Chp. 8 DNA structure and function/karyotypes - 9BioH
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is an autosome?
Any chromosome that isn’t a sex chromosome.
What is a centromere?
A structure in a chromosome holding two chromatids together.
What is a chromosome?
A structure containing DNA for an organism.
What is a chromosome number?
The total count of chromosomes in a cell.
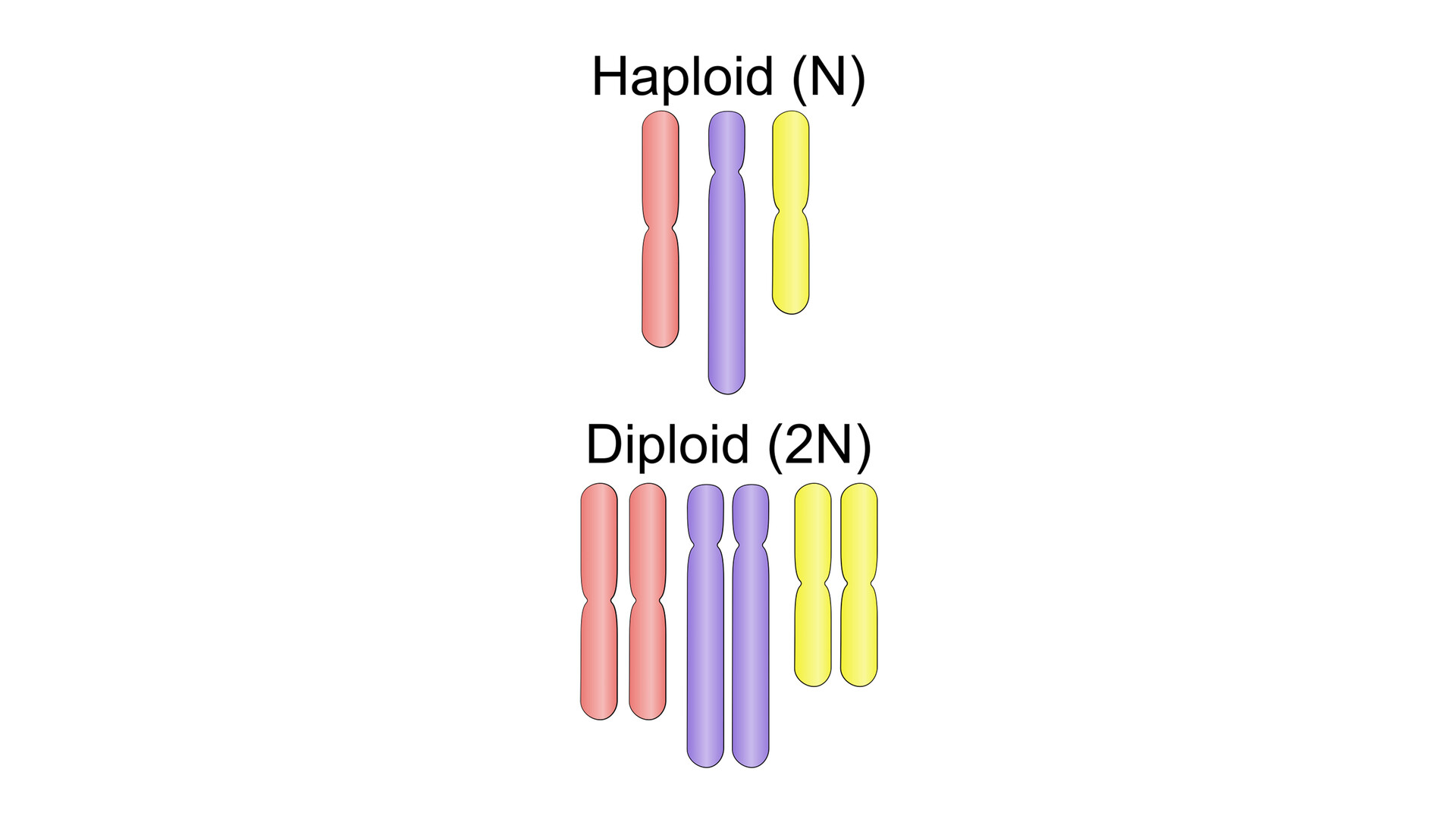
What is diploid?
The presence of two complete sets of chromosomes in an organism's cells, with each parent contributing a chromosome to each pair.
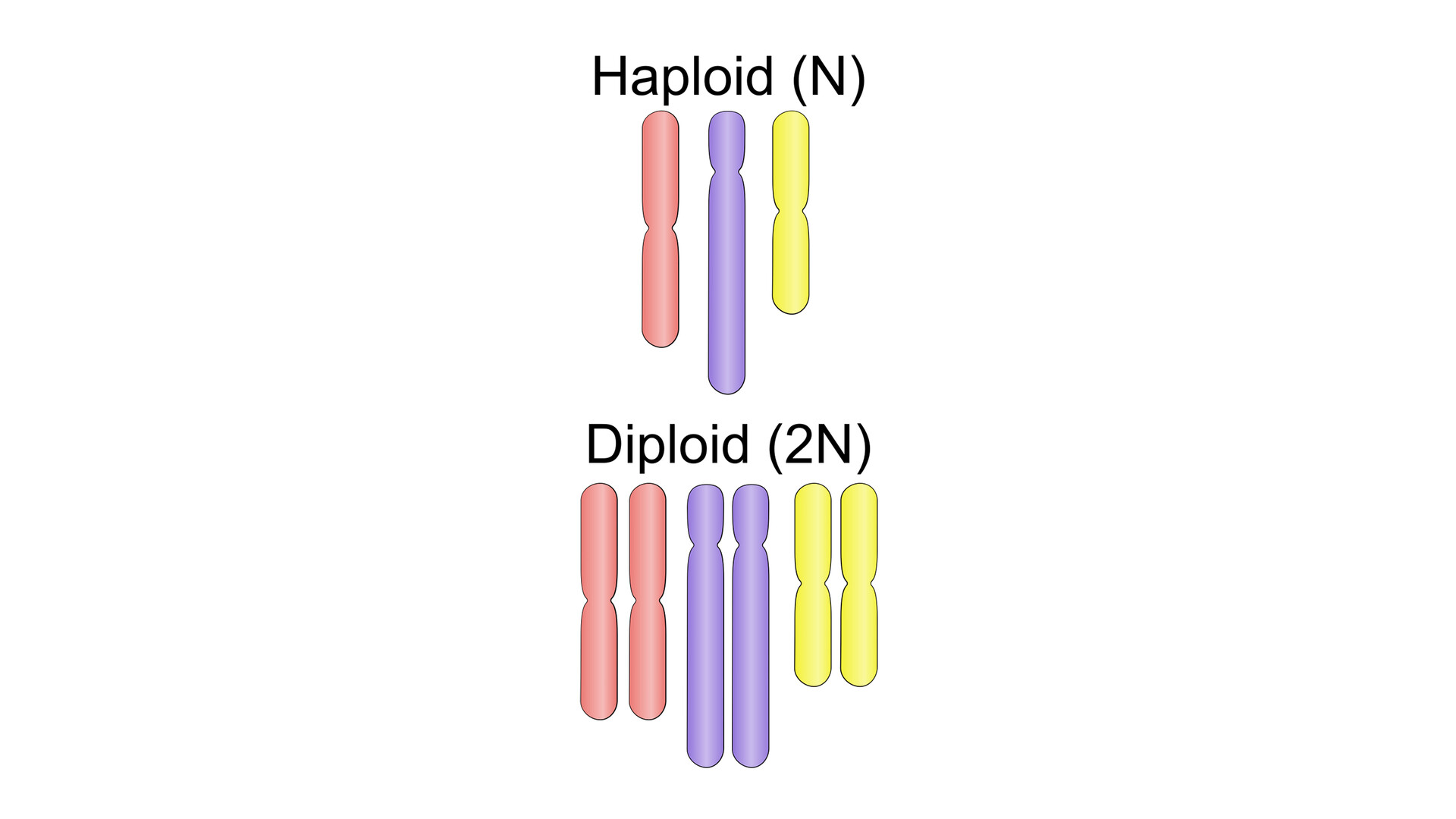
What is haploid?
The presence of a single set of chromosomes in an organism's cells.
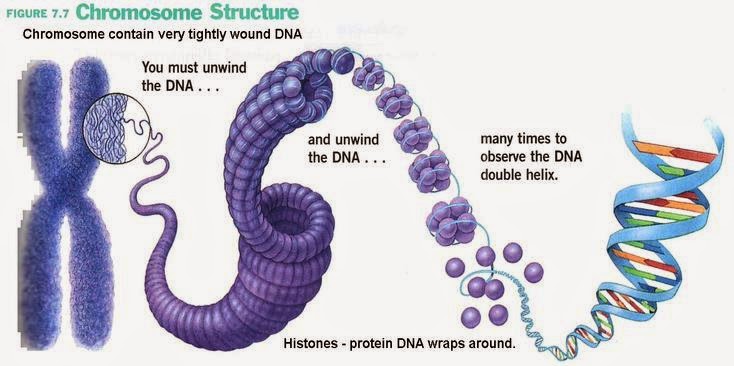
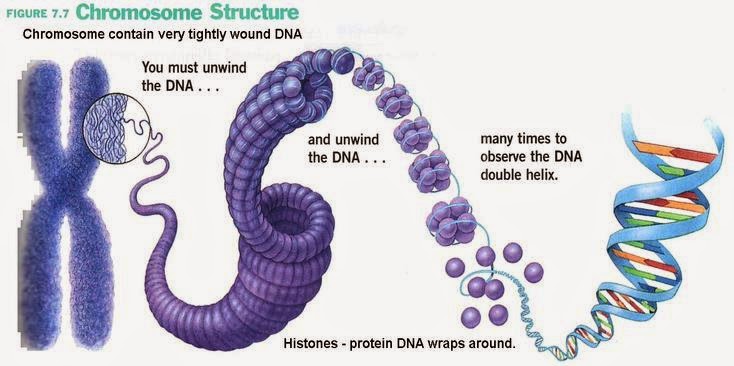
What is a histone?
A protein that provides structural support for a chromosome.
What is a karyotype?
An image of the chromosomes of an individual
What is a trisomy?
3 copies of one chromosome
How is DNA organized into chromosomes?
DNA wraps at regular intervals around proteins called histones (like a yo-yo or spool)
This spool is known as a nucleosome
Then it coils like an old phone cord
What are sex chromosomes?
Chromosomes determining the sex of an organism.
What are sister chromatids?
The identical, copied halves of a chromosome formed during DNA replication.
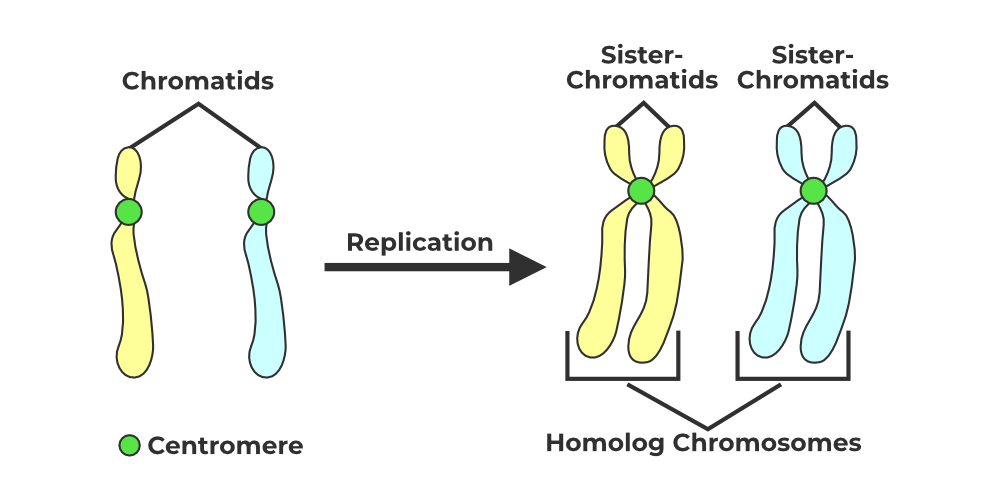
How are chromosomes arranged into order?
Size
Banding pattern
Location centromere
Size below/above centromere
What is DNA ligase?
An enzyme that seals remaining gaps in “new” DNA
What is DNA polymerase?
An enzyme that assembles new DNA strands, using parent strands as templates, in a 5’ to 3’ direction.
What is DNA replication?
The process of copying DNA so that each new cell receives a copy of the parent cell's DNA.
What is a DNA sequence?
The order of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine in a DNA.
What is hybridization?
The process of base pairing between 2 strands of DNA to form a double helix, and is driven by hydrogen bonding.
What is a primer?
A short DNA sequence that sets the base for DNA replication.
How is DNA replication semi-conservative?
semi- means half, and -conservative means to save. One strand of each DNA is parental (conserved) and the other is new.
What is a mutation?
A permanent change in the DNA sequence of a cell’s chromosome. Occurs when the proofreading and repair of DNA fails, so an error occurs.
What is differentiation?
When cells are different in form and function.
Is a one-way path
Once a cell is differentiated, most of it’s DNA has been turned off
For cloning, DNA has to be reprogrammed for it to be used.
What is a somatic cell?
Any cell of an organism other than reproductive cells (ex: blood cells, muscle cells, etc.)
What is reproductive cloning?
Researchers remove a mature somatic cell, such as a skin cell, from an animal that they wish to copy. They then transfer the DNA of the donor animal's somatic cell into an egg cell, that has had its own DNA-containing nucleus removed.
What did Griffith’s research discover?
Bacteria are capable of transferring genetic information through a process known as transformation. This paved the way for the discovery of DNA being the carrier of genetic information.
What did Watson and Crick discover?
Made the first 3D model of the structure of DNA, based on Rosalind Franklin’s research.
What did Chargaff discover?
Found that in DNA, the ratios of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine are equal.
What did Franklin discover?
Discovered the double helix structure of DNA.
What did Hershey and Chase research?
Proved DNA was the component that passes information from one generation to the next, by working with bacteriphage (a type of virus that infects bacteria)
What kind of structure is DNA organized into?
Chromosomes
What is the structure of a DNA nucleotide?
A sugar (deoxyribose,) a 3 phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing base.
What are the nitrogen-containing bases?
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
Is DNA parallel or an anti-parallel?
Anti-parallel
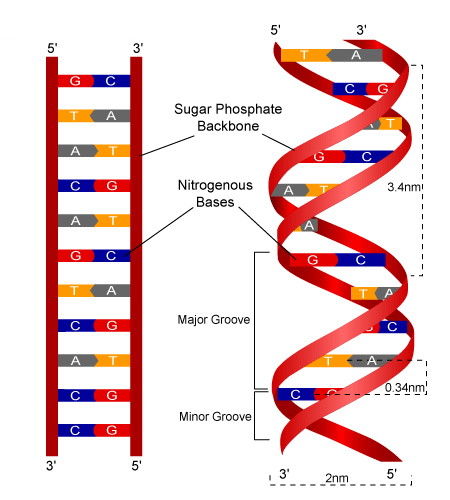
Labeling of a DNA strand:
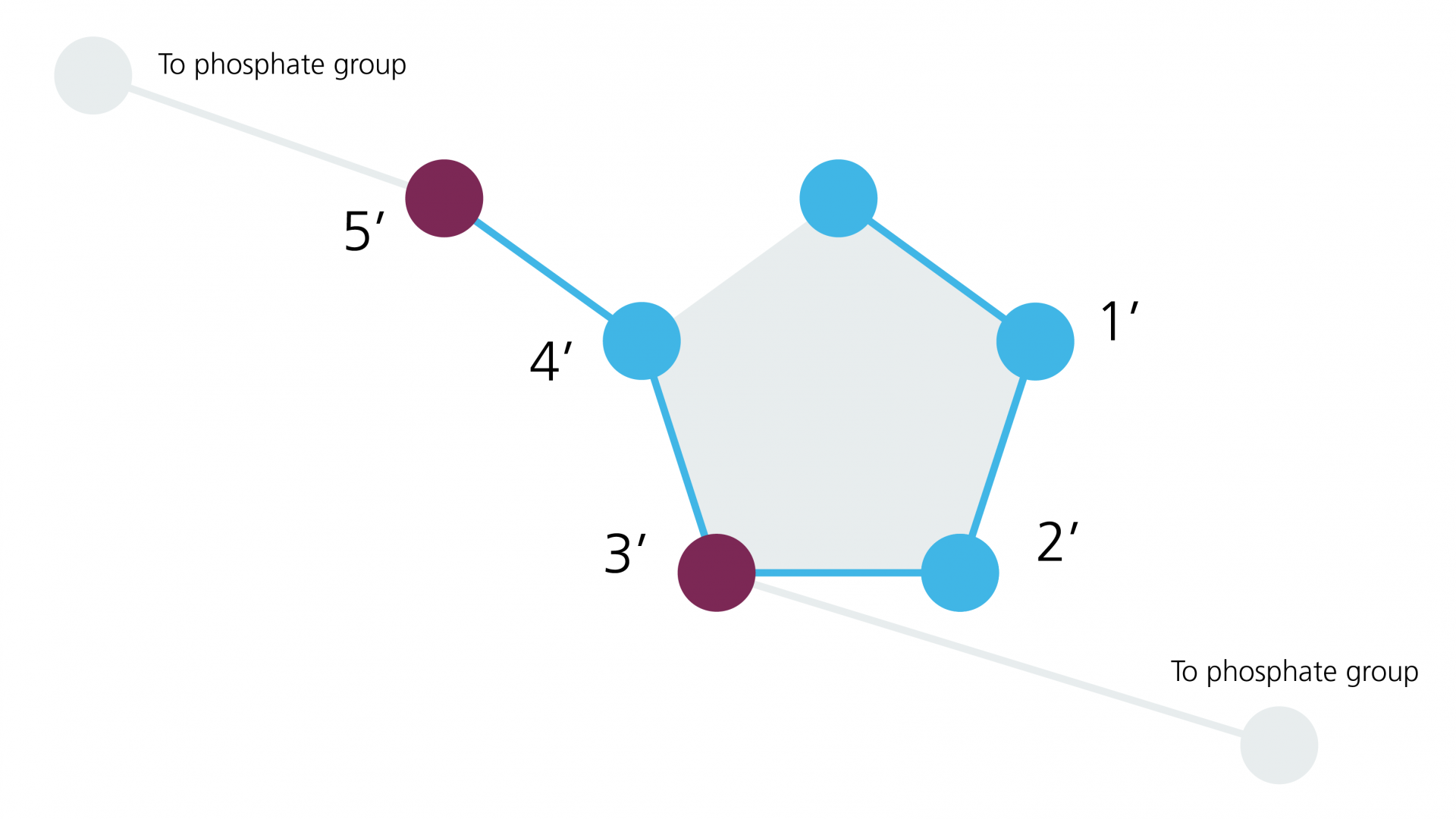
What is a monosomy?
Having only one copy of a chromosome other than the sex chromosomes.
What is Turner’s syndrome?
Having only one sex chromosome
What is Klinefelters syndrome?
Having an extra X chromosome in male individuals
What is Down syndrome?
Having an extra copy of chromosome 21
What is the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes?
Autosomes determine somatic traits and are the same in both males and females. Sex chromosomes contain the genes for sex determination and are different in males and females.
Steps of DNA replication:
Helicase unzips DNA
SSB proteins bind to DNA to prevent them from bonding back together, and Primase primes DNA with primers.
DNA polymerase builds new strands in 5’ to 3’ direction
Okazaki fragments occur, and Ligase glues the gaps between fragments.
Name the four main enzymes involved, and their functions.
Helicase: Unzips DNA
DNA Polymerase: Replicates DNA to build new strands
Primase: Makes primer to show where DNA Polymerase needs to start
Ligase: Glues DNA fragments together
How are directional synthesis and semi-conservative synthesis related to DNA replication?
Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. New DNA is made by enzymes called DNA polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize DNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
How do replication errors occur in DNA?
Most occur due to DNA polymerase working very fast. And, it cannot copy damaged DNA well.
What does most DNA polymerase do to help prevent mistakes?
They can proofread their work, and correct a mismatch by reversing the synthesis reaction to remove the mispaired nucleotide.
What can cause DNA damage?
Ionizing radiation from X-rays
Most UV light
Gamma rays
What happens when DNA gets damaged?
DNA breaks
Causes covalent bonds to form between bases on opposite strands
Fatally alters nucleotide bases
Causes adjacent nucleotide dimers (when two monomers interact with each other) to form
Are all mutations dangerous?
No, some give rise to variation in traits and evolution.
How SCNT (somatic cell nucleus transfer) works:
Undifferentiates a somatic cell by turning its unused DNA back on
An unfertilized egg’s nucleus is replaced the the nucleus of a donor’s somatic cell
The egg’s cytoplasm reprograms the transplanted DNA to direct the development of an embryo, which is then implanted into a surrogate mother.
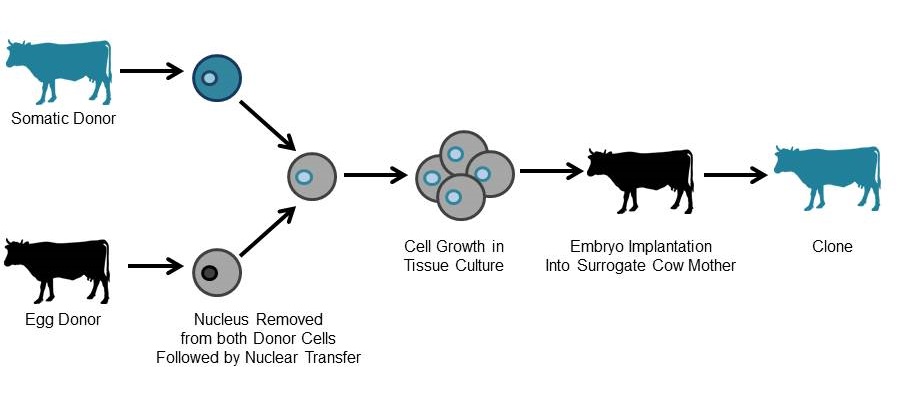
What is cloning?
To make an identical copy of something
What happens with an adult somatic cell during the cloning process?
It will not start dividing to produce an embryo because the cell has already differentiated (obtained unique characteristics)
How long is human DNA?
2 meters (6.5 feet)