ECON 248 13.1 Supply AND Demand For Loanable Funds And Foriegn-Currency Exchange
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
The sources of supply for loanable funds are (), () and ().
Private Saving(Household Saving), Public Saving(Government Budget Surplus), Net Capital Inflows
The sources of demand for loanable funds are () and ().
Domestic Investment, Foreign Investment
When supply of loanable funds from (1) is insufficient to meet the demand of it for (), (1) increases and NCO becomes ().
National Saving, Domestic Investment, Negative
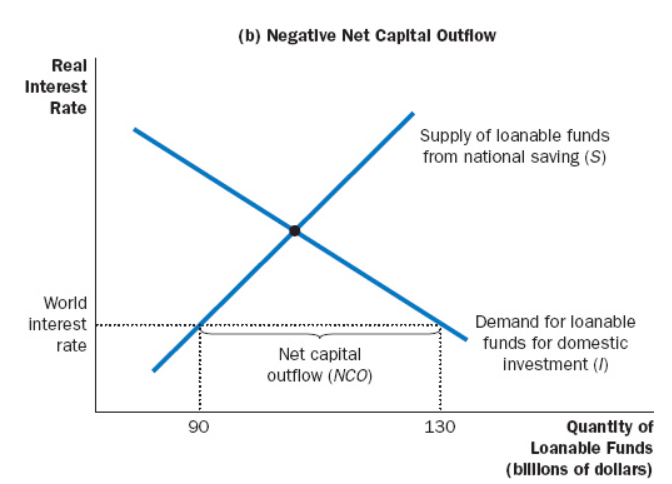
Excess supply of loanable funds can be used to buy ().
Foreign Assets
() (r*) determines the quantity of loanable funds demanded for domestic investment and the quantity of funds made available from national saving.
World Interest Rate
Loanable Funds Supplied(Saving) - Loanable Funds Demanded(Investment) =
Net Capital Outflow(Net Exports)
The demand curve for a currency slopes () while the supply for it slopes ().
Downwards, Upwards
The source of supply for foreign currency are (), while the sources of demand are ().
Net Capital Outflow, Net Exports
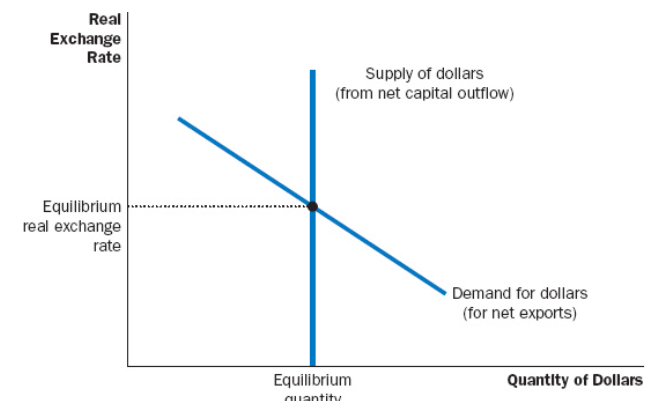
An (1) in foreigner income will increase the demand for Canadian goods. This would cause an (1) in net exports, and the value of the Canadian dollar and cause the demand curve to shift ().
Increase, Right
When a domestic Country wants to buy a foreign bond, it needs to exchange its currency with the other Country’s currency. So it () domestic dollars to the foreign Country.
Supplies
When a foreign Country buys a domestic good, it () domestic dollars in foreign exchange market.
Demands
() balances the supply and demand in the market for loanable funds.
Real Exchange Rate
When a Country’s real exchange rate appreciates, it means that their goods are () compared to foreign goods, causing exports to () and () to rise.
Expensive, Fall, Imports