3.1.1.1 fundamental particles
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:17 AM on 10/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1
New cards
what has happened to the model of atomic structure and why?
It has evolved over time due to changes in knowledge and scientific understanding
2
New cards
what was the model of the atom known as in 1897?
the ‘plum pudding model’
3
New cards
describe the ‘plum pudding model’
an atom that consisted of a sphere of positive charge, with small negatively charges distributed/embedded evenly within it
4
New cards
what experiment disproved the plum pudding model in 1909?
the Rutherford scattering experiment → positively charged alpha particles (He2+ ions) were fired at a very thin sheet of gold
5
New cards
explain why the Rutherford scattering experiment showed that the plum pudding model was incorrect
* if the ppm was correct, most alpha particles would be slightly deflected by the positive sphere
* however most of the particles passed straight through the gold without any deflection and a small number deflected backwards
* however most of the particles passed straight through the gold without any deflection and a small number deflected backwards
6
New cards
what atomic model did the results of the scattering experiment result in and why?
* a small positively charged nucleus (some He2+ deflected backwards)
* surrounded by a cloud of negative electrons
* most of the atom is empty space (most He2+ passed straight through)
* surrounded by a cloud of negative electrons
* most of the atom is empty space (most He2+ passed straight through)
7
New cards
what are the differences between the current model and the plum pudding model?
the current model has
* a nucleus in the centre
* protons and neutrons in the nucleus
* electrons in shells
* a nucleus in the centre
* protons and neutrons in the nucleus
* electrons in shells
8
New cards
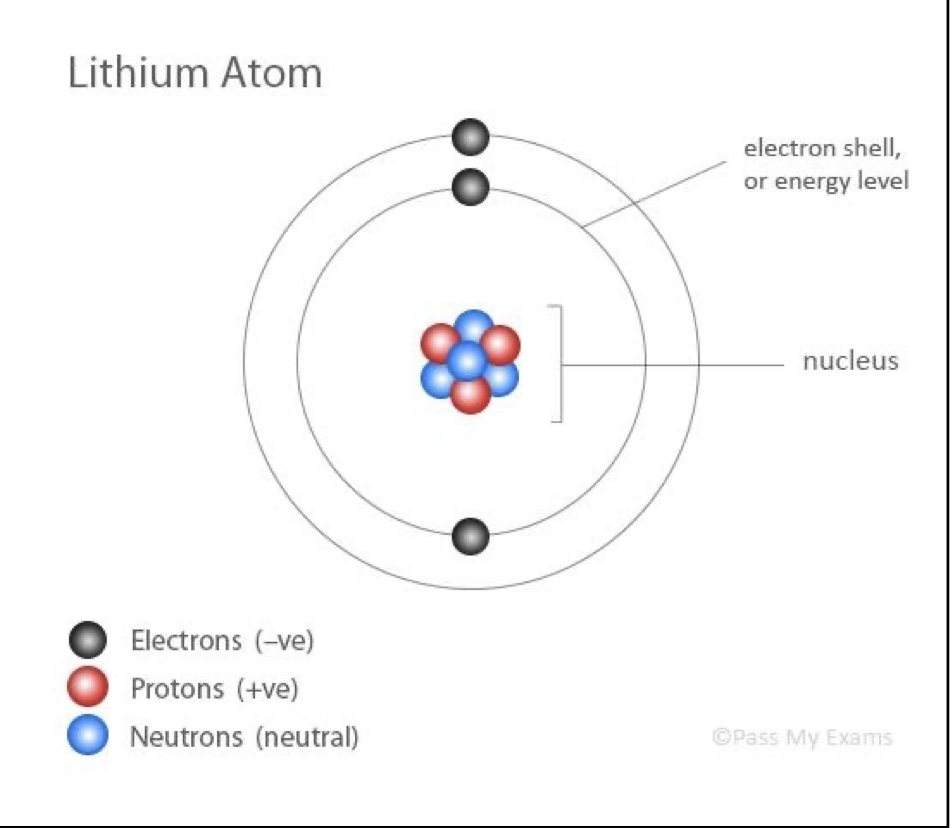
describe the current model of the atom
an atom consisting of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons
* nucleus has an overall positive charge + contains almost entire mass of atom
* atom has a neutral charge (electrons = protons)
* nucleus has an overall positive charge + contains almost entire mass of atom
* atom has a neutral charge (electrons = protons)
9
New cards
what change did Bohr introduce to the atomic model (after the scattering experiment)?
he stated that electrons orbit the nucleus at fixed distances/energy levels
10
New cards
give the relative mass + relative charge for a proton, neutron + electron
Mass Charge
proton: 1 +1
neutron: 1 0
electron: 1/1840 -1
proton: 1 +1
neutron: 1 0
electron: 1/1840 -1