psychology 2910 - lecture 4 (central tendency)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Mean
Arithmetic mean or "average." The sum of scores divided by the number of scores
Mode
The most frequent value
- If two scores are tied for most frequent, then the distribution is bimodal
- If more than two scores are tied for most frequent, there's no mode to report
Median
The score that divides the distribution in half; can be hard to calculate
- 50th percentile
- Half the scores are above, and half the scores are below
What are the characteristics of the mean?
1. Changing a score changes the mean
2. Adding/subtracting a score changes the mean (except when the score is the mean)
3. Adding/subtracting a constant value to each score adds/subtracts that value to the mean
4. Multiplying/dividing by a constant value has the same effect on the mean
5. Sample mean is an unbiased estimator of the population mean (no tendency to under- or overestimate population value)
What is the median when there's an odd number of scores?
Median is the middle value (i.e. if median is 13, there would be three scores above and three scores below)
What is the median when there's an even number of scores?
Median is the point midway between the two middle scores (i.e. between 5 and 6 is 5.5); median has "hypothetical" value that's not in the set of scores
If the data is not cooperative, what is the median?
Need to calculate the precise median
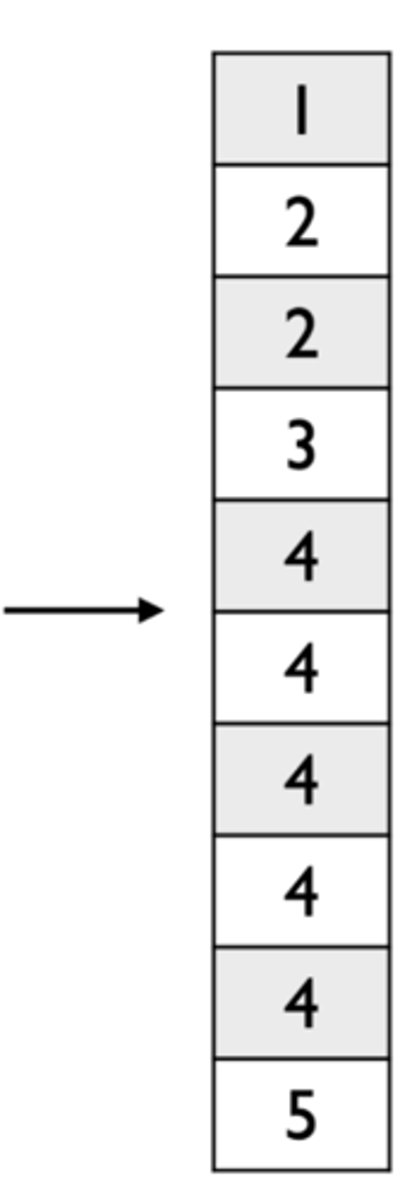
Real Limits
Boundaries of intervals for scores on continuous scale
For a value of 4:
- Lower Real Limit (LRL): 3.5
- Upper Real Limit (URL): 4.5
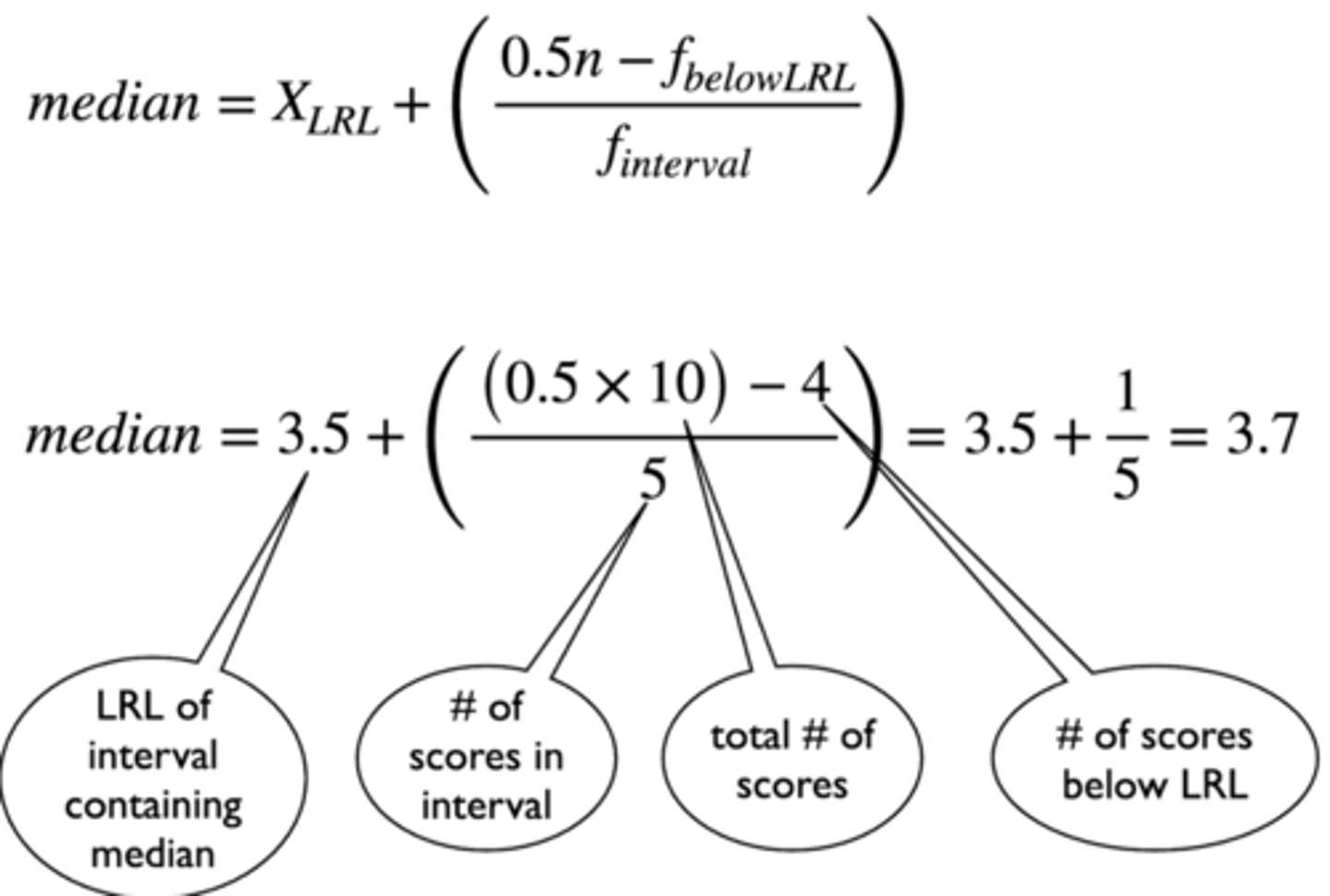
How do you calculate the precise median?
- Determine the real limit of intervals containing the median: if the median is 4, then 3.5 and 4.5
- Total number of scores: 10
- Number of scores below: 4
- Number of scores in interval: 5
What is the median for discrete variables?
If the median number of children is 3.7, that doesn't make sense; therefore, round to 4
How can the mean be misleading?
Computationally simple and the most frequently reported
Affected by extreme scores; mean salary of the 1996-97 Chicago Bulls was $4.4 million; all but two players made less than $4 million
When should the median be used?
Computationally difficult and not reported when it should be (i.e. median of Chicago Bulls salary is $1.3 million); most spreadsheets do not report precise median
Should be used when there are extreme scores or skewed distributions, undetermined values (e.g. timed out), open-ended distributions (e.g. five or more), ordinal scale (e.g. rank)
When should the mode be used?
- Nominal scales (the most common boy's name in B.C. in 2010 is Ethan)
- Discrete variables [most common number of children in a family is two; but median (rounded) gives additional info]
Why shouldn't we use the term "average"?
Imprecise and could refer to:
- Mean (arithmetic mean)
- Median
- Mode
- Geometric mean (usually used when scores change in a relative fashion, such as filters trapping dust in an amount relative to the amount of air flowing through them)
- Harmonic mean (usually used for rates, such as speed)