10 Elementary Steps
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
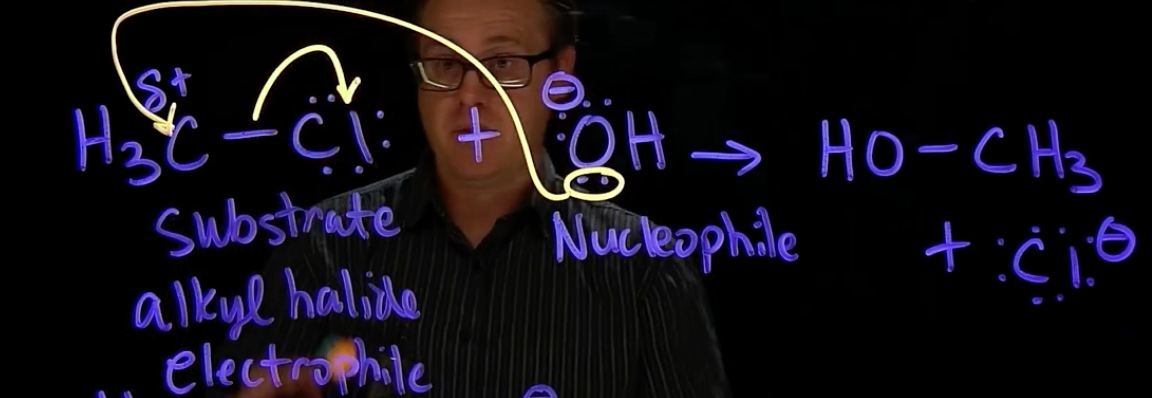
SN2
nucleophile attacks electrophilic carbon & leaving group leaves
Proton Transfer (P.T.)
e- rich species attacks H on e- poor species
bond between H & e- poor species breaks
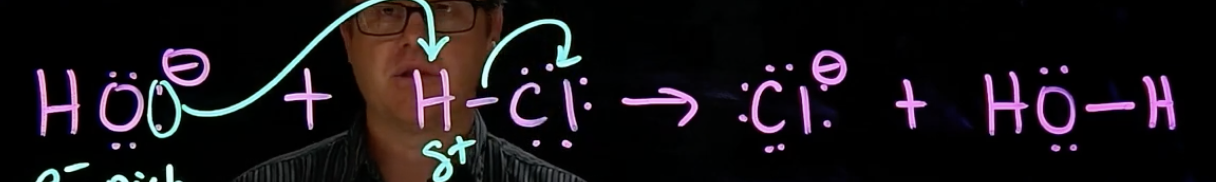
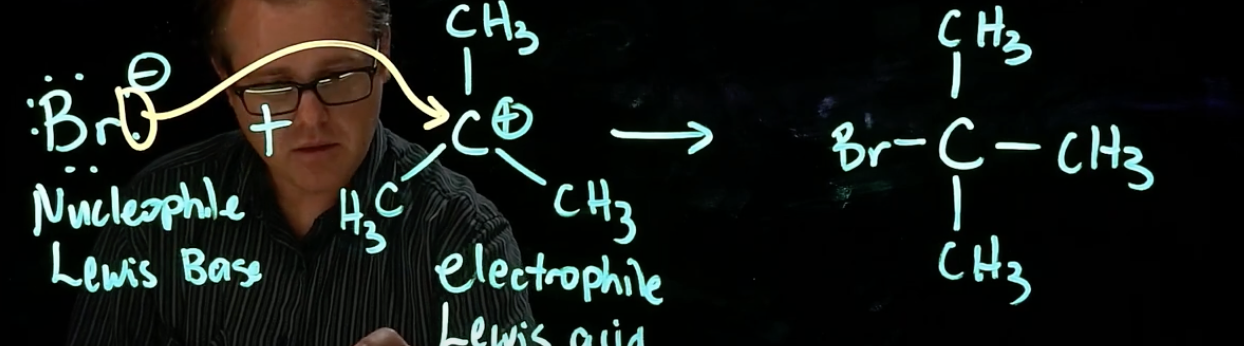
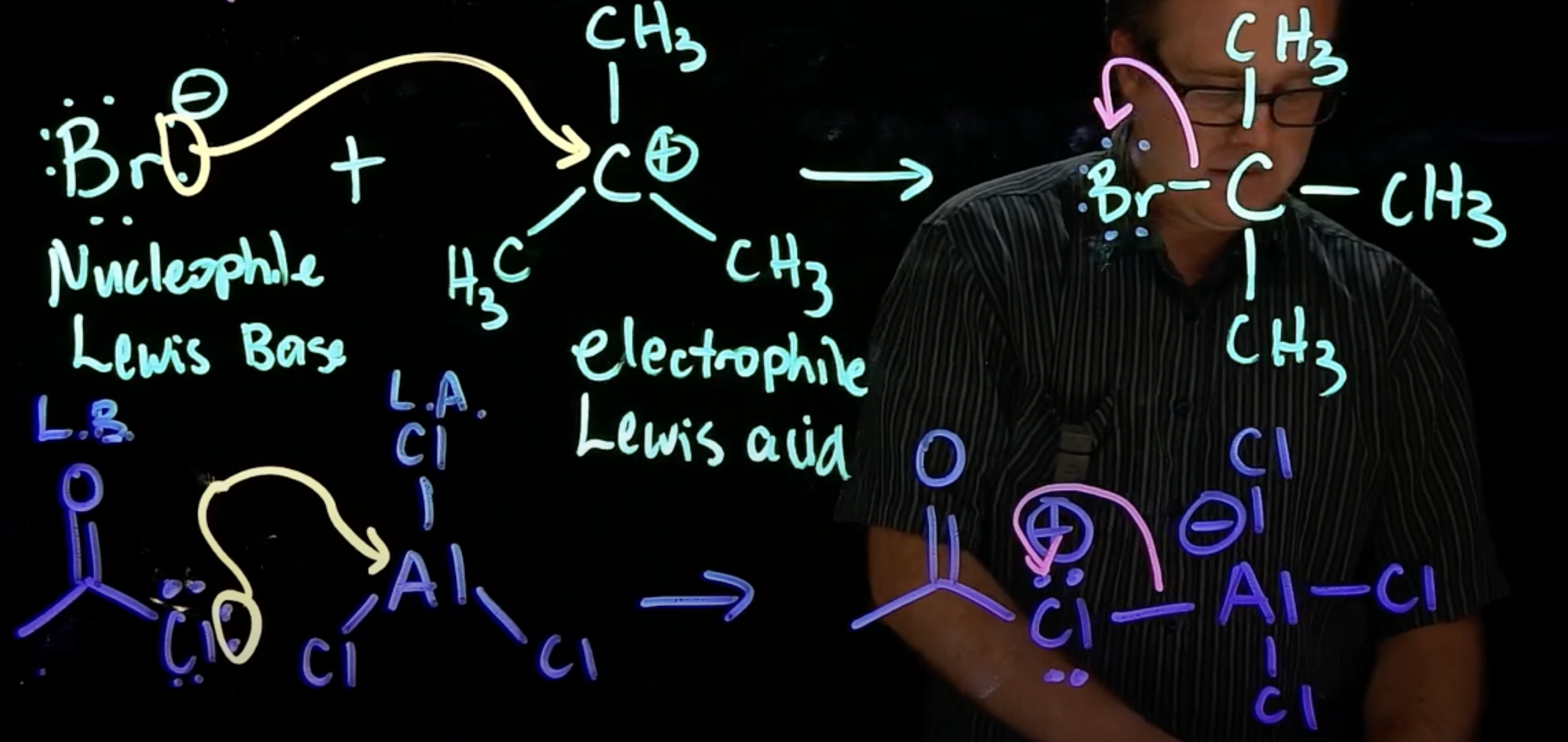
Coordination step
nucleophile attacks carbocation (lewis base attacks lewis acid)
Heterolysis
exact opposite of a coordination step
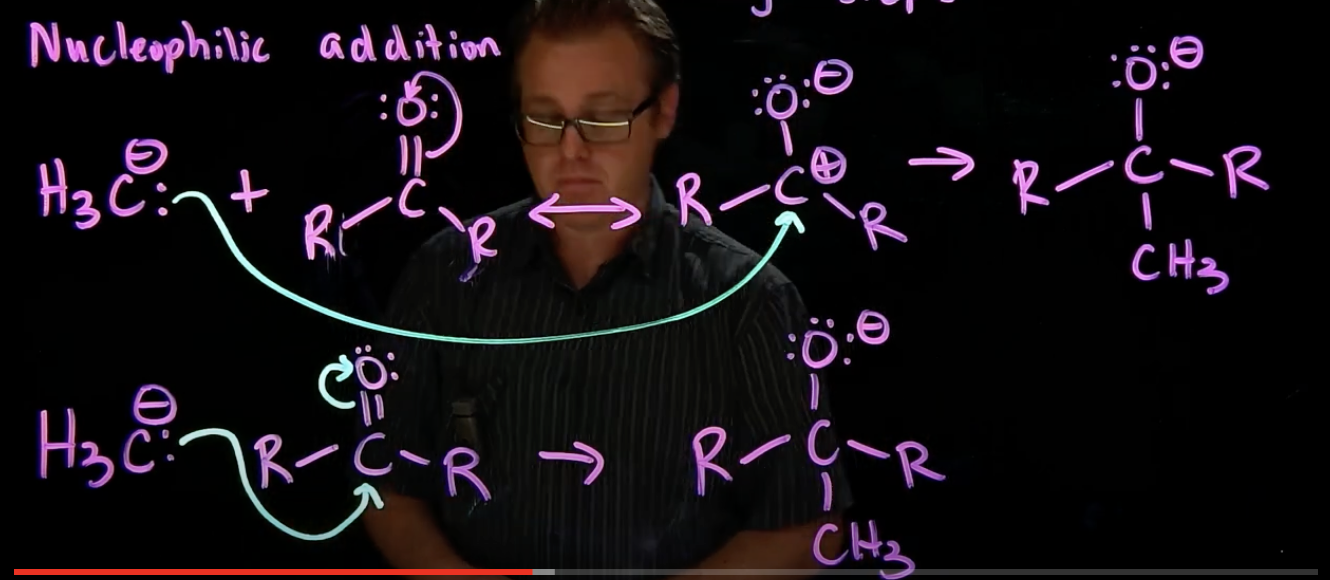
Nucleophilic addition
nucleophile attacks polarized, electrophilic carbon
pi bond breaks
Nucleophilic Elimination
electrons on negatively charged species in tetrahedral intermediate go back to carbon
leaving group leaves
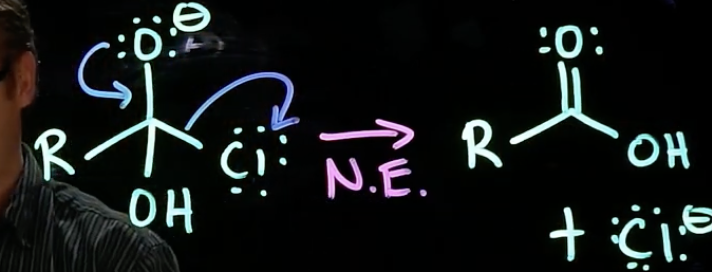
E2
hydrogen & leaving group have to be anti- pari planar to each other
base attacks hydrogen on beta carbon
bond between hydrogen & beta carbon breaks and goes to bond between beta & alpha carbon
leaving group leaves

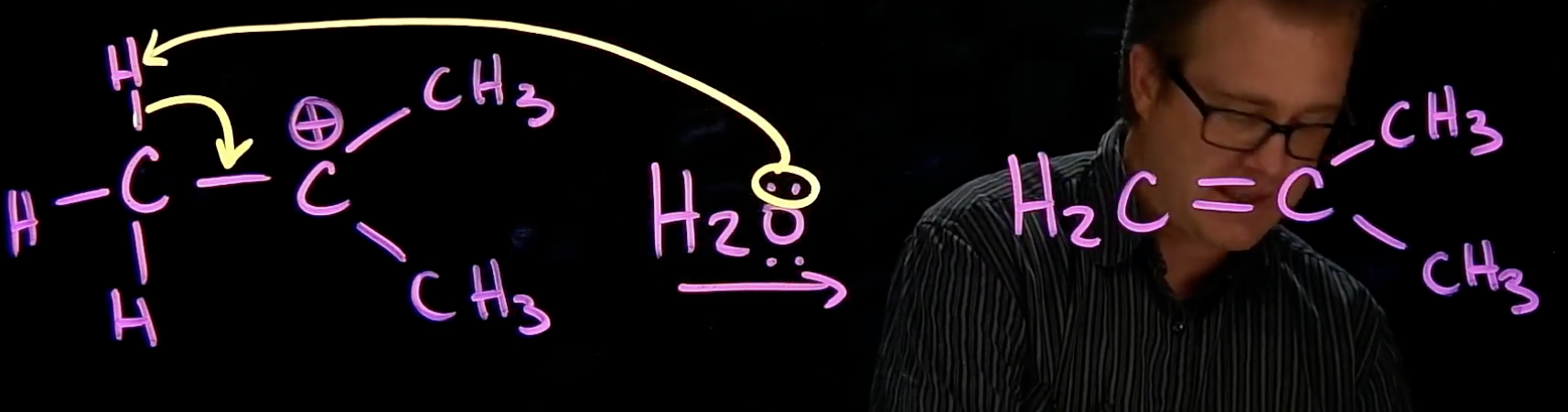
Electrophile Elimination
base grabs hydrogen
hydro-carbon bond moves to create alkene
Electrophilic Addition
pi bond grabs H & L.G. leaves

1,2 Hydride / 1,2 - Alkyl Shifts
take H attached t o B carbon & move it to create new carbocation
new carbocation has to be more stable
Sn1
heterolysis then coordination (Sn2 but in two steps)
E1
heterolysis then electrophile elimination (E2 but in two steps)