Muscular System Quiz Questions
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Which of the following best describes the neurotransmitter released from a typical motor neuron?
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholinesterase
Norepinephrine
Choline
Calcium
acetylcholine
Which of the following best describes Myasthenia Gravis (MG) and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (LEMS)?
a. MG, postsynaptic disease; LEMS, presynaptic disease
b. MG, presynaptic disease; LEMS, presynaptic disease
c. MG, postsynaptic disease; LEMS, postsynaptic disease
d. MG, presynaptic disease; LEMS, postsynaptic disease
a
A 45-year-old man has botulinum toxin (Botox®) injections in the frontalis muscles. Which of the following sets of changes are most likely to occur in the treated muscles with repeated injections over a period of 10 years?
decreased fiber diameter, decreased fiber number, decreased contraction velocity
Which represents the correct temporal order of events for skeletal muscle?
nerve action potential, end plate potential, muscle action potential
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease in which antibodies cause damage to which of the following?
a. Acetylcholine
b. Ligand-gated channels on postsynaptic membrane
c. Ligand-gated channels on presynaptic membrane
d. Voltage-gated channels on postsynaptic membrane
e. Voltage-gated channels on presynaptic membrane
b
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome is an autoimmune disease in which antibodies cause damage to which of the following?
a. Acetylcholine
b. Ligand-gated channels on postsynaptic membrane
c. Ligand-gated channels on presynaptic membrane
d. Voltage-gated channels on postsynaptic membrane
e. Voltage-gated channels on presynaptic membrane
e
A 59-year-old college professor visits his physician because of muscle fatigue that worsens later in the day. The physician notices that the man has droopy eyelids and seems to have an overall weakness in his muscles. After the intravenous administration of Tensilon, which blocks degradation of acetylcholine, the droopy eyelids and symptoms of muscle weakness appear to subside. Which of the following best describes the patient's condition?
Encephalitis
Fibromyalgia
Flaccid paralysis
Myasthenia gravis
Poliomyelitis
myasthenia gravis
A 3-year-old child is admitted to the emergency department of University Hospital. The child exhibits extreme salivation, lacrimation, tremors, and tachycardia. The slight erythema and mild edema found on the child's hand suggest a spider bite. The mother acknowledges that the child has a fascination with spiders and has seen black widow spiders in the yard. The neurotoxic venom of the black widow spider (i.e., latrotoxin or latrophilin) can increase the flux of calcium ions into the presynaptic terminal. What is the likely outcome of a black widow spider bite?
a. Decreased acetylcholine release from nerve terminals
b. Hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membranes
c. Hyperpolarization of presynaptic membranes
d. Increased acetylcholine release from nerve terminals
e. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
d
Which of the following represents the correct temporal order of events for skeletal muscle?
nerve action potential, muscle action potential, muscle contraction
Binding of calcium to which structure or molecule initiates a contraction in smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle?
smooth calmodulin, skeletal troponin, cardiac tropinin
Rigor mortis is caused by a decrease in which of the following?
a. Acetylcholine
b. Actin-myosin cross-bridges
c. Myoplasmic calcium levels
d. Interstitial lactate levels
e. Muscle ATP levels
e
A father and his 10-year-old daughter died suddenly of suffocation after ingesting smoked whitefish chubs from the Great Lakes. Three other family members are sick, complaining of dry mouths despite drinking copious amounts of fluids. Their upper eyelids droop. Their vision is clear, but their pupils are wide and do not narrow when a light is flashed. Two of them require artificial respiration. The suspect is botulism (Clostridium botulinum). The surviving patients begin improving soon after receiving the only treatment available, E antitoxin. The deadly effect of botulinum toxin results from which of the following?
a. Decreased release of acetylcholine
b. Decreased release of norepinephrine
c. Depletion of muscle calcium stores
d. Skeletal muscle tetany
e. Stimulation of ryanodine receptors
a
Which of the following best describes the correct temporal order of events for the opening of nicotinic acetylcholine (nACh) channels on the muscle membrane, the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels on the muscle membrane, and initiation of presynaptic action potentials (AP)?
presynaptic AP, nACh channels, voltage gated Na channels
Which of the following structures covers the Active Sites on the F-actin portion of the thin filaments in a skeletal muscle fiber when myoplasmic calcium levels are low?
a. Tropomyosin
b. Troponin
c. Myosin head
d. Myosin filament
e. Titin
b??? shouldnt it be A
Which of the following best describes the function of Titin?
a. Thin filament
b. Thick filament
c. Molecular spring
d. Contractile protein
c
Which of the following best describes the thick and thin filaments of skeletal muscle?
a. Thin filament is actin; thick filament is myosin
b. Thin filament is myosin; thick filament is actin
c. Thin filament is titin; thick filament is actin
d. Thin filament is actin; thick filament is titin
a
Which of the following best describes a Type II muscle fiber?
a. Small diameter
b. High capillary density
c.High myoglobin content
d. Easily fatigued
e. Many mitochondria
e
Which of the following best describes a Type II muscle fiber?
Small diameter
High capillary density
High myoglobin content
Easily fatigued
Many mitochondria
easily fatigued
Which of the following best describes the relationship between isometric and isotonic contractions in a given skeletal muscle under normal conditions?
a. Isometric contraction precedes isotonic contraction.
b. Isotonic contraction precedes isometric contraction.
c. Isometric and isotonic contractions occur simultaneously.
a
A 28-year-old man has been training as a distance runner for the past 6 years. Compared with a sprinter, which of the following is most likely to be decreased in the skeletal muscles of this athlete during resting conditions?
a. Capillary density
b. Glycolytic enzyme content
c. Mitochondrial volume density
d. Myoglobin content
e. Oxidative capacity
b
A physiology experiment is conducted in which a skeletal muscle twitch is initiated using an electrical stimulator. Which factor contributes to the termination of a typical skeletal muscle twitch?
a. Calcium uptake by sarcoplasmic reticulum
b. Closure of transverse tubules
c. Depletion of calcium stores from sarcoplasmic reticulum
d. Exhaustion of muscle ATP stores
e. Stimulation of dihydropyridine (DHP) receptors
a
A 24-year-old medical student goes to the local gym to lift weights. She begins by bench-pressing 100 pounds as a warm-up procedure and then gradually increases the weight. Which of the following occurs as she adds more weight?
a. Decreased frequency of motor nerve action potentials
b. Decreased velocity of motor nerve action potentials
c. Increased frequency of motor nerve action potentials
d. Increased velocity of motor nerve action potential
e. Involvement of fewer motor units
c
When a person lifts a 25-pound weight, what type or types of muscle contraction are involved?
a. Isometric contraction only
b. Isotonic contraction only
c. Isometric contraction followed by isotonic contraction
d. Isotonic contraction followed by isometric contraction
c
A 29-year-old woman has been training as a distance runner for the past 5 years. Which set of changes best describes the skeletal muscles of this woman compared with a sprinter?
capillary density
oxidative capacity
myoglobin content
fiber diameter
increased, increased, increased, decreased
A 45-year-old man goes to the local gym to lift weights. He begins by bench-pressing 130 pounds as a warm-up procedure and then gradually increases the weight. Which of the following sets of changes occur as he adds more weight?
activation of motor units; frequency of motor nerve action potentials
increased, increased
The dark color of Type 1 skeletal muscle can be attributed to a relative abundance of which of the following compared to Type 2 skeletal muscle?
Blood capillaries
Mitochondria
Myoglobin
Myosin ATPase
Oxidative enzymes
myoglobin
High frequency stimulation of a skeletal muscle causes tetanic contraction because the intracellular concentration of which of the following substances increases and remains at high levels?
ATP
Calcium
Potassium
Sodium
Troponin
calcium
The increase in muscle mass that typically occurs with weight training is most likely caused by an increase in the number of which of the following?
Capillaries
Mitochondria
Muscle fibers
Myofibrils
myofibrils
The relatively high maximum velocity of shortening of a skeletal muscle containing predominately Type 2 fibers can be partially attributed to a relative abundance of which of the following substances, compared to a muscle containing predominately Type 1 fibers?
Blood capillaries
Mitochondria
Myoglobin
Myosin ATPase
Oxidative enzymes
myosin ATPase
Electrical coupling between adjacent cells in visceral smooth muscle can be attributed to which of the following?
Dense bodies
Gap junctions
Intermediate fibers
Mechanical junctions
Potassium channels
gap junctions
Smooth muscle contraction is more energy efficient compared to skeletal muscle contraction because smooth muscle has a latch state that allows prolonged muscle contraction with relatively little energy usage.
a. Both the statement and the reason are correct and related.
b. Both the statement and the reason are correct but not related.
c. The statement is correct, but the reason is not.
d. The statement is not correct, but the reason is correct.
e. Neither the statement nor the reason is correct.
a
The contraction of smooth muscle can be attenuated even when intracellular calcium levels are high. This unique ability of smooth muscle can be attributed to variations in the activity of which of the following?
a. Actin
b. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
c. Calcium-calmodulin complex
d. Calmodulin
e. Myosin light chain phosphatase
e
Multiple elements can regulate the contraction of smooth muscle, including endocrine, neurocrine, and paracrine factors. This level of diversity in the control of smooth muscle contraction can be attributed to a diversity of which of the following?
a. Actin-myosin arrangement
b. Calcium sensitivities
c. Receptors and transduction mechanisms
d. Motor end plates
e. Subneural cleft architecture
c
Unlike skeletal muscle, the contraction of smooth muscle requires which of the following?
a. Activation of ryanodine receptors
b. Phosphorylation of myosin light chains
c. The presence of intracellular calcium
d. Troponin binding of calcium
e. Voltage activation of dihydropyridine receptors
b
Which of the following factors can initiate smooth muscle contractions?
hormones
paracrine factors
autonomic nervous system
yes, yes, yes
An increase in calcium sensitivity for contraction of smooth muscle can be caused by a decrease in the levels of which of the following substances?
a. Actin
b. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
c. Calcium-calmodulin complex
d. Calmodulin
e. Myosin light chain phosphatase
e
Which of the following is the correct temporal order of events for the smooth muscle?
a. Myosin light chain (MLC) dephosphorylation, contraction, relaxation, MLC phosphorylation
b. MLC dephosphorylation, contraction, MLC phosphorylation, relaxation
c. MLC dephosphorylation, relaxation, MLC phosphorylation, relaxation
d. MLC phosphorylation, contraction, MLC dephosphorylation, relaxation
e. MLC phosphorylation, contraction, relaxation, MLC dephosphorylation
f. MLC phosphorylation, MLC dephosphorylation, contraction, relaxation
d
Smooth muscle can maintain a contraction for a relatively long time with minimal energy usage because the latch mechanism is present in smooth muscle.
true
The control mechanism of smooth muscle contraction is myosin-based because the calcium-calmodulin complex binds to myosin light chain kinase.
true
Which of the following best describes a major source of calcium that initiates contraction of smooth muscle?
Extracellular fluid
Longitudinal tubules
Mitochondria
Sympathetic nervous system
Terminal cisterna
extracellular fluid
When an electrical impulse traveling along a motor neuron arrives at a neuromuscular junction,
a. there is an increase in the secretion of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.
b. calcium is transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
c. a new electrical impulse is generated that returns the message to the original nerve.
d. myosin-actin cross-bridges are destroyed.
e. sliding of actin and myosin filaments is inhibited.
a
After nervous stimulation stops, what prevents ACh in the synaptic cleft from continuing to stimulate contraction?
a. acetylcholinesterase destroying the ACh
b. calcium ions returning to the terminal cisternae
c. the tropomyosin blocking the myosin once full contraction is achieved
d. the action potential stops going down the overloaded T tubules
a
The neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle is acetylcholine.
true
__________________ ions move ________the synapsing neuron to participate in vesicle movement to the cell surface and ______________ of the neurotransmitter.
Ca++, into, exocytosis
sarcomere
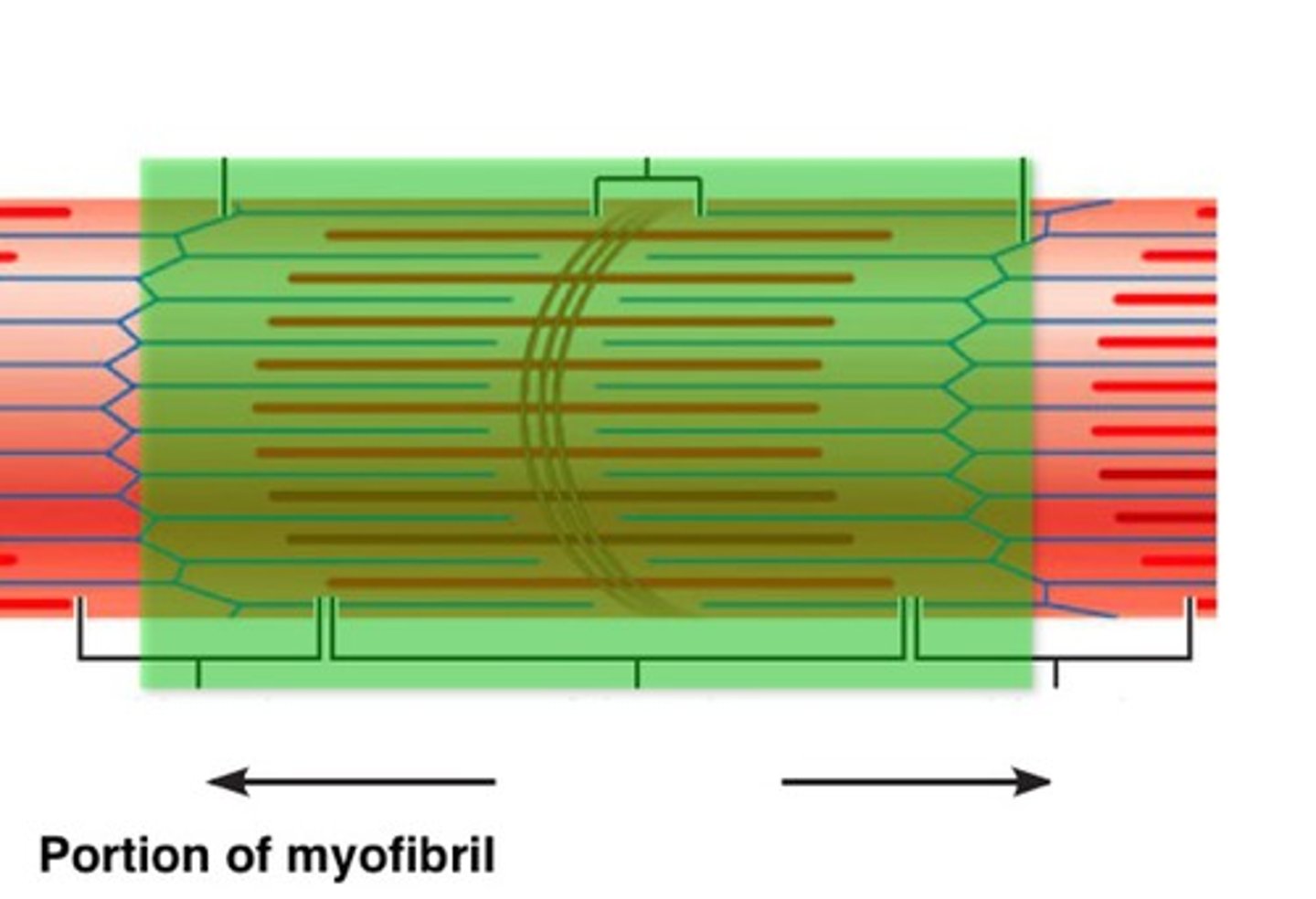
myofiber
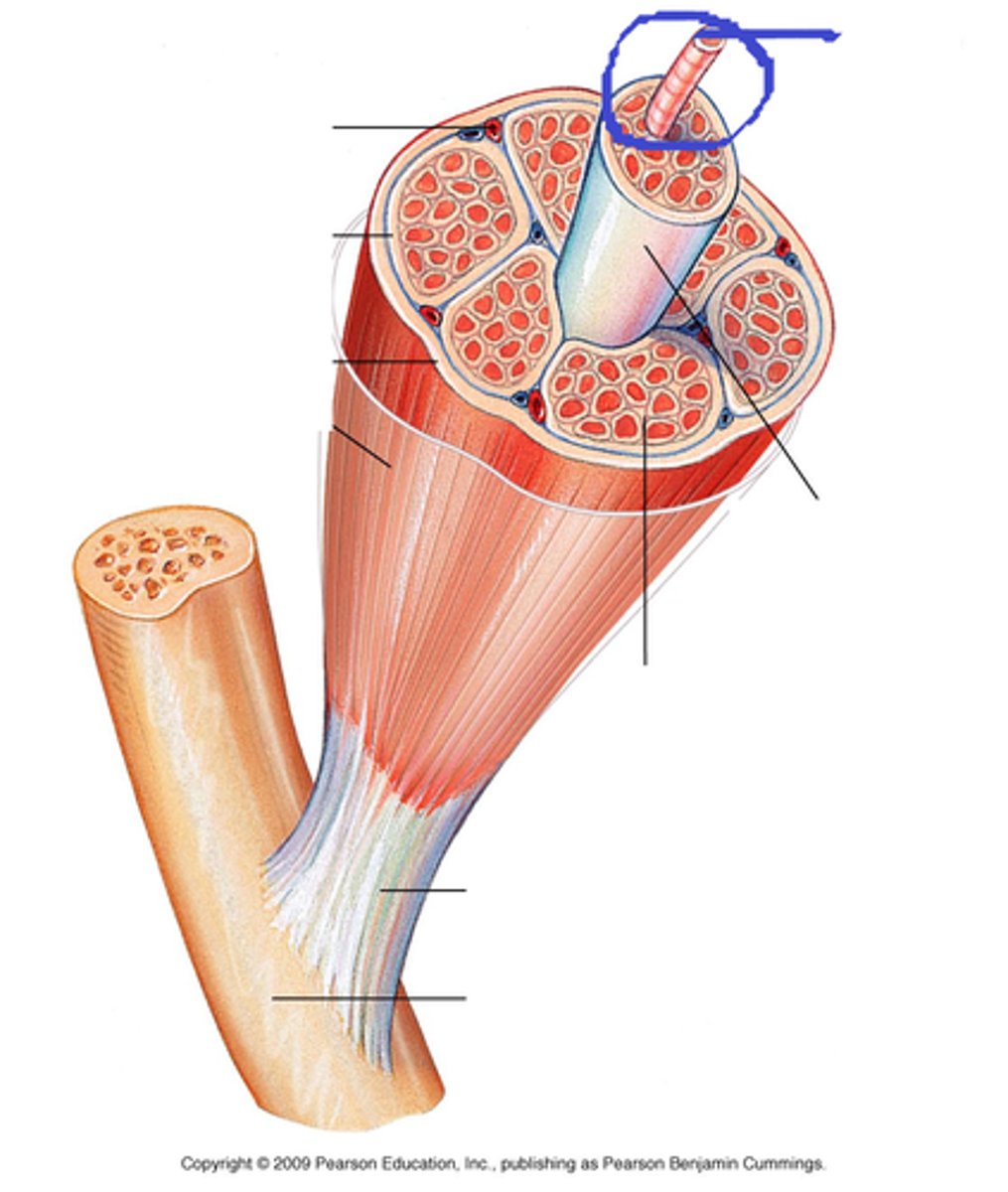
sarcolemma
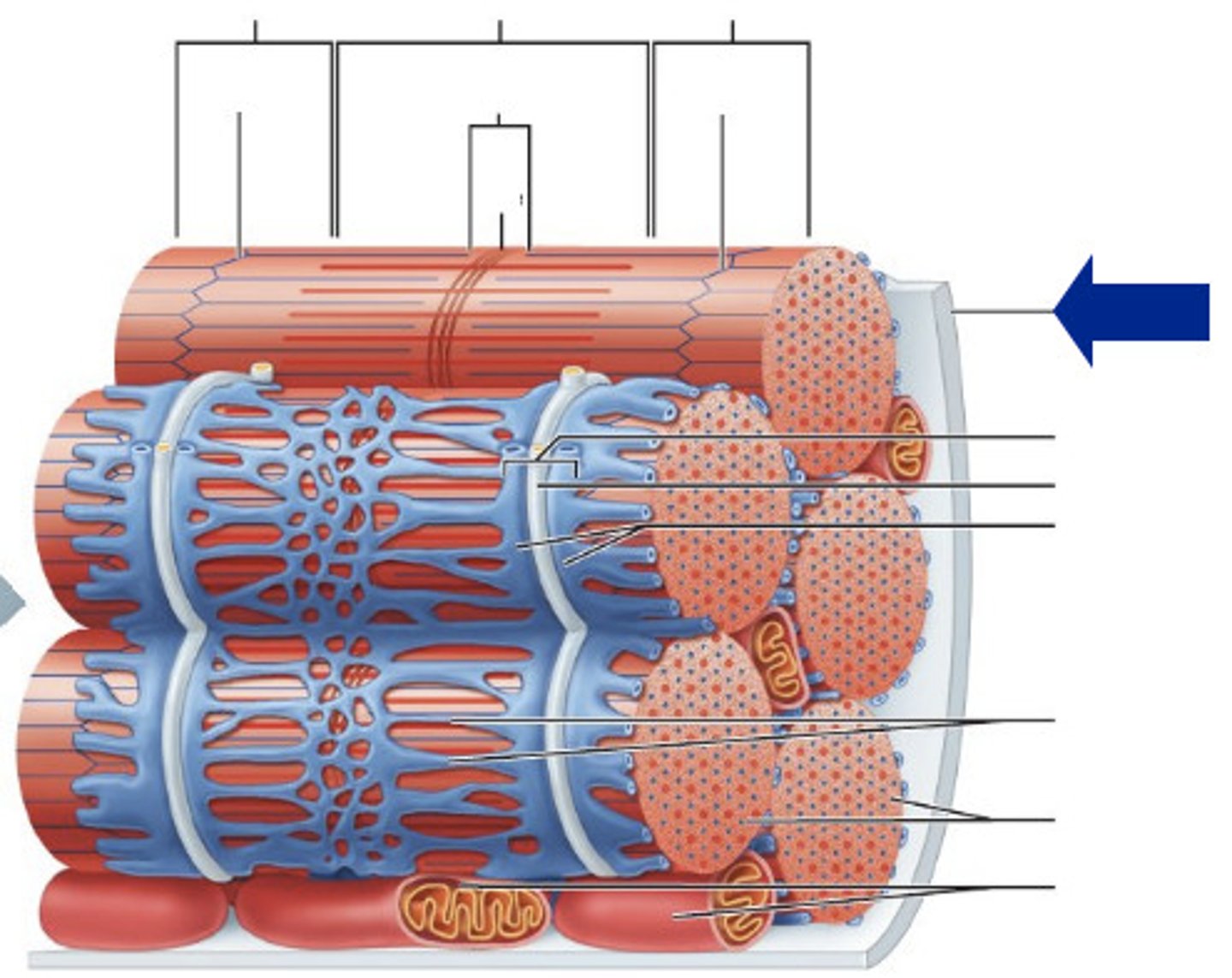
myofibril
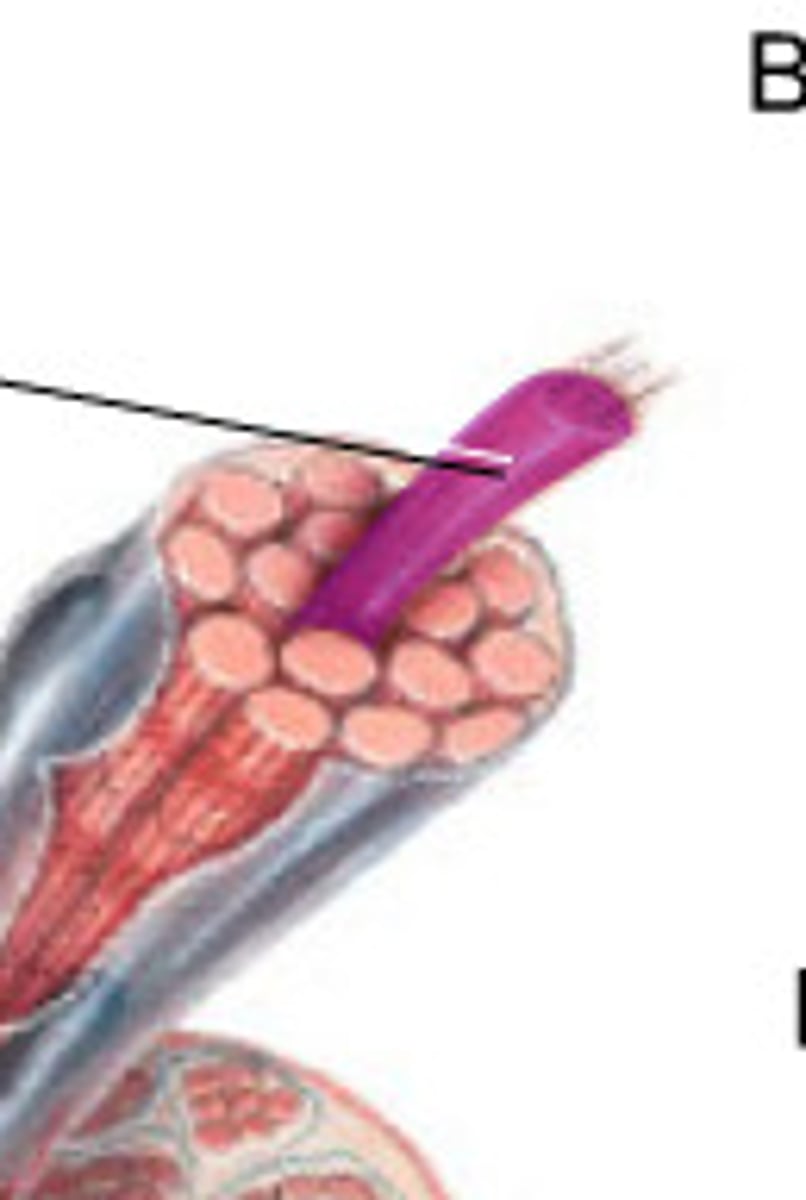
The structural and functional unit of skeletal muscle is the:
a. Sarcolemma
b. Actin myofilament
c. Sarcomere
d. Myosin myofilament
c
Which of the following is the protein found in the thick myofilament?
Dystrophin
Titan
Actin
Myosin
myosin
Which of the following best describes the function of Titin?
Thin filament
Thick filament
passive elasticity
Contractile protein
tension generation
passive elasticity
What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles?
a. Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the actin binding sites on the myosin molecules.
b. Tropomyosin is the chemical that activates the myosin heads.
c. Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules.
d. Tropomyosin is the receptor for the motor neuron neurotransmitter.
c
Hypothetically, if a muscle were stretched to the point where thick and thin filaments no longer overlapped, then
a. ATP consumption would increase because the sarcomere is ""trying"" to contract"
b. no muscle tension could be generated
c. maximum force production would result because the muscle has a maximum range of travel
d. cross bridge attachment would be optimum because of all the free binding sites on actin
b
In isotonic contractions, the muscle changes in length and the tension remains constant through most of the contractile period.
true
The type of skeletal muscle fiber that is most resistant to fatigue is the fast fiber.
false
Which of the following best describes a typical Type I skeletal muscle fiber?
a. Oxidative, high capillary density, many mitochondria
b. Glycolytic, low capillary density, few mitochondria
c. Small diameter, glycolytic, many mitochondria
d. Large diameter, few mitochondria, fast twitch
e. High myoglobin content, low capillary density, fast twitch
a
Which of the following best describes a Type II muscle fiber?
a. Small diameter
b. High capillary density
c. High myoglobin content
d. Easily fatigued
e. Many mitochondria
d
Which of the following best describes the relationship between isometric and isotonic contractions in a given skeletal muscle under normal conditions?
a. Isometric contraction precedes isotonic contraction.
b. Isotonic contraction precedes isometric contraction.
c. Isometric and isotonic contractions occur simultaneously.
a
When a person lifts a 25-pound weight, what type or types of muscle contraction are involved?
a. Isometric contraction only
b. Isotonic contraction only
c. Isometric contraction followed by isotonic contraction
d. Isotonic contraction followed by isometric contraction
c
A length-tension diagram is shown below. This plot shows that the amount of tension generated is constant and does not vary with the length of the muscle.
false
A length-tension diagram is shown below. The amount of passive tension generated ____________ as muscle length increases.
increases
Transfer of electrical signals between adjacent cells in visceral smooth muscle can be attributed to which of the following?
Dense bodies
Intermediate fibers
connexins
Mechanical junctions
Potassium channels
connexins
The contraction of smooth muscle can be attenuated even when intracellular calcium levels are high. This unique ability of smooth muscle can be attributed to variations in the activity of which of the following?
a. Actin
b. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
c. Calcium-calmodulin complex
d. Calmodulin
e. Myosin light chain phosphatase
e
Unlike skeletal muscle, the contraction of smooth muscle requires which of the following?
a. Activation of ryanodine receptors
b. Phosphorylation of myosin light chains
c. The presence of intracellular calcium
d. Troponin binding of calcium
e. Voltage activation of dihydropyridine receptors
b
An increase in calcium sensitivity for contraction of smooth muscle can be caused by a decrease in the levels of which of the following substances?
a. Actin
b. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
c. Calcium-calmodulin complex
d. Calmodulin
e. Myosin light chain phosphatase
e
Which of the following is the correct temporal order of events for the smooth muscle?
a. Myosin light chain (MLC) dephosphorylation, contraction, relaxation, MLC phosphorylation
b. MLC dephosphorylation, contraction, MLC phosphorylation, relaxation
c. MLC dephosphorylation, relaxation, MLC phosphorylation, relaxation
d. MLC phosphorylation, contraction, MLC dephosphorylation, relaxation
e. MLC phosphorylation, contraction, relaxation, MLC dephosphorylation
f. MLC phosphorylation, MLC dephosphorylation, contraction, relaxation
d
Smooth muscle can maintain a contraction for a relatively long time with minimal energy usage (as compared to skeletal muscle) because
a. the latch mechanism is present in smooth muscle.
b. it has more acetylcholine receptors.
c. is has more Calcium receptors
d. calcium quickly detaches from Calmodulin
e. it has more mitochondria
a