Circoviridae and Papillomavirdae
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
which family is one of the smallest viral pathogens of animals?
Circoviridae
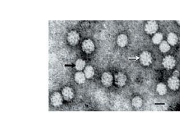
Can you describe the shape of the viral genome of circoviridae?
1) circular
2) single stranded DNA
what are the three forms of
Psittacine Beak and Feather Disease (PBFD)
1) Per acute form
2) Acute form
3) Chronic form

what is the virus that displays these clinical signs?
Psittacine Beak and Feather Disease (PBFD)
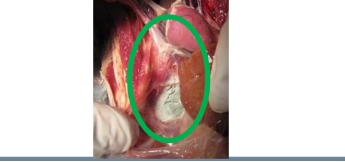
Describe this secondary finding within PBFD
Fungal infection in a young
African Grey Parrot secondary
to PBFD
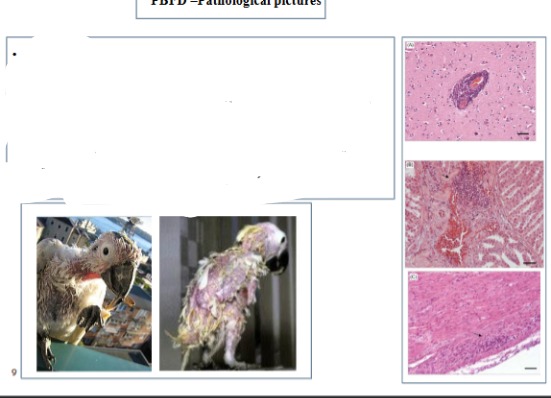
What virus presents these pathological findings?
PBFD
what kind of bodies are present in PBFD and where is it located?
1) Intra-cytoplasmic “botryoid” inclusions in follicular epithelium in
macrophages
What are the different types of Porcine circoviruses?
1) PCV-1
2) PCV-2
3) PCV-3
4) PCV-4 (most recently identified).
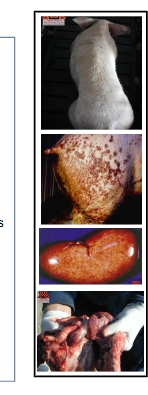
What do these lesions show/indicate?
1) Post-weaning Multisystemic Wasting Syndrome (PMWS) (image 1)
2) Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome (PDNS) (image 2&3)
3) From these viruses, there can be reproductive symptoms (image 4)
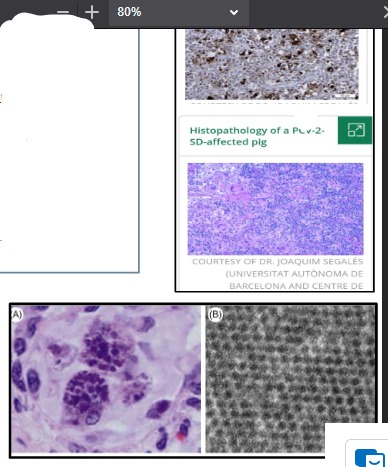
what kind of inclusion bodies are these and what virus is it associated with?
(Botroyid) & PCV-2 (known to cause significant depletion of lymphocytes)
Which family has the genus Chicken anemia virus (CAV)
Anelloviridae
what family did CAV switch from?
Old: Circoviridae
New: Anelloviridae

what are clinical signs indicative of?
CAV
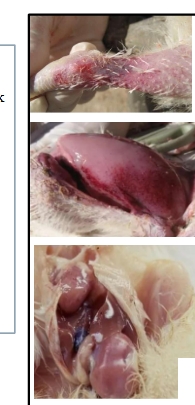
what are these postmortem lesions indicative of?
CAV
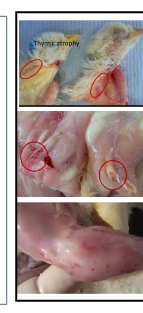
what are these clinical lesions indicative of pt 2?
CAV- showing atrophy of thymus which is a VERY important characteristic of this virus
which species is affected by the Torque TENO SUS VIRUSES (TTV)?
Pigs
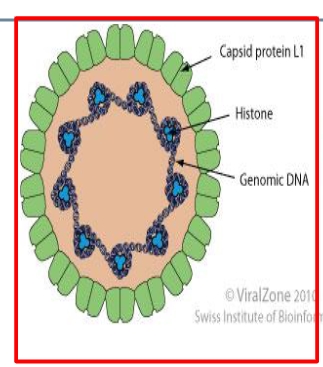
Describe the viral genome in papillomaviruses
1) Circular dsDNa
what are the diseases caused by papillomavirus?
1) Bovine papilloma virus 1-10 (affects cattle but 1 & 2 affects equine known as sarcoid)
2) Equine papilloma 1,2 ONLY affects horses
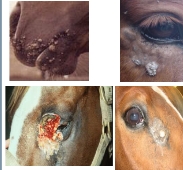
What is the papillomavirus that can lead to benign tumor formation called Sarcoids and who species affect?
BHV-1 and horses
What are the two subtypes of papilloma viruses that affect cattle?
1) Squamous papillomas
2) Fibropapillomas
which papillomas viruses are associated with neoplasia in cattle?
1) BPV-2→ Bladder cancer
2) BPV-4 → upper alimentary cancer
if cattle encounter the bracken fern, they are HIGHLY susceptible to developing cancer

which BPV does this sign correspond to?
BPV-2 & remember prone to causing bladder cancer due to those plants

which BPV does this correspond to?
BPV-4 & causes GIT cancer dont forget about the bracken fern plant

what does this BPV correspond to?
BPV-5 & gives rise to flat rice-grain lesions

What does this BPV correspond to?
BPV-6 and gives rise to frond shape warts (ewww)
which equine papillomavirus does this correspond to ?
EcPV-1 & it is the most common type!

which equine papillomavirus does this correspond to?
EcPV-2
Just to recap: what causes equine sarcoid?
BPV-1 & 2
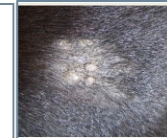
what type of sarcoids is this?
occult (flat)
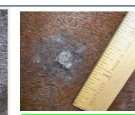
what type of sarcoids is this?
verrucose (wart-like)
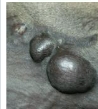
what type of sarcoids is this?
Nodular
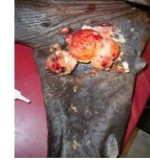
what type of sarcoids is this?
fibroblastic
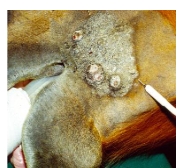
what type of sarcoid is this?
mixed
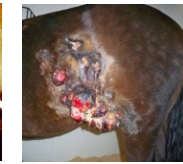
what type of sarcoid is this?
Malevolent
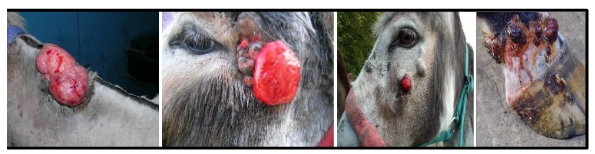
what type of lesion is this present in donkeys?
sarcoids
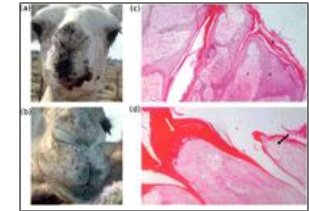
what kind of lesions are present in camel papillomavirus
Cauliflower-like nodule and a round oval raised nodule
What are the oral papillomas present in dogs?
1) CPV→ oral papillomas
2) CPV-2→ cutaneous papillomas
3) CPV-3-7, 12,14-16→ pigmented plaques
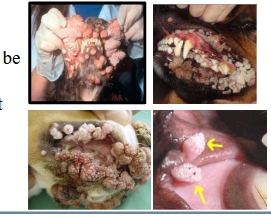
Although viral papillomas are rare in cats, what is the virus associated with it?
FcaPV-1: oral viral papillomas

What type of lesion is this and what is it caused by?
Feline sarcoids caused by BPV14 due to coming in contact with cattle
what is the papillomavirus that affects rabbits and what does it show?
shope papillomavirus and it is prone to causing cancer in them.

what type of viral genome is present in family polymaviridae
1) small, closed circular, dsDNA
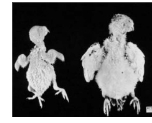
what virus is responsible for the affected bird on the left?
Avian Polyomaviruses of Birds/Budgerigar fledgling disease polyomavirus & mortality is 100%
what type of inclusion bodies are involved in Budgerigar fledgling disease polyomavirus
Basophilic intra-nuclear inclusions
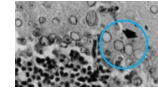
What type of inclusion bodies are seen in larger psittacine birds?
mononuclear
phagocytic cells with inclusions
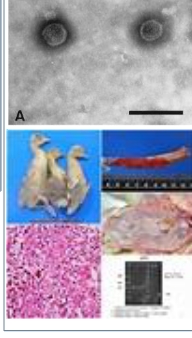
what virus causes these type of lesions and signs in geese?
Goose hemorrhagic polyomavirus (GHPyV)
which polymaviruses affect lab animals?
K virus -designated as a murine pneumotropic virus (MPtV),
what is the non-enveloped, ds-DNA virus in the polyomarvirus genus of the family Papovaviridae
Simian vacuolating virus 40(SV40)

what virus is responsible for these clinical signs?
French Moult in budgies