Gen Bio 1 unit 4 exam (simplified)
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
translator
the process that takes the information passed down from DNA as a messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together by peptide bonds. It is essentially a translation from one code (nucleotide sequence) to another code (amino acid sequence)
transcription
The process of making an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence. This copy then carries the gene’s protein information encoded in DNA.
translation
The process that takes the information passed from DNA as a messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds.
DNA structure
DNA is double stranded, forming a double helix. DNA is deoxyribose. DNA uses the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. RNA uses adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine
RNA structure
RNA is usually single stranded, RNA contains ribose. RNA uses adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine
DNA replication
_____ creates identical DNA strands
transcription
_____ converts DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA). Translation then decodes mRNA into amino acids, forming proteins needed for life functions.
RNA polymerase
Transcribes the genetic information stored in DNA to RNA. The _______ produces a single stranded RNA molecule. Both polymerases require a DNA template strand and free nucleotides
DNA polymerase
_____ produces a double stranded DNA molecule, Both polymerases require a DNA template strand and free nucleotides
TATA box
The ____ can define the direction of transcription and indicates the DNA strand to be read. Proteins called transcription factors bind to the _____ and recruit an enzyme called RNA polymerase, which synthesizes RNA from DNA.
RNA processing
The sequence of events through which the primary transcript from a gene acquires its mature form. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes process their ribosomal and transfer RNAs. The major difference, however, is in the processing messenger RNAs
What is the difference between a primary transcript and a “finished” mRNA. Are they the same in eukaryotes? Are they the same in prokaryotes? Why?
3 types of RNA’s
Messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
codons
A _____ is a three-letter genetic sequence found in both DNA and RNA. It codes for a specific amino acid or start and stop signals for the protein synthesis process
anti-codon
A unit of 3 nucleotides that are complementary to a mRNA codon. It identifies which tRNA binds to which mRNA. They are located at one end of a transfer RNA molecule
template strand
The DNA sequence that can duplicate itself during mRNA synthesis
codon chart
How can you decipher the genetic code?
yes
(ex: human insulin gene was used to transform bacteria)
Can you take a gene from a human and put it in a bacterium?
5’-3’ designation
The two strands of DNA double helix are antiparallel, this 5’-3’ DNA synthesis can take place continuously on only one
promoters?
A region of DNA where transcription of a gene is initiated. Helps RNA polymerase to find where a gene starts
5’ caps
The group at the beginning (5’ end) is called a ____, Both the _____ and tail protect the transcript and help it get exported from the nucleus and translated onto the ribosomes found in the cytosol. They are found in eukaryotic cells.
poly-A tails
The group at the end (3’ end) is called a ____.Both the 5’ cap and ____ protect the transcript and help it get exported from the nucleus and translated onto the ribosomes found in the cytosol. They are found in eukaryotic cells.
introns
An _____ refers to the non-coding sequences found in DNA or RNA.
exons
____ refers to the coding portions of DNA or RNA.
heteronuclear RNA
Transcribed RNA that has not been processed.
protein domains
The exons match the _____, then duplication, permutation and rearrangement of such exons would create
The ribosome
Where does a tRNA line up to a mRNA?
stages of protein synthesis.
Initiation, elongation, and termination
AUG
What is the start codon?
Methionine
What amino acid is the first in every protein made?
The endoplasmic reticulum
Where are secreted proteins synthesized? Why?
The ribosomes
Where are proteins that work in the cytoplasm synthesized?
UGA
A stop signal in the universal genetic code, or the terminator codon.
AUG
The standard start codon for translation of a gene, encodes the amino acid methionine (Met or M). It also establishes the reading frame for the ribosome to follow, adding corresponding amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
amino-acyl-tRNA synthetase
An enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA
tRNA molecule
Contains a set of three nucleotides called an anticodon. The anticodon of a given___can bind to one or more specific mRNA codons. Its “L shaped structure” functions as an adaptor that translates this codon sequence in the mRNA into the suitable amino acid of that codon. As the link between amino acids and nucleic acids,____ determine the genetic code.
small ribosomes
decode the genetic information
large ribosomes
catalyze peptide bond formation.
initiation
In _____, the ribosome gets together with the mRNA and the first tRNA so translation can begin.
elongation
prokaryotes
In _____, protein synthesis is coupled, meaning transcription and translation occur simultaneously.
eukaryote
in _____ protein synthesisit occurs in stages.
central dogma
theory stating that genetic information flows only in one direction, from DNA, to RNA, to protein, or RNA directly to protein.
polyribosomes
Increases the efficiency of protein production by a single mRNA. They are found in eukaryotes.
types of point mutations
missense, nonsense, silent
missense point mutation
a DNA change that results in different amino acids being encoded in different amino acids being encoded at a particular position in the resulting protein.
nonsense point mutation
a change in DNA that causes a protein to terminate or die or end its translation earlier than expected.
silent point mutation
mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype
frameshift mutation
A genetic mutation caused by a deletion or insertion in a DNA sequence that shifts the way the sequence is read.
vertical exchange of genetic material
refers to the passage of plasmid from mother to daughter cells.
horizontal exchange of genetic material
refers to the passage of a plasmid from donor to any recipient outside of cell division (often through conjunction).
transformation
The process by which foreign genetic material is taken up by a cell.
transduction
The process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another.
conjugation
The process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct (“donor”) contact.
pilus
A ___ is a thin, rigid fiber made of protein that protrudes from the cell surface. The primary function of ____ is to attach to a bacterial cell to specific surfaces to other cells.
plasmid
A small circular DNA molecule found in bacteria and some other microscopic organisms.
antibiotics
Medicines that fight bacterial infections in people and animals. They work by killing the bacteria by making it hard for the bacteria or by making
yes ?
Do eukaryotic cells typically have plasmids that are used to transmit genetic information?
operon
A functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter.
operator
The DNA sequence where the repressor molecule binds to the operon model. Present in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
promoter
A region of DNA where transcription of e gene is initiated.
repressor
A protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes. Works by binding to the promoter region of the gene(s), which prevents the production of messenger RNA (mRNA).
tryptophan
An amino acid needed for normal growth in infants and for the production and maintenance of the body’s proteins, muscles, enzymes, and neurotransmitters. It is an essential in amino acids
Amino acids (in polypeptide chains)
What macromolecules are enzymes made of?
corepressor
Proteins that regulate the process of gene expression indirectly by binding to the repressor protein. Operates with the transcription factors to reduce the rate of gene transcription.
lactose
The principal sugar (or carbohydrate) is naturally found in milk and dairy. Composed of glucose and galactose.
repressor proteins
_____ bind to DNA and prevent RNA polymerase from being able to attach to the DNA and synthesize mRNA.
inducer proteins
_____ bind to repressors, causing them to change shape and preventing them from binding to DNA.
Anabolic
What type of pathways (anabolic or catabolic) are usually controlled by repressible enzymes?
Increased cAMP leads to enhanced expression
How does cAMP contribute to the control of the lac operon?
lac operon
A set of structural genes that code for proteins to digest lactose, that can be turned on and off.
bacterial and eukaryotic gene control
Both rely on proteins that act as activators that “turn on” gene expression or repressors that “turn off” gene expression.
cell differentiation
How generic embryonic cells become specialized cells. This occurs through a process called gene expression.
The process by which dividing cells change their functional or phenotypical
histones
A protein that provides structural support for a chromosome.
chromosome
histones assist in DNA packaging:
DNA wraps around the histone proteins which helps give the _____ a more compact shape.
nucleosome
Serves as a gene repressor, and a repressor of all transcription factors.
Tandem repeats, Interspersed repeats, Terminal repeats
3 types of repetitive DNA
Tandem repeats
serves as genetic markers to track inheritance in families.
Interspersed repeats
Terminal repeats
Huntington’s Disease and fragile X syndrome
What conditions result from triple repeats of DNA sequences?
gene families
Groups of homologous genes that are likely to have highly similar functions.
myoglobin
Myoglobin has only one polypeptide chain, and its function is to store the oxygen for use by muscle tissue.
hemoglobin
______ has 4 polypeptide chains, and its function is to transport oxygen.
the initiation f transcription
Explain at which steps/level of the central dogma gene expression can be controlled in eukaryotes.
epigenetics
The study of how your behaviors and enviroment can cause changes that affect the way your genes work
DNA methylation
Regulates gene expression by recruiting proteins involved in gene repression or by inhibiting the binding of transcription factors to DNA.
acetylation
A critical epigenetic modification that changes chromatin architecture and regulates gene expression by opening or closing the chromatin structure.
Nucleic acids and proteins
what macromolecules are viruses made of?
obligate parasite
A parasitic organism that is not able to complete its life cycle without exploitation of suitable host.
retrovirus
A virus that uses RNA as its genomic material.
direct contact with contaminates.
How do flu virusus go from infecting animals to humans? Acquired through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated environments.
Double-stranded DNA, double-stranded RNA, single-stranded DNA, or single-stranded RNA.
Describe 4 different type of nucleic acids that viruses may contain.
‘enveloped’ virus
The outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling within host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes.
bacteriophage
Viruses that infect and replicate only in bacterial cells.
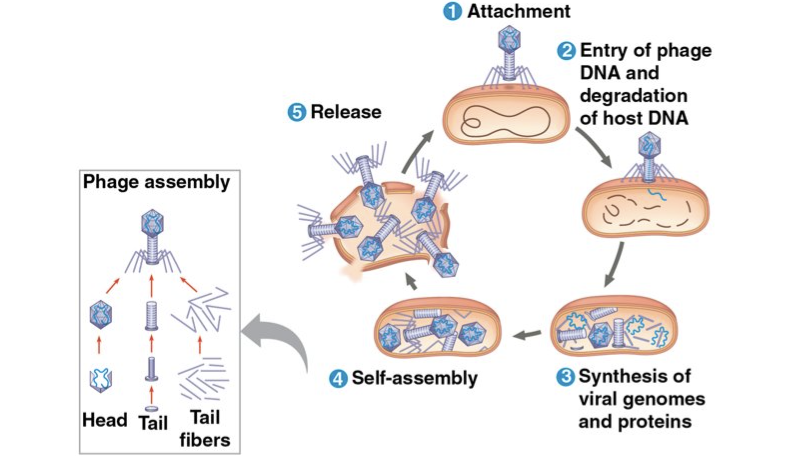
lytic cycle
The _____is a phage replicative cycle that culminates in the death of the host cell
The ____ produces new phages and lyses (breaks open) the host’s cell wall, releasing the progeny viruses
A phage that reproduces only by the ______ is called a virulent phage
Involves the reproduction of viruses using a host cell to manufacture more viruses; the viruses then burst out of the cell.
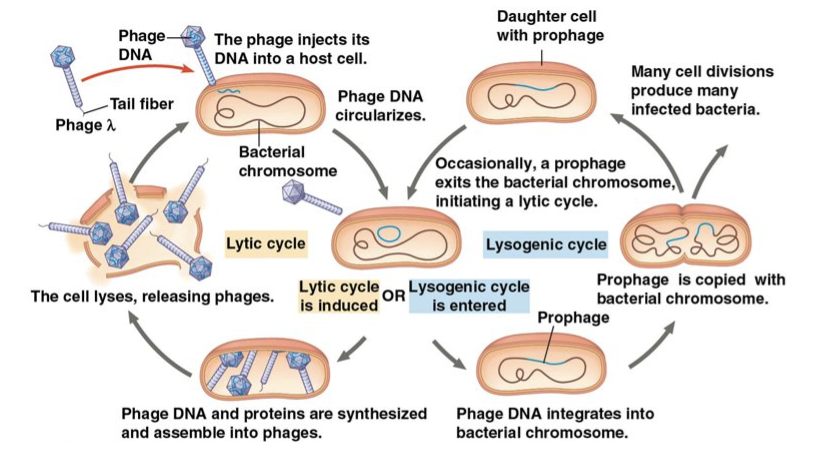
lysogenic cycle
The ______ replicates the phage genome without destroying the host
The viral D N A molecule is incorporated into the host cell’s chromosome
Phages that use both the lytic and ______ cycles are called temperate phages
A viral reproductive stage where the virus’s DNA is being replicated using the host cell’s DNA. During its infection, the virus uses the host to help copy its DNA or genetic information, but it is not producing any proteins.
prions
A type of protein that can cause disease in animals and humans by triggering normally healthy proteins in the brain to fold abnormally. The scientific community had a hard time accepting it because some features of the diseases caused by _____ and viruses are similar.
pandemic
An epidemic that affects a wide geographic area.
Illness, sex, stress, sunlight, and fatigue
What is the cause of herpes outbreaks?