Biosignalling
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Cell Signaling Pathways/Cascades
Understand the participants
first messengers versus second messengers
Amplification
variety of downstream outcomes
complicated and intertwined
Protein-protein interactions
Typically stimulated with external ligand binding to GPCRs or receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
Pathways involve lots of kinases
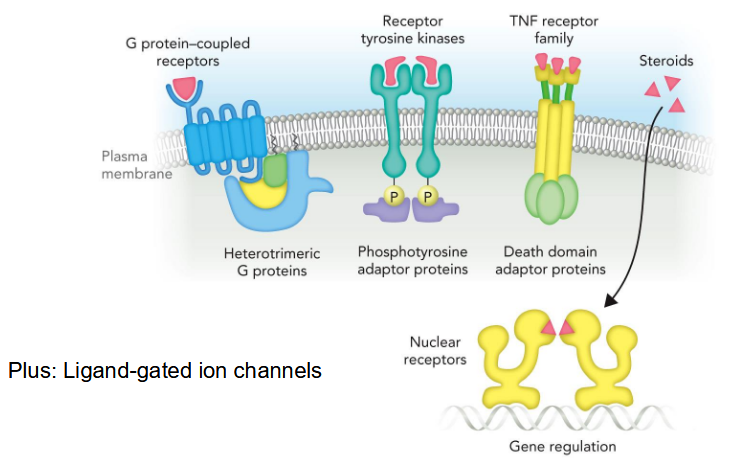
Classes of Receptor Proteins in Eukaryotes
G-protein coupled receptors → heterotrimeric G proteins
receptor tyrosine kinases → phosphotyrosine adaptor proteins
TNF receptor family → death domain adaptor proteins
steriods → nuclear receptors → gene regulation
Ligand-gated ion channels
Autocrine signalling
self-signalling
paracrine signalling
short range; growth factors
endocrine signalling
long range; hormones
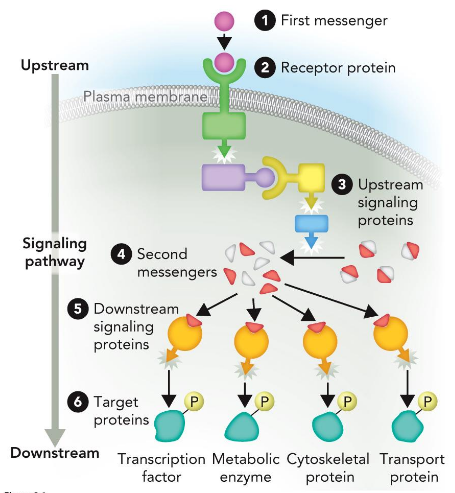
First messengers
many diverse responses
Second Messengers
Small, nonprotein intracellular molecules that amplify receptor-generated signals
ex.
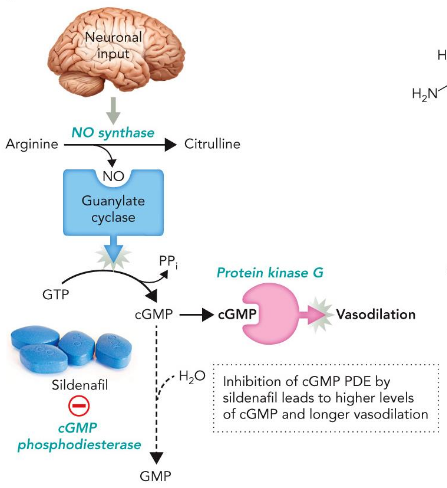
Cyclic GMP (cGMP)
cAMP
Diacylglycerol (DAG)
Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3)
Ca2+
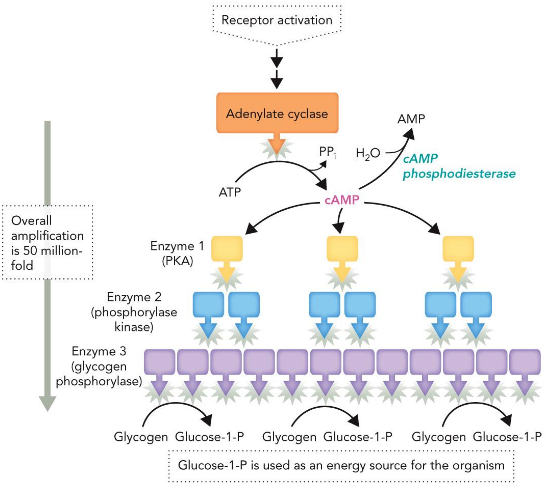
Signal Amplification
50M fold
Modulating Cell Signaling Pathways Therapies
sildenafil citrate or ozempic
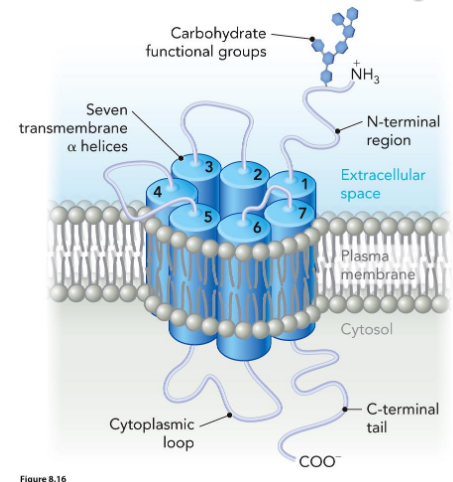
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
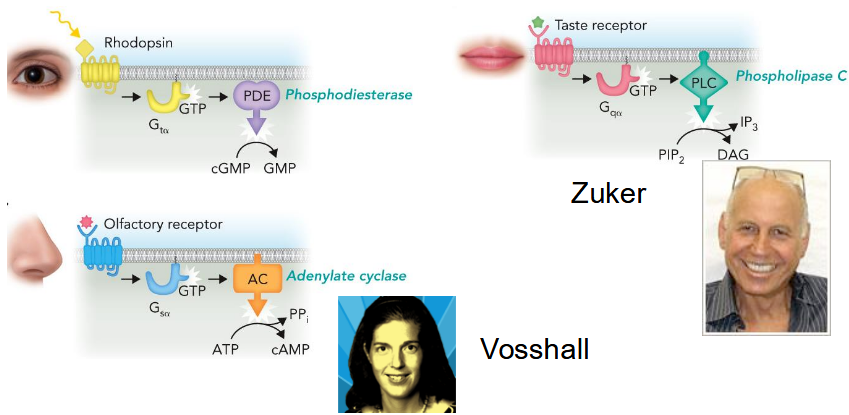
involved in sensory perceptions such as: Vision, Taste, Smell
Contain seven trans-membrane alpha helices
Also called “serpentine” receptors or 7-transmembrane receptors
ex. rhodopsin (responds to photon)
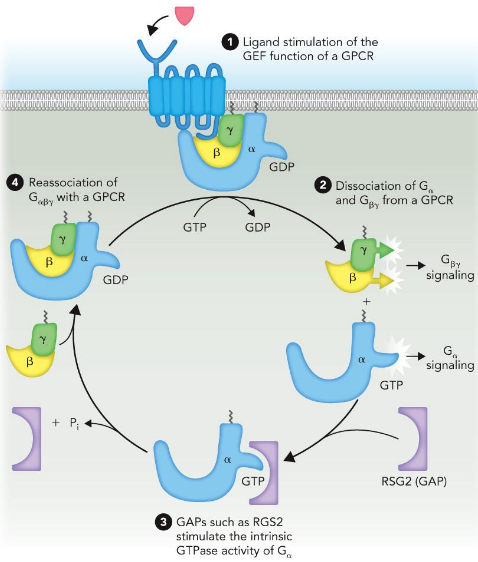
G-protein Cycle
Sequential stimulation by GEFs: Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor and GAPs: GTPase Activating Protein
Which enhances signaling?
Which dampens signaling?
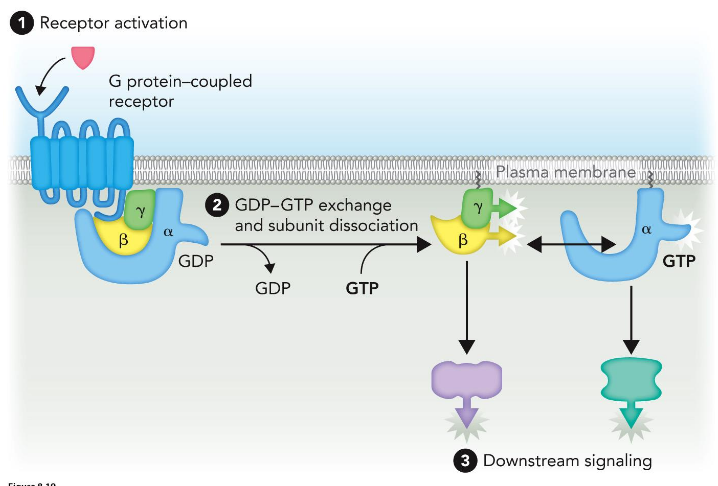
GPCR Activation
Sensory Perception Mechanisms and GPCRs
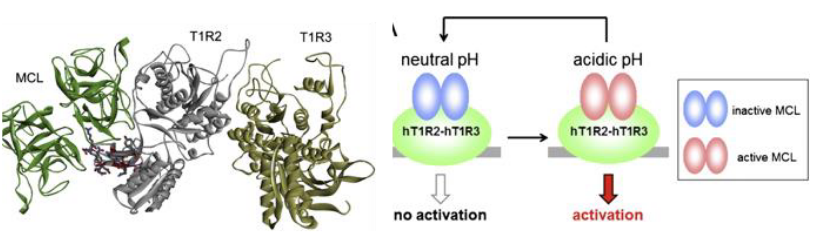
miraculin
pH-dependent allosteric agonist/antagonist of a sweet taste receptor
miracle berry
Generalized Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activity
ex. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)
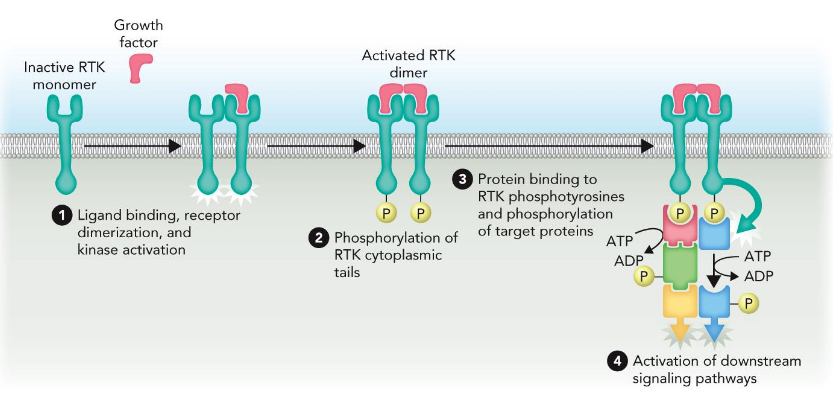
How can you tell EGFR is activated?
Ligand bound, receptor dimerized, phosphorylated
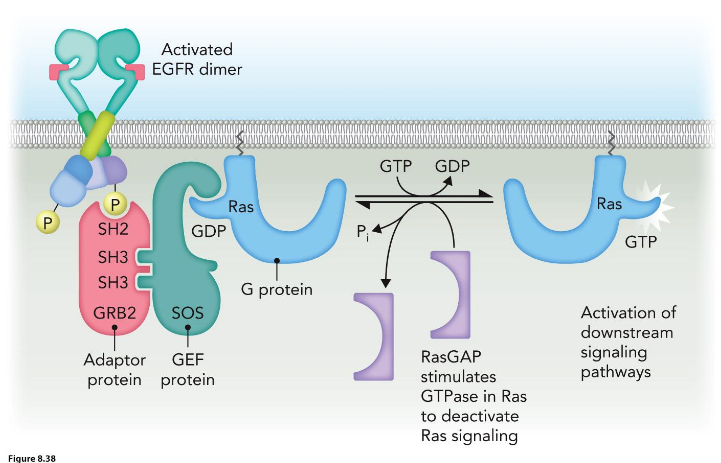
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEP)
enhance G-protein signalling via GTP
GTPase activating protein (GAP)
diminishes G-protein signalling via GTPase activity
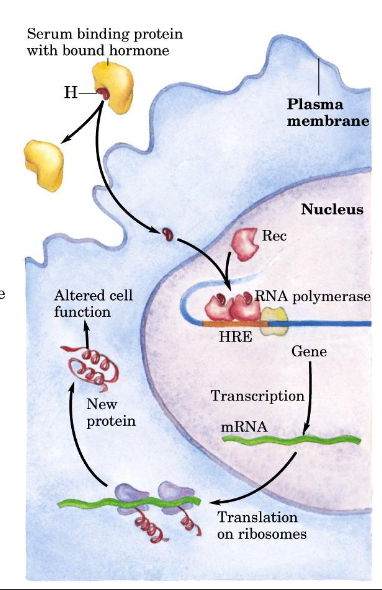
Nuclear Hormone Receptors
steroid (lipid) hormones/metabolites diffuse through membrane, enter cell and bind to receptor in cytoplasm/nucleus
changes conformation of receptors, dimerise, bind to regulatory regions called hormone response elements
regulates transcription
produce cellular response
ex. glucocorticoid, estogeb, angrogen, progesterone, aldosterone, retinoid X, vitamin D, retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, peroxisome proliferator-activated
Steps in Signal Transduction
Release of the primary messenger
Reception of the primary messenger
Delivery of the message inside the cell by the second messenger
Activation of effectors that directly alter the physiological response
Termination of the signal
How do G-proteins get activated?
What do they do in their activated states?
How do they become inactivated?
How do messages get amplified?
How do messages get integrated?