History of Subatomic Particles
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is matter and what is it composed of?
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It is composed of different particles:
Atoms Every element consists of one type of atom.
Molecules Molecules form when atoms join together in groups.
Ions. Ions are particles that have an electric charge
name the 6 scientists we studied.
1. Dalton
2. Crookes – Cathode Rays (Electron)
3. Thomson – Electron/Plum Pudding
4. Millikan – Oil Drop (Electron)
5. Rutherford – Nucleus/Proton
6. Chadwick - Neutron
summarise Dalton’s atomic theory
–All matter is made up of small particles called atoms.
–Atoms are indivisible.
–Atoms cannot be created or destroyed.
what experiment did Crookes conduct?
Crookes passed electric current through air at low pressure in a vacuum tube.
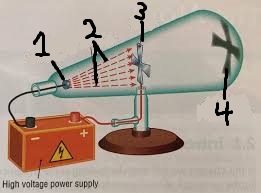
label this diagram
cathode(-)
cathode rays
anode(+)
shadow of the Maltese cross
What did Crookes find from this experiment.
•The radiation of electrons was shown when adding a high voltage current to the cathode, a shadow of a Maltese cross was formed. •The formation of the shadow also showed that the rays travelled in straight lines
When a paddle was place on rails inside the tube, when the current was applied, what happened?
•When current was applied the paddle travelled down the tube away from the cathode.
•The wheel always turned away from the cathode showing the movement came from cathode rays.
Thomson followed up on Crookes experiment, what did he do?
•He obtained a narrow beam of cathode rays by passing them through a small hole in an anode (positive electrode).
•This beam passes between 2 parallel metal plates onto a fluorescent screen at the end of the tube.
What were his findings?
•When the plates were uncharged, the beam travelled straight down the tube to a spot.
•Putting a + charge on the top plate made this spot (& the rays) move upwards.
•This showed the cathode rays consisted of negative charged particles and Thomson called these electrons (as proposed by Irish Scientist Stoney).
describe Thomson’s Plum Pudding diagram.
Atom is a sphere of positive charges with negative charges (electrons) embedded.
How did Millikan contribute to the atom?
•Millikan sprayed tiny drops of oil between 2 charged metal plates. •He used x-rays to ionise the air (it lost electrons)
•The oil picked up these electrons to become negatively charged. •He used a microscope to focus on one specific droplet and when he applied a positive charge to the top plate, the drop rose.
•He adjusted the charge until the drop became stationary.
What did Rutherford discover?
Rutherford discovered the nucleus through scattering of alpha (tiny) particles
what were the observations of Rutherford’s experiment?
Most alpha particles pass straight through the gold foil.
Some alpha particles are deflected at large angles.
A small number of alpha particles are reflected back along their own paths.
what were the conclusions? of Rutherford’s experiment?
Most of the atom is empty space.
The alpha particles are repelled when they pass near the small positive nucleus.
A small number of alpha particles collide head on with the nucleus.
describe Rutherford’s model of the atom.
In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume of the atom.
What else did Rutherford do and the conclusion?
•Rutherford bombarded the other substances with alpha particles. •When small atoms were bombarded, small positive particles were given off and these were called protons.
what did Chadwick discover? And how he did it?
•James Chadwick discovered the neutron by bombarding beryllium with alpha particles.
what did the alpha particles do to the neutrons?
•Alpha particles knocked neutrons out of the nuclei of the Be atoms. •These neutral particles were hard to detect so they were passed through paraffin wax to knock protons out of it.
Name the sub-atomic particles, their charge and mass and where their found?
proton= +1 = 1 = the nucleus
neutron= 0 = 1 = the nucleus
electron= -1 = 1/1840 = outside the nucleus in orbits.