Perception of Size and Depth in Visual Processing
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Pictorial (monocular) cues
Cues that provide depth information using a single eye, including occlusion, relative height, relative size, perspective convergence, familiar size, atmospheric perspective, texture gradient, and shadows.
Motion cues
Cues that provide depth information based on motion, including motion parallax, deletion, and accretion.
Binocular cues
Cues that provide depth information using both eyes, allowing for stereopsis.
Stereopsis
The perception of depth that arises from the brain's processing of the slightly different images received from each eye.
Binocular rivalry
A phenomenon that occurs when each eye is presented with a different image, leading to a competition between the two images for perception.
Monocular rivalry
A phenomenon where two different images are presented to the same eye, leading to a competition for perception.
The Size-Distance equation
A formula that relates the perceived size of an object to its distance from the observer.
Illusions of depth and size
Visual phenomena where the perceived depth or size of an object does not correspond to its actual dimensions.
Occlusion
A pictorial cue where an object that is partially blocked by another object is perceived as being farther away.
Relative height
A pictorial cue where objects positioned higher in the visual field are perceived as being farther away.
Relative size
A pictorial cue where objects that are smaller in size are perceived as being farther away.
Perspective convergence
A pictorial cue where parallel lines appear to converge as they recede into the distance.
Familiar size
A pictorial cue that uses knowledge of the typical size of objects to judge their distance.
Atmospheric perspective
A pictorial cue where distant objects appear hazier and less detailed than closer objects due to the atmosphere.
Texture gradient
A pictorial cue where the density of texture elements increases with distance, indicating depth.
Shadows
A pictorial cue where the presence and direction of shadows provide information about the position and distance of objects.
Motion parallax
A motion cue where objects closer to the observer appear to move faster than objects that are farther away.
Deletion & accretion
Motion cues that involve the gradual occlusion (deletion) and revelation (accretion) of objects as the observer moves.
Accommodation
An oculomotor cue that refers to the adjustment of the eye's lens to focus on objects at different distances.
Convergence
An oculomotor cue that refers to the inward movement of the eyes when focusing on a nearby object.
Rebounding bias
The tendency to perceive motion as rebounding or reversing direction after an initial movement.
Relative size
If two same-size objects appear different size, the one that appears smaller is farther.
Relative height
Below horizon: Objects with higher base are farther. Above horizon: Objects with lower base are farther.
Perspective convergence
Parallel lines of the road appear to converge as they get farther.
Familiar size
Knowing the relative sizes of familiar objects can help resolve which one is closer.
Atmospheric perspective
Far away objects are dimmer and bluer due to particles in the atmosphere.
Texture gradient
Texture patterns shrink as they get farther away.
Motion parallax
A depth cue that involves the apparent motion of objects as the observer moves.
Binocular disparity
Difference between the images on the left and right eyes.
Corresponding points on the retinas
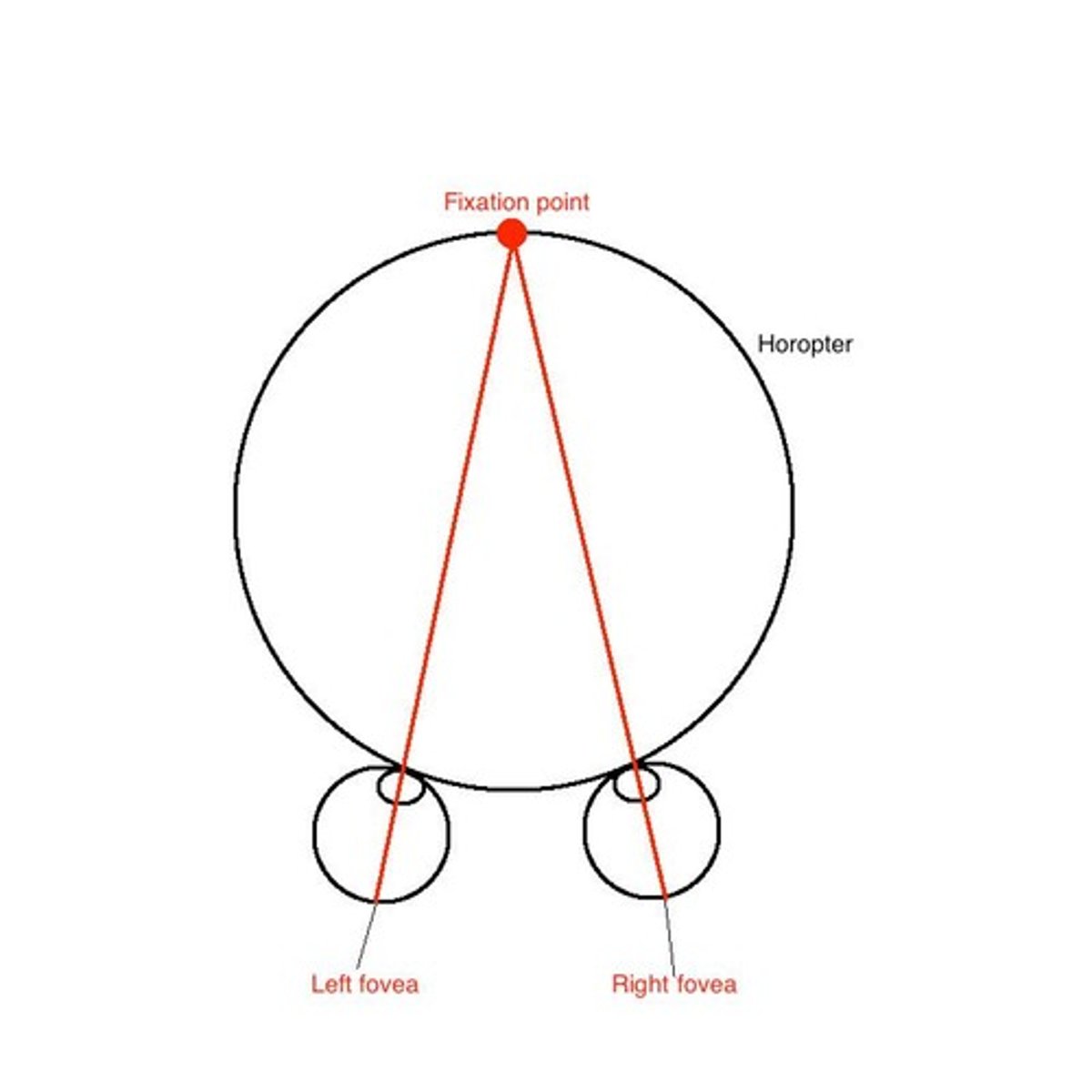
When we converge on an object, the object falls in the same place on the two retinas; namely, on the foveas.
Horopter
The set of points in the visual scene that project to corresponding points on the two retinas (given a certain fixation).
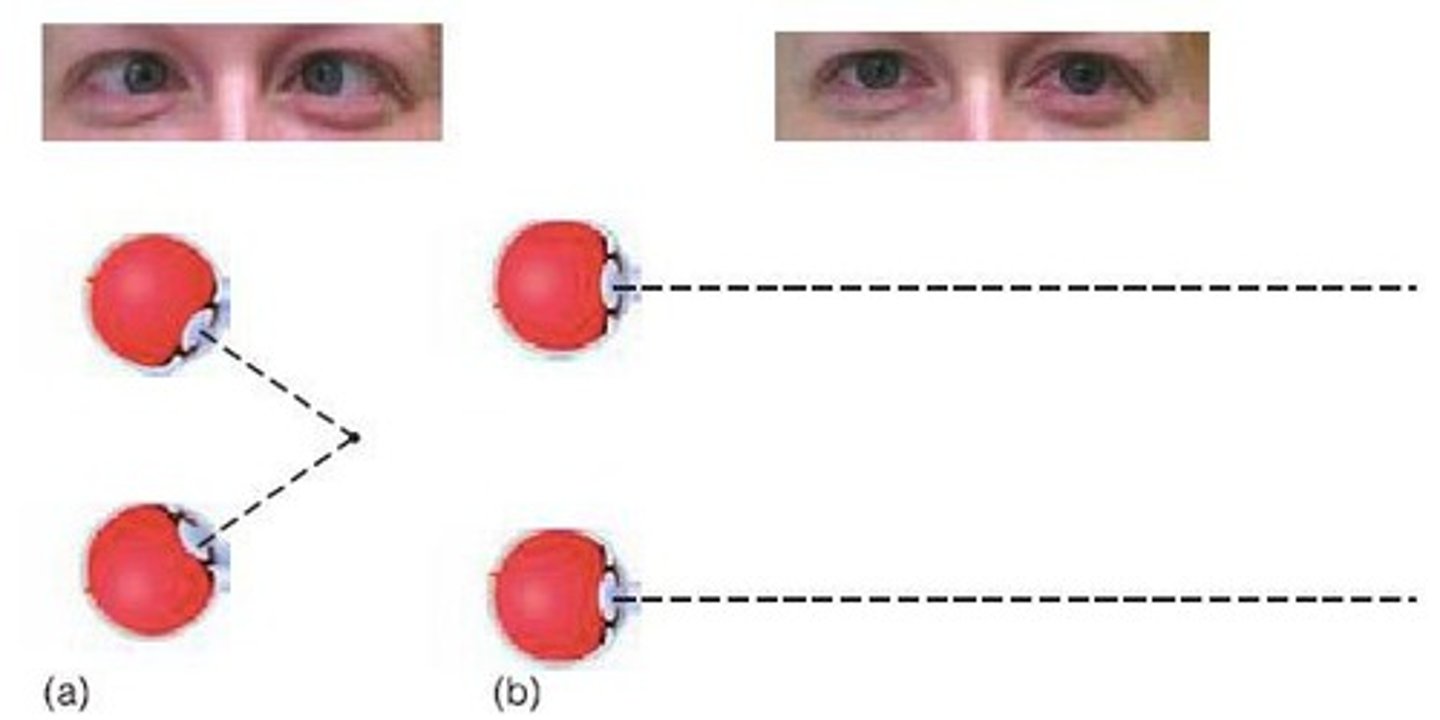
Convergence and divergence
To properly fuse an object that is not in our current horopter, we need to converge or diverge our eyes and accommodate our lenses.
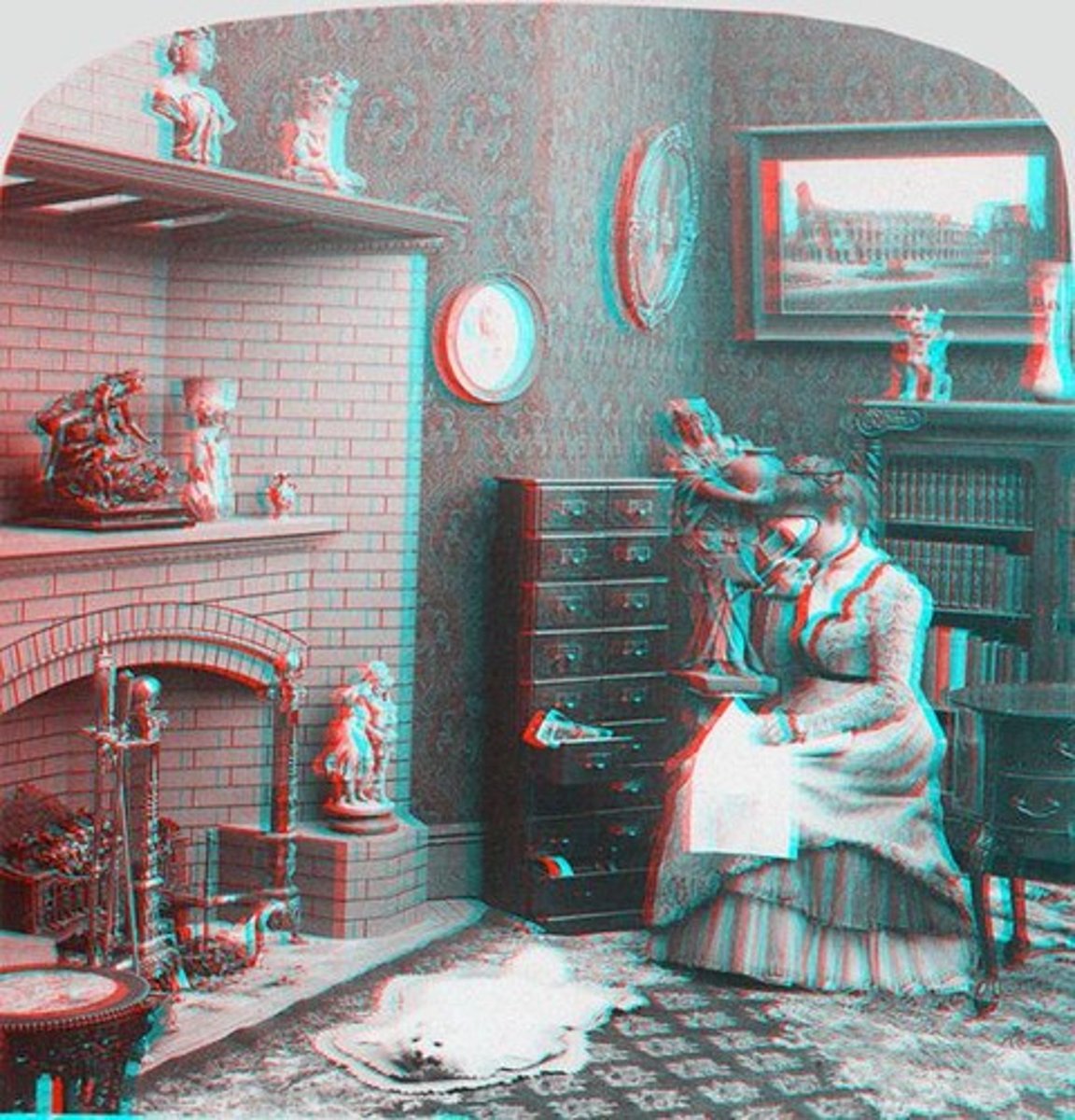
Stereopsis
The impression of a 3-dimensional world provided by binocular cues.
Red/blue (or red/cyan) 3D glasses
One lens is a red-pass filter and the other is a blue-pass filter. Images are created by taking two images with camera lenses ~6cm apart and applying filters.

Size-distance equation
Size ~ Retinal angle x Distance (estimated).
Ponzo illusion
Estimating size requires estimating distance.
Crazy chair illusion
An example of a size-depth illusion.
Ames room
A room designed to create an optical illusion of size.
Sidewalk art
Art created by Julian Beever that creates an illusion of depth.
Simultaneous size contrast
A phenomenon where the perceived size of an object is influenced by the size of surrounding objects.
Dynamic Ebbinghaus
An illusion where the perceived size of a central circle is affected by the size of surrounding circles.
Temporal dynamics of binocular rivalry
Refers to the timing and switching of percepts in binocular rivalry.
Indirect process of size perception
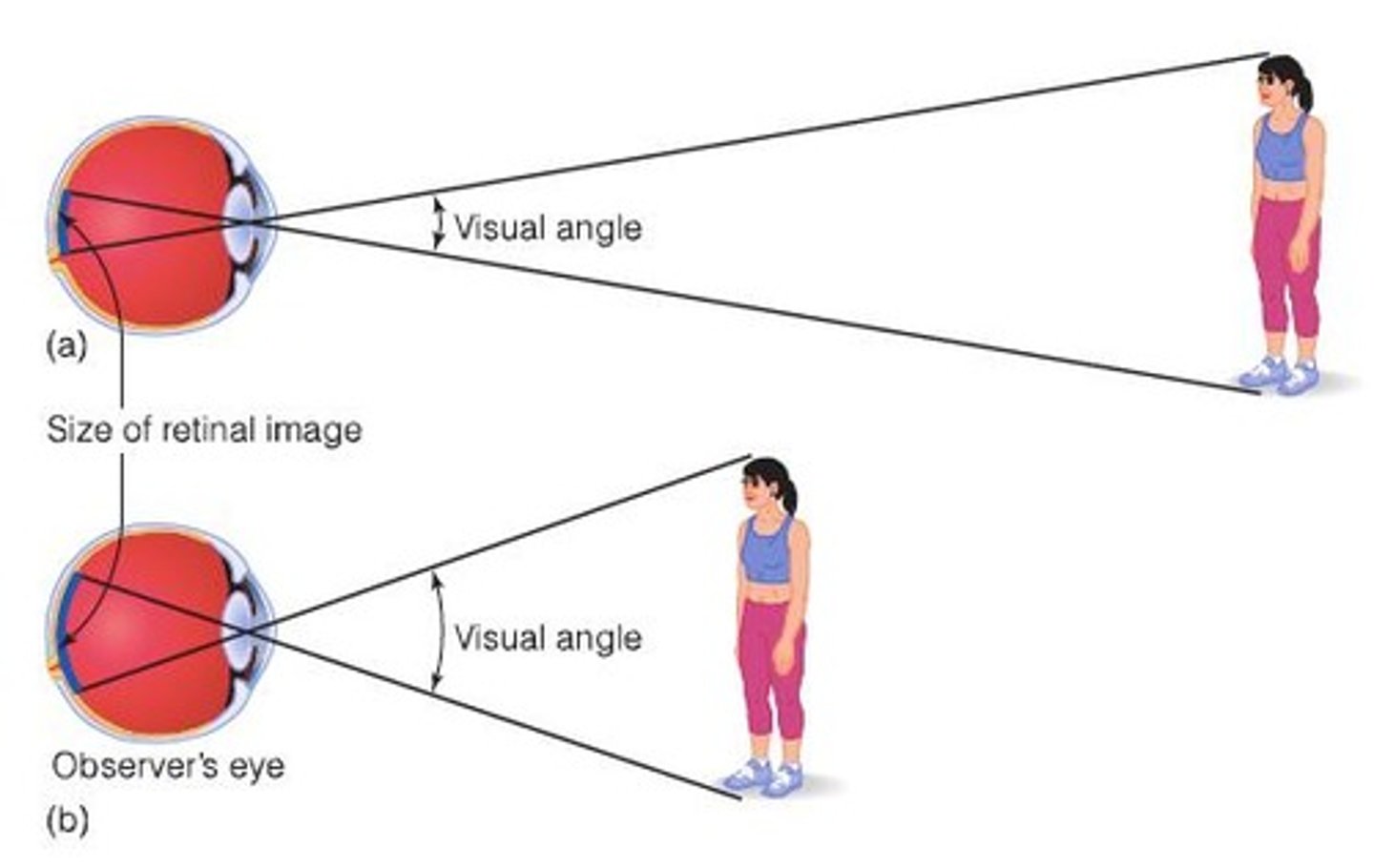
We only really ever know the visual angle of an object; to perceive true size, we estimate distance.
Distance estimation cues
Estimation of distance can be based on occlusion, familiarity, perspective, binocularity, etc.
Visual angle
The angle formed by the lines of sight to the edges of an object.
True size estimation
Combining distance estimates with known visual angle allows us to estimate true size.