patho (immunity)
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Universal experience,
results from positive (wedding)or
negative(death) experiences
stress
stress is a body response to
change
stress can ________ impact homeostasis
negatively
what are the 3 stages of the stress response
-Alarm stage (fight or flight)
- Resistance stage (cortisol goes to normal, fight or flight goes down)
- Exhaustion stage (if the stressor is not removed and stays prolonged, super bad 4 u)
experiencing a stressor over and over again can cause
desensitization
_______- _________ syndrome: Confines damage to one area
Local adaptation
Stress conditioning factors:
genetics, age, gender, history,
and support
maladaptive rxns to stress
alcohol, drugs, overeating, oversexual, gambling
what effects can stress have on the resp system? (3)
-asthma
-hay fever
-increased respiration
what effects can stress have on the endocrine system? (2)
-diabetes melitus
-hyperglycemia
what effects can stress have on the genitourinary system? (5)
-diuresis
-frigidity
-impotence
-irritable bladder
-menstrual irregularity
what effects can stress have on the GI system? (5)
-diarrhea
-gastritis
-irritable bowel syndrome
-nausea and vomiting
-ulcerative colitis
what effects can stress have on the cardiovascular system? (4)
-stroke
-coronary artery disease
-heart rate and rhythm disturbances
-hypertension
what effects can stress have on the nervous system? (8)
-anxiety
-depression
-fatigue
-insomnia
-loss of motivation
-nervous tic
-neuropsychological manifestations
-overeating
what effects can stress have on the immune system? (3)
-autoimmune disease
-immunodeficiency
-immunosuppression
what effects can stress have on the integumentary system? (5)
-acne
-eczema
-hair loss
-neurodermatitis
-psoriasis
what effects can stress have on the musculoskeletal system? (4)
-inflammatory disease of connective tissue
-tension headache
-muscle contraction backache
-Rheumatoid arthritis
our body is constantly under assault by
microbes
our immune system is self-________ and self-___________.
this means it must be able to distinguish self from nonself
regulated and self-limiting
What are the two key activities of the immune system?
defense and attack
Innate immunity is
first line of defense
which immunity is nonspecific but immediate: recognizes nonself but not specific pathogens
Innate
is innate immunity completely impenetrable?
no not completely... cut on ur skin, can even have small tears in GI lining
which immunity type includes skin and mucous membranes, chemicals, and microbiome
Innate
what raise your body temp?
Pyrogens
if Innate Immunity is step 1, is step 2
Adaptive Immunity
___________ immunity is when your body made it's own antibodies and it can take 7-10 days
active
___________ immunity is when you get antibodies from somewhere else, such as from pregnant mother when a baby
passive
giving ur own blood before surgery and receiving it back after is an example of what type of transplant?
Autologous
Hyperacute tissue rejection happens in
first 3 days
Type 1 Diabetes, Lupus, and Rheumatoid Arthritis are examples of _____________ diseases
Autoimmune
what is an example of a stressor that can exacerbate Lupus?
pregnancy
you are more likely to get sick when
stressed
Mr. Pierce is 45 years old and holds a high-stress job in the financial sector. He complains to
an examining nurse practitioner about frequent headaches, difficulty sleeping, and seeming
always to be coming down with a cold. Mr. Pierce wonders if the nurse could "give him
something" for these problems.
Mr. Pierce is single, has no children, and is a self-described workaholic. He takes an occasional
walk on the weekends but otherwise has no regular physical exercise. He smokes several cigars
a day. He said his diet is pretty much whatever the nearest restaurant is serving. He does not
take any medication but admitted to "occasionally" smoking marijuana. His weight is
appropriate and his physical examination is unremarkable.
Lab work is ordered, but even without it, the nurse is fairly certain about the cause of Mr.
Pierce's headaches, insomnia, and infections
What is Mr. Pierce most likely experiencing?
A. Hypersensi
C. The stress response
Hypersensitivity reactions are AKA
allergic reactions
what cells get triggered during an inflammatory response in Innate Immunity?
mast cells
_________ immunity is nondiscriminatory and has the same response sequence regardless of cause of whether it is local or systemic.
Innate
the acute phase of innate immunity happens...
immediately after injury until the threat is eliminated
during the ________ phase of innate immunity, vasodilation and vasoconstriction, phagocytosis, and fibrinogen occur
acute
during the ________ phase of innate immunity, granulomas and granulation tissue form
chronic
the chronic phase of innate immunity happens if...
if acute phase does not resolve issue. then chronic phase will last till healing is complete
the _________ phase of innate immunity often occurs in the presence of resistant organisms
chronic
Pyrogens are released when exposed to
bacteria
_____________ cause a systemic inflammatory response (fever) which can be life-threatening
Pyrogens
Pyrogens make an unfavorable environment for __________ proliferation
bacterial
Interferons are released from _________ cells, and then bind to ___________ cells
virus-infected;
uninfected
interferons are like little shields released by the infected/dying cell given to protect it's uninfected buddies .... interferons stop virus from replicating when entering uninfected cells
kk
when interferons are released during a viral attack, they bind to uninfected cells and...
release an enzyme that prevents viral replication
plasma proteins enhance ___________
antibodies
complement proteins are a type of
plasma protein
complement proteins are activated by
antigens
since they are a type of plasma protein, complement proteins do what during an immune response?
they enhance antibodies
Complement proteins are found in which type of immunity?
innate
__________ immunity is also known as acquired defenses, and it pursues that which escapes ________ defenses
adaptive; innate
adaptive immunity is specific to organisms, meaning...
it has memory that develops over time
____________ immunity is used to distinguish self from nonself and between each pathogen
adaptive
cellular immunity, meaning antigens are targeted to be destroyed, is found in _________ immunity
adaptive
humoral immunity, which means antibodies are produced against an antigen, is found in _____ immunity
adaptive
helper T cells and suppressor T cells are __________ cells
regulator
effector T cells are
cytotoxic killer T cells
4 types of T cells:
Cytotoxic T cells
Helper T cells
Suppressor T cells
and ?
regulator T cells
helper T cells and suppressor T cells
where are regulator T cells and effector T cells produced? where do they mature?
produced in bone marrow
mature in thymus
which immune cells would be found in a patient with cancer, viruses, hypersensitivity, or transplant rejection?
T cells
Cellular immunity (which directly destroys the antigen) has to do with _______ cells.
Humoral immunity (which produces antibodies against an antigen) has to do with _______ cells
T cells;
B cells
which cells produce antibodies 72 hours after initial exposure?
B cells: memory B cells and immunoglobulin (aka Ig aka means antibody) secreting B cells
which type of immunity destroys the antigen?
which type of immunity makes antibodies against the antigen?
destroys: cellular immunity
antibodies against: humor immunity
immunoglobulin-secreting cells are ____ cells
B, remember immunoglobin means antibodies
which type of cells ensure a quicker response to same antigen in the future?
memory cells!
__________ immunity (antibodies) is found in active and passive acquired immunities
Humoral
LIFESPAN IMMUNITY
1. Immunity in infancy is based on maternal ______for ________ months, granting temporary passive immunity
2. breastfeeding transfers ______ antibodies
3. which of these can a newborn's immune system respond to?
-protein antigens
-polysaccharides
-glycoproteins
and their immune functions are limited
4. In adolescence, hormonal changes impact the immune system since B cells and macrophages have _____ _____ this () risk for autoimmune and inflammatory disorders
5. __________ _____________ means the sexes respond
differently to infection/vaccination
6. ______ decreases immune response in immune senescence these changes are multifactorial meaning have multiple causes
7. during _________ _______ there is lower B- and T-cell production, but increased apoptosis of these cells
8. Comorbidity significantly impacts immunity and autoimmune disorders become more likely due to...
1. IgG; 3 to 6
2. IgA
3. only protein antigens
4. hormone receptors, increases
5. immune dimorphism
6. age
7. immune senescence
8. misinterpretation of signals flooding body bc comorbidity
Many newborn immune functions are ________ and antibodies transferred to them maternally have low affinity
limited
Risk for inflammatory and autoimmune
diseases increases when?
in adolescence
Because B cells and macrophages have hormone changes
__________ _____________ means the sexes respond
differently to infection/vaccination
immune dimorphism
______ decreases immune
response in immune
senescence
Age
Age-related immune system changes are ____________
multifactorial
during _________ _______ there is lower B- and T-cell production, but increased apoptosis of these cells
immune senescence
the simultaneous presence of two or more diseases or medical conditions in a patient
Comorbidity
Comorbidity (multiple diseases/conditions at once) significantly impacts immunity and autoimmune disorders become more
likely due to...
misinterpretation of signals flooding the body
3 malfunctional/altered immune responses
1. exaggeration (hypersensitivity
2. misdirection (autoimmune
3. diminution (immunodeficiency
okay
type 1-4 helpful chart
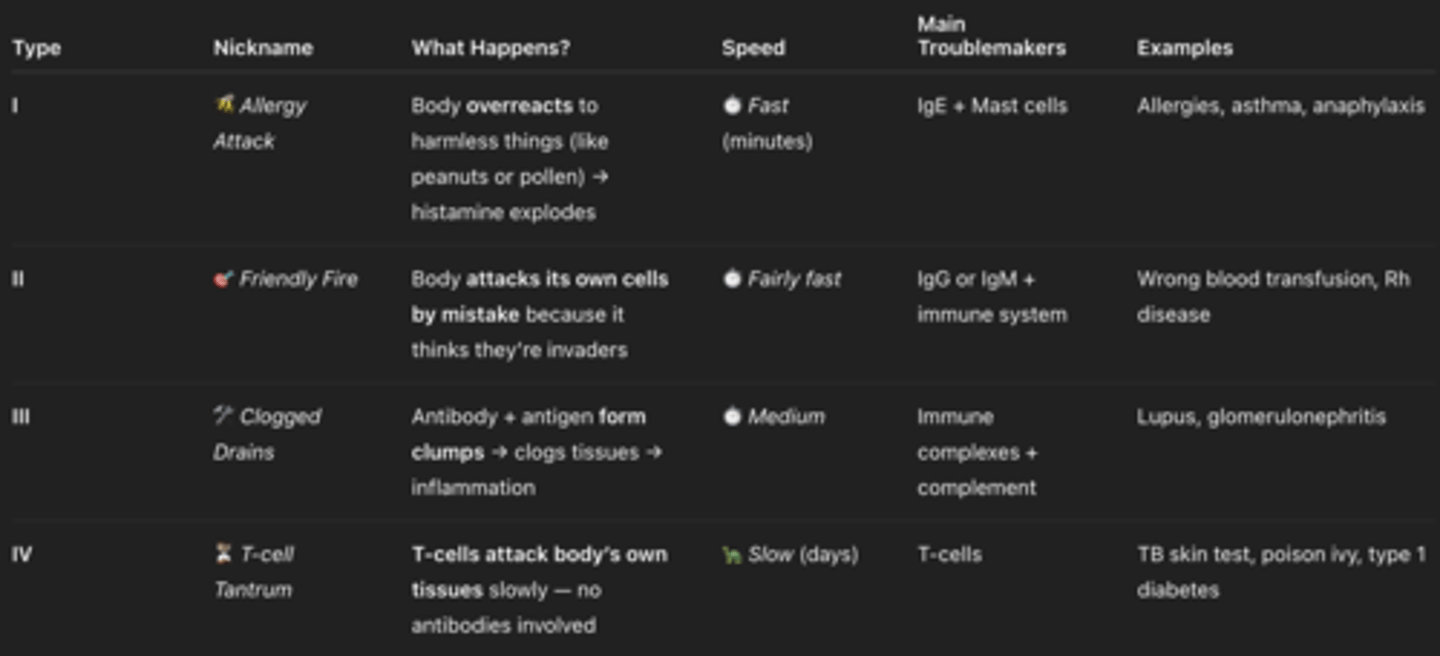
Type I Hypersensitivity is exaggerated mediated by () usually triggered by harmless causes immediate inflammation and pruritus (itching), usually needs more stimulus for bigger rxn , super bad worst case of type 1 rxn is called (anaphylaxis)
IgE antibodies
Type II Hypersensitivity is mediated by
IgG or IgM antibodies. host cells are damaged due to antibodies binding to cell surface. cell lysis and phagocytosis. EXAM.... EX OF TYPE II INCLUDE BLOOD TRANSFUSION RXN AND ERTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS
Type III Hypersensitivity is mediated by
immune complexes (combining of antigen-antibody complexes activates complement system) antibody excess but relatively low conc of the antigen. ex lupus
on test... lupus is an autoimmune disorder
kk
Type IV Hypersensitivity is mediated by
cell-mediated T cells. 2 phases: initial phase triggered by primary contact . effector phase each next exposure
Definition/Mechanism of Action for Type I Hypersensitivity
T-helpers stimulate B cells to produce IgE.
IgE sensitizes mast cells and basophils
Type ____ Hypersensitivity can be local or systemic and requires repeated exposure to large doses of allergen
I
Type III Hypersensitivity can be local or systemic. true or false?
true
Type ___ Hypersensitivity is immediate
I
Type ___ Hypersensitivity is usually* immediate
II
which Hypersensitivity types are delayed?
Type III and IV
which Hypersensitivity type targets a single cell?
Type II
Type II Hypersensitivity is known as
cytotoxic hypersensitivity
Definition/Mechanism of Action for Type II Hypersensitivity
IgG or IgM antibodies
bind to antigen on
individual's own cells,
triggering antibody
production in
macrophages
Definition/Mechanism of Action for Type III Hypersensitivity
Circulating antigen-
antibody complexes
accumulate in tissue,
triggering inflammation.
Definition/Mechanism of Action for Type IV Hypersensitivity
Cell-mediated (T cells) find
antigen presentation and release
cytokines.
This causes severe tissue
injury, and fibrosis
which type of Hypersensitivity has 2 phases? what are these 2 phases?
Type IV
sensitizing and effector (first phase body is like oh u exist memory cell remember this one , 2nd phase is when it comes back those memory cells recognize it now and attack)
Rheumatoid arthritis is which Hypersensitivity?
Type III
A patient's immune system reacting to a Tuberculin test is which Hypersensitivity type?
Type IV