
methanol also has permanent dipole dipole interactions because its polar
more energy required to overcome IMF
methane doesn’t have HB or pddi between molecules
compare bpt of methanol to methane
methanol has a higher bpt than methane
compare volatility of methanol to methane
methane has a lower volatility
(same reason as bpt)
compare solubility of methanol to methane
methanol more soluble
has an OH group that can form HB w water
methanol is a polar molecule
like dissolves like
what effect does increasing carbon chain length have on alkanes vs alcohols
LF can accumulate and be stronger than HB
HB are individually stronger than LF
how are alcohols classified
based on the no. of carbons the C bonded to the OH group is bonded to
a primary alcohol
the -OH is joined to a carbon that isn’t joined to more than 1 carbon
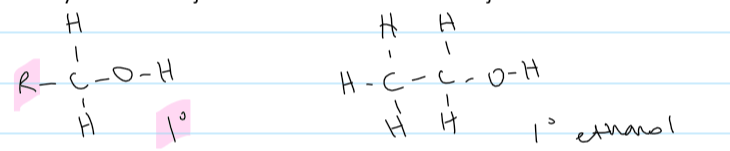
a secondary alcohol
the -OH is joined to a carbon that is joined to 2 other carbons
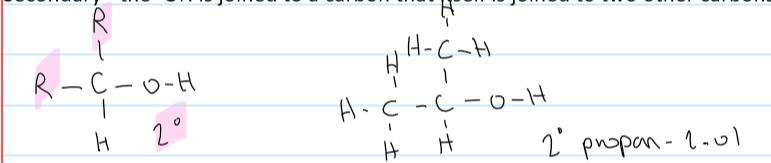
a tertiary alcohol
the -OH is joined to a carbon that is joined to 3 other carbons
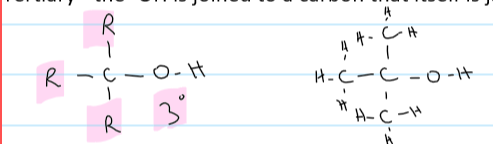
reactions of alcohols
combustion
oxidation
dehydration
substitution
what functional groups can be produced in oxidation of alcohols
aldehydes
ketones
carboxylic acids
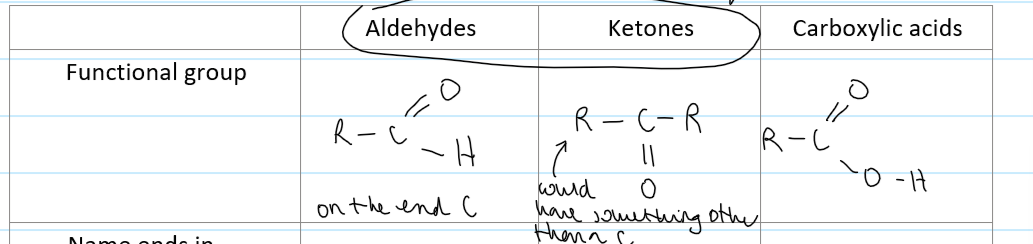
what is the ending for an aldehyde
-al
what is the ending for a ketone
-one
functional group of an aldehyde
on the end carbon

functional group of a ketone
NOT on an end carbon
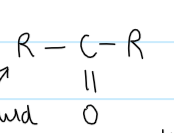
structural formula for an aldehyde
-CHO

structural formula for a ketone
-CO-
IMF between aldehydes
LF
permanent dipole-dipole interactions (C=O)
IMF between ketones
LF
permanent dipole-dipole interactions
IMF between carboxylic acids
LF
permanent dipole-dipole interactions
HB
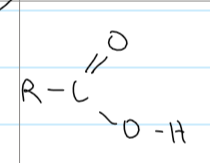
bpts of alkanes, aldehydes and alcohols
alkane (lowest) (only LF)
aldehyde (permanent dipole-dipole interactions)
alcohol (highest) (HB)
why do solubility of aldehydes and ketones decrease as the molecules get bigger
more HBs in water need to be broken to fit the aldehyde/ketone between the water molecules
however only 1 HB gets formed in exchange
not energetically favourable
conditions for oxidation of alcohols
acidified (by adding dilute H2SO4) potassium (or sodium) dichromate (VI)
heating of mixture
what colour does potassium dichromate (VI) go if it is reduced
orange to green

how is the oxidising agent written in equations
[O]
what do the products of oxidation of alcohols depend on
whether it was a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol
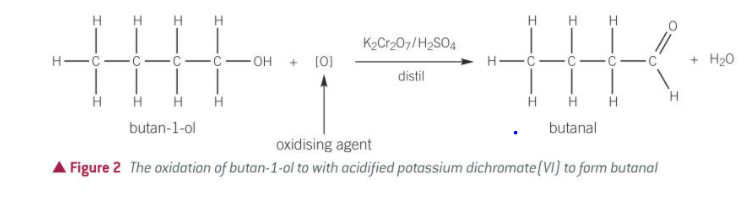
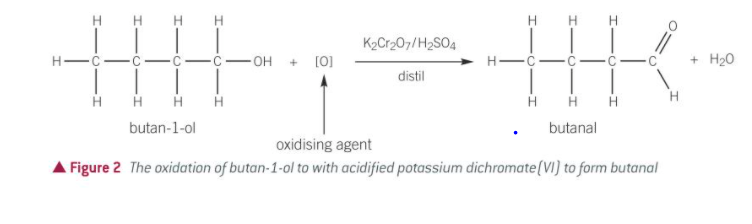
possible products of oxidation of a primary alcohol
aldehyde
gentle heating
distilled off as formed to collect
carboxylic acid
excess oxidising agent
heating under reflux
conc. sulfuric acid
stuff needed for formation of an aldehyde from a primary alcohol
gentle heating
K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
distill
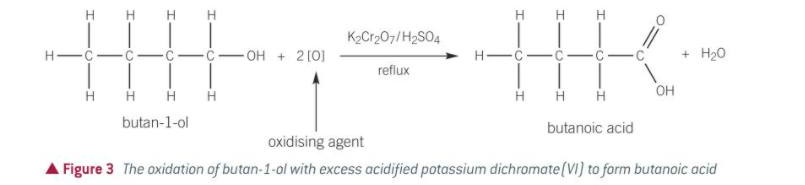
stuff needed for formation of a carboxylic acid from a primary alcohol
excess oxidising agent 2[O]
(K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 acidified potassium dichromate (VI))
heating under reflux
concentrated H2SO4
![<ul><li><p>excess oxidising agent 2[O]</p></li><li><p>(K<sub>2</sub>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub>/H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4 </sub>acidified potassium dichromate (VI))</p></li><li><p>heating under reflux</p></li><li><p>concentrated H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub></p></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f5122196-cc40-49ae-b550-d355a61d8594.png)
stage 1 of oxidation of a primary alcohol
gently heating with acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
produces aldehyde
aldehyde separated from mixture as soon as it forms to prevent stage 2 taking place
can be separated by distillation
stage 2 of oxidation of a primary alcohol
forms a carboxylic acid
requires vigorous oxidation w excess oxidising agent
heating under reflux
concentrated sulfuric acid
oxidation stage 1 w ethanol equation
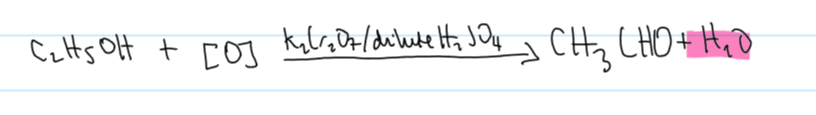
oxidation stage 2 w ethanol equation
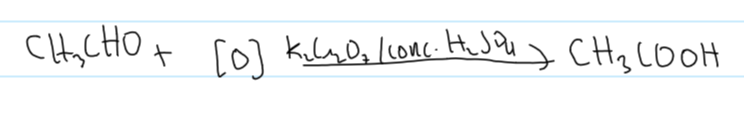
overall equation for oxidation of a primary alcohol
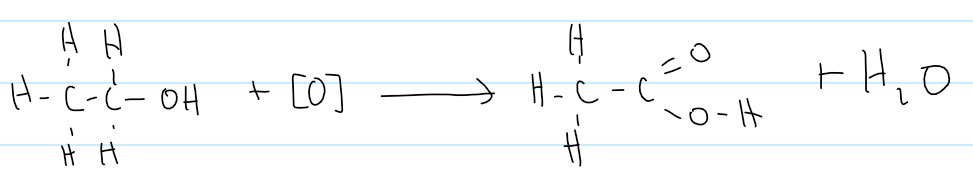
how does reflux ensure the carboxylic acid is formed rather than an aldehyde
the aldehyde can’t escape as it’s repeatedly condensed back
what is the colour change of oxidation of a primary alc and why
orange to green
oxidising agent
Cr reduced

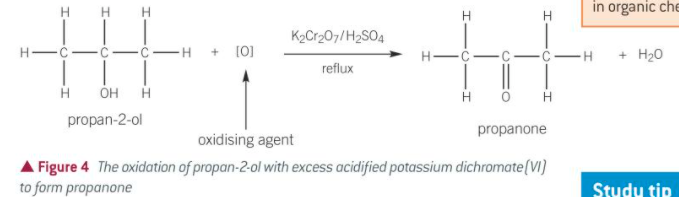
what is formed when a secondary alc is oxidised
ketones
what are secondary alcohols oxidised with
acidified potassium dichromate (VI) K2Cr2O7/H2SO4
the H2SO4 is dilute
equation for oxidation of secondary alc
why don’t tertiary alcs oxidise
don’t oxidise
there’s no H on the adjacent C that can be lost
what is meant by a dehydration reaction
alcohol → alkene
loss of H2O molecule
elimination reaction
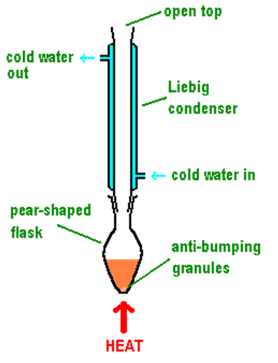
what is meant by heating under reflux
constant reaction between reactants
evaporating then condensing
completing without losing volatile reactant
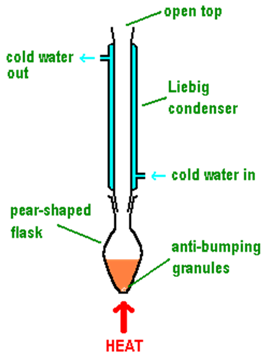
what r the benefits of heating under reflux
good for volatile substances (liquids → gases)
dehydrating agents
conc. H2SO4
conc. H3PO4
heated Al2O3
conditions for dehydration of alcohols
a dehydrating agent (H2SO4, H3PO4, Al2O3)
alc heated under reflux
what kind of reaction is dehydration of alcs
elimination
what happens in a dehydration of an alc rxn
C=C is reformed
alkene + water produced
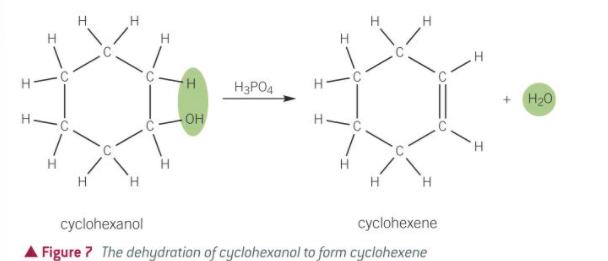
how would you prove the product is an alkene
add orange bromine water
goes from orange to colourless if alkene
how many possible products can be made in the dehydration of butan-2-ol
2 depending on which H next to the OH group is taken
but-1-ene
but-2-ene

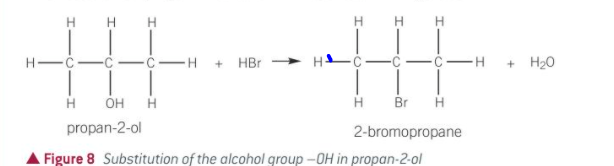
what is produced when alcohols react with hydrogen halides
haloalkanes
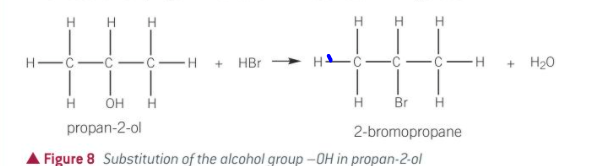
what happens in a substitution reaction with HBr
alc is heated under reflux with dilute H2SO4 and a sodium halide
the HBr is formed in situ
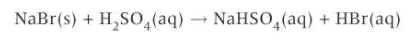
stuff needed for substitution w hydrogen halides + alcohol
a sodium halide e.g. NaBr(s)
dilute H2SO4
heated under reflux
how is the HX formed in an alcohol + hydrogen halide rxn
in situ (in place)
step 1 of substituion
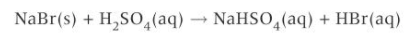
step 2 of substitution