MOLECULES TO CELLS EXAM REVIEW PART 1
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
inputs of photosynthesis
water, CO2, sunlight
relationship between stromata and thylakoids
stromata allow carbon dioxide in and out of cells and the thylakoids house chlorophyll which is a pigment in plants absorbing the suns photons
describe photosystem II→the first stage in light reactions
occurs in the thylakoid membrane that houses chloroplast
chlorophyll in PSII and electrons becomes excited
electrons flow into thylakoid membrane and it becomes negativly charged→beginning electron transport chain
as the electrons move thorugh thylakoid emebrane they operate on proton pumps which pulls hydrogen ions into the membrane
in this process water molecules are broken down to supply the electrons from hydrogen and oxygen is realased
PSI chlorophyll gets excited and move through the thylakoid membrane to ATP synthase
in this process NADPH is created through electrons bonding H+ and NADP
large amount of hydrogens in the thylakoid want to diffuse through ATP synthase and bond ADP to another phosphate creating ATP
ATP and NADPH are important creations
what light stimulates most photosynthesis
red and blue
definition of photosynthesis
process that converts sunlight into glucose
calvin cycle light independent reactions of photosynthesis
RuBP bonds with CO2
ATP and NADH break down the six carbon molecule into phosphoglycerate→ 2 PGA
some of these will bond to create glucose and some will be broken down further to keep cycle going and create RuBP
formula of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
what inhibits beta oxidation (fatty acid breakdown)
malonyl CoA which is formed during synthesis of fatty acids
difference between CAT 1 and CAT 2
carnitine acyl transferase-1 functions in the mitochondrial membrane adding an acyl carntine and taking a CoA
carnitine acyl transferase-1 functions in the mitochondria in adding a carntine to leave with fatty acid CoA
catalyst
substance speeding up a chemical reaction but is not consumed in the reaction
what are required for enzyme activity
cofactors→vitamins and metals
process of converting pyruvate into acetyl CoA
pyruvate dehydrogenase
B1= removes Co2
B3=NAD+
B5=CoA
what is the michaelis menten equation
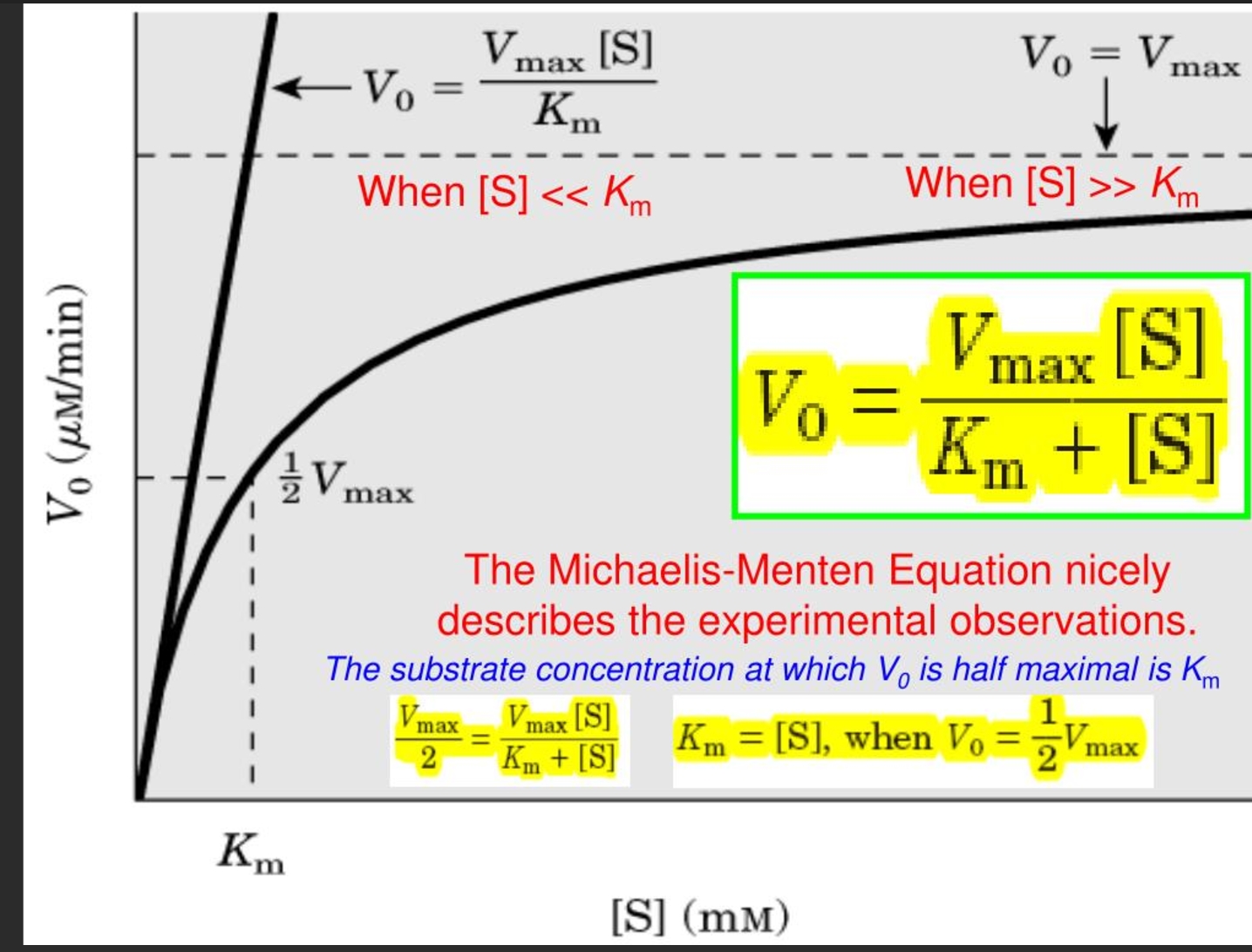
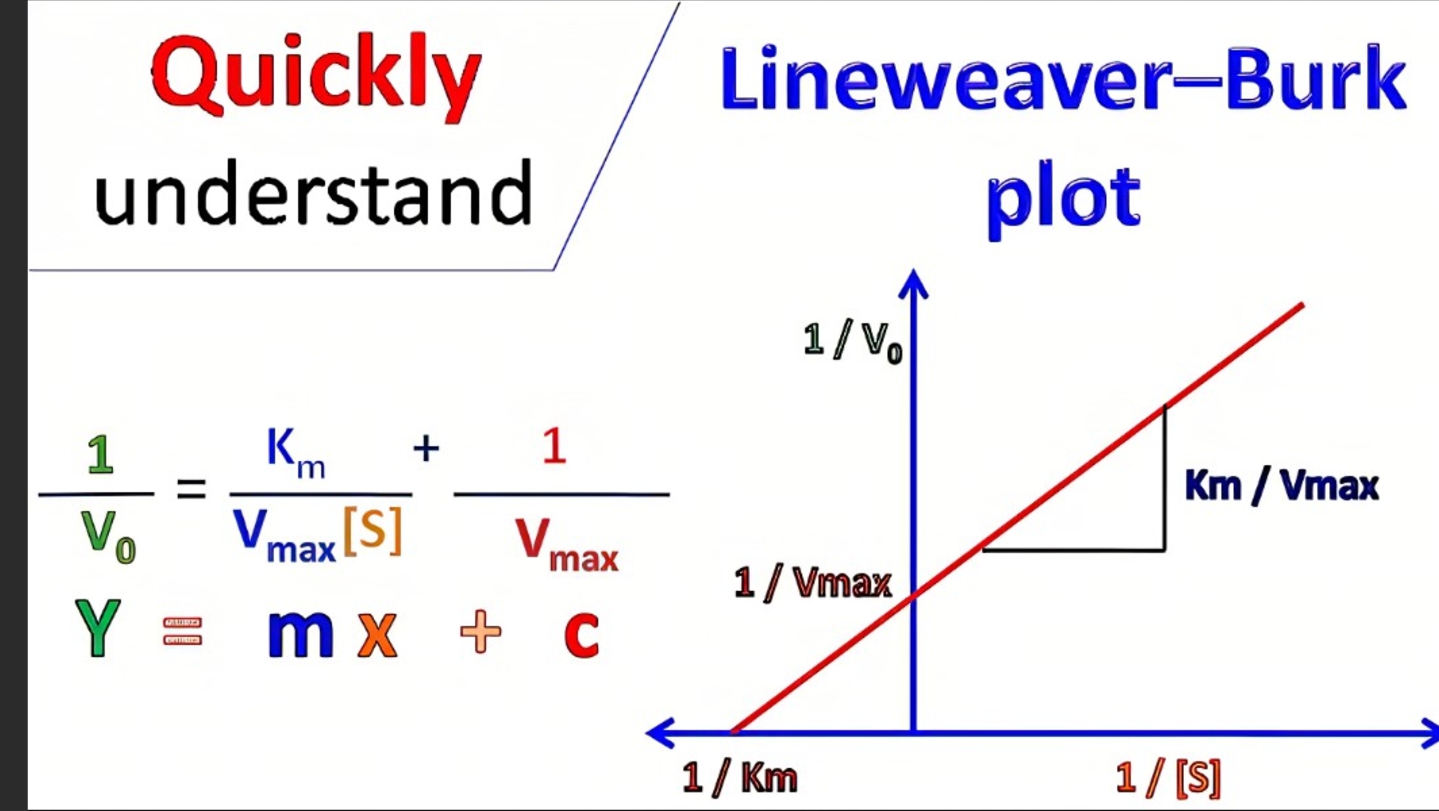
what is the line weaver burk plot equatin
differences in beta oxidation and fatty acid synthesis
fatty acid breakdown: two carbons sequentially removed, oxidizing agents are FAD+and NAD+,occurs in mitochondira
fatty acid synthesis: carbon units are added via molonyl-ACP, reducing agent is NADPH, and it occurs in the cytoplasm
what connects carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and how
mitochondrial citrate carrier→citrate carried out of TCA if ATP is high for fatty acid synthesis which breaks down to acetyl CoA
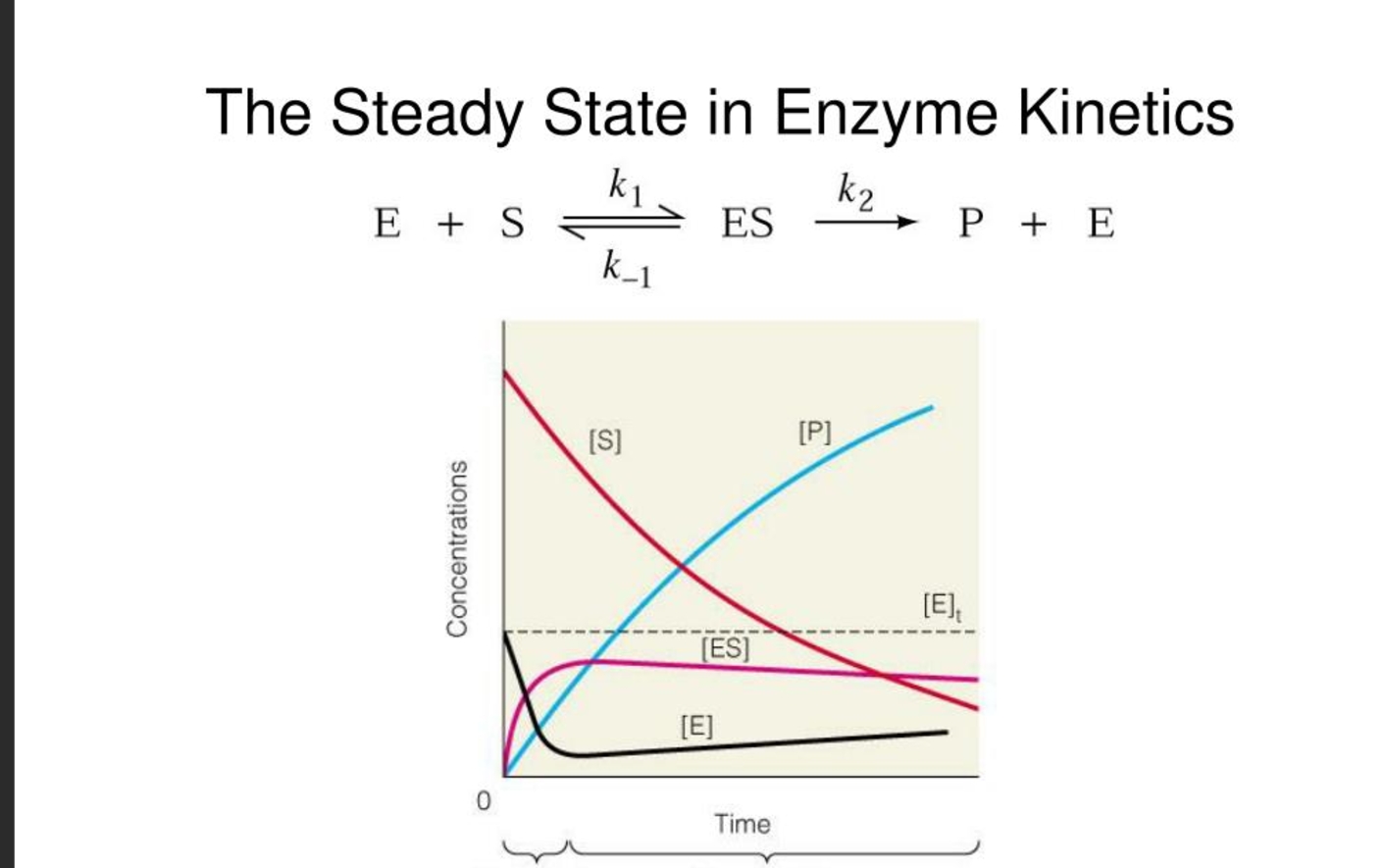
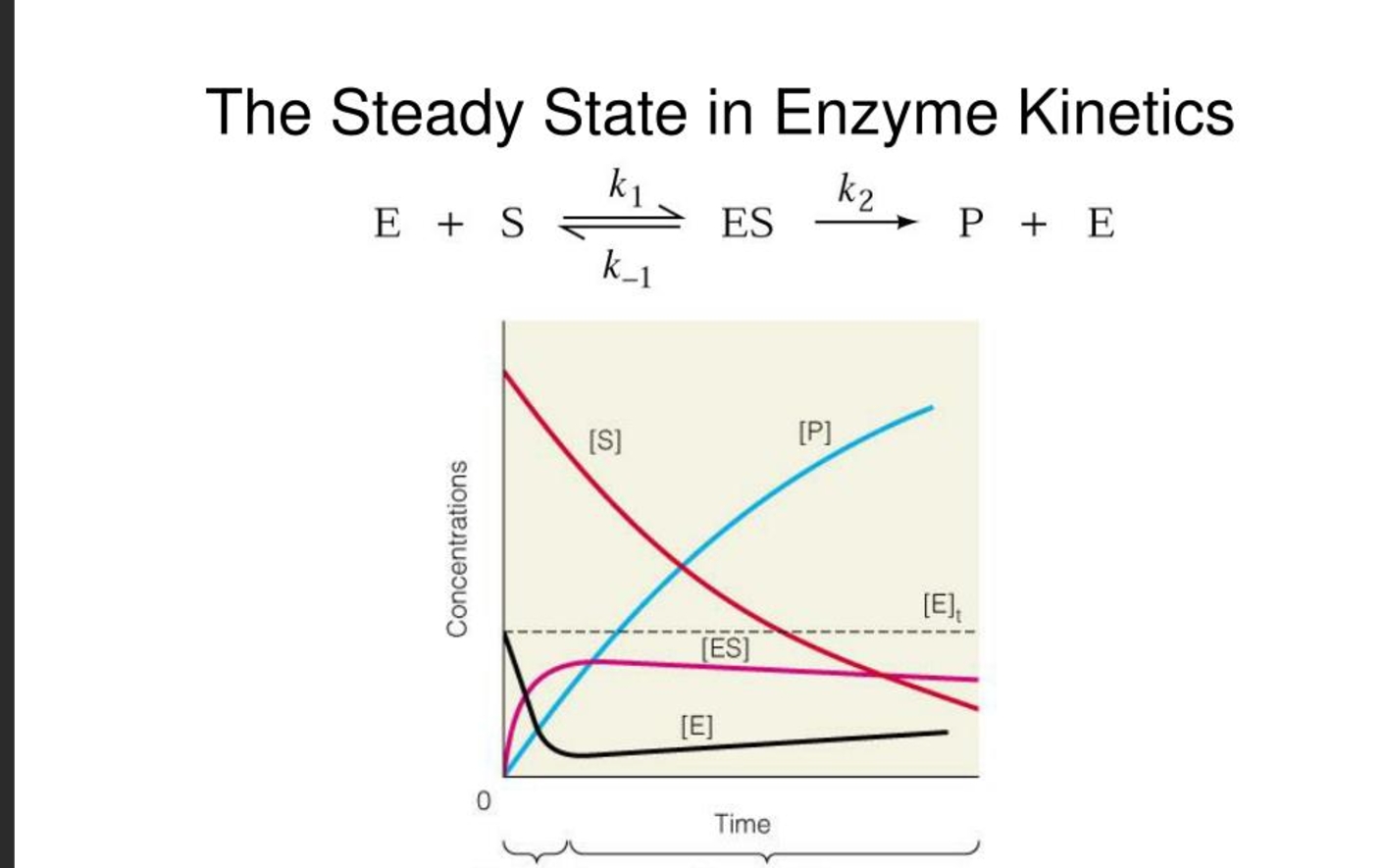
what is the steady state assumption in enzyme kinteics
what happens in competitive inhibition versus uncompetitive inhibiton
competitive→increase in kM because more substrate is needed byt Vmax unaffacted
uncompetitive→decrease in KM and decrease in Vmax