A&P II - Reproductive Quiz
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
AMAB Reproductive System
Structures:
testes
system of ducts - epididymis, vas deferent, ejaculatory, duct, urethra
accessory sex glands - seminal vesicle, prostate gland, bulbourethral gland
supporting structures - penis, scrotum
spermatic cord: encloses vas deferens, lymphatics, nerves
Prostate
produces fluid that nourishes and transports sperm (seminal fluid)
sperm in fluid
prostate secretes an alkaline substance that constitutes approximately 30% of seminal fluid
Testes
produce and release testosterone and sperm
lobules - about 200-300/testicle
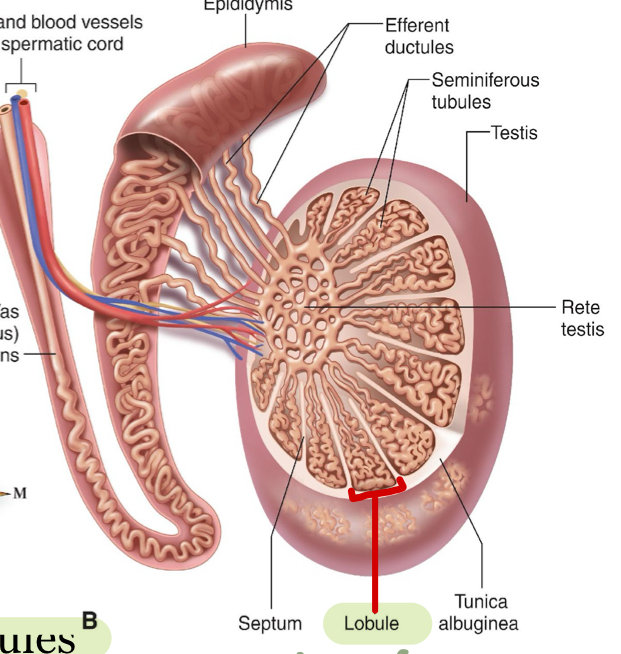
Epididymis
store the sperms for maturation and transport it to vas deferens
vasectomy: cut vas deferens
Seminiferous tubules & spermatogenesis
Sertoli cells - embedded within the seminiferous tubule, stimulated by FSH to secrete nutrients for sperm production and form the blood testes barrier
mechanical support & protection for germinating sperm cells
Pathway of Sperm
Testicles - where sperm is produced
Epididymis - sperm is stored
Vas deferens - transports sperm
Seminal vesicle
Prostate
Urethra
Exits through the meatus
AFAB Reproductive System
create an oocyte & a fertile environment for the zygote that arises after fertilization
egg = oocyte when it has not met sperm; zygote when met with sperm
born with a set # of eggs: 1-2 million
paired ovaries
Ovaries
produce oocytes
hormone - progesterone and estrogen
oogenesis: process of maturing oocytes (egg formation)
1 mature egg per month; alternating ovaries
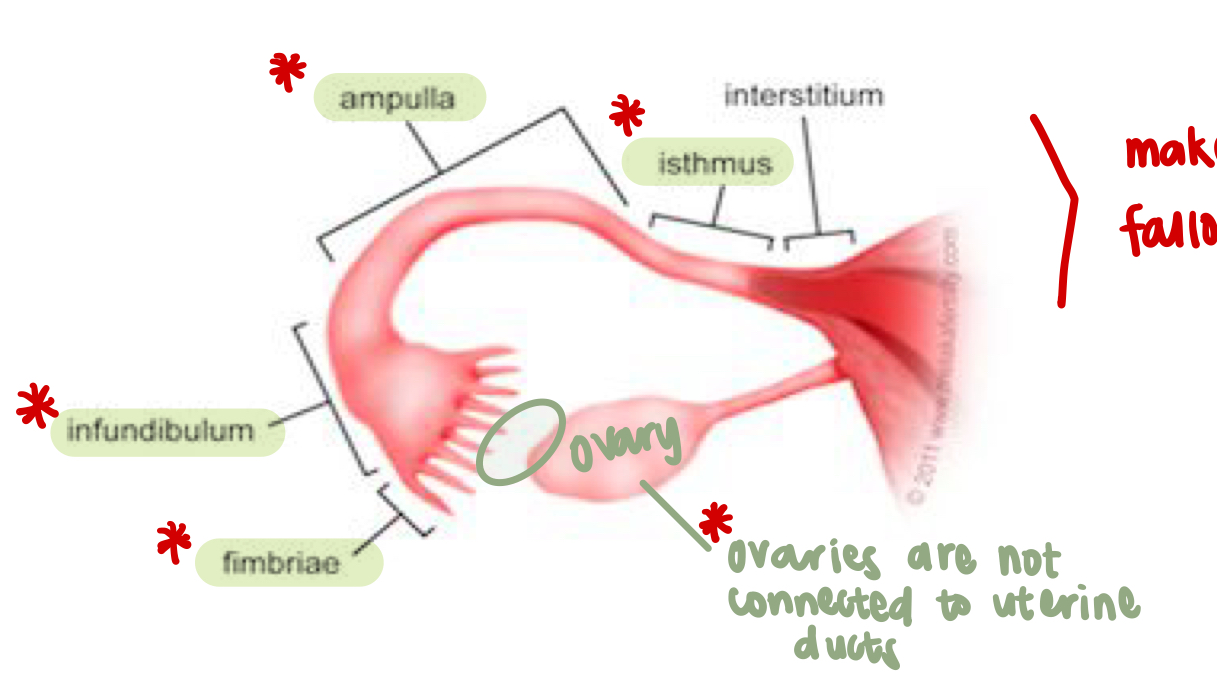
Fallopian tubes (uterine tubes)
consists of three main parts:
infundibulum with fimbriae, ampulla, and isthmus
Ovaries are not connected to uterine ducts (see photo)
Uterus & Vagina
layers of uterus:
endometrium - innermost layer; layer that sheds during menstruation
myometrium - middle
perimetrium - outer
ciliary action: moves the ovum through uterine tubes
ectopic pregnancy: egg implants outside of uterus
4 Phases - Follicular phase:
Begins at menstruation until ovulation. Pituitary gland releases follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), stimulating the development of follicles in the ovaries, each containing an egg.
4 phases - Ovulation:
This usually occurs on day 14, a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of a mature egg from one ovary.
4 Phases - Luteal Phase:
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms to corpus luteum (which secretes progesterone). Progesterone prepares the uterus for potential implantation of the fertilized egg & help maintain pregnancy if conception occurs.
4 Phases - Menstruation:
If fertilization does not occur, corpus luteum degenerates, leading to a drop in progesterone levels. This will cause the endometrium to shed, resulting in menstruation.
Clitoris
small organ made of erectile tissue
can be filled with blood during a sexual response
behind labia minora
Amenorrhea
absence of menstruation
failure to menstruate
secondary to amenorrhea:
anorexia - low calories, body in survival state; decrease production of estrogen & progesterone
extreme exercise - stress response; hypothalamus - decrease FSH & LH
stress - stress causes the release of cortisol, if there is too much cortisol, it will affect the menstrual cycle; high levels of cortisol = levels of hormones needed to trigger ovulation and menstruation to decrease