The Kingdoms: Bacteria, Archea, Fungi and Protists
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
is Bacteria uni or multicellular
unicellular
bacteria cell wall composition
petidoglycan, complex
gram stain
used to identify if a cell is bacteria. thick/complex walls with many layers stain purple/positive. less/no layers or with a caosud stain pink/negative
mutualism
when 2 organisms live closeby and both benefit from this association
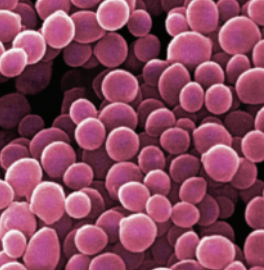
cocci
cocci shape benefits
high volume, low surface area, resists drying out
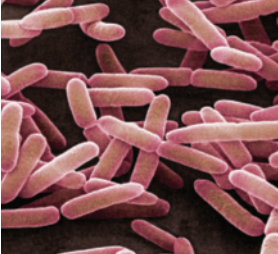
bacilli
bacilli shape benefits
increased surface area for nutrient absorbtion
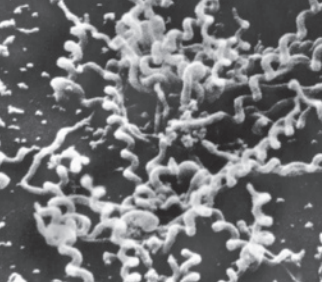
spirilli
spirilli shape benefits
ease of movement
diplo arangement
pairs
strepto arangement
strip/chain
staphylo arangement
cluster
metabolism of bacteria
both autorophic and heterotropic
autotrophs
synthesize their own organic food molecules from an abiotic origin
photoautotrophs
convert light to chemical energy for nutrience
chemoautotrophs
synthesize organic compounds from chemicals for nutrience
heterotrophs
cannot synthesize their own organize compounds, obtain from biotic sources
obligate aerobe
cannot survive without oxygen
obligate anaerobe
cannot survive in presence of oxygen
faculatative aerobe
can live with/without oxygen
reproduction in bacteria
asexual
asexual reproduction
produces identical offspring
binary fission
process of prokaryotic parent cells splitting into 2 identical daughter cells, chromosone duplicates then splits
DNA structure in bacteria
1 circular chromosone found in nucleoid region
can all bacteria move
some, not all
pili
small hair-like structures for movement and attatching to cells/surfaces
plasmid
small number of genes form a loop of DNA in bacteria cells
capsule
surrounds bacteria cell, protects it
conjugation
when 2 bacterial cells transfer plasmids through a pili bridge
transformation
when a bacterial cells takes in a plasmid from the environment
horizontal gene transfer
when a prokaryotic cell takes genetic information from another epxies
endospore
when living conditions are poor, bacteria transorms into resistant structures and survive extreme conditions
antibiotic resistance
overusing antibiotics can cause bacteria to adapt and become more resistant, making antibiotics ineffective
impacts of bacteria to society
pathogenic, can produce important vitamins, in food, produce medicines
impacts of bacteria to environment
decomposers, help culce nutrients, help ballance food webs
sexual reproduction
results in non-identical offspring
archaea cell wall composition
glycoprotien
archaea uni/multicellular
unicellular
can all archaea move
some, not all
reproduction in archaea
asexual binary fission
extremophiles
organisms that can thrive in extreme environments
methanogens
can live in anaerobic environemtns
halophiles
live in high saline environments
extreme thermophiles
can live in hot environments
physchrophiles
can live in cold environements
acidophiles
live in low pH/acidic environements
chloroplast
site of photosynthesis is eukaryotes
mitochondria
site of cellular respiration in eukaryotes
serial endosymbiosis
plasma membrane infolded creating endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus. engulfed aerobic heterotrophic bacteria creating mitochondria. engulfed photosynthetic bacteria creating choloroplast
mesophiles
lives in normal environments
how can you prove mitochondria and chloroplast have endosymbiotic origin
they both have their own cirular DNA chromosone and divide by binary fission (like bacteria)
are protists aquatic or terestrial
most aquatic
are fungi aquatic or terestrial
terestrial
protozoa
animal like protists, unicellular heterptrophs
protist algae
plant like protists, multicellular photosynethic
molds
fungi like protist, decomposers, motile
how do unicellular protists reproduce
asexually by binary fission or sexually by conjugation
how do multicellular protists reproduce
a combination of sexual and asexual reproductive phases called alternation of generations
haploid
1 set of chromosones
alternation of generations
multicellular protists life cycle, gameophyte produces gametes (n) which fuse together to form zygotes (2n) and copy through mitosis to form a sportophyte that produces copies through meiosis making spores that form into a gameophyte that specializes cells in gametes
diploid
2 sets of chromosones
chemical in cell wall of protists
cellulose
meiosis
process that results in non identical haploid gametes
fertilization
process of 2 gametes fusing
gamete
haploid sex cell
zygote
first cell of a new organism resulting from fertilization
protist impact to society
food source, manufacturing industry (toothpaste, paint), pathogens (malaria, bever fever)
protist impact to environment
consumers, decomposers, form symbiotic relationshops with other organisms
are fungi uni/multicellular
multicellular
can fungi move
no
cell wall composition in fungi
chitin
strategy to obtain organic molecules in fungi
heterotrephic - extracellular digestion
sexual/asexual reproduction in fungi?
both
hyphae
elongated cells that form branding filamentous structure (irregular shaped cell)
septum
cell wall that divides hyphae into individual cells
mycellium
branching network of hyphae filament
fruiting body
reproductive structure of fungi that produce spores
saprophytic
fungi derive nourishment from dead/decaying organic matter
extracellular digestion
fungi live next to/within food source and release digestive enzymes into surrounding that break down organiz matter. the fungi aborbs the nutrients through cell membrane of hyphae
parasitism
1 organism benefits, 1 organism is harmed
commensalism
1 organism benefits, 1 is not impacted
mutualism
both organisms benefit
mycorhizzae
mutualism between fungi and plant roots. plant provides sugar for fungi through photosynthesis. fungi increases absorbtion of nutrients through extracellular digestion
lichen
mutulistic relationshop between green algea and fungi. the plant provides sugar. the fungus provies structural support and nutrients (h20, co2)
budding/fregmentation
asexual reproduction of fungi. peices of hyphae seperate and grow new hyphae
asexual spores
asexual reproduction of fungi. form along hyphae, break free and germinate
mitosis
asexual reproduction of fungi. fungus cell divides forming spores that can survive harsh conditions
sexual fungi life cycle
spores produce hyphae with cells containing haploid nuclei that fuse to produce dikaryotic cells with 2 haploid nuclei. hypahe grow into large mycellium that produces a mushroom cap with gills on its underside. haploid nuclei inside spore producing cell fuse to form a zygote with a diploid nucleus. each zygote produces 4 haploid nuclei that are released as spores.
fungi importance to society
food soruce, used medicinally/recreationally
fungi importance to ecosystems
decomposers, form important symbiotic relationships, pathogenic, apart of food web