Biochem Lecture 1 (Amino Acids, Protein Folding)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Proteins
linear heteropolymers of amino acids, that have a primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
Functions of amino acids (besides building proteins)
Fuel for ATP synthesis, neurotransmitters, precursors of hormones and bioactive agents (ex. histidine- histamine)
Amino acids
building blocks of proteins (among other things)
L-amino acids
in proteins, amino acids are in the structure of an _-_________ ______
alpha
in an amino acid, the _-carbon always has four substituents
tetrahedral
the molecular geometry of an amino acid
proline, acidic, basic, hydrogen, alpha
All amino acids (except _________, have an _______ carboxyl group, a _______ amino group, and an __________-hydrogen connected to the alpha-carbon
unique
the R group is ____________ to each amino acid
alpha carbon
when naming the carbons of the amino acid, you start at the _______-______________ and go down the R group
glycine, gly, G, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
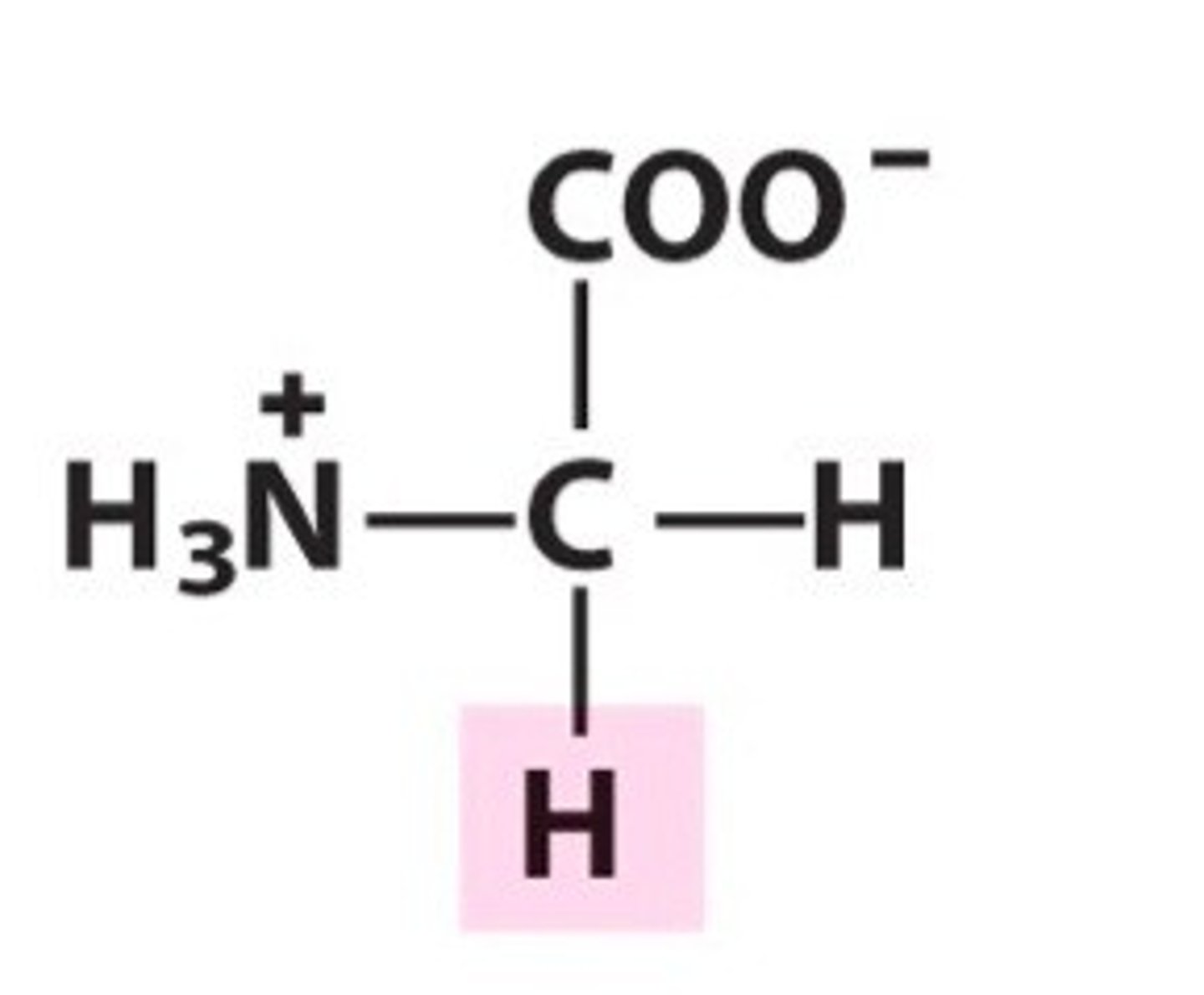
alanine, ala, A, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
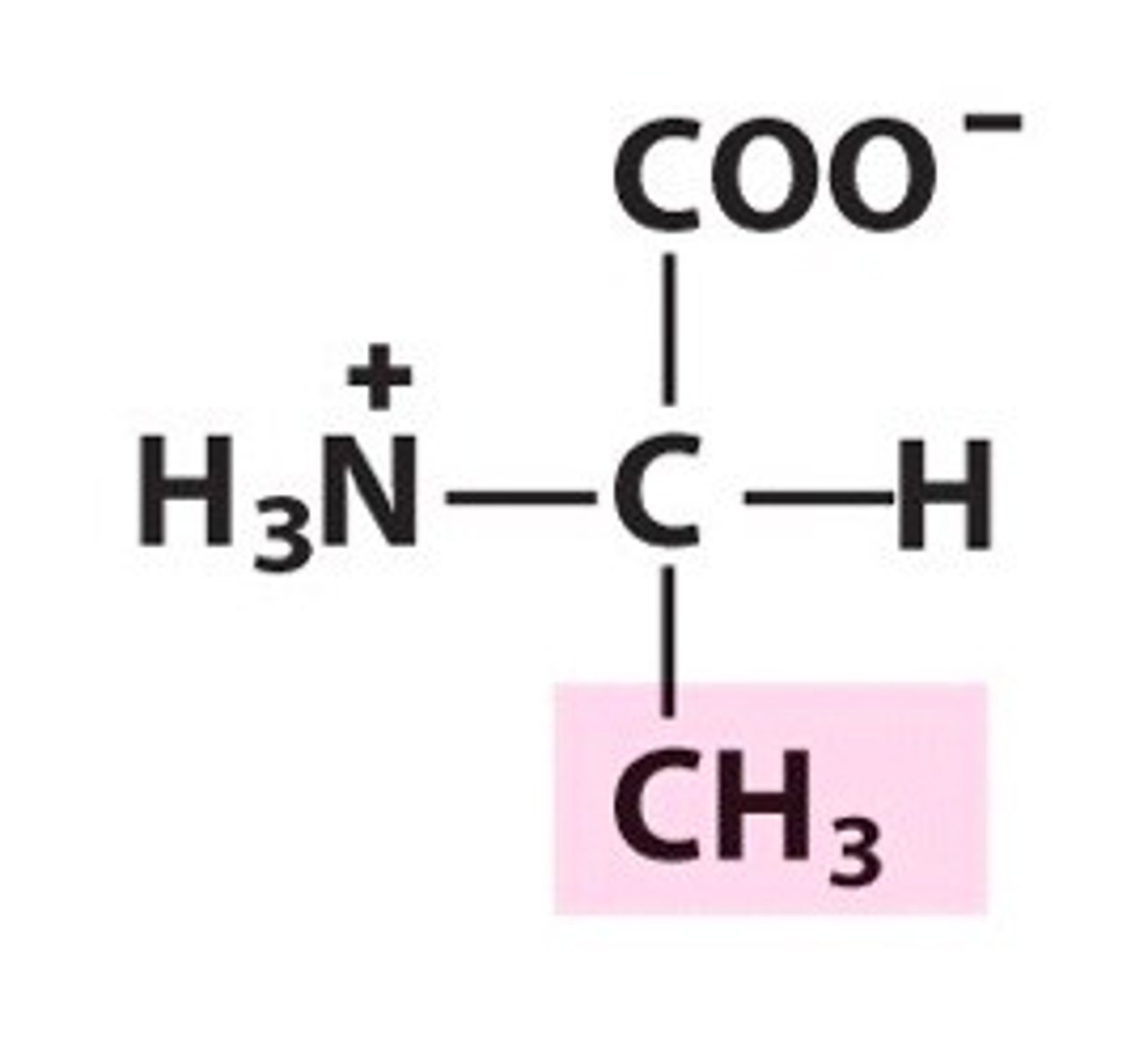
valine, Val, V, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
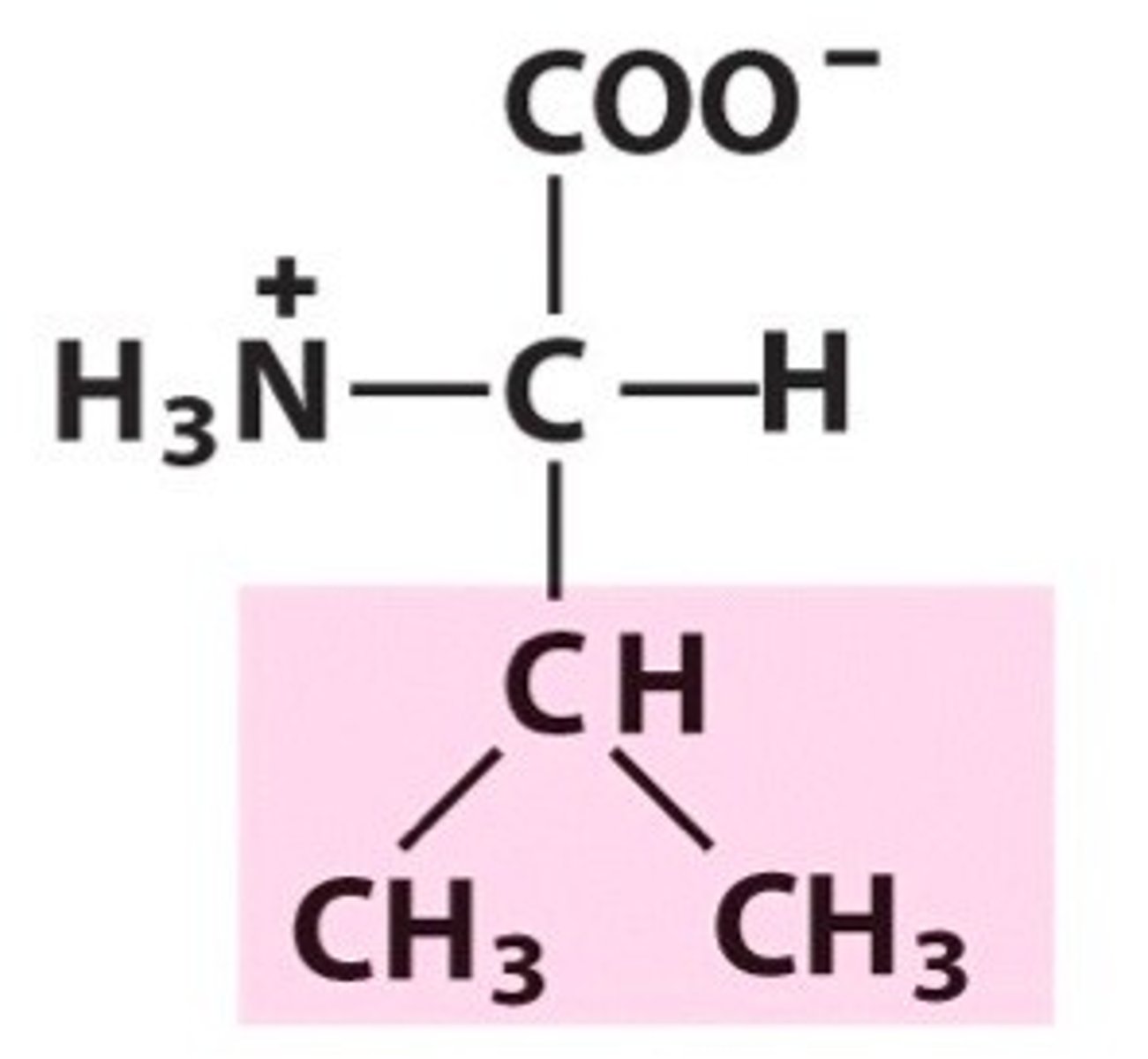
methionine, Met, M, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
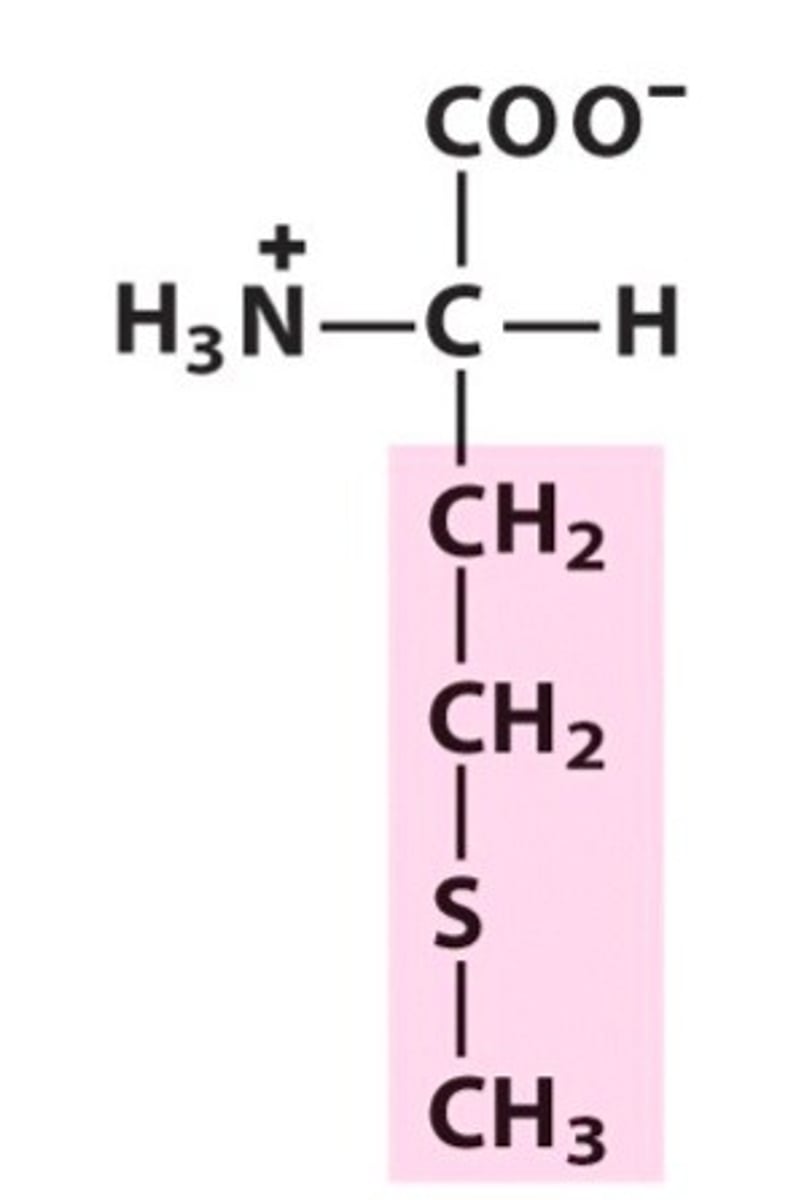
proline, pro, P, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
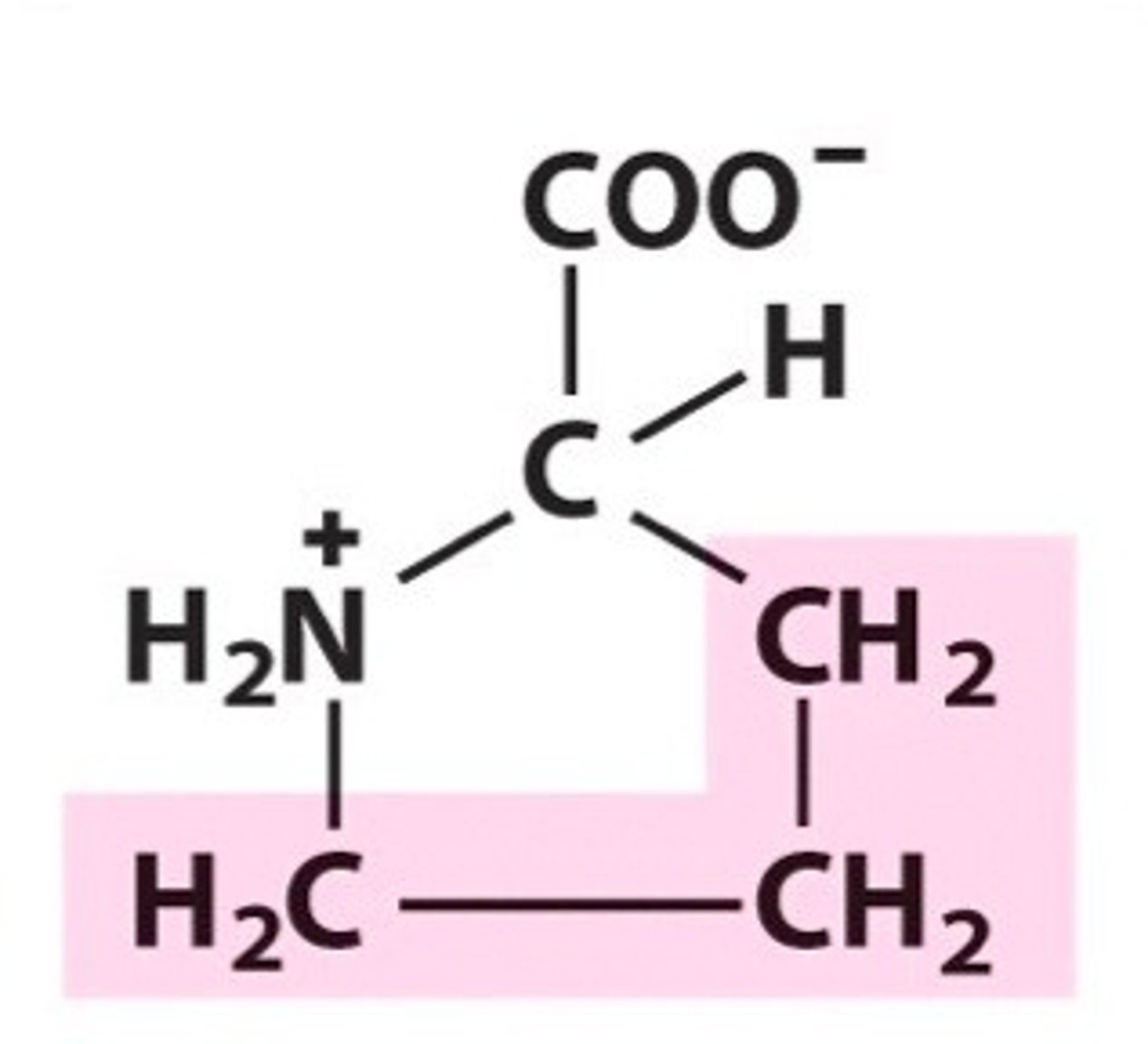
leucine, leu, L, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
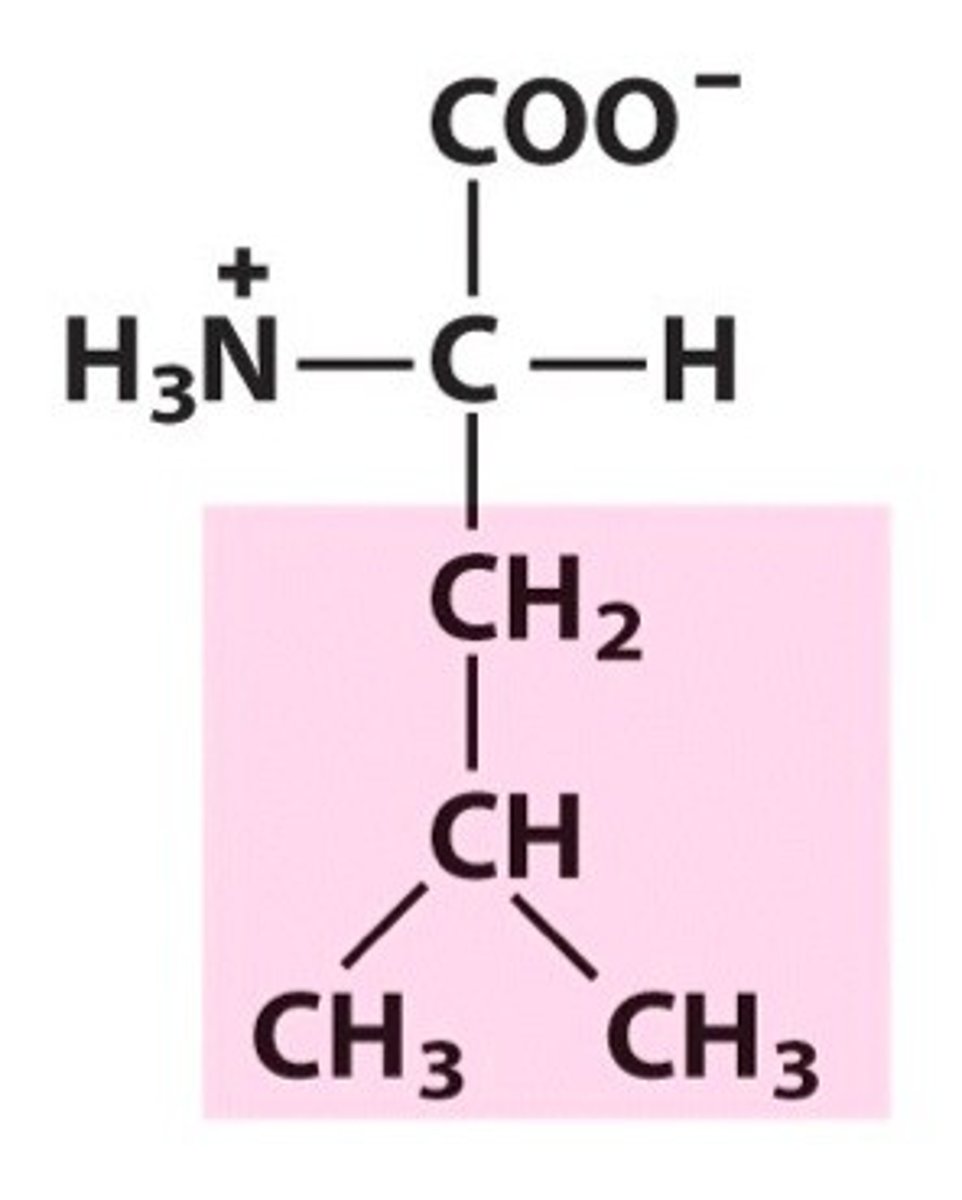
isoleucine, Ile, I, nonpolar/aliphatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
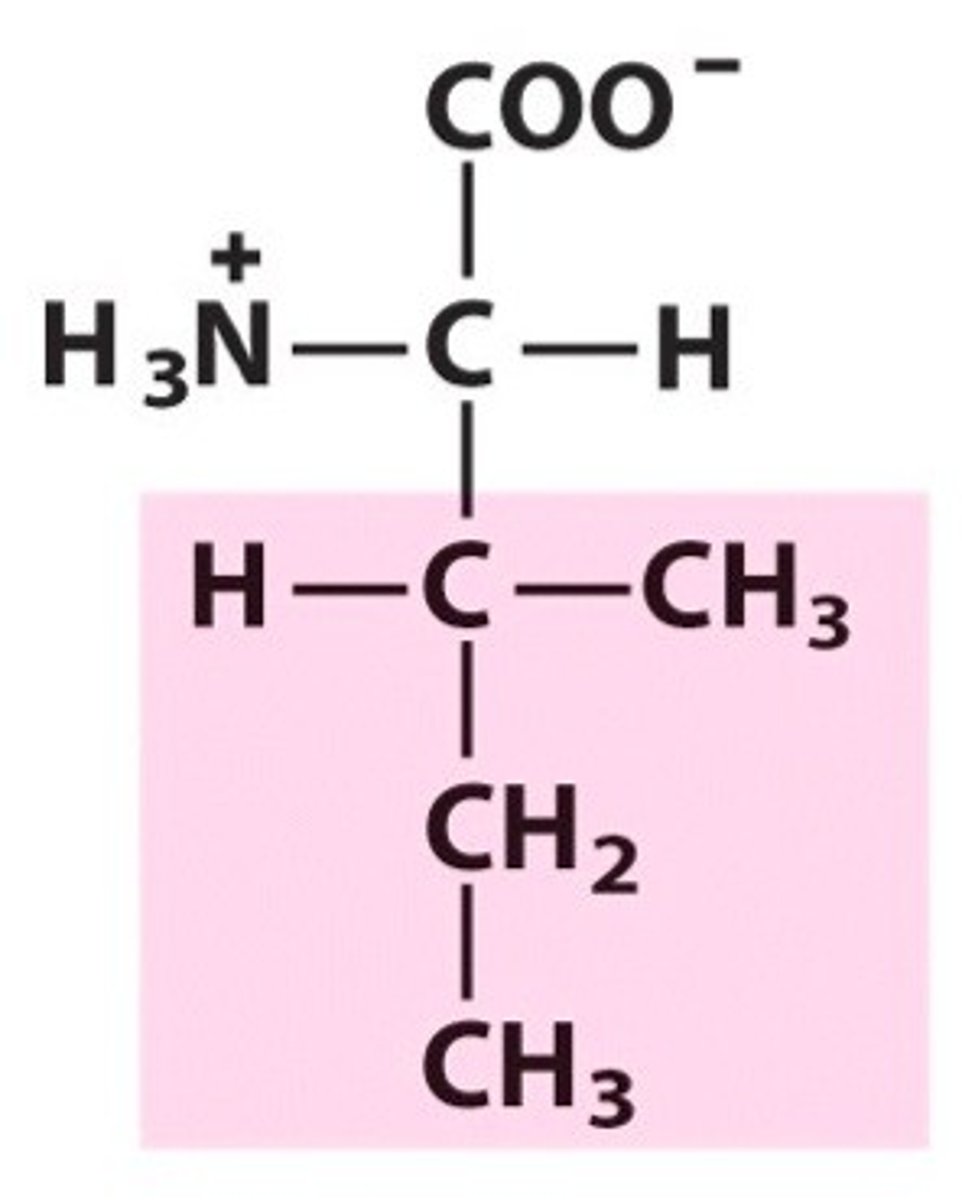
phenylalanine, Phe, F, aromatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
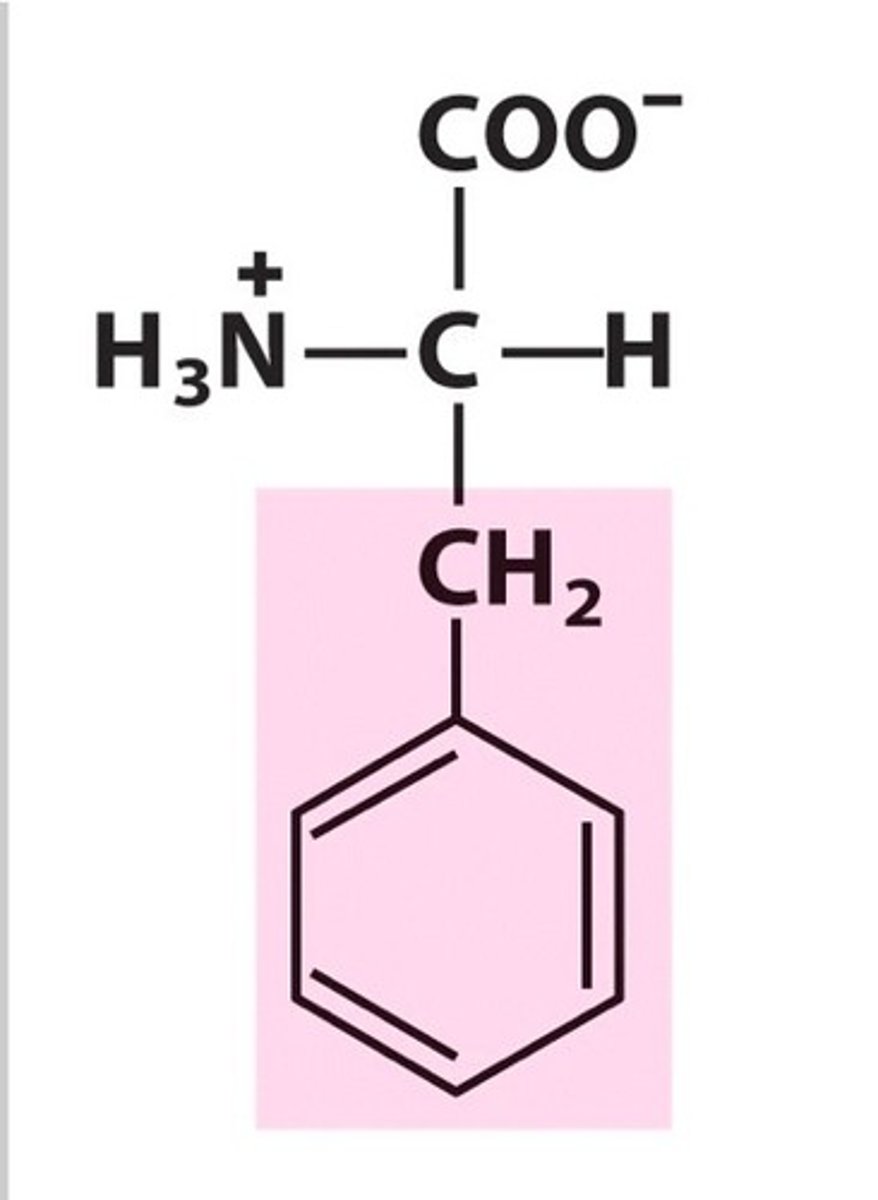
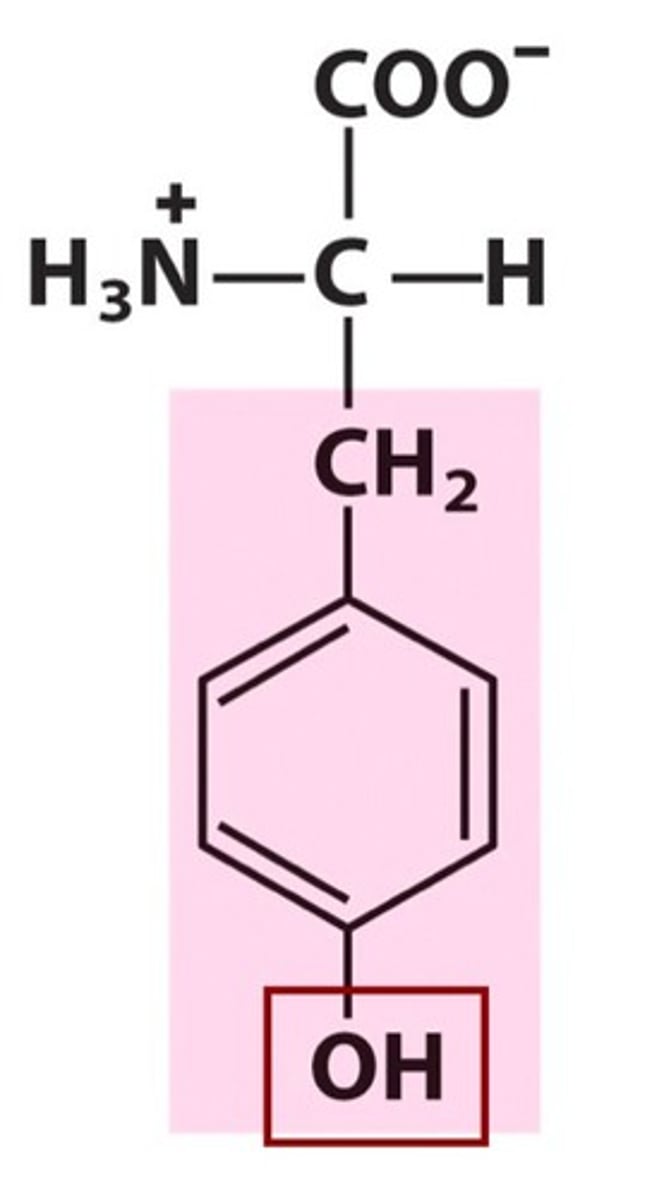
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y, aromatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
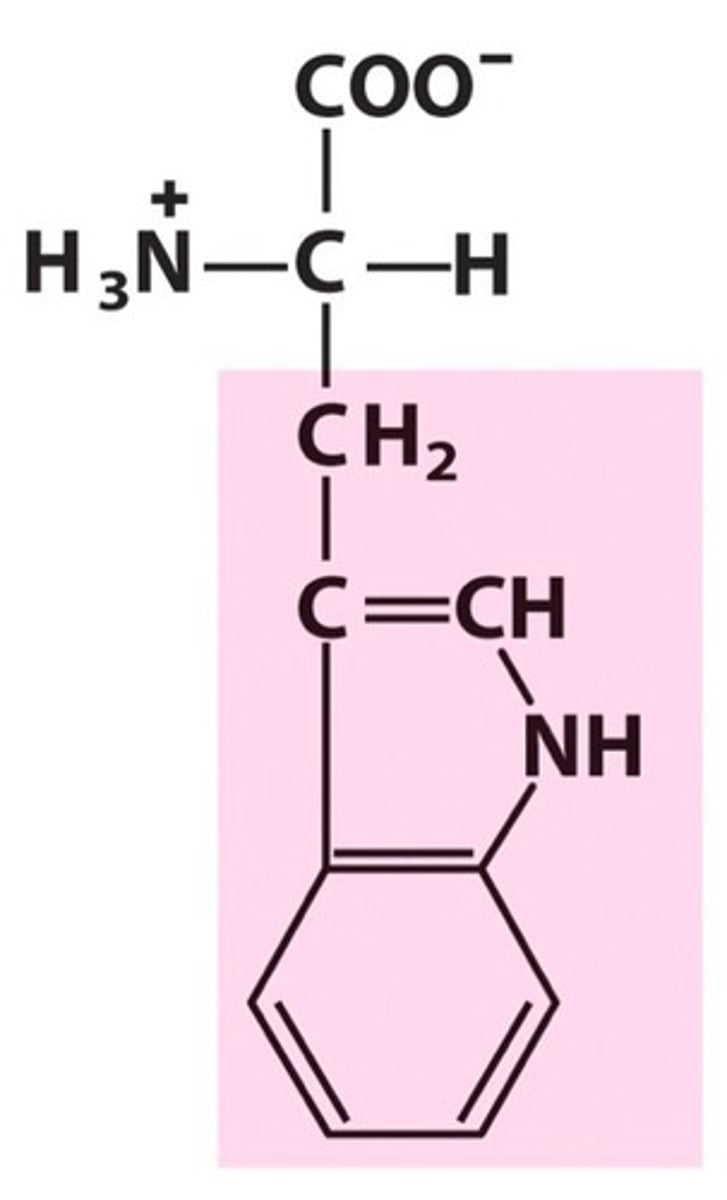
tryptophan, Trp, W, aromatic
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
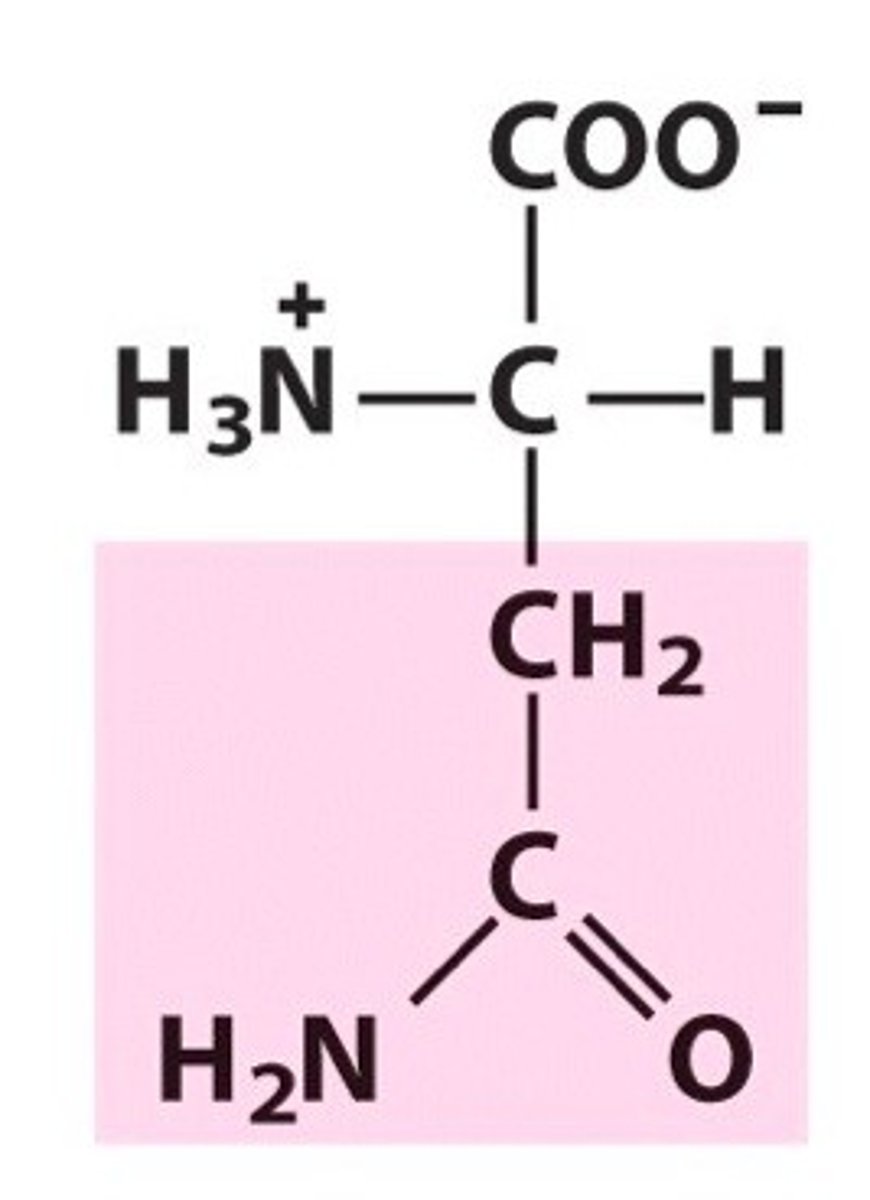
asparagine, Asn, N, polar/uncharged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
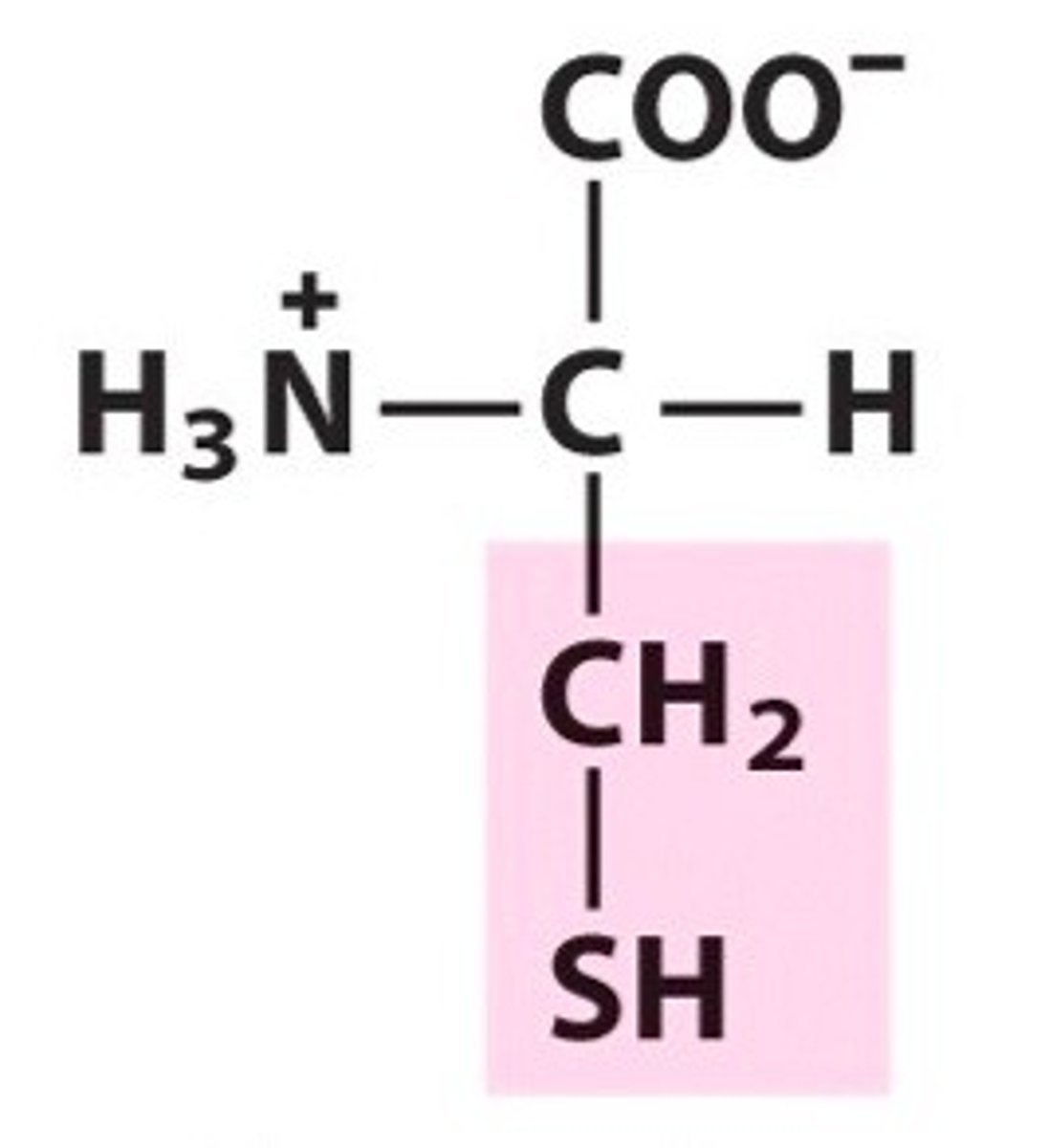
cysteine, Cys, C, polar/uncharged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
serine, Ser, S, polar/uncharged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
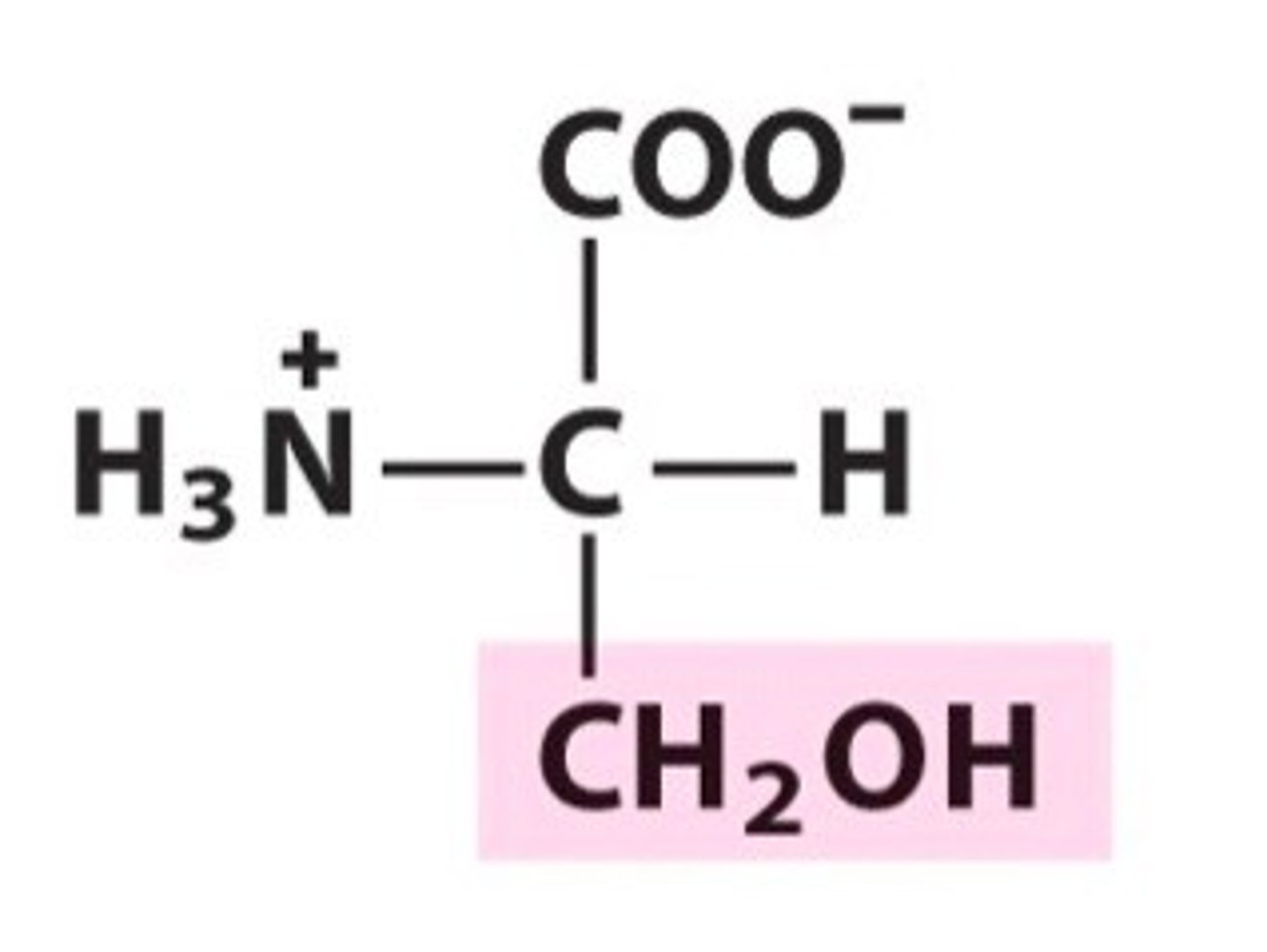
Threonine, Thr, T, polar/uncharged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
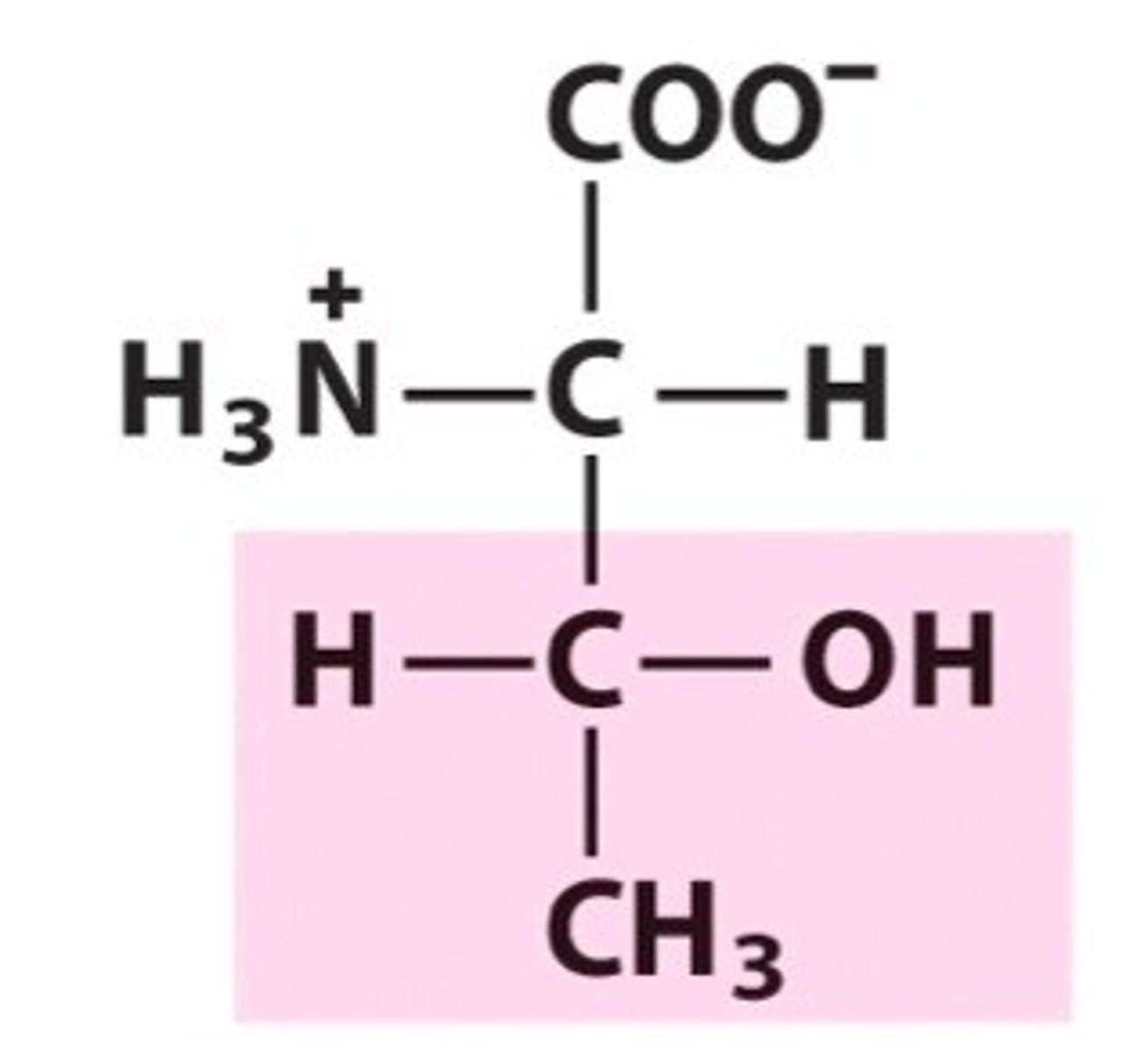
Glutamine, Gln, Q, polar/uncharged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
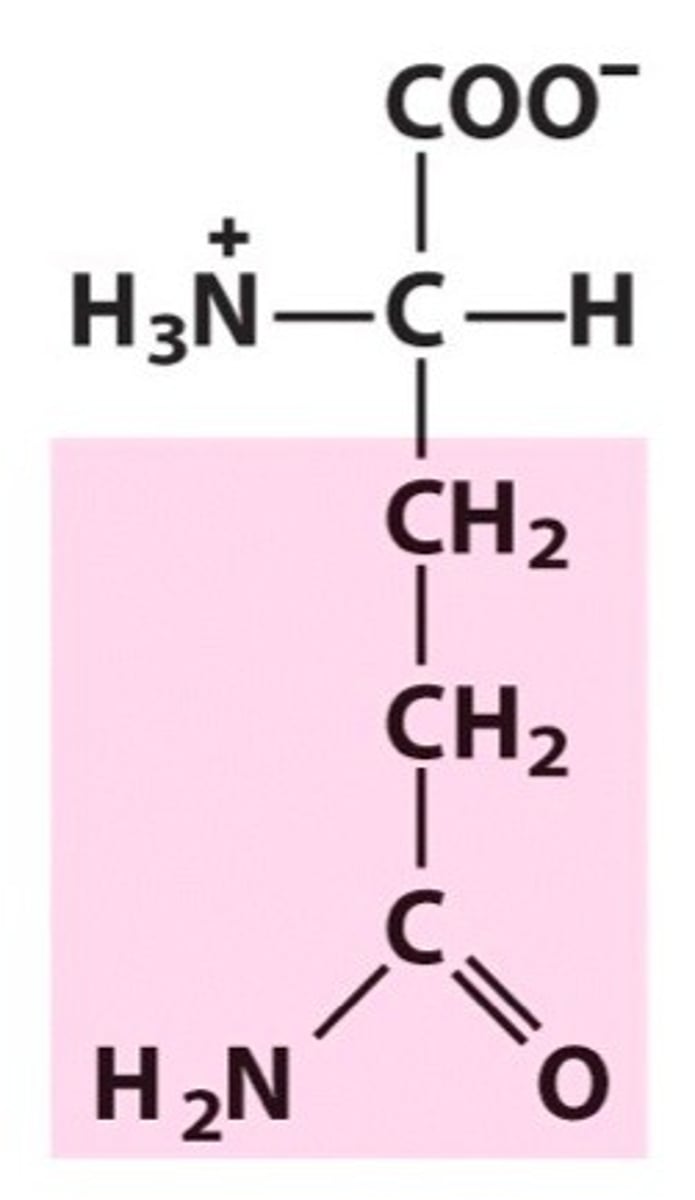
Arginine, Arg, R, positively charged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
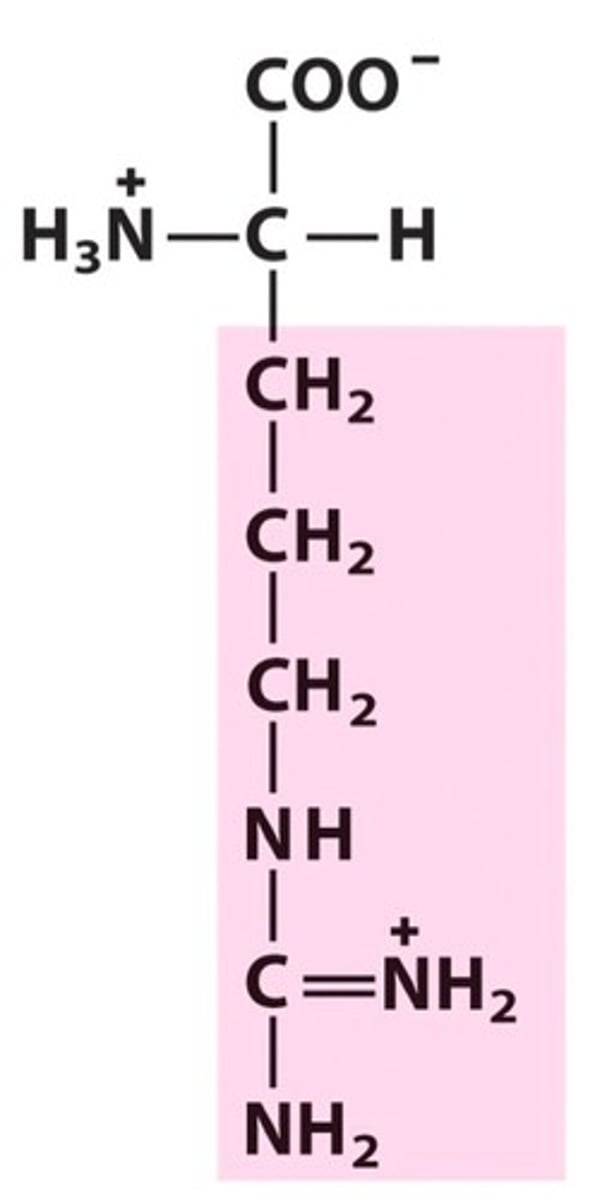
Histidine, His, H, positively charged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
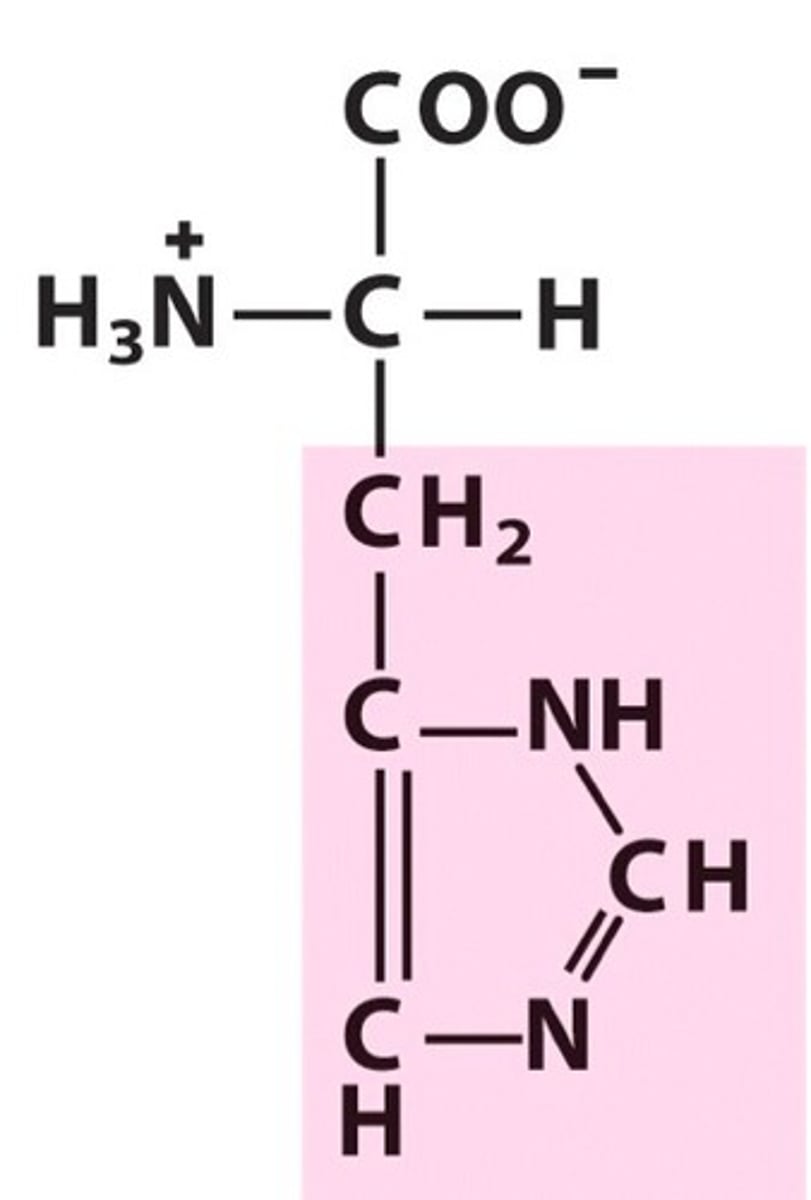
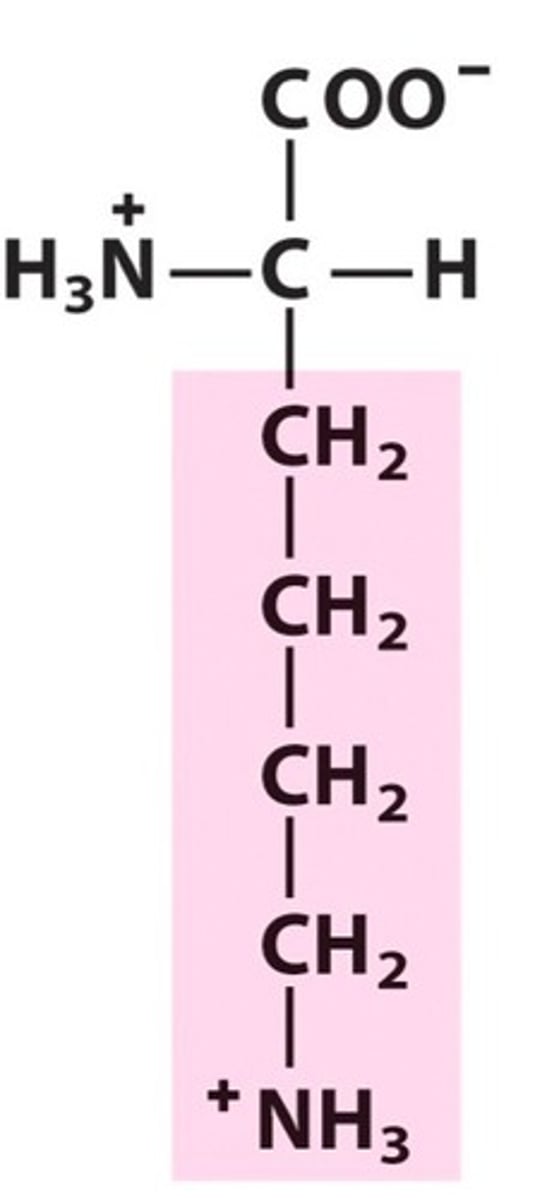
Lysine, Lys, K, positively charged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
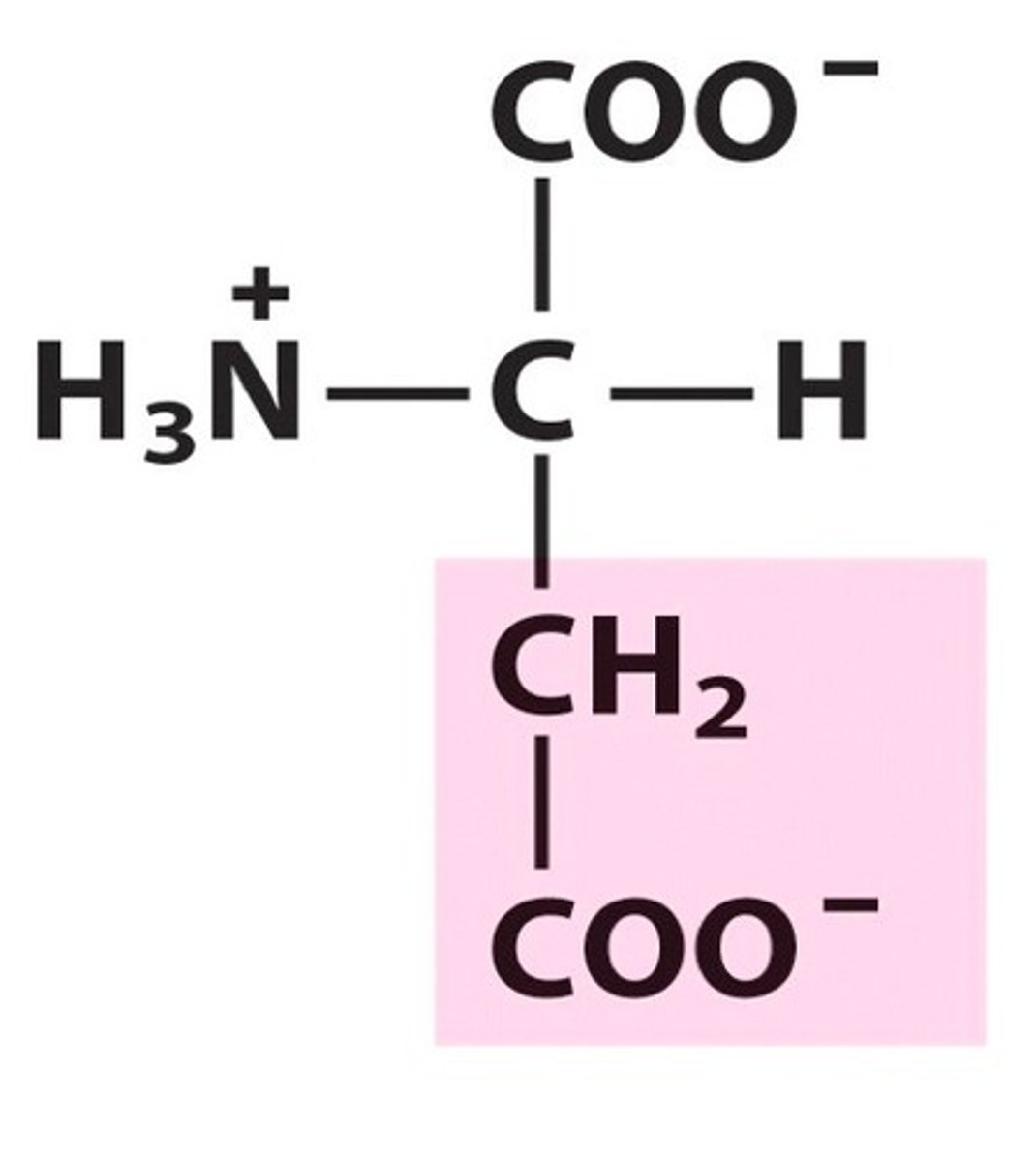
Aspartate, Asp, D, Negatively charged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
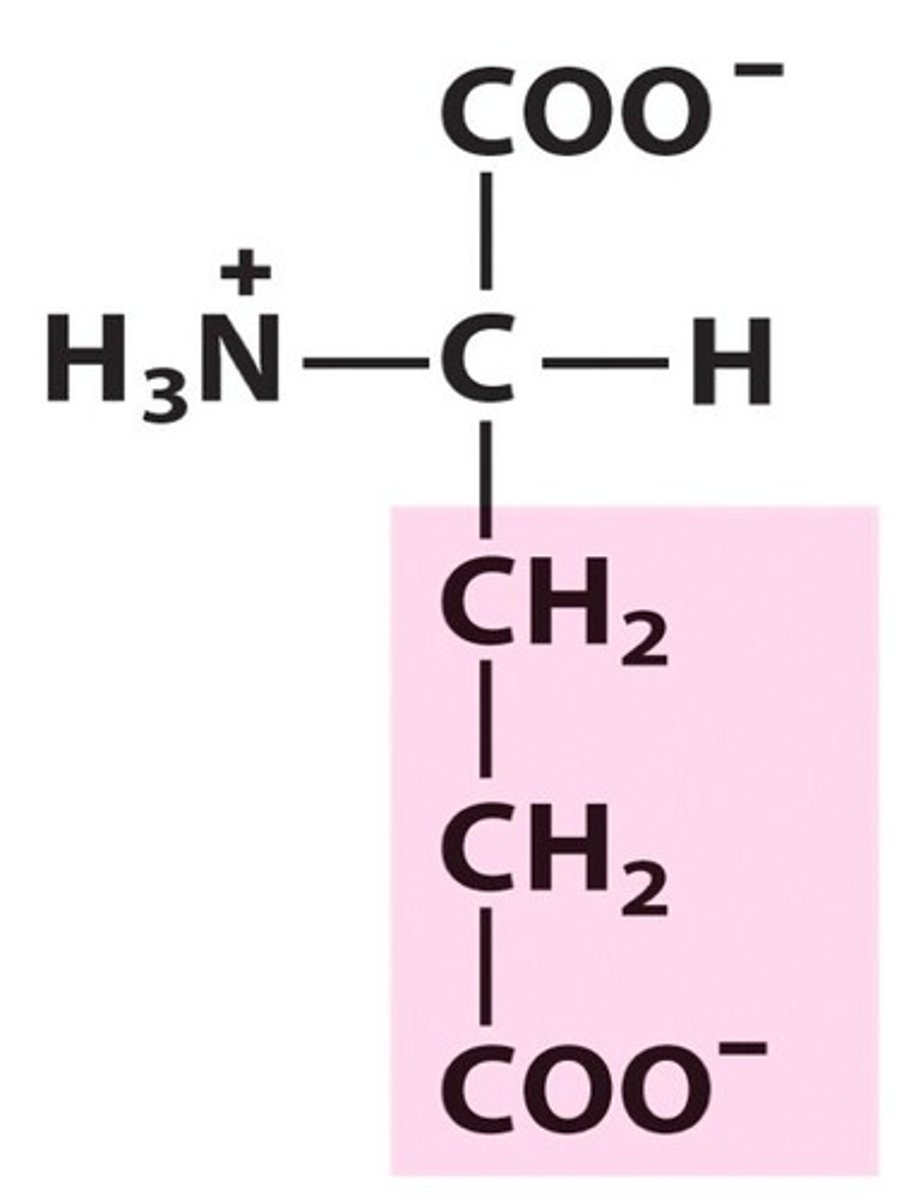
Glutamate, Glu, E, Negatively charged
name, 3 letter abbreviation, 1 letter code, category
Half
For a weak acid or base, the pKa is the pH at which the group is _______ protonated
Amine, carboxylic acid
two functional groups in every amino acid
Acidic, neutral, basic (alkaline)
for amino acids, at ___________ pH both groups are protonated, at a ___________ the carboxyl group is deprotonated, amino group is protonated, at a ____________ pH both groups are protonate
Zwitterion
at a neutral pH the carboxyl group is negative, and the amino group is positive causing a net neutral charge, also known as
protonated, deprotonated
if pH
3D
most protein molecules adopt a specific ____ conformation
native fold
the specific 3D conformation of a polypeptide
hydrophobic effect
the release of water molecules from around hydrophobic amino acids increases net entropy, happens due to this effect and allows protein to fold
hydrogen bonds
the type of interaction that allows alpha helices and beta sheets due to the interaction of N-H and C=O bonds
van Der walls interactions (LDFs)
medium range weak attraction between all atoms that stabilizes the interior of the protein
Electrostatic interactions
the long range strong interactions between permanently charged groups that stabilize a protein (can also be from salt bridges)
Partial double bond, rotate
the peptide bond has some resonance, meaning that it is a _____ _______ __________, and this restricts that amount that the bond can ________
ramachandran plot
Shows favorable phi-psi angle combinations. 3 main "wells" for α-helices, ß-sheets, and left-handed α-helices.
Phi angle
angle around the alpha carbon-amide nitrogen bond
Psi angle
angle around the alpha carbon-carboxyl carbon bond
alpha helix
type of secondary structure that is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the NEARBY residues
beta sheet
type of secondary structure that is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between ADJACENT SEGMENTS that may not be nearby
random coil
an irregular arrangement of the polypetide chain that is also a type of secondary structure
N, N+4
the helical backbone of an alpha helix is held together by hydrogen bonds between the backbone of N-H and C=O, of the _ amino acid and the _+_ amino acid
3.6 residues per turn
a right handed alpha helix has ____ residues per turn
out, perpendicular
on an alpha helix, side chains point _____ and are roughly ____________ with the helical axis
4-5 angstroms
the inner diameter of an alpha helix is this measurement
10-12 angstroms
the outer diameter of the helix (with side chains) is this measurement, which lets it fit well into the major groove of dsDNA
1, 8
residues _ and _ lie on top of each other in an alpha helix
antiparallel beta sheet
this type of beta sheet has one row start at N terminus and end at C terminus from left to right, and then the next row will start with the C terminus, and end with the N terminus from left to right (alternating)
parallel beta sheet
this type of beta sheet has each row start at the N terminus and then end at the C terminus (all the same)
antiparallel
this type of beta sheet is stronger than the other because of the strong LINEAR Hydrogen bonding, because the other has weak H bonding due to the bending nature of the H bonds
glycine, proline
these two amino acids are usually in beta turns to connect the antiparallel beta strands
side chains
the tertiary structure of a protein folds due to interactions from the _____ _________ of the amino acids
quaternary structure
the structure of a protein that is multiple different subunits to form one protein complex
fibrous
type of protein that is shaped like a long strand/sheet, usually provides structural support as its function
globular
the type of protein that has a spherical shape, usually is an enzyme or regulatory protein
membrane proteins
this type of protein has a hydrophobic surface, and a hydrophilic interior in order to properly cross hydrophobic membranes
True
ture or false, a protein can have a mix of shapes of proteins