Structures Sem 1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1 N/mm² =
1 MPa (mega pascal)
Moment of resistance formula (engineer’s theory of bending)
M/I = σ/y
M = σZ
Elastic section modulus formula
Z = I / y
2nd moment of area for a rectangle
I = bd³/12, where b is the base and d is the height.
z = I / y, how do we find I?
ΣIcc + ΣAh2 , where A is the area of the sections and h is the distance from the centroid to the neutral axis.
How to find position of the neutral axis / centroid
ȳ = Σ(Ay) / ΣA, where A is the area and y is the distance of the centroid of the section from the reference axis.
Moment of resistance equation for rectangular section unsimplified
M = (σmax bd2) / 6
because equation is M / I = σmax / y, rearrarange for M and we know that for a rectangle:
I = bd3/12, max y = d/2, so equation becomes:
M = (σmax) (bd3/12 ÷ d/2)
M = (σmax) (bd3/12 × 2/d)
so M = (σmax bd2) / 6
Moment of resistance formula for simply supported beam (max bending moment)
M = wL² / 8, where w is the uniform load and L is the span length.
Moment of reisitance formula for cantilever beam (max bending moment)
M = wL² / 2, where w is the uniform load and L is the length of the cantilever.
Equation of max shear force for simply supported beam
V = wL / 2, where w is the uniform load and L is the span length.
Equation of max shear force for cantilever beam
V = wL, where w is the uniform load and L is the length of the cantilever.
Standard timber sizing lengths
100, 125, 150, 175, 200, 225 mm
Sagging
+ve bending: compression at top, tension at bottom
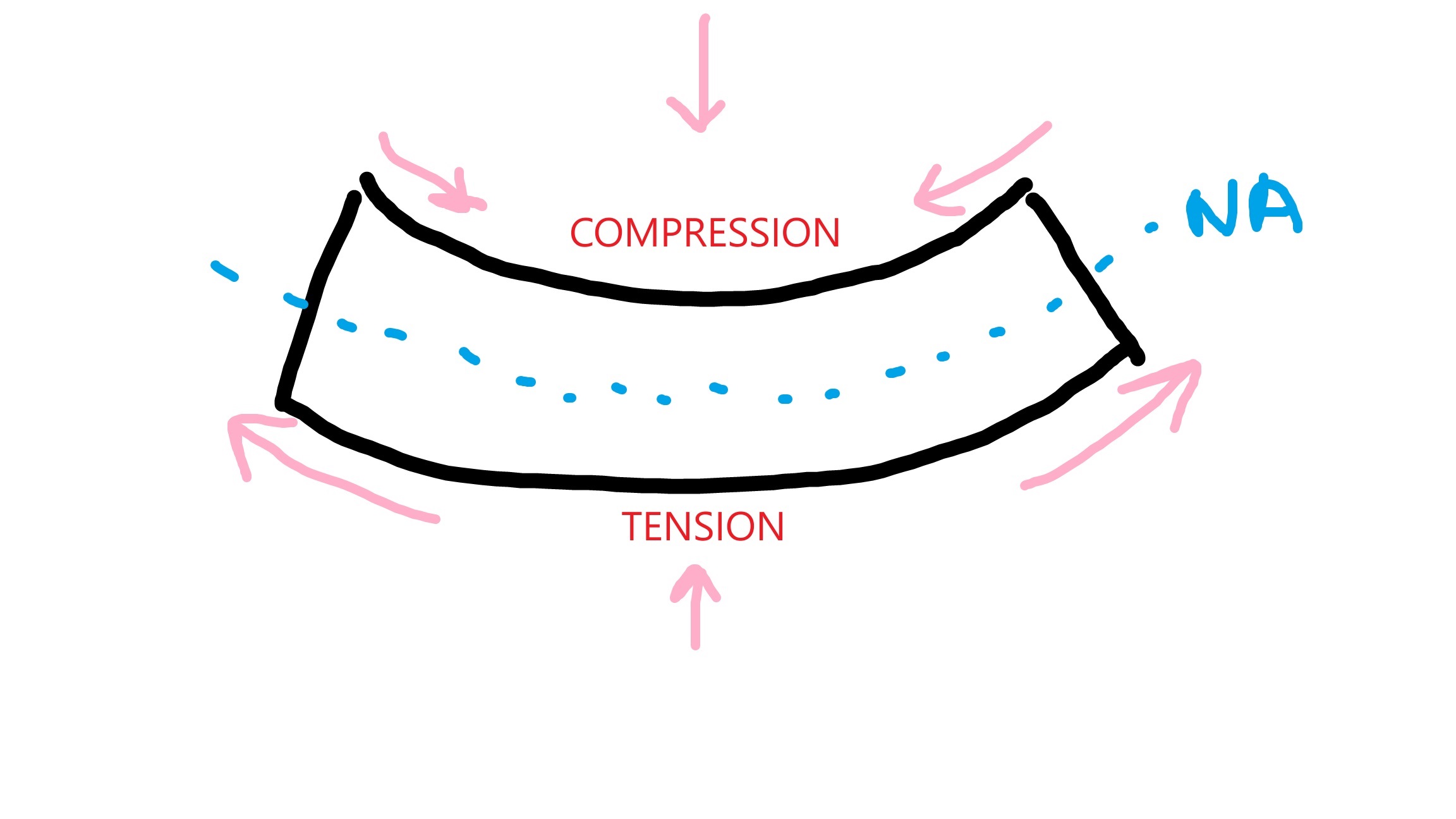
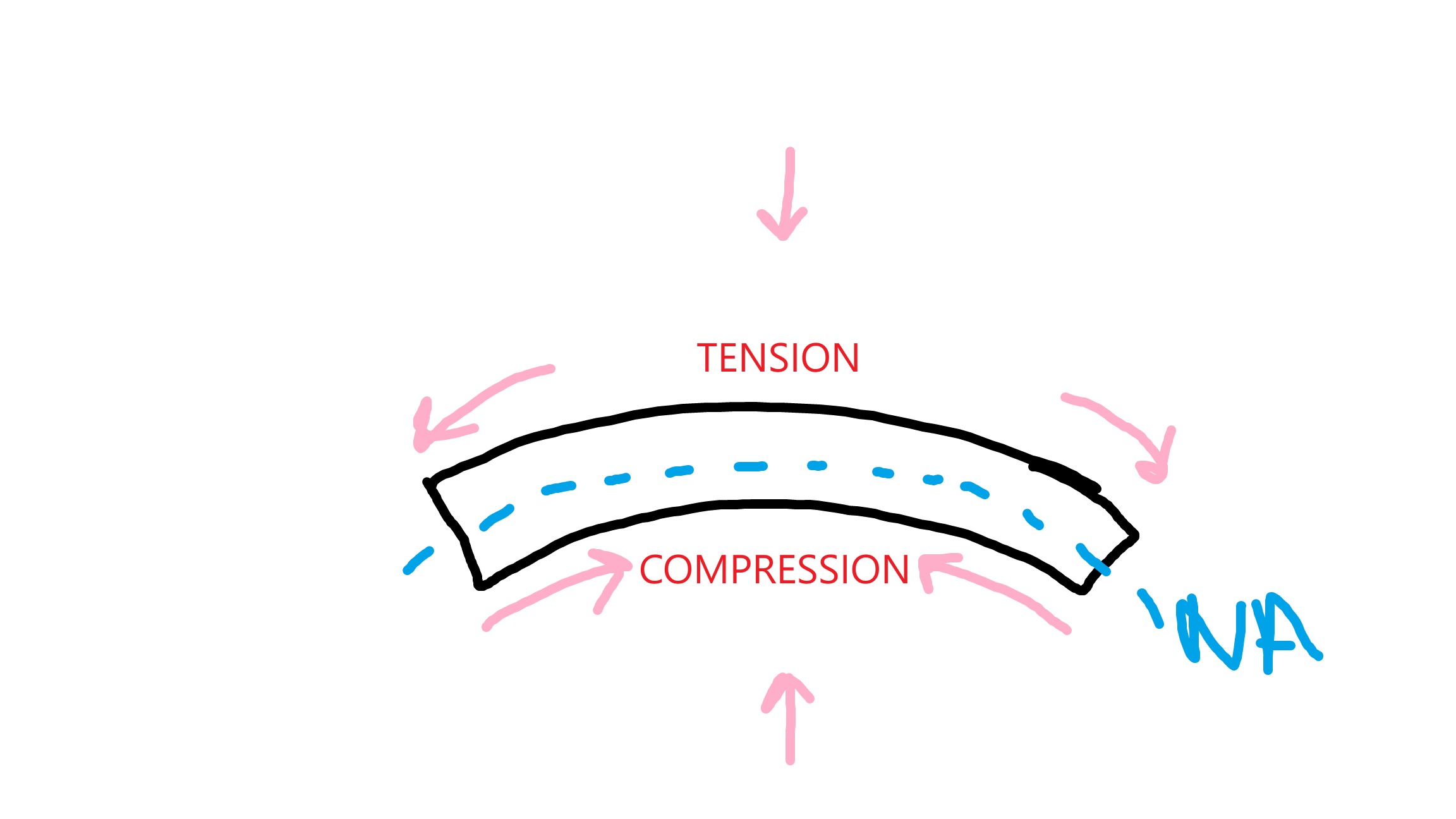
Hogging
-ve bending: tension at top, compression at bottom
Newton’s first law
An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net external force.
Newton’s second law
F = ma
Change in momentum is equal to the net force applied to an object over time.
Newton’s third law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction
Reactions at roller
1
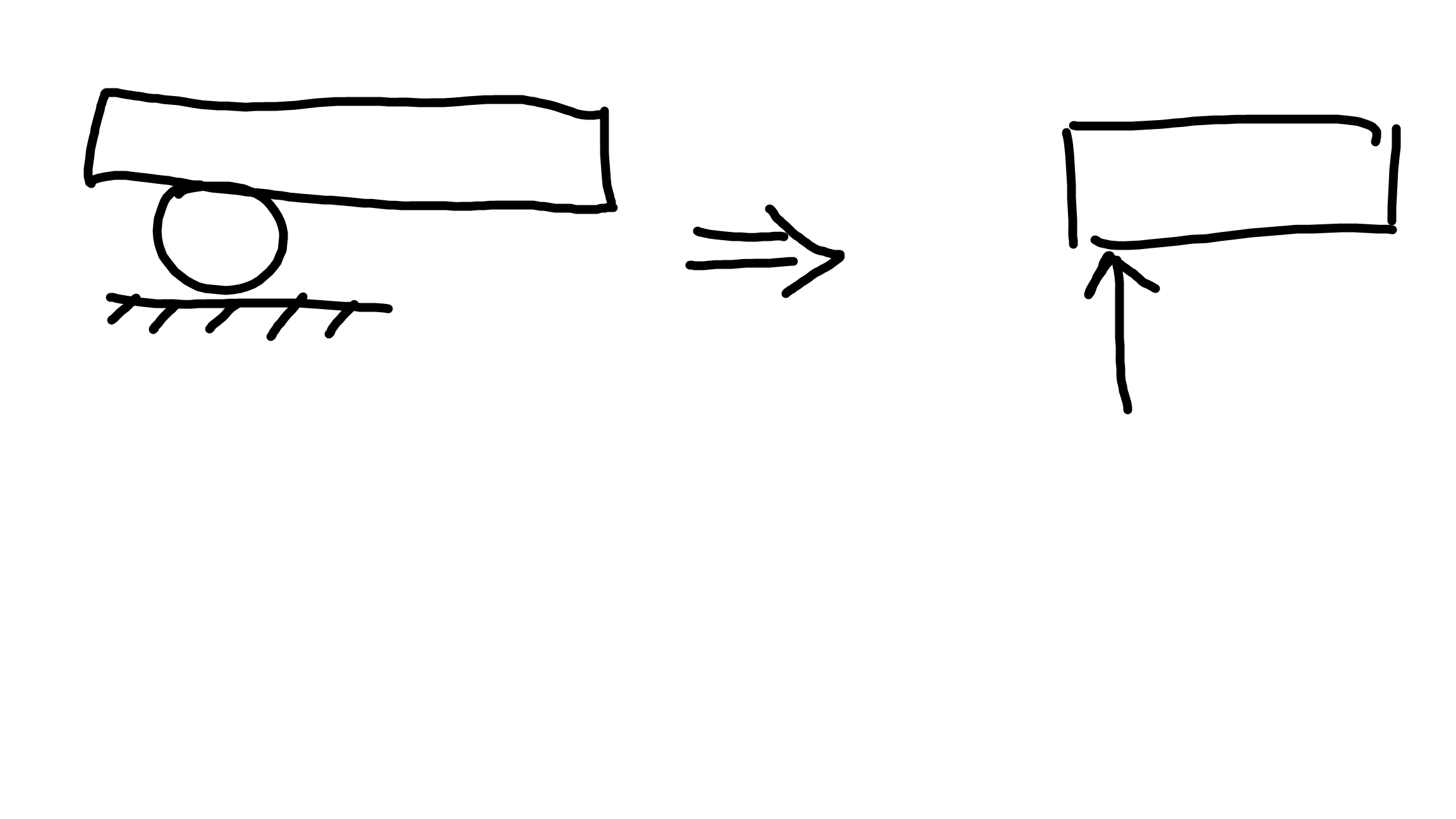
Reactions at hinge (external pin)
2
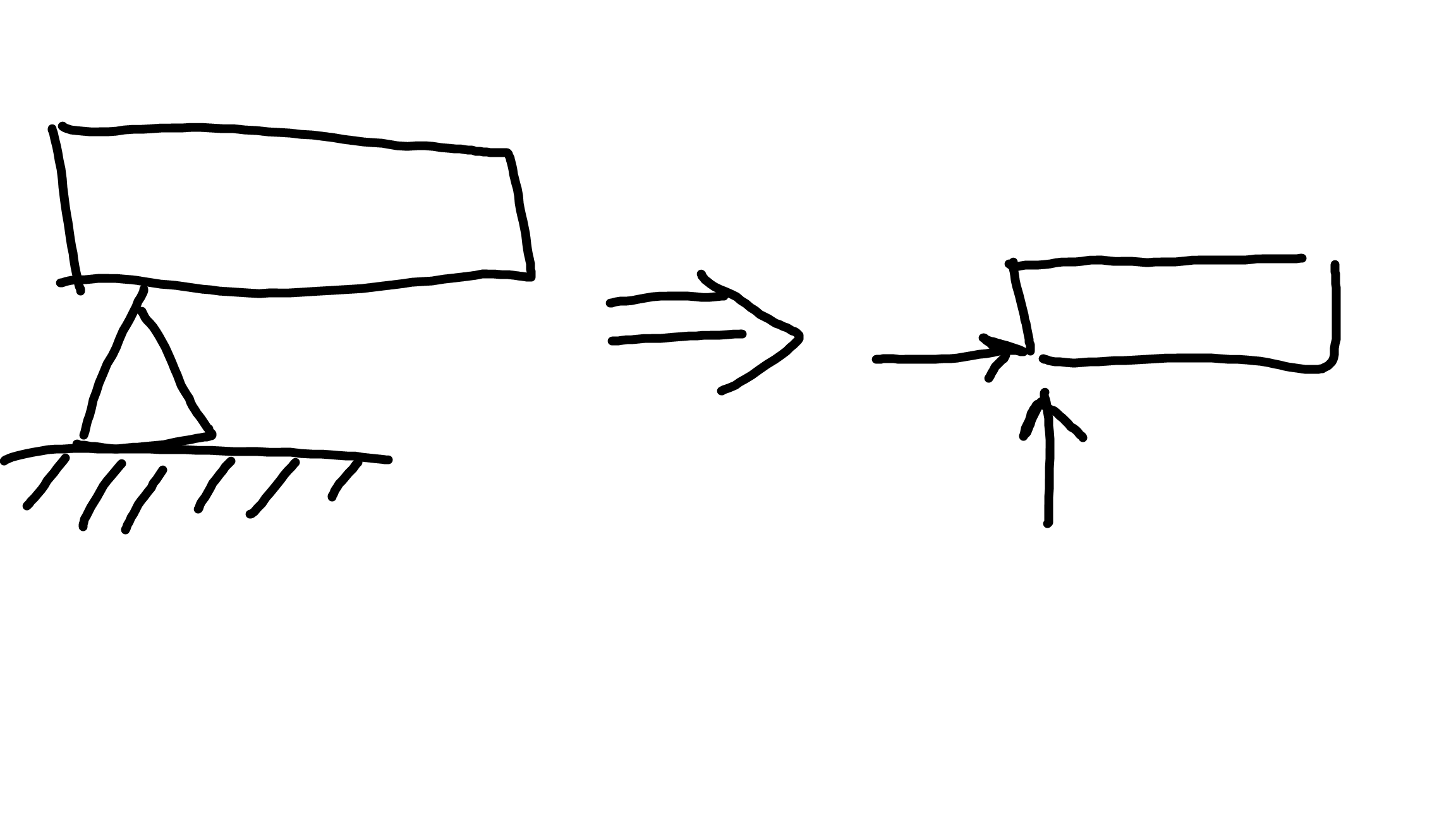
Reactions at encastre
3
Reactions at link
1
Young's Modulus Equation
Stress / Strain
E = σ / ε
Stress equation
σ = F / A
Strain equation
ε = ΔL / L
Shear force definition
The unbalanced force in a beam acting perpendicular to the primary axis
Poisson's Ratio definition
The ratio of lateral to longitudinal strain
What is the limit of proportionality
The point at which stress is no longer proportional to strain in a material which obeys hookes law - it has gone past its elastic limit
Modulus of elasticity definition
Ratio of direct stress to direct strain
When drawing a shear force diagram, when would we use a vertical jump vs a sloping line for change in shear?
Vertical jump = for point loads
Sloping line = for UDLs (uniformly distributed loads, the ones kN/m lots of arrows)
Point of contraflexure meaning
Point where the resultant bending moment is zero
Equation for number of degrees of freedom
2j (2 × number of joints)
Equation to know if structure is statically determinate
m + r = 2j (m = number of members, r = number of reactions, j = nodes / joints)
Centroid definition
The center of mass / gravity of a structure
Reason for calculating 2nd moment of area
Characterises the deflection of a shape under load
Bending moment definition
The internal force that occurs in a structure when an external force bends the structure
Elastic section modulus definition
A measurement of how much a beam can bend without breaking
It is a ratio of the second moment of area to the distance from the neutral axis to the outer fibers
Description of tension failure in reinforced concrete
Failure only occurs after large deflections of beam because the concrete is weak in tension but the steel will yield when subjected to excessive stress
Description of compression failure in reinforced concrete
Failure will be sudden without warning because concrete resists compressive stresses however concrete is brittle
Description of shear failure in reinforced concrete
Sudden failure and often fails at a very low load