Market
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
supply + demand
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Surplus
excess supply
Qs > Qd
Shortage
excess demand
Qd > Qs
Equilibrium price (Market-clearing price)
price at which the Qd = Qs
Equilibrium quantity
quantity that corresponds to equilibrium price
Disequilibrium Price
a price other than equilibrium price
a price at which Qd does not = Qs
Disequilibrium
a state of either surplus or shortage in a market
Equilibrium
“at rest”
Qs = Qd
lower the price
if a surplus exists
raise the price
if a shortage exists
Consumers’ surplus
difference between maximum price a buyer is willing and able to pay for a good or service and the price actually paid for it
Max buying price - price paid
Producers’ surplus
difference between the price sellers receive for a good and the minimum/lowest price for which they would have sold the good
Price received - minimum selling price
Total surplus
Consumers’ surplus + producers’ surplus
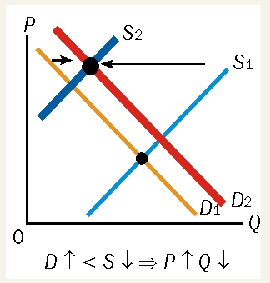
demand rises, supply is constant
equilibrium price rises
change in price = Qs rises as well
upward movement in supply curve
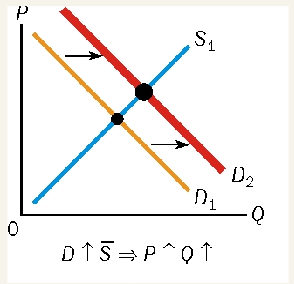
demand falls, supply is constant
equilibrium price falls
change in price = Qs falls as well
downward movement in supply curve
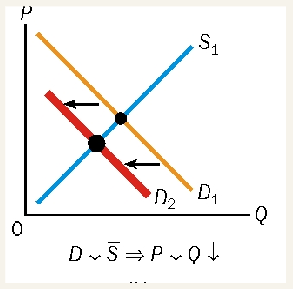
supply rises, demand is constant
equilibrium price falls
change in price = Qd rises as well
downward movement in demand curve
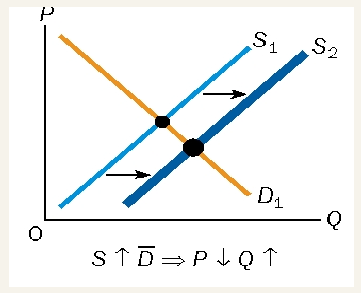
supply falls, demand is constant
equilibrium price rises
change in price = Qd falls as well
upward movement in demand curve
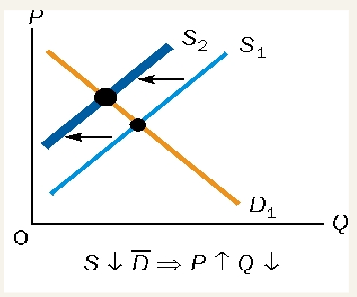
demand rises, supply falls by equal amount
equilibrium price rises
equilibrium quantity remains constant
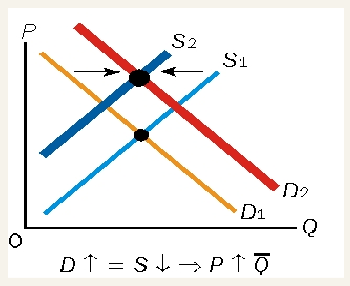
demand falls, supply rises by equal amount
Equilibrium price falls
Equilibrium quantity is constant
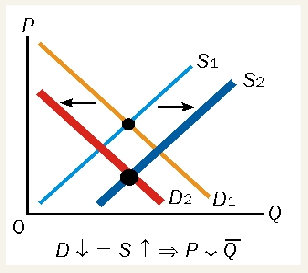
demand rises by greater amount than supply falls
equilibrium price rises
equilibrium quantity rises
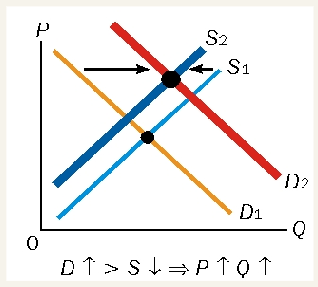
demand rises by small amount that supply falls
equilibrium price falls
equilibrium quantity falls