Hand ATP (anatomy, physiology & technique)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Radius
Big bone in the forearm; running lateral to the body
Ulna
Small bone in the forearm; running medial to the body
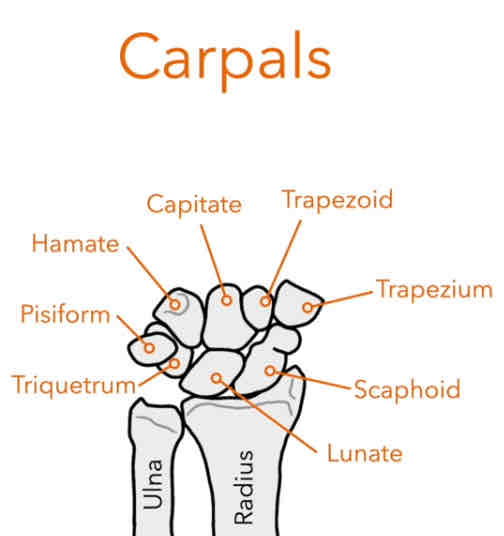
What is the name of the wrist bones?
Carpals
How many carpals bones do we have?
8
What acronym can be used to remember the carpal bones
S.L.T.P.H.C.T.T: So Long To Pinky, Here Comes The Thumb
•S- Scaphoid
•L- Lunate
•T- Triquetrum
•P- Pisiform
•H- Hamate
•C-Capitate
•T- Trapeziod
•T- Trapeizum
Flexor Retinaculum
A ligament that covers the anterior side of the carpal tunnel
Medial Nerve
A wrist/hand/forearm nerve that causes carpal tunnel syndrome when pinched
Metacarpals
Bones of the hand
How many metacarpals do we have?
5
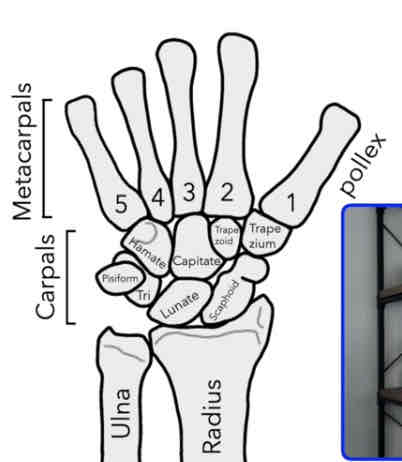
Phalanges
Bones of the fingers
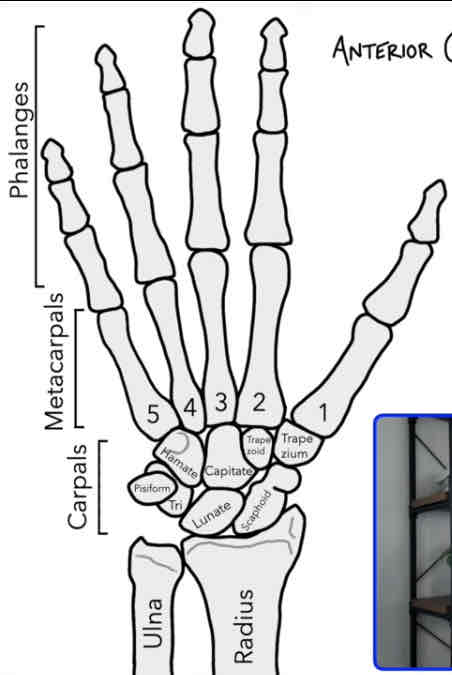
How many phalanges do we have in each finger?
3: proximal phalanx, middle phalanges and distal phalanges (tip of the finger)
How many phalanges does the thumb have?
2: proximal phalanx and distal phalanx
-no middle phalanx
Joints
Part of the body where two or more bones meet to facilitate movement.
Radiocarpal Joint (RC)
Between the radius and scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum.
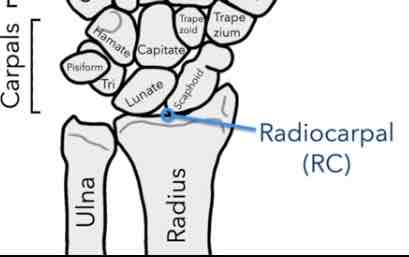
What type of Joint is a Radiocarpal joint?
•Condyloid joint: allowing two different degrees of motion (Flexion & Extension and Abduction & Adduction of the wrist)
•Synovial joint: wrist needs a lot of movement, also having articular cartilage (smooth lining) reducing the friction between the bone
-synovial fluid; acts further as a lubricant reducing more friction
Carpometacarpal Joint (CMC)
Between the carpals and metacarpals
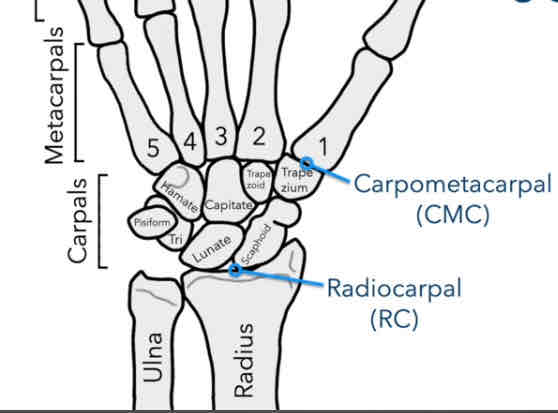
How many carpometacarpal joints do we have?
5
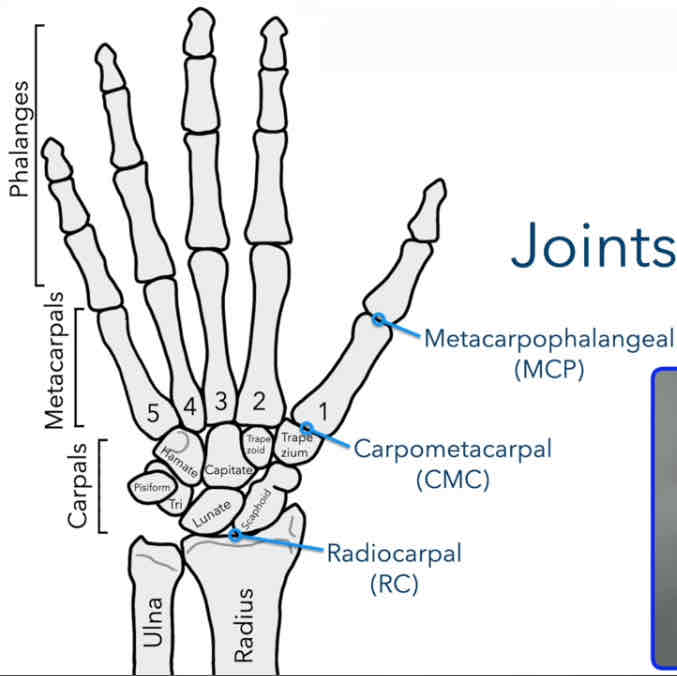
Metacarpophangeal Joint (MCP)
Between the metacarpals and phalanges (knuckles)
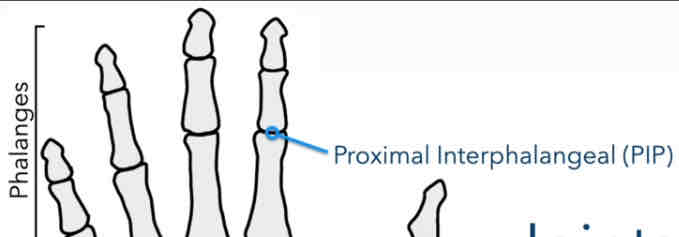
Proximal Interphalangeal Joints (PIP)
Between the proximal phalanges and middle phalanges
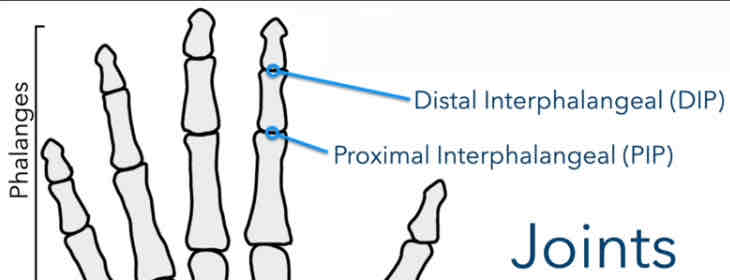
Distal Interphalangeal Joints (DIP)
Between middle phalanges & distal phalanges
Ligaments
Holds bone to bone
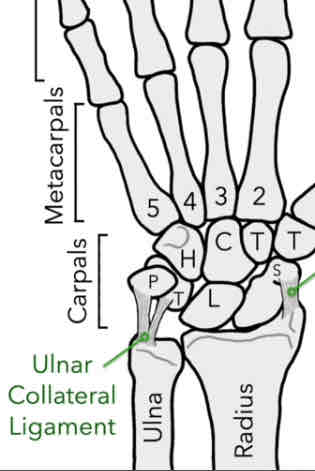
Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL)
Connects the end of the ulna bone to the pisiform and triquetrum
*prevents the bone from over-adduction
Palmer Radiocarpal Ligament (PRL)
Series of 4 ligaments; makes up PRL (anterior):
Radioscaphocapitate
Radioscapholunate
Long Radiolunate
Short Radiolunate
*prevents the hand from over-extension
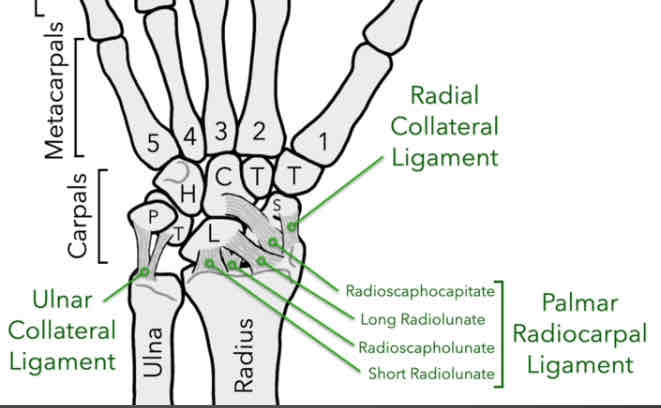
Radioscaphocapitate
Connects the distal end of the radius, moving up to the scaphoid bone and onto the capitate bone.
Radioscapholunate
Connects the distal end of the radius to the scaphoid and lunate bones.
Long Radiolunate
Connects the distal end of the radius to the lunate bone; taking a long pathway.
Short Radiolunate
Connects the distal end of the radius to the lunate bone; taking a short pathway
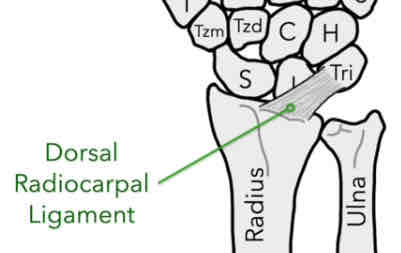
Dorsal Radiocarpal Ligament (DRL)
Connects the distal end of the radius to the triquetrum (posterior)
*prevents over-flexion of the wrist
Muscles of the Radiocarpal Joint
Flexorcarpiulnaris (FCU)
Flexorcarpiradialis (FCR)
Extensorcarpiulnaris (ECU)
Extensorcarpiradialis (ECR)
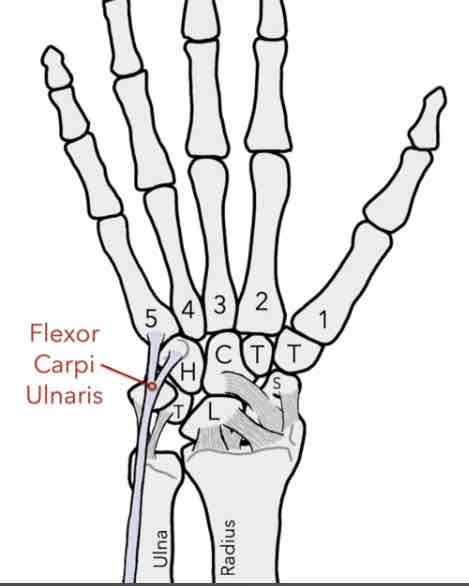
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris (FCU) Muscle
The Muscle connects to the hook of Hamate and the anterior side of the proximal base of the 5th MC.
-flexion and adduction
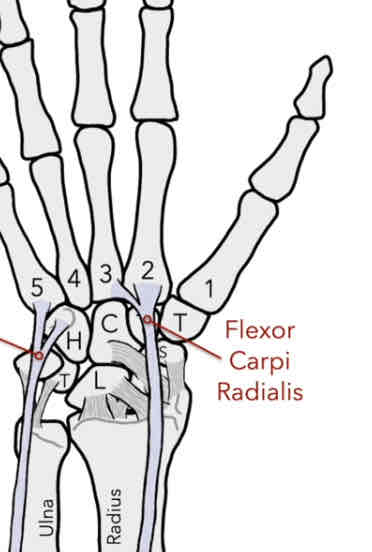
Flexor Carpi Radialis (FCR) Muscle
The muscle has an insertion on the anterior side of the proximal base of the 2nd & 3rd MC
-flexion and abduction
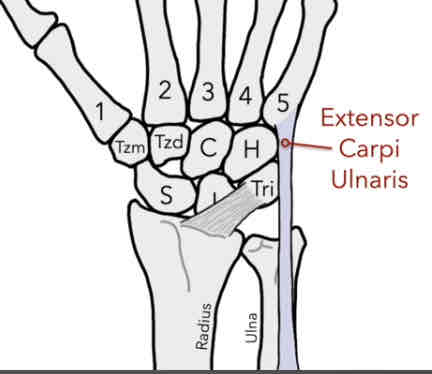
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris (ECU)
The muscles connects on the posterior side on the proximal base of the 5th MC (pinky finger).
-extension and adduction
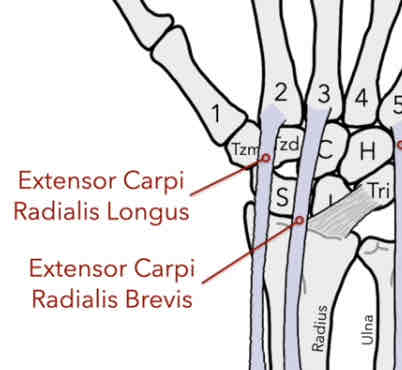
Extensor Carpi Radialis (ECR)
• Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis (ECRB)- muscle has insertion on the posterior side of the proximal base of the 3rd MC (middle finger)
-brevis: “short”
•Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus (ECRL)- muscle has an insertion on the posterior side of the proximal base of the 2nd MC (index finger)
-longus: “long”
-extension
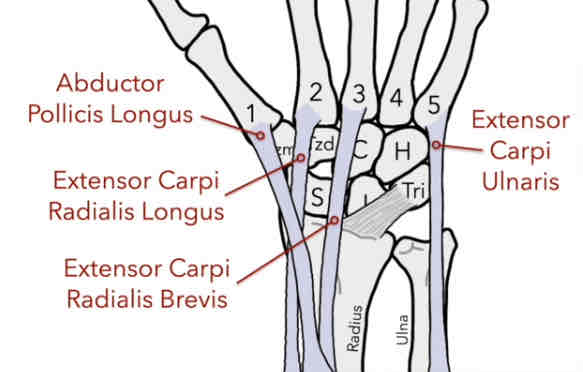
Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL)
The muscle has an insertion to the posterior side of the proximal base of the 1st MC (thumb)
-extension and abduction
Pathological fractures
Occur when force or impact didn’t cause the break to happen; an underlying disease leaves the bones weak and brittle
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
A pinched nerve in the wrist that can cause pain, numbness and swelling in the fingers.
Arthritis
Joint inflammation; which is caused by wear and tear (gout) as a result of buildup of uric acid