TF - Gait Deviations Lecture
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
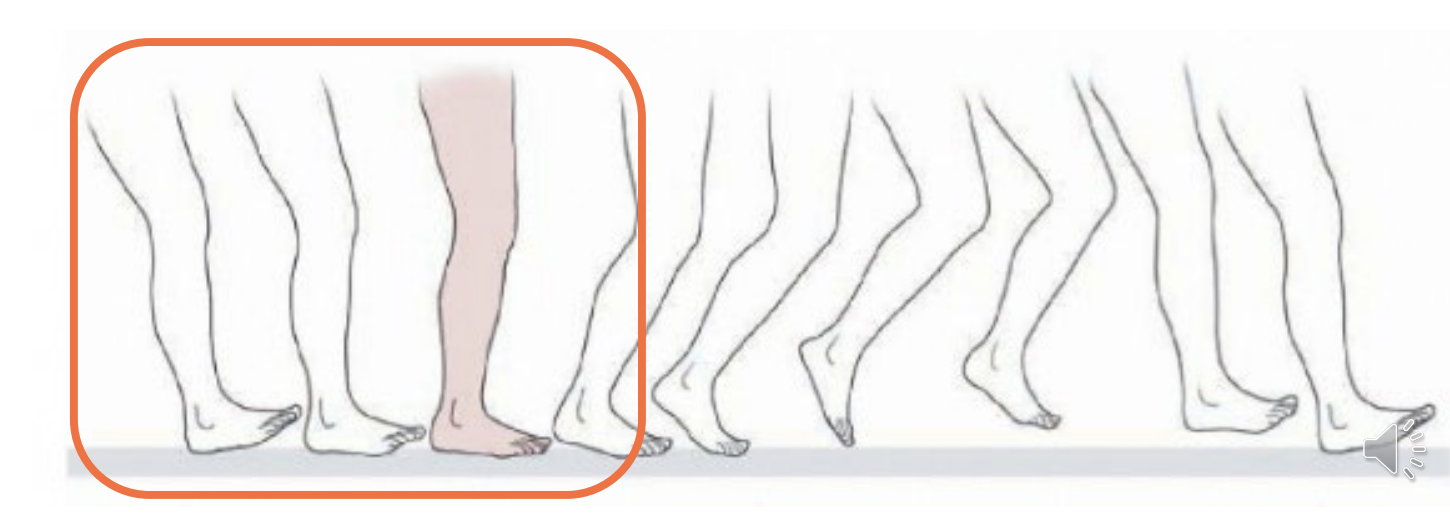
Functional Lengthening
During Stance Phase
hip extension, knee extension, plantar flexion
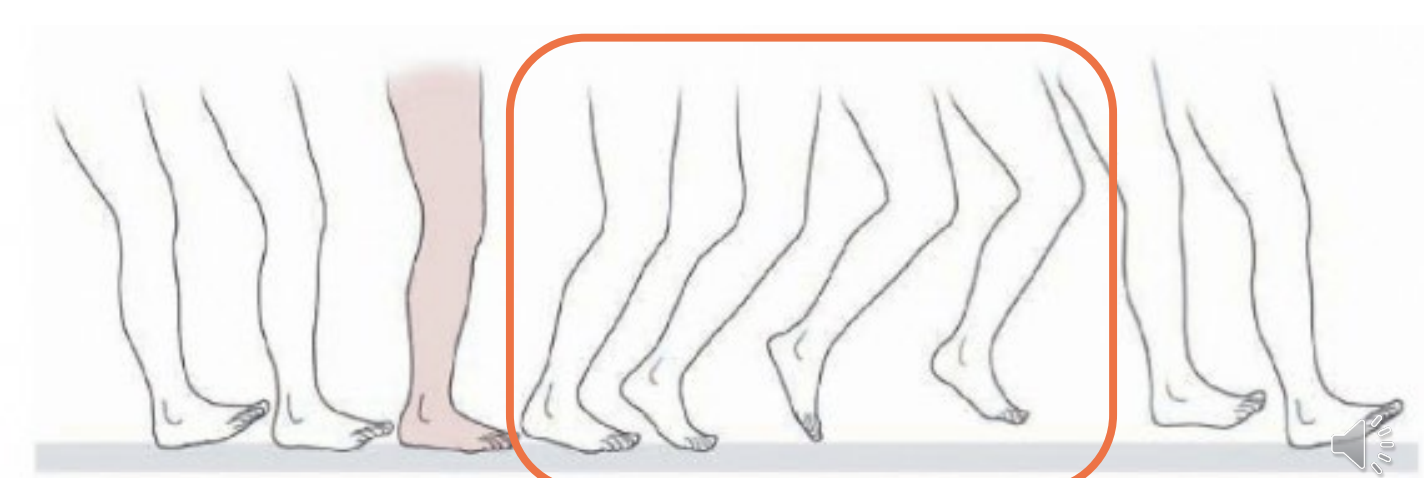
Functional Shortening
During Swing Phase
hip flexion, knee flexion, dorsiflexion
Leg Length Discrepancies
One leg is longer than the other leg, can be the cause to many of the following gait deviations.
Potential Causes
Pseudo-LLD (inability to functionally shorten the prosthesis)
incorrect alignment/measurement
poor suspension
incorrect resistance to knee flexion
incorrectly adjusted extension bias
Knee Instability
During Initial Contact (Heel Strike)
Characterized by a ‘shaking’ at the knee during initial stance phase. Hip extensors fire then relax and then fire again due to the instability.
Potential causes
knee set too far anterior (relative to socket)
excessive resistance to PF
increased shoe heel height (anterior leaning pylon)
insufficient initial socket flexion
weak hip extensors
Abducted Gait
Throughout Swing and Stance
Characterized by patient demonstrating a laterally deviated prosthesis throughout swing and stance phases of gait.
Potential Causes
pressure on the pubic ramus
pain at the distal lateral femur
inadequate support on the femur from the lateral wall
prosthesis too long
excessive socket abduction
weak contracted abductors
lack of balance or insecurity
Lateral Trunk Bending
TWO KINDS - Towards the sound side and towards the prosthetic side
Midstance
Characterized by the patient’s shoulders moving outside the base of support while the pelvis maintains its position over the base of support.
Toward the Sound Side Potential Causes
excessive foot outset
wide ML dimension of socket
weak hip abductors
poor balance
Towards the Prosthetic Side Potential Causes
prosthesis too short
excessive foot inset
insufficient socket adduction
wide ML dimension of socket
pain at the pubic ramus
contracted hip abductors
poor balance
Lateral Thrust/Shift
Midstance
Characterized by the patient maintaining their shoulders over the base of support while the pelvis moves outside the base of support. Also referred to as Trendelenburg gait.
Potential Causes
weak hip abductors
poor alignment
balance issues
patient habit
Drop Off
Heel Off (Prosthetic Side)
Characterized by early prosthetic knee flexion near midstance. Appears to buckle or bend.
Potential Causes
toe lever too short
knee center too far anterior for the patient’s ability
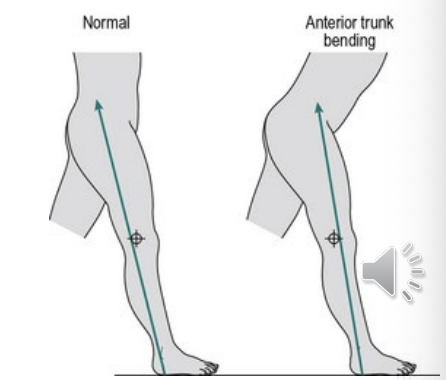
Excessive Lumbar Lordosis
Throughout gait cycle - mostly during stance
Characterized by patient maintaining an increased lumbar lordosis throughout the gait cycle.
Potential Causes
insufficient socket flexion
painful ischial weight bearing (improperly shaped posterior wall)
weak core muscles or hip extensors
hip flexion contracture
short residual limb (decreased functional lever arm)
Medial Whip
Preswing (Toe-off)
Characterized by the heel rising medially at the beginning of swing phase
knee axis in excessive external rotation
socket donned with too much external rotation
silesian belt worn too tightly
weak limb musculature
Lateral Whip
Preswing (Toe-off)
Characterized by the heel rising laterally at the beginning of swing phase.
Potential Causes
knee axis in excessive internal rotation
socket donned with too much internal rotation
weak limb musculature
Circumduction
Swing Phase
Characterized by swinging the prosthesis laterally in a wide arc during swing phase.
Potential Causes
excessive resistance to knee flexion
prosthesis aligned with too much stability
prosthesis too long
medial brim pressure
inadequate suspension
patient lacks confidence or has inadequate hip flexion
Vaulting
Swing Phase
Characterized by active heel rise during stance of the sound side while the prosthetic side completes swing phase.
Potential Causes
prosthesis too long
excessive resistance to knee flexion
prosthesis aligned with too much stability
extension bias too strong
inadequate suspension
patient habit
Terminal Impact
Terminal Swing
Characterized by rapid forward movement of the shank allowing the knee to reach full extension with too much force prior to heel strike.
Potential Causes
insufficient knee friction
extension bias too strong
patient forcefully extends hip at end of swing phase to ensure the knee is in full extension at initial contact
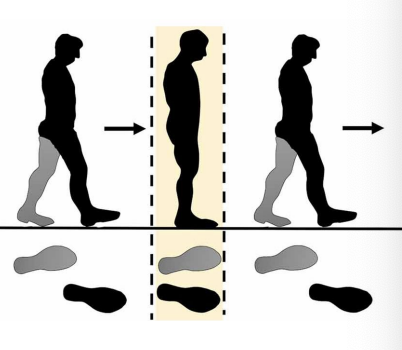
Uneven Step Length
Terminal Swing (Prosthetic side - long step)
Characterized by fixed relationship between the trunk and the limb. Patient does not have the ability to extend on the prosthetic side
Potential Cause
insufficient initial socket flexion (unaccommodated hip flexion contracture)
Uneven Step Length
Terminal Swing (short prosthetic step)
Potential Cause
poor balance
poor suspension
weak hip flexors
painful socket
insufficient knee friction
unstable knee
relatively uncommon
OR initial contact (prosthetic side - short step)
Toe Drag
Initial to Midswing
Characterized by the prosthetic foot contacts the ground near midswing. It stops the progression of swing and is a significant fall risk for the patient.
Potential Causes
weak hip abductors on the sound side
poor balance
poor suspension/socket fit
Poor Suspension
Throughout Swing
Characterized by the prosthesis sliding down the residual limb during swing phase. Creates a functionally long prosthesis. Creates a functionally long prosthesis. Then the limb sinks back into the socket during stance phase and thus creates pistoning.
Potential Causes
ill fitting socket
faulty suspension
patient’s weight fluctuation
Foot Rotation at Heel Strike
Heel Strike to Early Stance
Characterized by the foot rotating laterally upon initiation of stance
Potential Causes
excessively firm heel or PF bumper
poor alignment
weak quad musculature
patient fear of instability
How to Assess Complex Deviations
identify the phase of gait that the deviation occurs
differentiate patient causes from prosthetic causes
make one change at a time in order to determine the effect
these deviations often require a combination of incremental changes as well as gait training