Principles-Production of X-rays
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Production of X-rays
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What type of radiation are X-rays?
a form of electromagnetic radiation
The electromagnetic spectrum includes X-rays with wavelengths between ….?
0.1 and 0.5 angstrom
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength in electromagnetic waves?
Inversely proportional
What are the conditions required for X-ray production?
Source of electrons
Accelerate electrons
Decelerate electrons
Target
All X-ray production occurs in a
vacuum
Anode is made up of
tungsten
In X-ray production, energy corresponds to the…
quality of the beam
Approximately 99% of the kinetic energy of incident electrons is converted to heat during …
X-ray production
What is the relationship between X-ray energy and the kinetic energy of incident electrons?
Directly proportional
What are the steps involved in heat production during X-ray production?
Electrons interact with outer-shell electrons of target atoms
Outer-shell electrons are raised to an excited energy level
Electrons drop back to their normal state
Infrared radiation is emitted as heat
What are the two types of target interactions that produce X-ray photons?
Bremsstrahlung and Characteristic
Bremsstrahlung radiation occurs when an incident electron is slowed by the force field of the
nucleus
The energy of Bremsstrahlung radiation depends on the energy of the incident
electron
What does the term kVp stand for in X-ray production?
kilo Voltage Peak
The average beam energy in Bremsstrahlung radiation is 30-40% of the
kVp selected
What type of interaction is responsible for characteristic radiation?
Inner-shell electron ejection
The emitted radiation in characteristic interactions is specific to the target
element
The K-shell binding energy of tungsten is approximately
69.5 keV
What determines the energy of the characteristic X-ray photon emitted during electron transitions?
Difference in binding energies
A heterogeneous beam contains a broad spectrum of energies
Bremsstrahlung emission spectrum
Bremsstrahlung
Generated by incident electron being slowed by nucleus
Characteristic
Generated by electron transitions in inner shells
What is the tungsten binding energy?
69.5 keV
The average beam energy in X-ray production is 30-40% of the set …
kVp
What are the factors that affect the X-ray emission spectrum?
mA (mAs)
kVp
Filtration
Generator Type
What does mAs primarily affect in the X-ray beam?
Beam quantity
….determines the penetrability and quality of the X-ray beam.
The kVp
Higher filtration in X-ray production results in decreased beam
quantity
What effect does increased generator efficiency have on the X-ray beam?
Increased photon energy
low frequency
long wavelength
High frequency
short wavelength
what percentage is used for the production of xrays?
1%
What is coming from the cathode and hitting the anode?
Incident electrons (xray photons)
higher speed means
higher energy quality
The difference in origins of a low energy bremsstrahlung xray and a maximum energy xray, is that the maximum energy is produced when the incident electron:
gets extremely close to the nucleus
What does the term heterogenous mean, as it relates to the xray beam?
contains a variety of energies (polyenergetic)
xray tube heat production is dependent on …
the kVp and mAs selected
Define characteristic cascade
inner k shell electron is ejected from its orbit, outer shell drops down
What is the minimum kVp that will produce characteristic xrays?
70 kVp
define kVp
determines the quality (energy) of beam, highest energy of beam
Describe the relationship between the kVp and the average energy of the primary beam photons
They are directly proportional; the average beam energy is 30-40% of the selected kVp. A higher kVp leads to higher average energy of the primary beam photons.
which type of xray production involves ejecting an inner shell electron?
characteristic
which type of xray production involves a cascade effect?
characteristic
what type of interaction is responsible for the majority of the xrays produced in diagnostic xray?
Brems 80-90%
When mA is increased, with other technical factors remaining the same, What part of the emission curve is affected? and is it directly or indirectly proportional
Amplitude (height) of the emission curve. An increase in mA increases the quantity of X-ray photons, thus increasing the amplitude of the curve. directly proportional
how is the emission spectrum affected when kVp is increased? list two changes in the appearance
shifts to the right, increases in amplitude
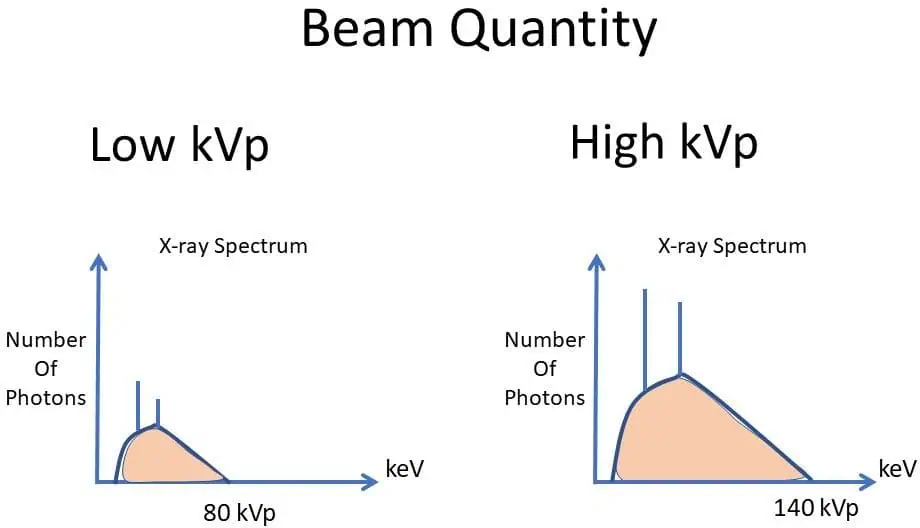
How is the average energy of the beam affected when kVp is increased?
increases
Brems radiation
loss of kinetic energy given off as xray photon
Energy of Brems Radiation
The energy of the incident electron
the charge of the nucleus
the proximity of the incident electron to the nucleus
Interactions farther from the nucleus
lower energy brems
interactions closer to the nucleus
higher energy brems
Tungsten electron Transition
The further out the electron comes to drop into vacancy, the greater the characteristic radiation produced, may be from any shell
where does the production happen?
within the tube
Higher filtration means
decreased in quantity