Hearing
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is hair responsible for
the transduction of sound
what is the pinna responsible for
collecting sound
what is the end of the ear canal
it is the ear drum which carriers sound to the middle ear (ossicles)
what is the smallest bone in the body
ossicles
what is the eustachian tube
it is the tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat regulating air pressure and draining fluid.
what is the cochlea and where does it take place
it is where sound transduction takes place
and the is a snail shape which is the size of a pea
in the cochlea, what is the malleus
it contacts the ear drum, then the incus, and finally the stapes, and oval window a small bone that transmits sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
what is the oval window
it is 20 times smaller than the tympanic membrane, which allows further amplification of sound vibrations into the cochlea.
what are 3 (S) fluid filled compartments
scala vestibuli
scala tympani
scala media
they all meet at the top of the cochlea in a region called the helicotrema.
what membrane separates the scala vestibuli & scala media
the vestibuli membrane
what membrane separates the scala media & the scala tympani
the basilar membrane
describe sound wave in the coclea
sound waves come into the ear which causes vibration of the tympanic membranes
this causes vibration of the ossicles & the vibration of the stapes which causes vibration of the oval window
this causes the perilymph in the scala vestibuli to vibrate
the sound wave then travels round the helicotrema into the scala tympani & dissipates into the wound window
what is the organ cotri
The organ of Corti is a structure located within the cochlea of the inner ear, containing hair cells that convert sounds which sits on the basilar membrane causing the hair cells to vibrate causing sound transduction into electrical signals for the brain to interpret.
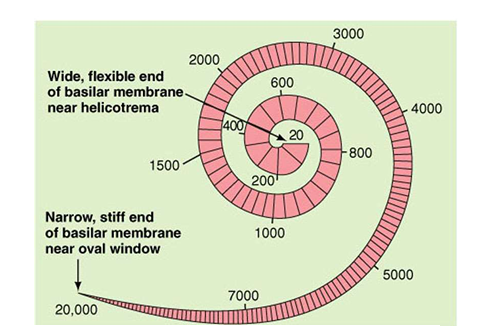
describe the basilar membrane
it coils around the cochlear, the top end is wide & flexible (responsive to low frequencies) whilst the base is narrow & stiff(responsive to high frequencies), playing a crucial role in vibration response to certain frequencies discrimination.
what is endolymph
it contains a high conc. of potassium, so when when the cation channel opens the potassium will move down the gradient into the hair cells, initiating depolarization of membrane potential
this then causes the opening of the volatge-gated channels which allows calcium into the channels, allowing calcium to move into the cells & allow the release of neurotransmitter, which signals to afferent neurons to transmit sound information to the brain.
what is a pitch and amplitude
the pitch of the note depends on the hair cells that are activated in the cochlea, while amplitude refers to the loudness, determined by the greater vibration