nervous system, synapses, reflexes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what passes along nerve cells
electrical impulses
gap between two neurones is called
a synapse
what is released across a synapse
when an electrical impulse reaches the end of a neurone it causes the release of chemicals (neurotransmitters). These chemicals then diffuse across the synapse and stimulate the next neurone to carry another electrical impulse.
what is the central nervous system
spinal cord and brain
what is the role of a receptor
to detect a stimulus
what is the role of a sensory neurone
transfers a signal from a receptor to the CNS
what is the role of a motor neurone
to transfer a signal from the CNS to an effector
what is the role of a relay neurone
transfer a signal from a sensory neurone to a motor neurone
what is a reflex
an automatic response to a stimulus
the pathway of a reflex arc
stimulus → receptor → sensory neurone → relay neurone → motor neurone → effector → response
two main types of effectors
muscles and glands
reflexes are (slow/ fast, automatic/conscious)
fast and automatic because they don’t in love conscious parts of the brain
examples of reflexes
sneezing, blinking when you get dust in your eye
why are reflexes important
protect us from harm
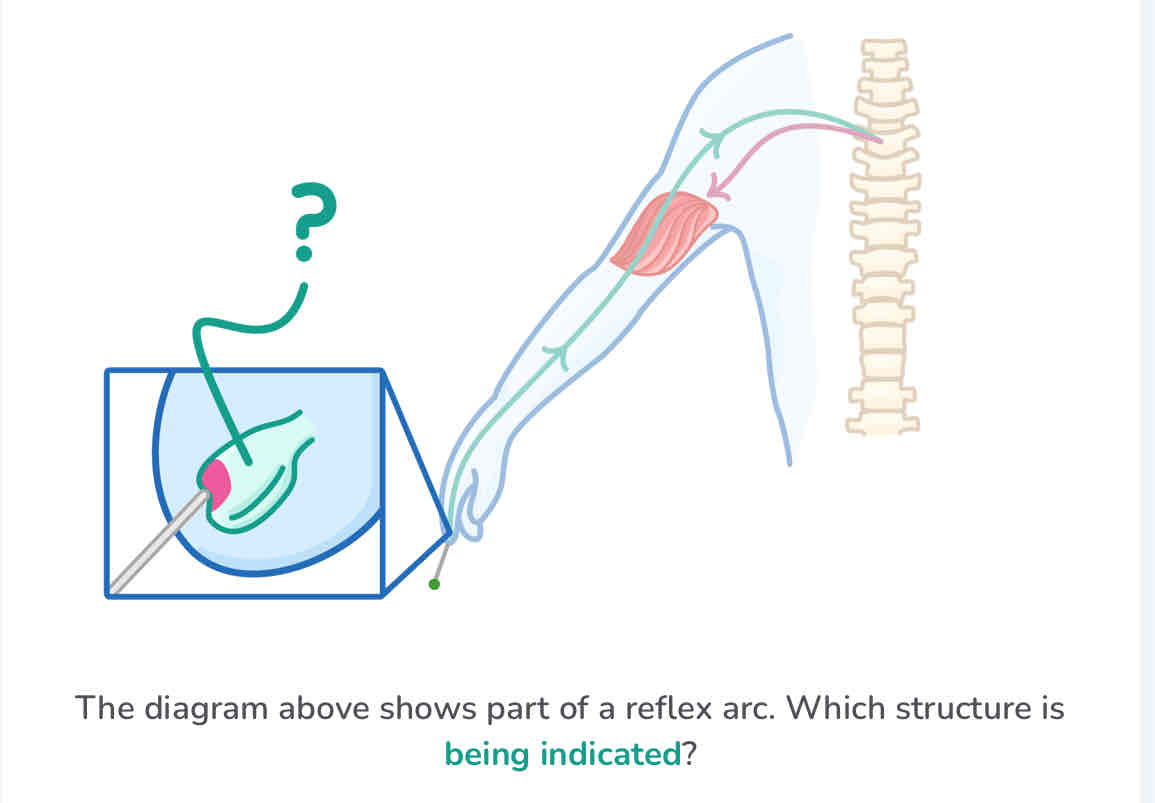
receptor
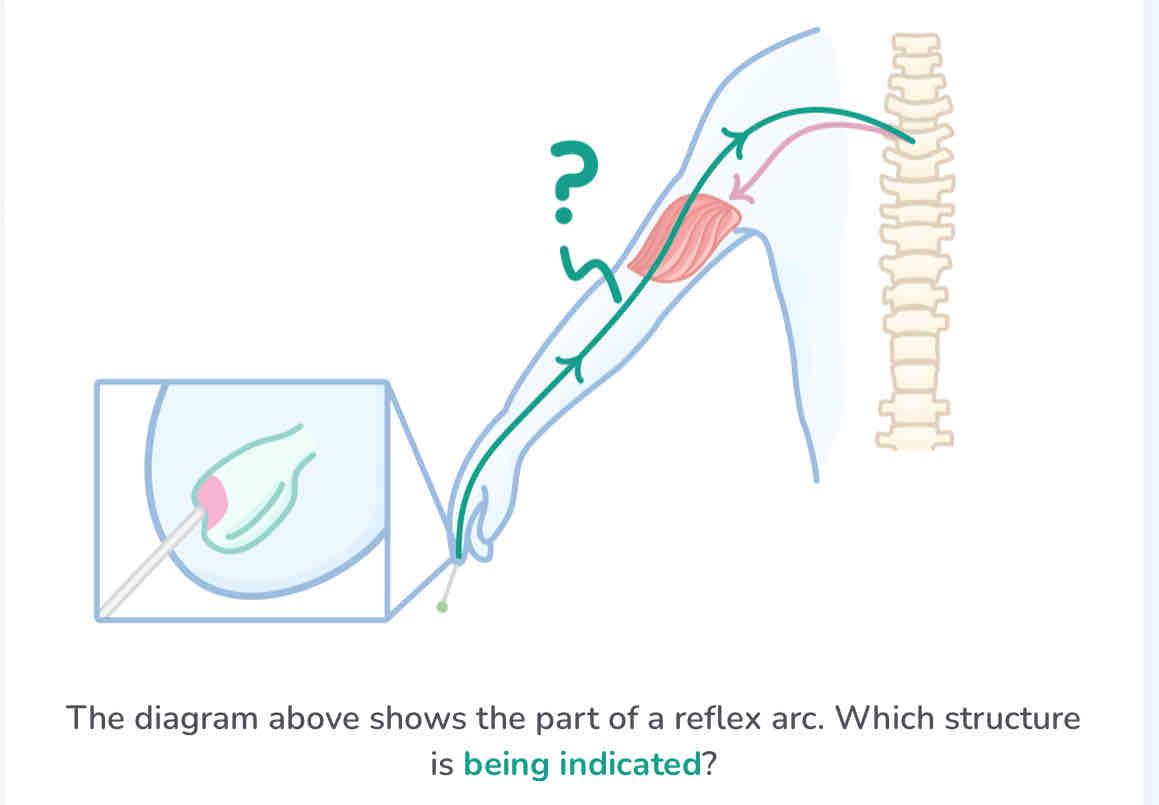
sensory neurone
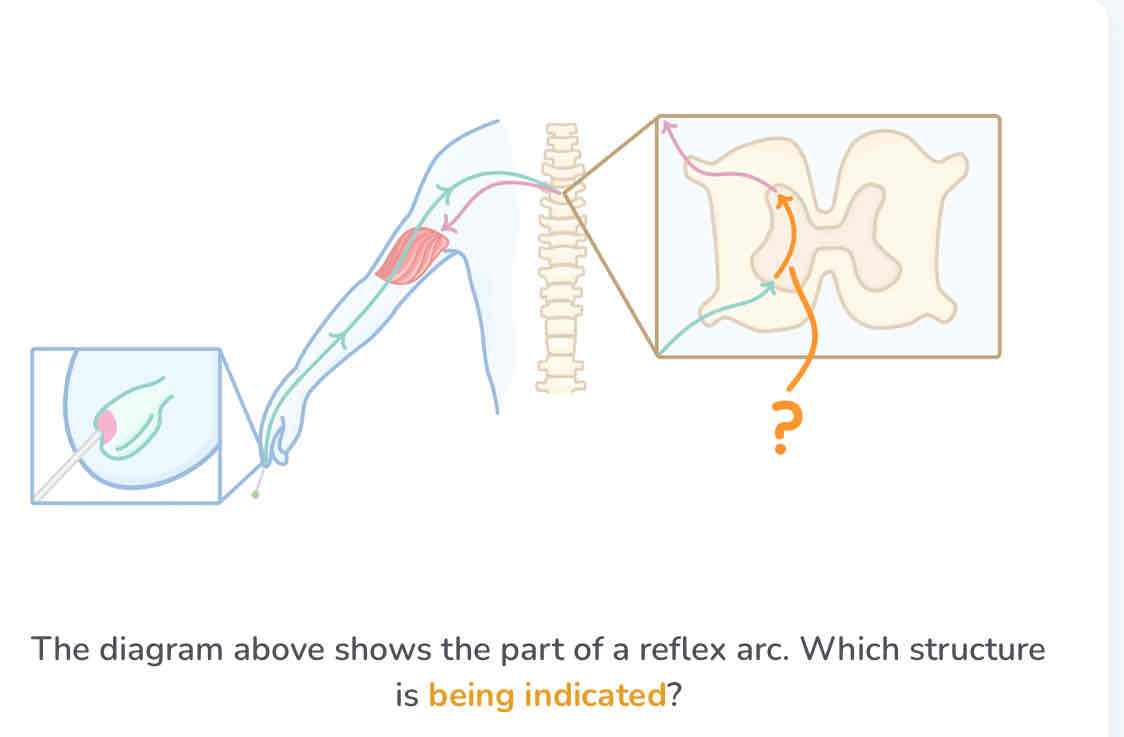
relay neurone
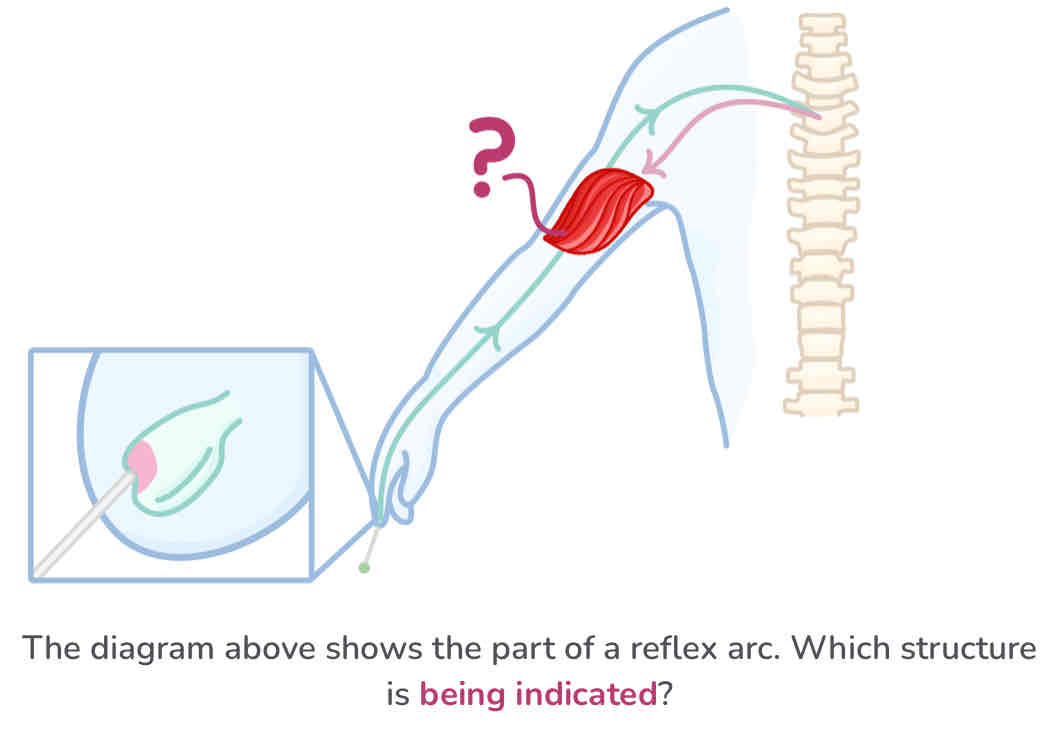
effector