Unit 3 - Chp 10 & 11 Muscular Tissue & System
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is the function of a tendon
Puts exertion on bones to contract, muscle to bone connection
Difference between origin and insertion
origin is where the muscle is planted, insertion is where movement occurs
Where is the weight (fulcrum) on a first second and third class lever
First class - in the middle (skull)
Second class - to the right (tippy toes)
Third class - to the left (elbow)
What muscles are responsible for chewing
massester & temporalis
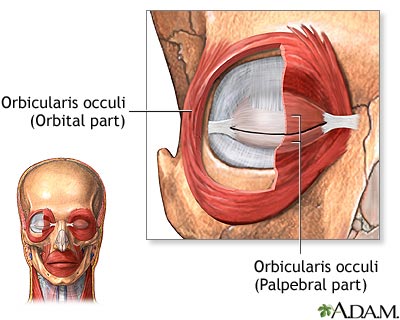
What muscle is responsible for closing the eye
orbicularis oculi muscles
Which muscle extends/flexes the elbow
bicep brachii - flexion
Tricep brachii - extension
which muscle turns the head
sternocleidomastoid muscle
Which muscle flexes/extends the spine
flexes - abdominal muscles
extends - erector spinae
Which muscle group extends vs flexes the knee
Flex - hamstring
Extend - quadriceps
What is compartment syndrome
when pressure constricts the structure in a compartment that leads to damaged blood vessels, can result in damaged nerves and scar tissue/contracture (perm. shortening of a muscle)
What is stored in the endoplasmic reticulum?
Calcium
What is plantar facilits and how do you treat it
chronic irritation of the heel (plantar aponuerosis), originates from calcenus and leads to pain in the heel.
treatment can be made via ice, cold packs, stretching, weight loss, prosthetics, steroids, or surgery
true or false : the tricep plays as the antagonist while extending the arm
false
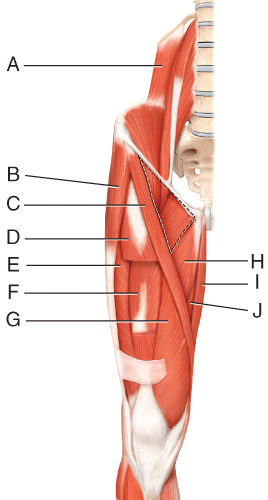
What muscles is C
Sartorius
which muscle pair is the agonist - antagonist of the forearm (flexes & extends)
biceps brachii & triceps brachii
Which muscle is a powerful arm extensor?
tricep brachii
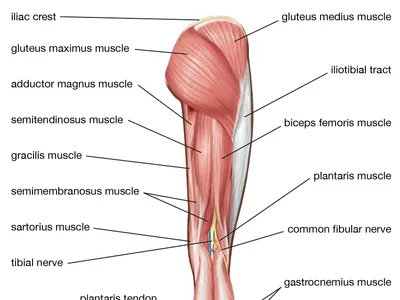
Where is the semitendious located
posterior compartment of the thigh
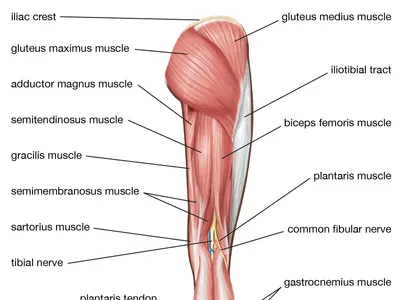
Where is the gracilis loacted
medial compartment of the thigh
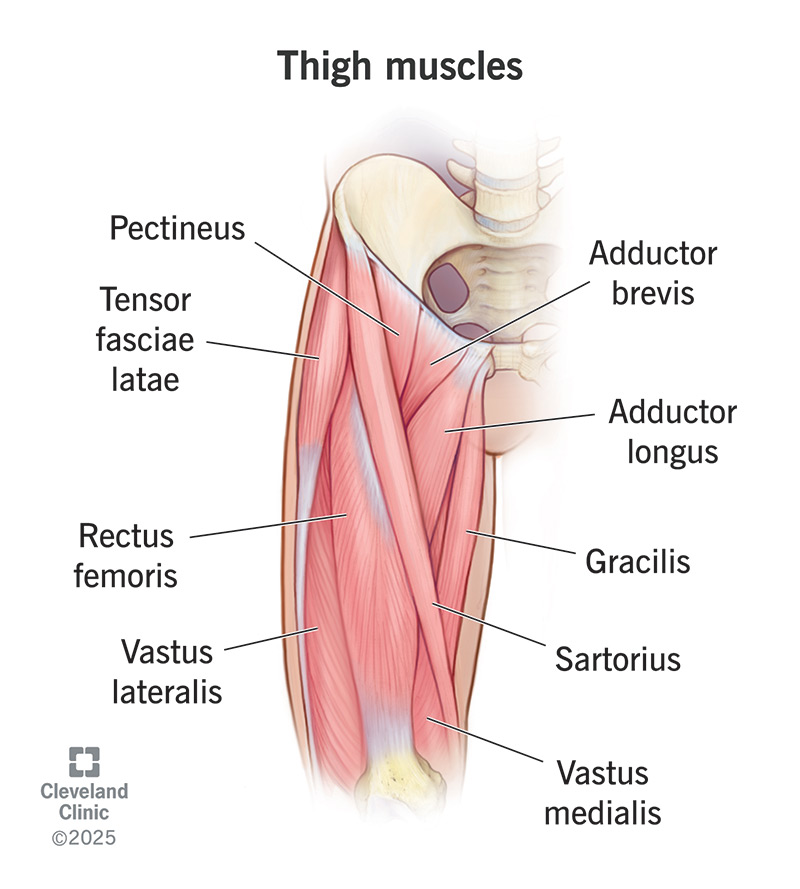
where is the bicep femoris loacted
back part of the knee, part of the hamstrings
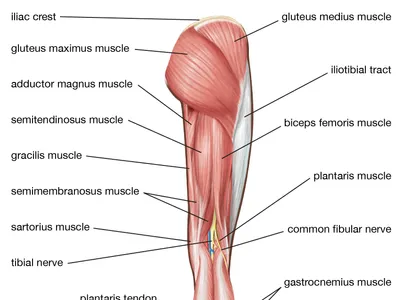
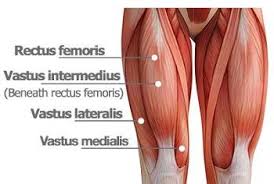
where is the vastus medialius located
anterior part of the thigh
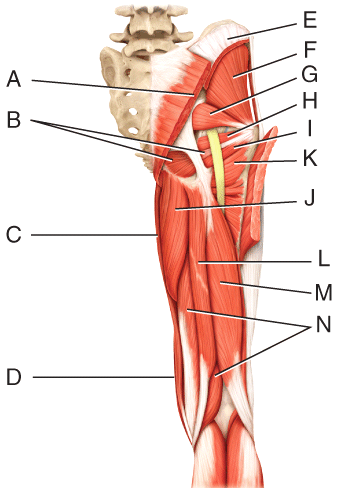
Which letters make up the hamstring
L - semitendinous
M - bicep femoris
N - semimembraneous muscle
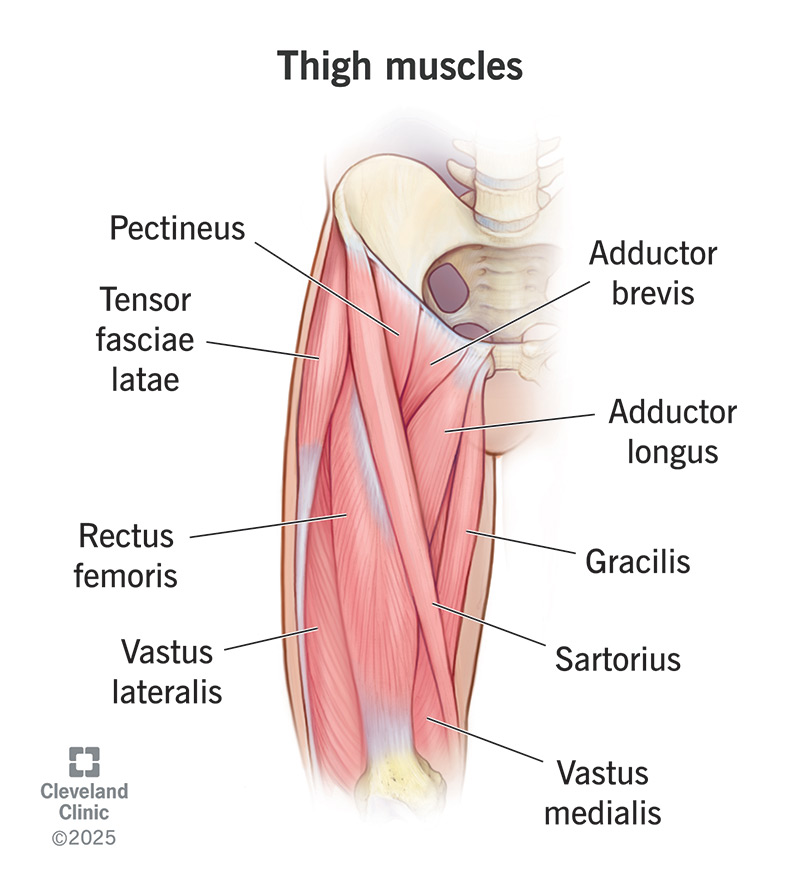
Which muscles make up the quadriceps
rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis
the elbow JOINT allows for what kind of movement
flexion & extension
What arm muscles combined help flex the forearm
biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis
A woman complains going up the stairs. the hip is weak but no signs of the hip or knee flexion being damaged. What muscle is most likely damaged
Gluteus maximus
Which muscles are c are considered the abs
rectus abdomis
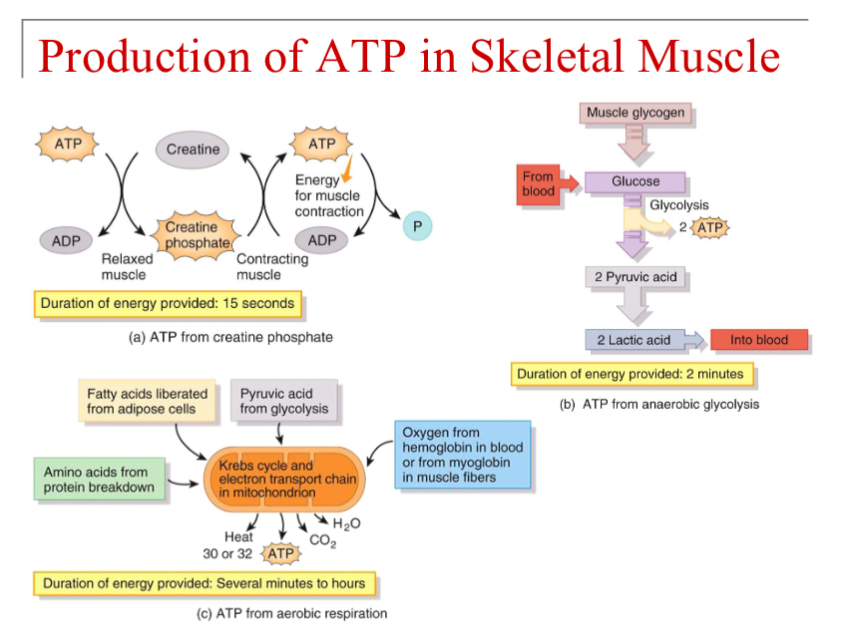
How do muscles derive the ATP necessary
to power the contraction cycle?
▪ Creatine phosphate
▪ Anaerobic glycolysis
▪ Cellular respiration
All of the above
What causes muscle fatigue?
Inadequate release of Ca2+ from SR
▪ Depletion of CP, oxygen, and nutrients
▪ Build up of lactic acid and ADP
▪ Insufficient release of ACh at NMJ
Oxygen Debt (why we breathe heavy after exertion)
Replenish CP stores
▪ Convert lactate into pyruvate
▪ Reload O2 onto myoglobin
What happens in a sacromere during a contraction
I band shortens, H zone disappears
Hypertrophy vs hyperplasia
hypertrophy = cells get bigger
hyperplasia = more cells are created, higher risk of cancer
What structures cause the straitions in muscle
A bands, H zone, I bands ****
What are the three connective tissue that covers skeletal muscle
epimysium - covers the entire muscle
perimysium - covers fascicles/bundles of muscle fibers
endomysium - wraps around each muscle fiber
What is the function of T tubules
transmit signal to release the calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to start the contraction & synchronizes the contraction
Difference of isometric & isotonic contraction
isotonic = shorten length in msucle w constant tension while isometric is no change in uscle length w/ tension
Different organelles of the muscle
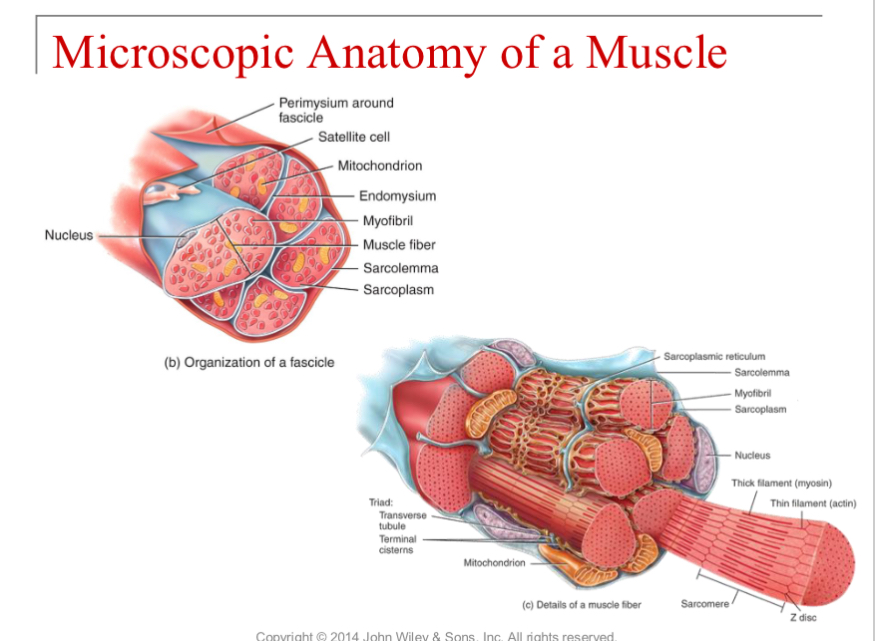
What are the components of the triad
One t tubule & 2 large areas of sarcoplasmic reticulum on either side of the t tubule (terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum)
excess atp produced will be then turned into
creatine phosphate
The site where a somatic neuron unit releases acetylcholine to stimulate a muscle fiber
neuromuscular junction
binding sites on actin are covered by what
tropomyosin
which structure allows the propagation of the muscle action potential
T tubules - acts as a conduit deep into the muscle fiber
Which structure acts a border between two sacromeres
Z discs
A treatment for myasthenia gravis is pyridostigmine which stops ACh from being broken down. Which does pyridostigmine inhibit?
AChE
What protein does calicum bind to
Troponin
A group of muscle cells stimulated by a single motor neuron is known as
a motor unit
How does a motor neuron stimulate a muscle cell
neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft to cause an action potential within the muscle cell
A powerstroke is caused by the ATP hydrolysis and phosphate release, which binds and moves what molecule
myosin (specifically myosin heads)
How are binding sites pn actin exposed
calcium attaches onto troponin which slides tropomyosin off binding sites on actin
What does tropomyosin block during muscle relaxation
myosin binding sites on actin