Biology GCSE combined science B2: Cell division
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
DNA
The chemical from which dna is made
Cell
the basic building block of a living organism
Gene
Small packets of DNA controlling a protein (characteristic)
Chromosome
Thread like structures holding genes
Nucleus
The part of the cell containing genetic information
List those 5 parts from largest to smallest
Cell, Nucleus, Chromosome, Genes, DNA, base pairs
What are new cells needed for?
Growth and to REPLACE old cells and to REPAIR tissue
How many pairs of chromosomes do we have?
23 pairs
How many chromosomes in each cell do we have?
46 chromosomes
Why do gametes (sex cells) only have half the number of chromosomes?
When gametes fuse in fertilisation, chromosomes will add up to 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes
What are the two types of cell division?
Mitosis(body/somatic cells) and meiosis(gamete/sex cells)
What are chromosomes made from?
Long strands of DNA
What are sections of DNA called and what are they for?
Sections of DNA are genes which code for a characteristic (protien)
What happens in stage 1 of mitosis and what is it called?
Interphase: Cell growth until parent cell with 4 chromatids is ready to replicate, then DNA replicates so that there are 4 chromoSOMES
What happens in stage 2 of mitosis and what is it called?
Nuclear division/mitosis: Nuclear membrane breaks down, each chromosome lines up at the centre of the cell, Chromosomes split and each 'arm' (chromatid) migrates to opposite ends of the cell, nuclear membrane reforms
What happens in stage 3 of mitosis and what is it called?
Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm and cell membrane divide, 2 identical daughter cells are produced
Explain why a cells genetic material has to be copied before it divides by mitosis
Chromosomes need to replicate to make sure the daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the parent
Explain why cells need to divide
to replace worn out/damaged cells, growth, repair tissue and organs
How does mitosis differ in mature animals
Mitosis doesn't take place for growth, slower rate of mitosis to repair and heal wounds
Where does mitosis take place in plants
In the meristems found in the shoot and root tips
When can an animal cells differentiate vs plant cells
Plant cells have the ability to differentiate throughout life, while animal cells differentiate at an early stage of development
Where do specialised sperm cells come from and how do they divide?
The testes, divide by meiosis because there are only 23 chromosomes in the gamete/sex cell
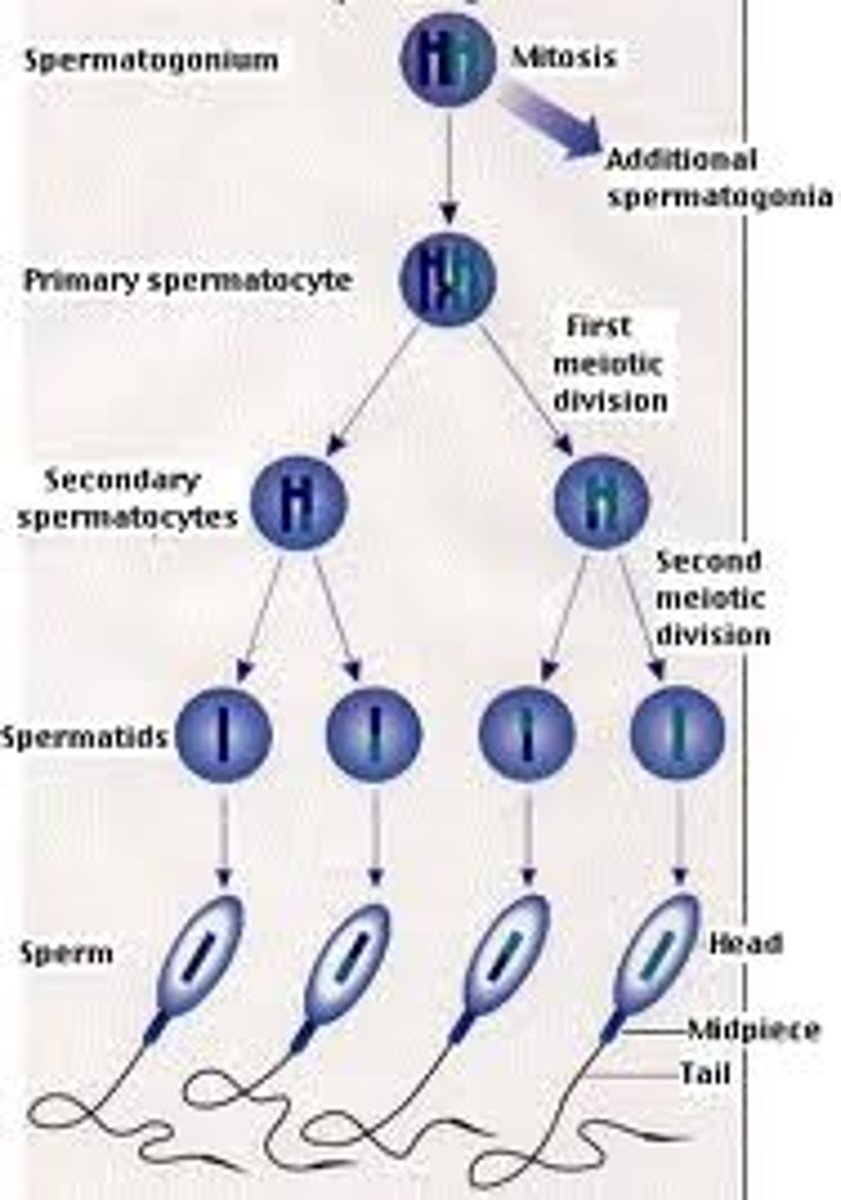
Where do specialised egg cells come from and how do they divide?
The ovaries, divide by meiosis because there are only 23 chromosomes in the gamete/sex cell
What is fertilisation?
fusion of male and female gametes/sex cells to form a zygote
Differentiation
To become 'different' or specialised
Specialisation
To become a specialised cell
Describe stem cells
Undifferentiated, unspecialised, have the potential to specialise to become other types of specialised cell
Where are stem cells found in?
In early human embryos or the bone marrow of adults
What are the purpose of specialised cells
To have different genes switched on to create a different structure and have a different function. It can only make more of the same cell
Where are stem cells found in plants?
Meristems in roots and stems
Why do humans stop growing?
Humans stop differentiating at an early stage of development because we loose many of our stem cells
What is a clone?
a genetically identical copy of a organism/cell
Why are plants cloned?
To produce identical copied of mature plants quickly and economically for reasearch, horticulture, and agriculture
What animal stem cells can be cloned and what for?
Embryonic stem cells(human embryos) and adult stem cells (bone barrow) can be cloned and made to differentiate into many different types of cell
What can treatment with stem cell cloning help?
Paralysis and diabetes
What happens in therapeutic cloning?
An embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient so the stem cells are not rejected and may be used for medical treatment. YOU CANNOT MAKE A HUMAN (illegal) it is only for research and treatment
What animal stem cells are the most useful?
Embryonic stems cells are more useful because they can differentiate into any type of specialised cell in the body, adults can only differentiate into their associated cell type (e.g. bone marrow stem cells -> red blood cells)
Who would benefit from stem cell research
Helps people with suffering diseases from faulty cells, Parkinsons disease: can replace faulty brain cells, Diabetes: replace insulin producing tissue in the pancreas, replace damaged spinal nerves so that limbs can work again, replace organs that no longer work
List pros of stem cells
Used to grow new organs for transplants; We can use stem cells from umbilical cords-no embryo destroyed; Embryonic stem cells offer the best chance of treating serious conditions; Adult stem cells can be manipulated to act like embryonic stem cells-no embryo needed; embryos that are used are spares from IVF
Cons of stem cells
Embryos cannot consent to being experimented on - unethical; Too much money is being spent on stem cell research when we could be developing new & better drug; All embryos have the potential to become babies, unethical to experiment/destroy; Treatment is experimental so risk of side effects such as cancer; Surgery always has risk; May be rejected