Biochem Lect 25: Bacteria Cell Wall + Glycolysis Part I
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
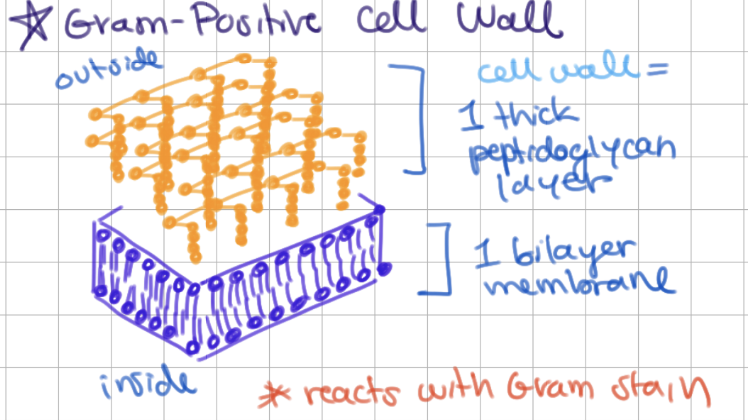
Gram-positive bacterial cell wall
1 bilayer + thick peptidoglycan layer
-
**reacts with Gram stain
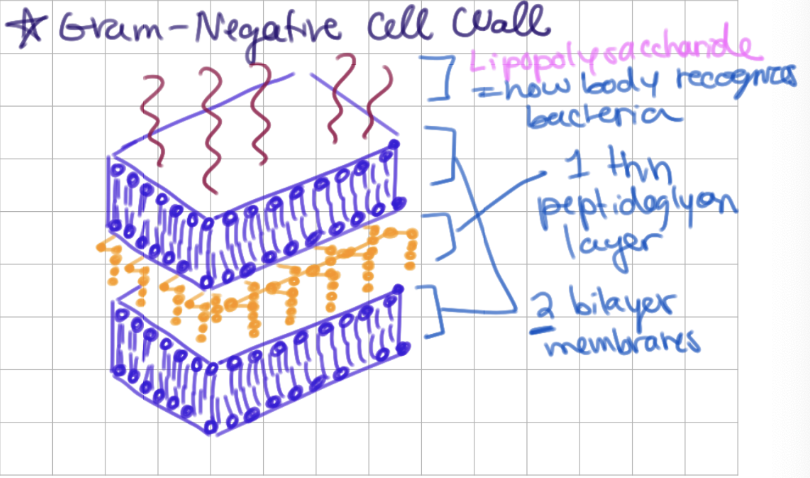
Gram-negative bacterial cell wall
2 bilayers + thin peptidoglycan layer
-
contains lipopolysaccharide
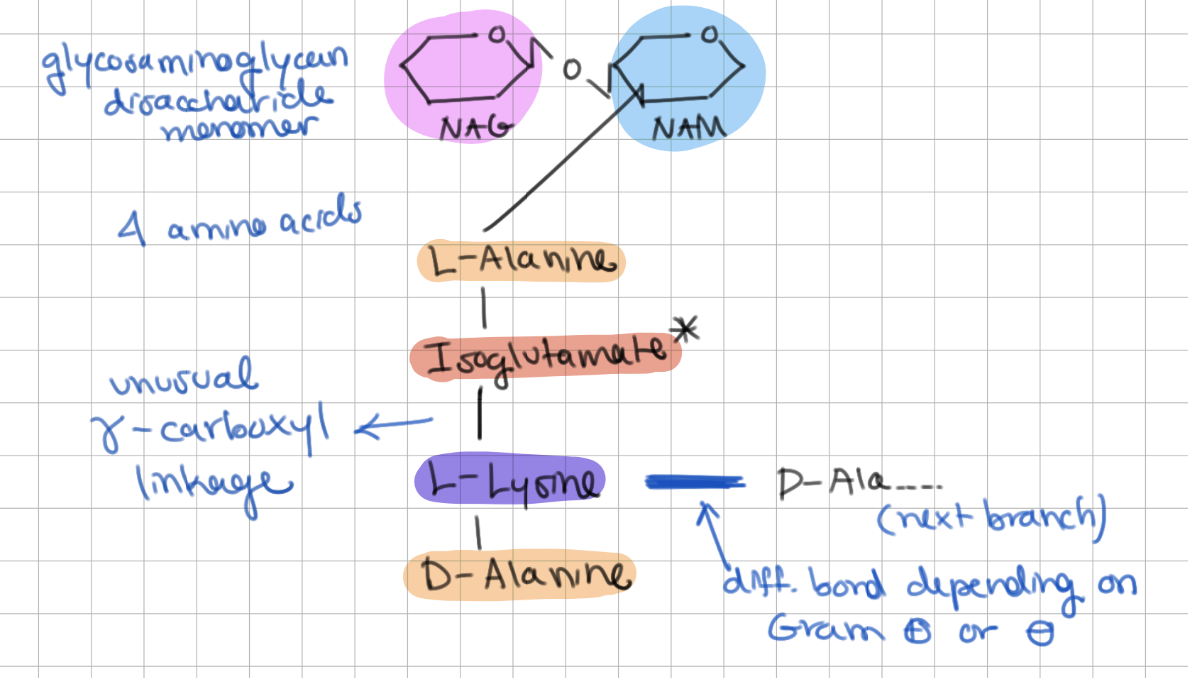
Peptidoglycan structure has 3 major components:
1) tetrapetide (4 amino acids)
2) ɣ-carboxyl linkage
3) glycosaminoglycan disaccharide (NAG-NAM)

What 4 amino acids are in peptidoglycan?
1) L-Alanine
2) Isoglutamate
3) L-Lysine
4) D-Alanine
-
(AEKA? LIL D?)
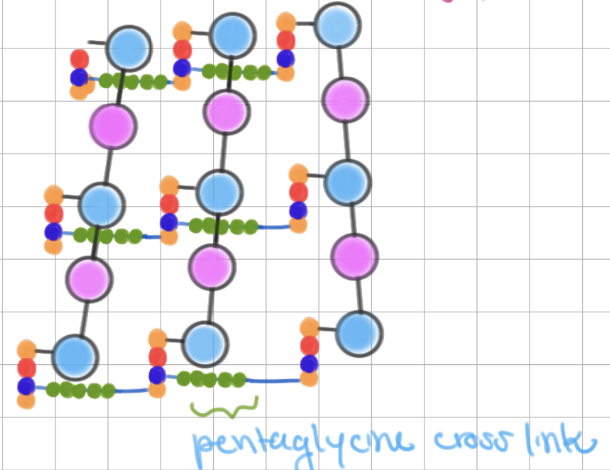
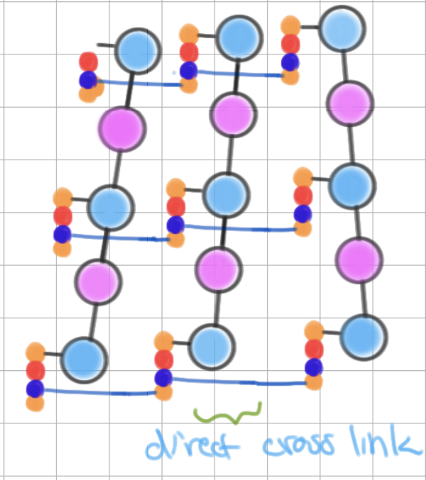
Gram-positive peptidoglycan
contains pentaglycine cross link- makes chain longer!
Gram-negative peptidoglycan
contains direct cross link
Lipopolysaccharide
lipid group + polysaccharide with many repeats attached to outer membrane
-
found in Gram negative bacteria
Glycoproteins can be _____ or ______
N-linked, O-linked
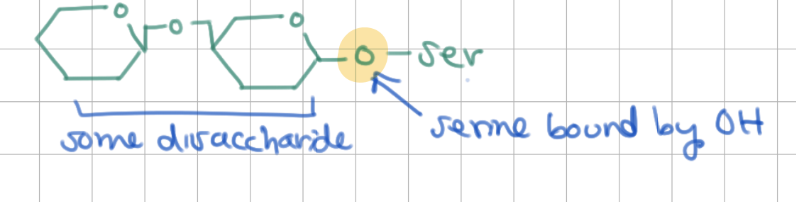
O-linked saccharides are attached to OH groups of which amino acids?
serine, threonine, hydroxylysine
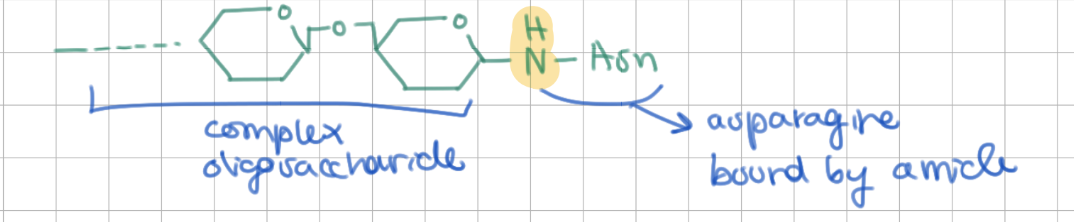
N-linked saccharides are attached to amide groups of which amino acids?
asparagine
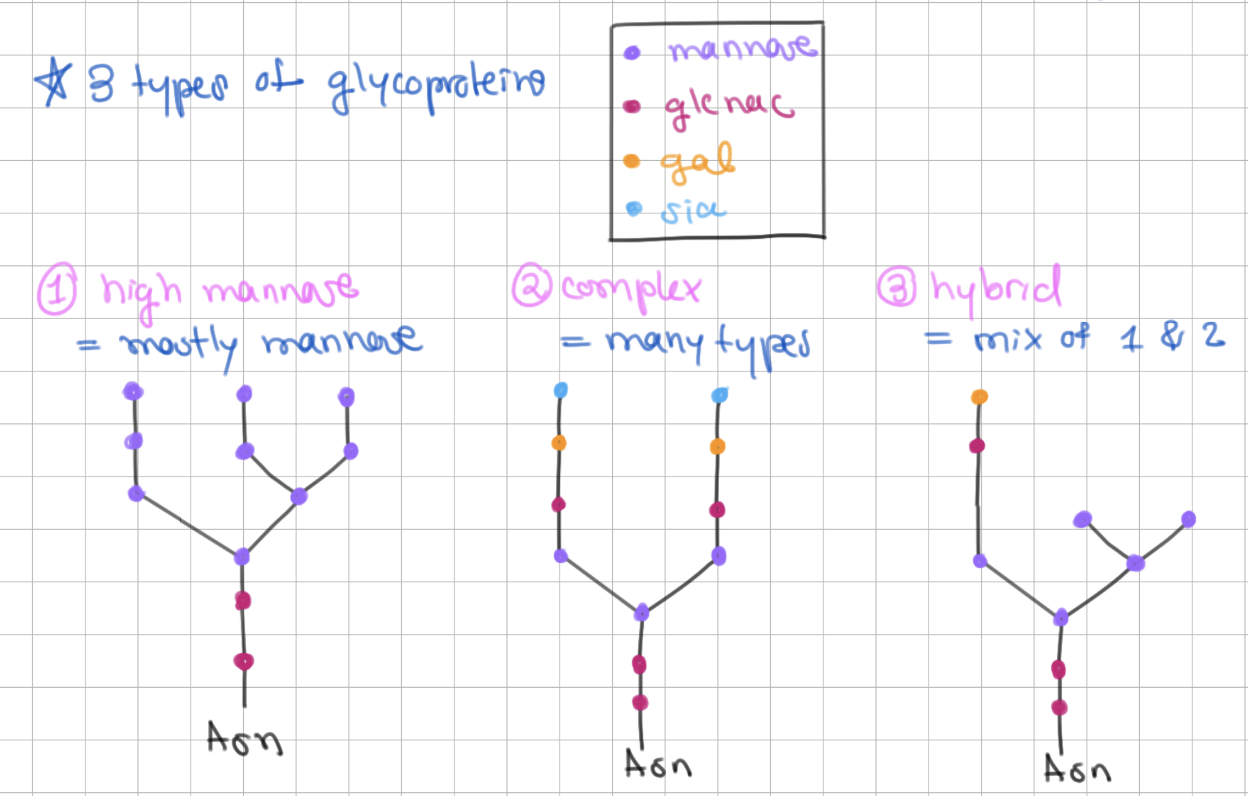
There are 3 types of N-linked glycoproteins
1) high mannose = mostly mannose
2) complex = many types
3) hybrid = mix of 1 + 2
Louie Pasteur discovered…
pasteurization and glycolysis
-
looked at fermentation of grape sugar
Glycolysis
“splitting sugar” to make ATP
Glycolysis is aerobic/anaerobic
anaerobic
products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
2 phases of glycolysis (overall summary)
Phase 1 = glucose → 2 G3P (-2 ATP)
Phase 2 = 2 G3P → 2 pyruvates (+4 ATP, +2 NADH)
Pyruvate has 3 possible fates
1) aerobic = TCA cycle → acetyl-CoA
2) anaerobic = lactic acid fermentation (ex: muscle) → lactate
3) anaerobic in yeast = alcoholic fermentation → ethanol + CO2
Only _% of glucose goes into glycolysis.
5
Overall Summary for Phase I
1) Gluc → G6P = phosphorylation of glucose
2) G6P → F6P = isomerization
3) F6P → F1,6 BP = 2nd phosphorylation
4) F1,6 BP → DHAP + G3P = Cleavage
5) DHAP → G3P = 2G3P
Phase I enzymes
1) Hexokinase/Glucokinase
2) Phosphoglucoisomerase
3) Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
4) Fructose bisphosphate (FBP) aldolase
5) Trios phosphate (3P) isomerase
Phase I Extra
1) -1 ATP (regulated/-ΔG/irreversible)
2)
3) -1 ATP (regulated/-ΔG/irreversible)
4)
5)
Reaction 1
Phosphorylation of glucose
Glucose → Glucose 6 Phosphate
Enzyme = Hexokinase/Glucokinase
-1 ATP
-
priming reaction (-ΔG)!

Step 1 purpose (2)
glucose can easily move in/out of cell, diffuses based on equilibrium
1) phsophorylating glucose traps it inside
2) lots of phosphorylation of glucose → glucose concentration is low so more glucose diffuses into cell
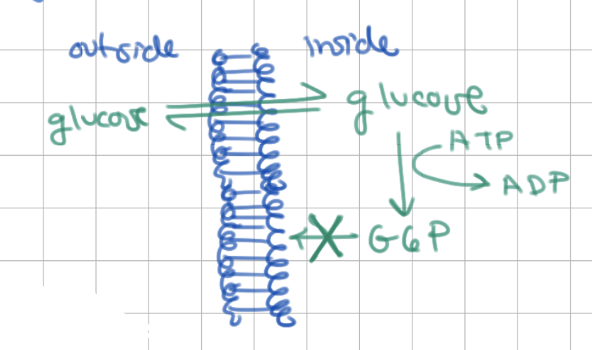
G6P is common to many metabolic pathways such as…
conversion to glycogen for energy storage (in liver/muscles)
carbohydrate synthesis
Hexokinase vs Glucokinase shape
Hexokinase = mostly closed → only little change needed for induced fit
Glucokinase = mostly open → lots of change needed for induced fit
Hexokinase vs Glucokinase function/affinity
Hexokinase
low Km = high affinity for glucose
found in most tissues
Glucokinase
high Km = low affinity for glucose
found in liver
only burn ATP when glucose is high !!!!
diabetes → produce low insulin → ___ levels of glucokinase (step 1)
low
-
so, cannot handle high glucose in diet and produce little glycogen in liver
(glycogen needs G6P)
Type I vs Type II Diabetes
Type 1 (insulin-dependent)
insulin not produced due to early-onset autoimmune dz
treated with insulin
Type 2 (non-inuslin-dependent)
insulin produced normally, but insulin-resistant cells
treated with lifestyle changes
Reaction 2
Isomerization of G6P
Glucose 6 Phosphate → Fructose 6 Phosphate
Enzyme = Phosphoglucoisomerase

Step 2 Purpose (2)
1) next step is difficult for hemiacetal OH but easy for primary OH
2) activates C3 for cleavage later (?)
Step 3 mechanism
1) open pyranose ring
2) proton removal → ene-diol formation
3) ring closure
*image shows ene-diol
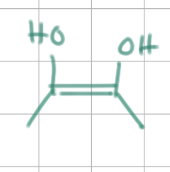
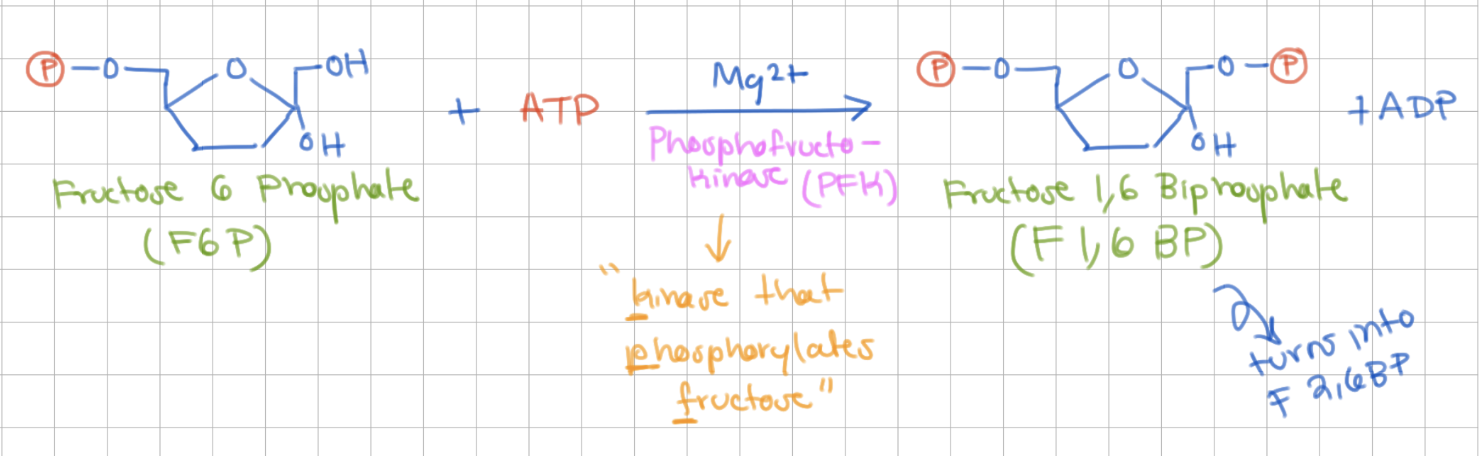
Reaction 3
Phosphorylation of F6P
Fructose 6 Phosphate → Fructose 1,6 Bisphosphate
Enzyme = Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
-1 ATP
-
priming reaction (-ΔG)!
COMMITTED STEP
PFK (Step 3) regulation:
ATP _____/AMP _____
citrate _____ (between glycolysis and TCA cycle)
F2,6BP _____
ATP inhibits/AMP activates
citrate inhibits (between glycolysis and TCA cycle)
F2,6BP activates
PFK binding sites (2)
1 high affinity substrate site
1 low affinity allosteric site (inhibitory)
PFK has sigmoidal kinetics at _ ATP and hyperbolic kinetics at _ ATP
high, low
high ATP = low affinity → inhibitory site active → cooperative behavior (sigmoidal)
low ATP = high affinity → inhibitory site not active → non-cooperative behavior (hyperbolic)
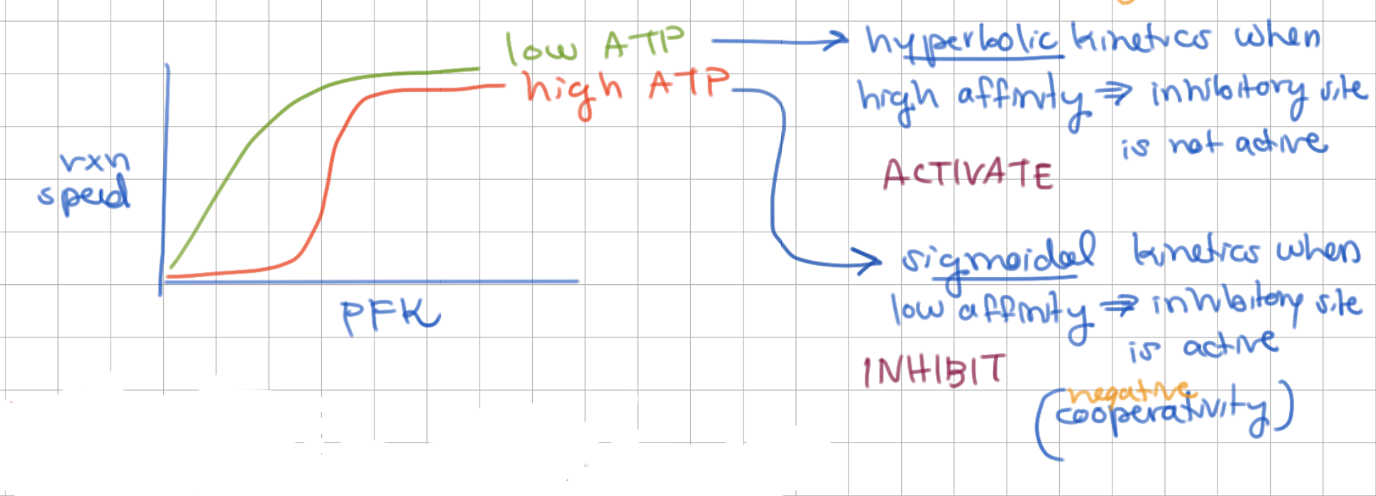
low ATP increases/decreases AMP due to ____ enzyme
increases AMP, adenylate kinase

F 2,6BP
i) regulator (not intermediate of glycolysis)
ii) created from F6P
-
activates PFK - and reverses ATP’s inhibition
(activatate = hyperbolic)
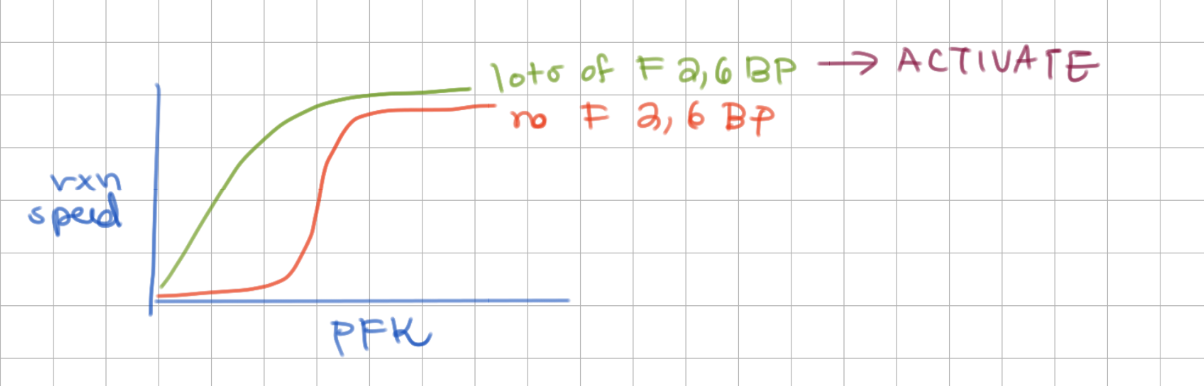
What can reverse ATP’s inhibition?
F2,6BP
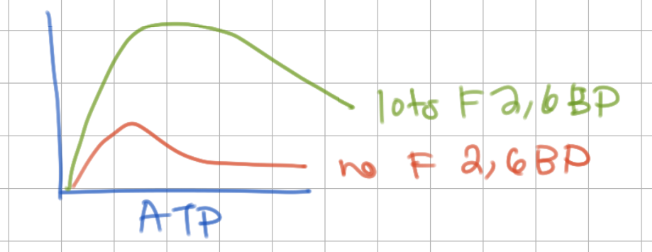
increase in glucose → F6P → F2,6BP → ____ PFK affinity. This is feedforward/feedback regulation.
increases, feedforward
Reaction 4
Cleavage
Fructose 1,6 Bisphosphate → DHAP + G3P
Enzyme = Fructose biphosphate aldolase
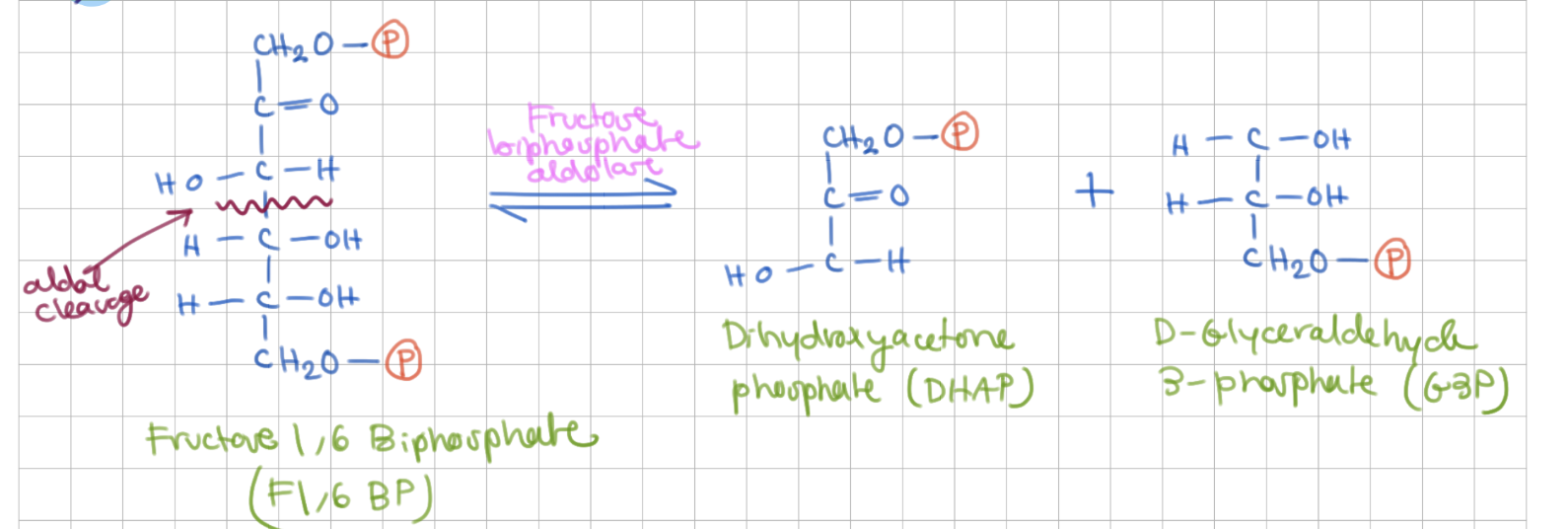
Step 4 mechanism involves _____ which is a reverse of ______
aldol cleavage, aldol condensation
aldol condensation
ketone attacks aldehyde → aldol

class I vs class II aldolase
class I
animals
Lys in active site
intermediate
SCHIFF base between carbonyl and lysine = intermediate
class II
bacteria
Zn2+ stabilized intermediate → no intermediate
Reaction 5
2 G3P
DHAP → G3P
Enzyme = Trios phosphate (3P) isomerase
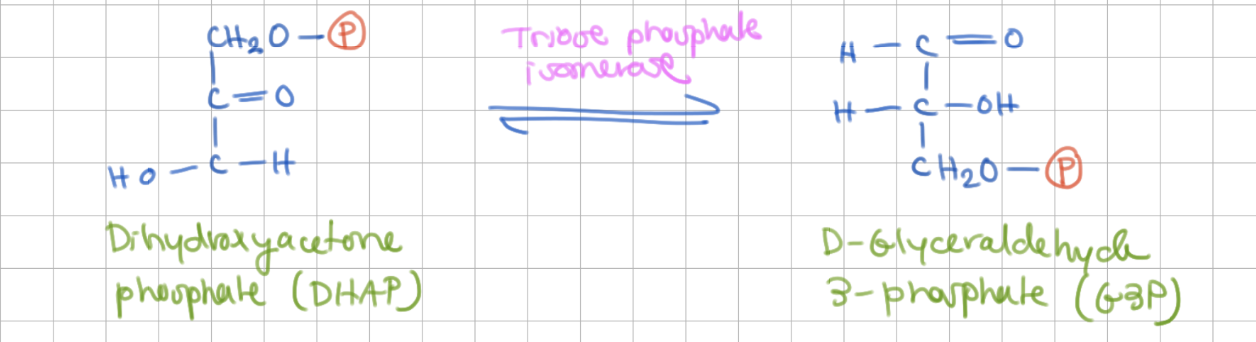
Step 5 mechanism
ene-diol formation
Glu in active site acts as general base
Which enzyme is described as a near-perfect enzyme?
3P isomerase
-
works as fast as possible, only limited by diffusion…