Antioxidants- basic nutrition
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:52 PM on 11/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
oxidation
loss of an electron
2
New cards
reduction
gain of electron
3
New cards
during metabolism
some lose electrons (oxidation)
4
New cards
free radical
unstable atoms, unpaired electrons an odd number
5
New cards
free radicals are a normal by product of which body processes?
Metabolism (breaking down nutrients to create the energy)
Immune response- causing inflammation
Immune response- causing inflammation
6
New cards
Free radicals formed from exposure to...
carcinogens: air pollution, UV rays, tobacco smoke, chemicals, medical radiation, some viruses, etc.
7
New cards
excessive free radical production
cell damage
‘steal’ electrons from stable atoms creating a chain reaction = more free radicals
‘steal’ electrons from stable atoms creating a chain reaction = more free radicals
8
New cards
antioxidants
donate electrons to free radicals
9
New cards
the "big three" antioxidants
Vit A, C, E
10
New cards
Vitamin E
Fat soluble, 90% stored in adipose tissue, 10% in the cell membrane
11
New cards
Vitamin E functions
- Primary function: antioxidant
- once oxidized Vit E can either excrete or recycle back to active Vit E
- Vit C donates an electron to recycled Vit E
- critical for normal fetal development of nerves and muscles
- improves absorption of Vit A
- Keeps the immune system strong against viruses and bacteria
- Important in the formation of red blood cells and it helps the body use vitamin K.
- Widens blood vessels and keeps blood from clotting inside vessels
- Vit E is added to veg oil and skin care
- once oxidized Vit E can either excrete or recycle back to active Vit E
- Vit C donates an electron to recycled Vit E
- critical for normal fetal development of nerves and muscles
- improves absorption of Vit A
- Keeps the immune system strong against viruses and bacteria
- Important in the formation of red blood cells and it helps the body use vitamin K.
- Widens blood vessels and keeps blood from clotting inside vessels
- Vit E is added to veg oil and skin care
12
New cards
Vit E protects...
Omega 3 and 6 (PUFA's) and other fatty component of cells from being oxidized= reduced heart disease
13
New cards
RDA of Vit E
15 mg of alpha-tocopherol (most active form)/day
UL= 1,000 mg/d
UL= 1,000 mg/d
14
New cards
sources of Vitamin E
spreads and dressing from veg oils, nuts, seeds, and some dark green leafy veggies
15
New cards
excess fo Vit E
usually from supplements
may cause increase for bleeding
may cause increase for bleeding
16
New cards
medication interaction with Vitamin E
Coumadin and aspirin act as anticoagulants and stop blood from clotting excessively. Vit. E can augment the action of these which may result in uncontrollable bleeding.
17
New cards
Vitamin C
water soluble
- two active forms- ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid
- two active forms- ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid
18
New cards
most animals make their own glucose besides...
humans and guinea pigs
19
New cards
functions of vitamin C
1. assist in collagen synthesis
2. assist in synthesis of DNA, bile, neurotransmitters and carnitine
3. assist in synthesis of hormones
- ensures proper levels of thyroxine
- epinephrine, norepinephrine, and steroid hormones
4. antioxidant
- important in extracellular fluid
2. assist in synthesis of DNA, bile, neurotransmitters and carnitine
3. assist in synthesis of hormones
- ensures proper levels of thyroxine
- epinephrine, norepinephrine, and steroid hormones
4. antioxidant
- important in extracellular fluid
20
New cards
collagen
a protein critical to all connective tissues
- Collagen assists in preventing bruising, ensures proper wound healing, and is a component of the tissue that mend broken bones.
- Without Vit. C, the body can’t form collagen= tissue bleeding.
- Collagen assists in preventing bruising, ensures proper wound healing, and is a component of the tissue that mend broken bones.
- Without Vit. C, the body can’t form collagen= tissue bleeding.
21
New cards
Vit C as an antioxidant
1. donates electrons to free radicals to prevent tissue and cell damage
- protects LDL cholesterol from oxidation which reduces CVD risk
- protects us from damage caused by ozone, vaping and cigarette smoke in lungs
2. Regenerates Vit. E after it has been oxidized by donating an electron which enables Vit. E to continue to protect our cell membranes.
3. Enhances immune fxn
4. In stomach- reduces formation of nitrosamines
- protects LDL cholesterol from oxidation which reduces CVD risk
- protects us from damage caused by ozone, vaping and cigarette smoke in lungs
2. Regenerates Vit. E after it has been oxidized by donating an electron which enables Vit. E to continue to protect our cell membranes.
3. Enhances immune fxn
4. In stomach- reduces formation of nitrosamines
22
New cards
sources of Vit C
Fresh is best. Steam, microwave, stir-fry to cook.
23
New cards
excess/ deficiency of Vit C
Toxicity not common
deficiency- scurvy will occur after 1 month
s/s bleeding gums, loose teeth, diarrhea, anemia
deficiency- scurvy will occur after 1 month
s/s bleeding gums, loose teeth, diarrhea, anemia
24
New cards
Those at risk of scurvy
poor, homebound, alcohol and drug abuse
25
New cards
Beta Carotene
Not necessary nutrient
1. inactive from of Vit A- 2 units of Beta carotene= one active unit of Vit A
2. carotenoid- fat soluble orange, red, and deep yellow pigment
3. fat- soluble- fight oxidation in the lipid portions of cell membranes
4. Weak antioxidant, BUT it enhances our immune system and protects the skin and eyes from UV damage.
5. sources: Sources: red, orange, yellow, deep green f/v.
Lightly cooking will increase amount released.
1. inactive from of Vit A- 2 units of Beta carotene= one active unit of Vit A
2. carotenoid- fat soluble orange, red, and deep yellow pigment
3. fat- soluble- fight oxidation in the lipid portions of cell membranes
4. Weak antioxidant, BUT it enhances our immune system and protects the skin and eyes from UV damage.
5. sources: Sources: red, orange, yellow, deep green f/v.
Lightly cooking will increase amount released.
26
New cards
- Vitamin A
- Generic term for a group of similar compounds called retinoids
- Fat soluble. 90% stored in liver.
- Requires retinol-binding proteins to transport to target cells.
- Fat soluble. 90% stored in liver.
- Requires retinol-binding proteins to transport to target cells.
27
New cards
Forms of Vit
Retinol- found in animal products. (beta-carotene is converted to this form)
--enzymes convert retinol into Retinoic Acid-
important in cell growth
-Retinal - found in the eye retina
--enzymes convert retinol into Retinoic Acid-
important in cell growth
-Retinal - found in the eye retina
28
New cards
Functions of Vit A
1. healthy vision-
Allows sight under low-lights
Enables us to see color
2. contributes to cell differentiation
3. Immunity (known since 1980’s)
4. antioxidant (not strong)
5. bone growth
6. acne treatment
Allows sight under low-lights
Enables us to see color
2. contributes to cell differentiation
3. Immunity (known since 1980’s)
4. antioxidant (not strong)
5. bone growth
6. acne treatment
29
New cards
benefits of Vit A
- maintains health of specialized tissues such as the retina
- aids in growth and health of skin and mucous membranes
- maintains health of specialized tissues such as the
retina
- promotes normal development of teeth, soft and skeletal issues
- aids in growth and health of skin and mucous membranes
- maintains health of specialized tissues such as the
retina
- promotes normal development of teeth, soft and skeletal issues
30
New cards
Excess of Vit A
HIGHLY TOXIC. May develop at 3-4 x’s the RDA.
- Toxicity rarely from food
- S/S- fatigue, decr. appetite, blurred vision, hair loss, liver damage.
- May be reversed if caught early.
- Toxicity rarely from food
- S/S- fatigue, decr. appetite, blurred vision, hair loss, liver damage.
- May be reversed if caught early.
31
New cards
sources of Vit A
meats (liver), milk, fortified cereal, margarine
32
New cards
Vit A deficiency signs
dry skin, dry eyes, night blindness, infertility, poor wound healing, acne breakouts, delayed growth, throat and chest infections
33
New cards
Antioxidant chemicals the Body synthesizes
1. Glutathione
- combination of three simple amino acids
cysteine, glycine and glutamine.
-Extracellular fluid
-Sulfur is it’s key chemical component
-Recycled in body
2. Uric Acid- most abundant in blood
-Synthesized from purine metabolism
-Circulates in blood and disables circulating free radicals.
-High concentrations in the blood may cause gout. r/t kidney issues
- combination of three simple amino acids
cysteine, glycine and glutamine.
-Extracellular fluid
-Sulfur is it’s key chemical component
-Recycled in body
2. Uric Acid- most abundant in blood
-Synthesized from purine metabolism
-Circulates in blood and disables circulating free radicals.
-High concentrations in the blood may cause gout. r/t kidney issues
34
New cards
Free radicals detoxifying enzyme systems
- Protect from f.r. damage
- Minerals as cofactors for the antioxidant enzymes
-Intracellular
- Minerals as cofactors for the antioxidant enzymes
-Intracellular
35
New cards
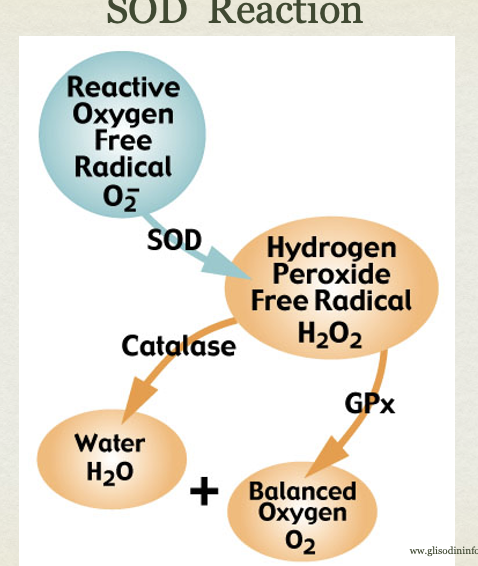
superoxide Dismutases (SOD) (enzyme system)
- either manganese, copper, or zinc cofactor
- critical in reducing oxidative stress in life-threatening diseases and reducing inflammation and pain
- critical in reducing oxidative stress in life-threatening diseases and reducing inflammation and pain
36
New cards
Catalase (Enzyme)
- Contains Fe as cofactor
- Converts H2O2 to water and oxygen
- Highly efficient
- Converts H2O2 to water and oxygen
- Highly efficient
37
New cards
Glutathione Peroxidases
- similar to catalase but different cofactor
- Cofactor- selenium
- convert H2O2 to water & oxygen
- Cofactor- selenium
- convert H2O2 to water & oxygen
38
New cards
benefits of free radicals
- Immune system uses cell-damaging properties of free radicals to kill pathogens
- act as a signaling involved in stress responses
- Must have H2O2 to produce thyroid hormone
- act as a signaling involved in stress responses
- Must have H2O2 to produce thyroid hormone