U4 AOS1: DP1 The demand for sleep (2023-2027)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Circadian Rhythm
Biological rhythms that occur approximately once every 24 hours
REM Sleep
A recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
Alpha Waves
The relatively slow brain waves of a relaxed, awake state.
Delta Waves
The large, slow brain waves associated with deep sleep.
Sleep
a naturally (usually) and regularly occurring ASC; characterised by a loss of awareness of your internal state and external surroundings
Ultradian rhythm
Recurrent cycle that is repeated within a 24 hour cycle (ie. less that 24 hours)
Eg. REM and NREM cycle
Patterns of REM: NREM
- Babies- REM 50% to NREM 50%
- Childhood to adulthood - REM 20% to NREM 80%
- Old age - REM 18% to NREM 82%
NREM sleep
non-rapid eye movement sleep; encompasses all sleep stages except for REM sleep
consciousness
the awareness of our thoughts, feelings and our environment at any moment in time
Normal Waking Consciousness (NWC)
awareness of your thoughts, feelings and behaviours, including internal and external events
Altered State of Consciousness (ASC)
is any state of consciousness which is distinctly different in level of awareness & experience from NWC in terms of - quality & intensity of sensations, feelings, thoughts, memories & perceptions
EEG
detects, amplifies and records electrical activity of the brain (in the form of brainwaves)
EOG
detects, amplifies and records electrical activity of the muscles surrounding the eyes
EMG
detects, amplifies and records electrical activity of the muscles of the body.
Sleep diary
a self-reported record of an individual's sleep and waking time activities, usually over a period of several weeks
Video monitoring
a type of data collection involving video and sound recordings of an individual in their sleeping period
Melatonin
A hormone produced by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
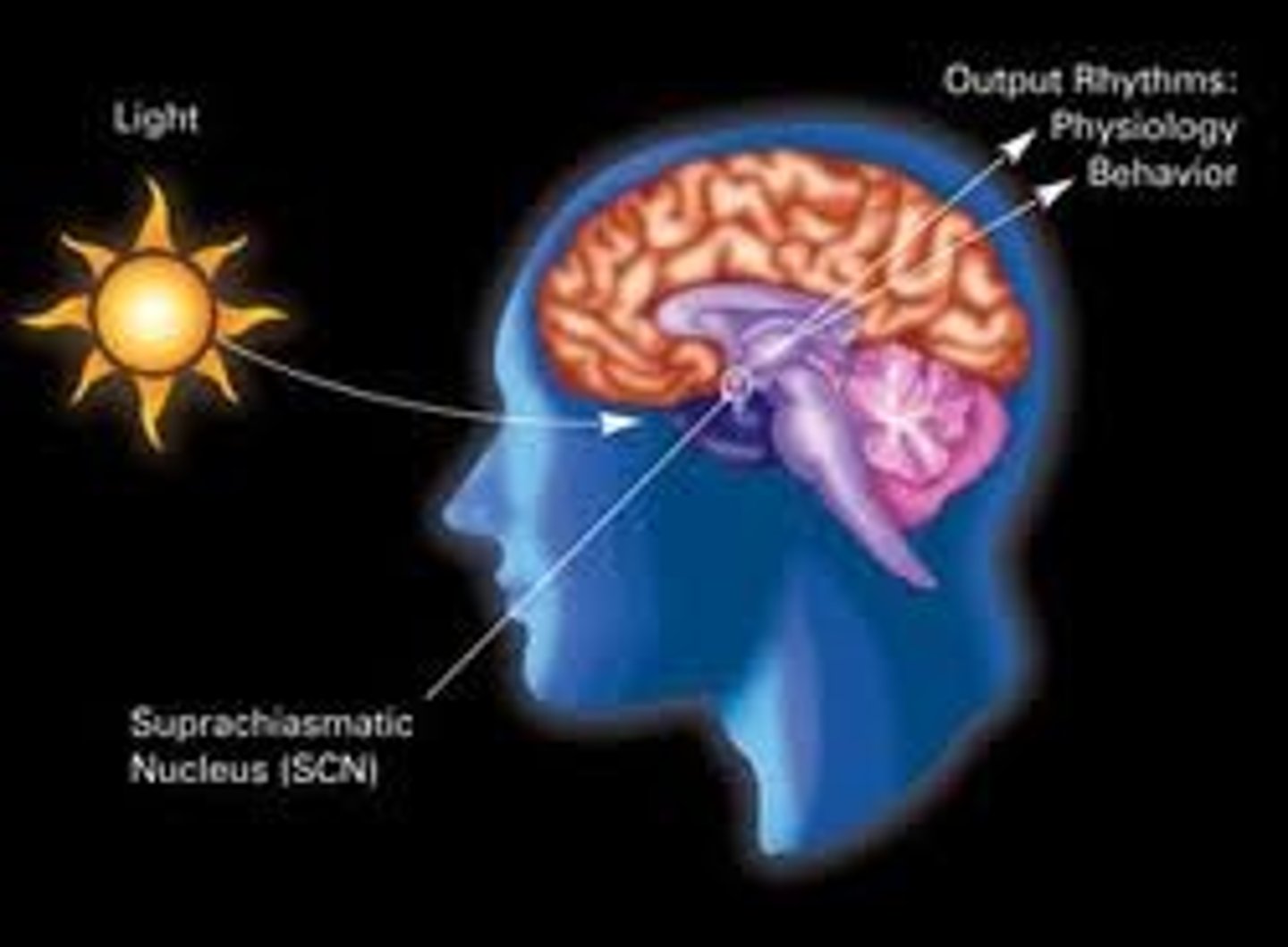
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
area of the hypothalamus in which the body's biological clock is located
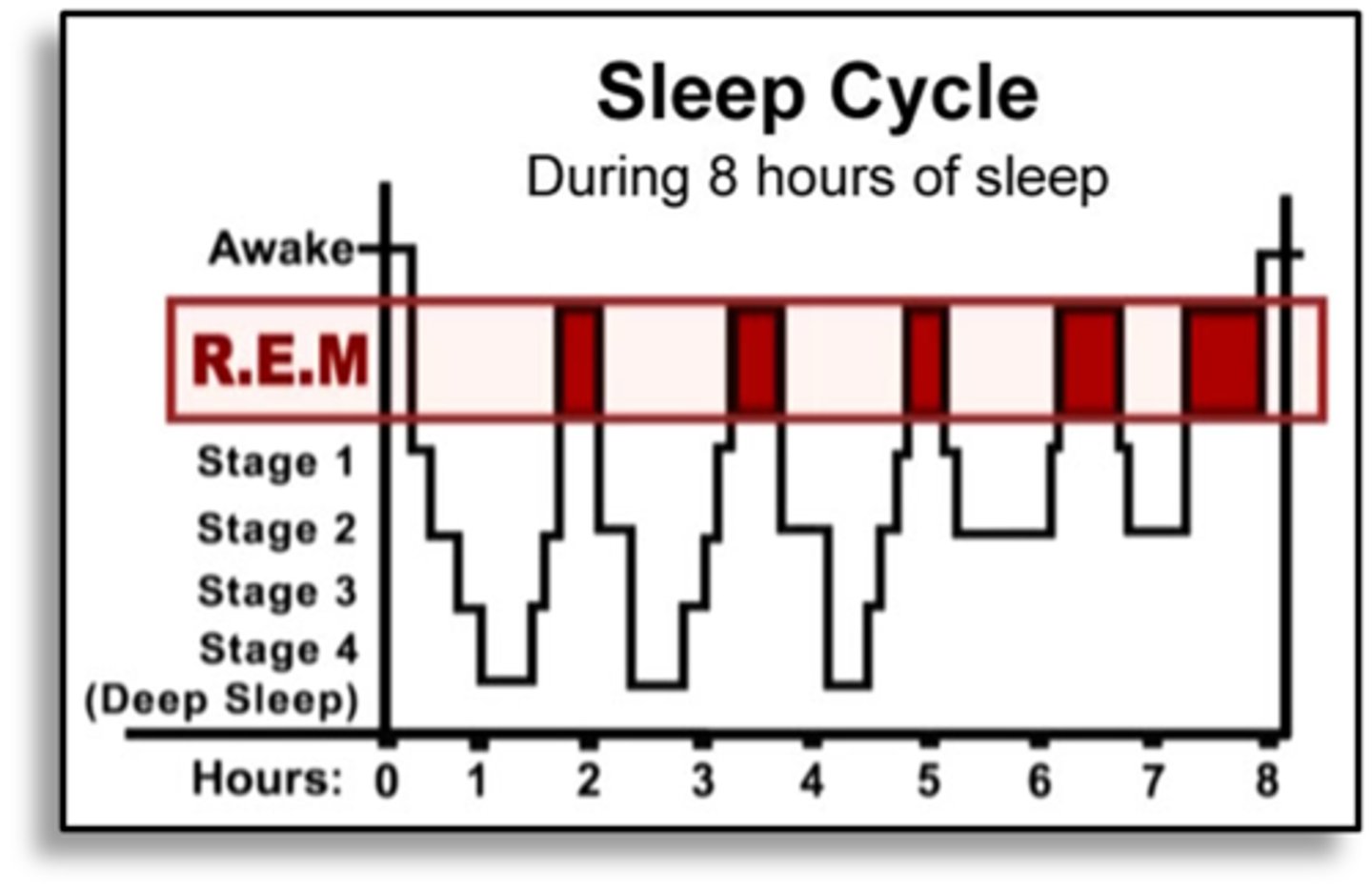
Hypnogram
A graphic depiction of a person's progress through the stages of sleep over the course of a night.
Sleep cycle
a period of sleep lasting about 90 minutes; passage through the three stages of NREM sleep (1-3), then reversal (3-1), followed by REM sleep
Sleep episode
the full duration of time spent asleep
Internal cues
involve information that originates within the body (such as the expression and suppression of particular genes, known as clock genes)
External cues
involve information from the environment, such as the presence or absence of light.
Pineal gland
gland that produces melatonin
Hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland; where the SCN is located
Cortisol
hormone responsible for increasing alertness and maintaining heightened arousal