Chapter 5
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
1
New cards
What is The human EGF receptor (HER) signaling network?
how cells communicate with their surroundings \n
2
New cards
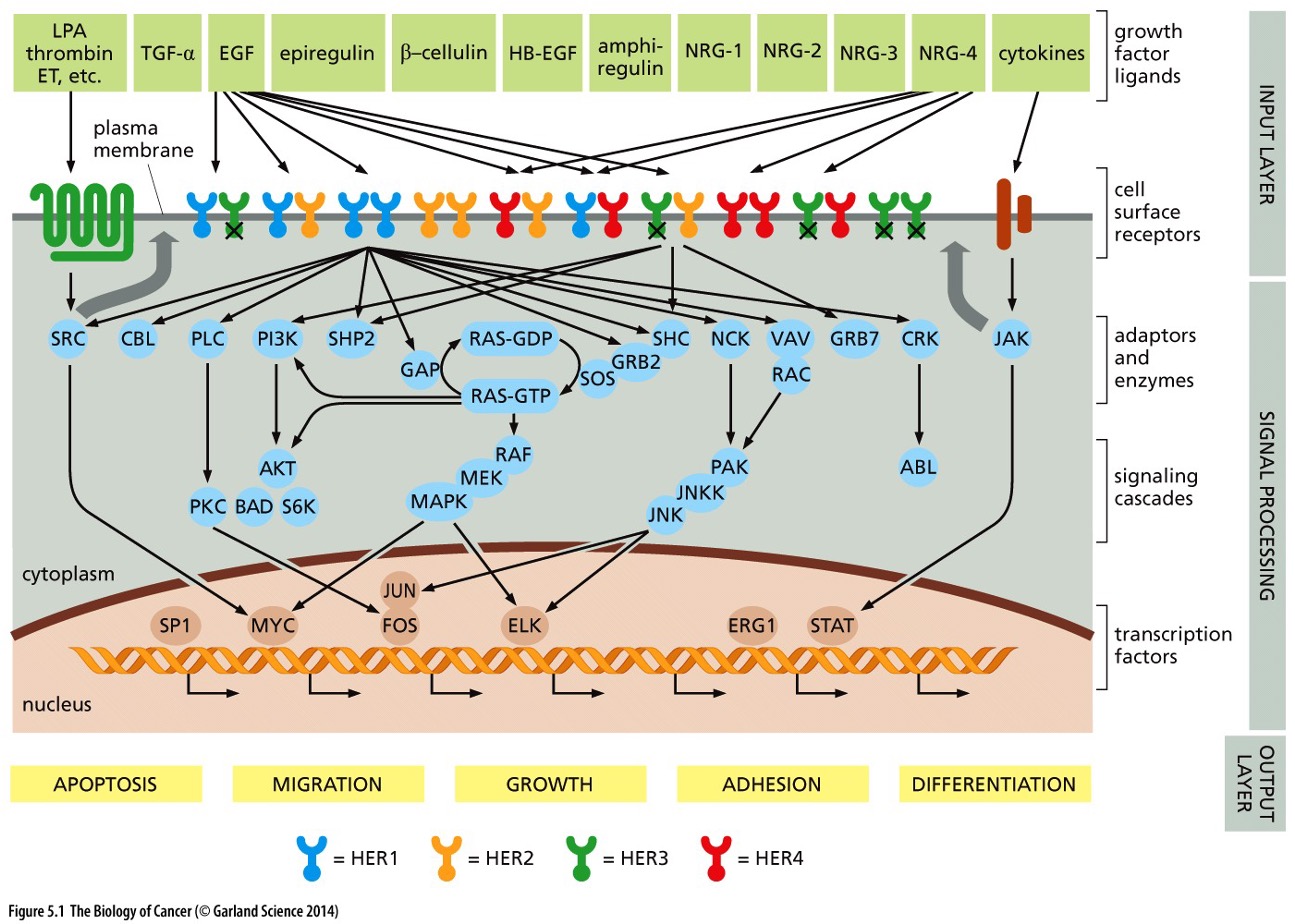
What does this picture show?
1. A variety of __***protein messengers***__ (growth factor ligands, light green rectangles, top) interact with a complex array of ***cell surface receptors***,
2. The cell surface receptors *transduce signals across the plasma membrane* (gray) into the cytoplasm.
3. There, a complex network of signal-transducing proteins processes these signals, funnels signals into the nucleus (bottom),
4. and ultimately evokes a variety of biological responses ("output layer," yellow rectangles, bottom). Many of the components of this circuitry, both at the cell surface and in the cell interior, are involved in cancer pathogenesis.
3
New cards
Growth Factors
Relatively small proteins that are released by some cells and move through the extracellular space and then bind to target cells
4
New cards
True or False: cells act autonomously
False
5
New cards
What makes the decisions about growth?
Decisions about growth must be made for the welfare of the entire tissue and whole organism
6
New cards
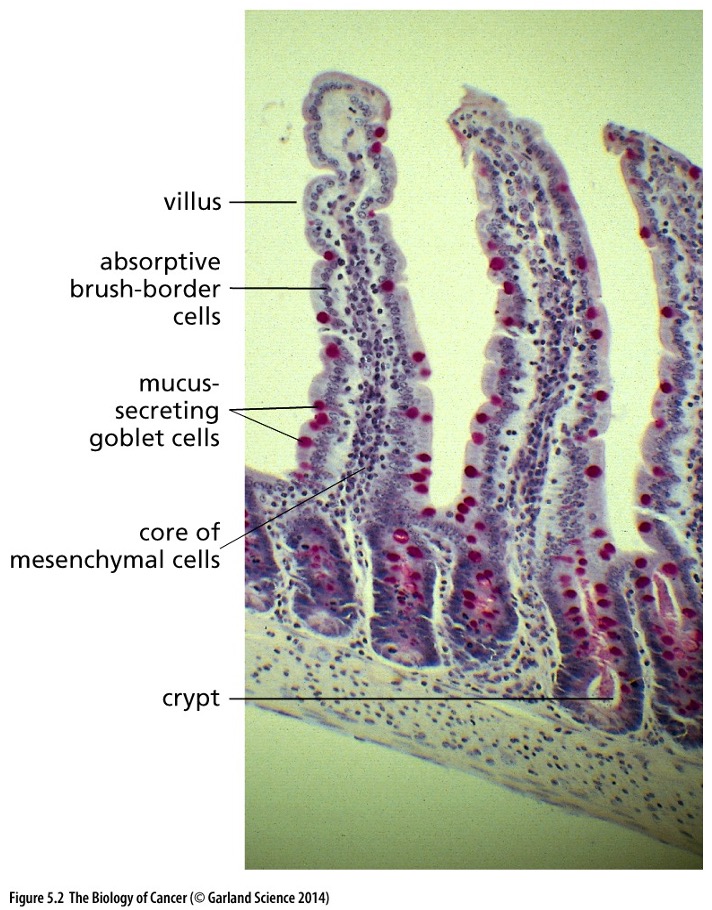
What does this picture show?
* each cell type must be tightly controlled via the epithelial lining of the small intestine.
* The relative numbers and position cell to cell signaling. New epithelial cells are generated in the crypts in order to replace others that have migrated to the tips and are eventually sloughed off
* The relative numbers and position cell to cell signaling. New epithelial cells are generated in the crypts in order to replace others that have migrated to the tips and are eventually sloughed off
7
New cards
What does proper tissue architecture depend on?
Proper tissue architecture depends on maintaining appropriate proportion of different cell types, replacement of missing cells, and discarding extra unneeded cells
8
New cards
What is PDGF?
A mitogen
9
New cards
Mitogen
something that is **able to induce cells to proliferate**
10
New cards
What do platelets do at a wound site?
* are aggregating – clot formation
* Platelets also initiate the healing process by releasing growth factors (PDGF)
* Platelets also initiate the healing process by releasing growth factors (PDGF)
11
New cards
What does PDGF do when released by platelets?
PDGF attracts fibroblasts to the wound site and induces them to proliferate
12
New cards
What does Src protein function as?
Src operates as a kinase
13
New cards
How can oncoproteins trick cells into proliferating?
Oncoproteins can trick the cell into believing that it has encountered growth factors in its surroundings
14
New cards
What does PDGF stand for
platelet-derived growth factor
15
New cards
True or False: growth factors only cause cells to grow and proliferate
False
Growth factors can cause proliferation and/or change cell shape by inducing changes in cytoskeleton
Growth factors can cause proliferation and/or change cell shape by inducing changes in cytoskeleton
16
New cards
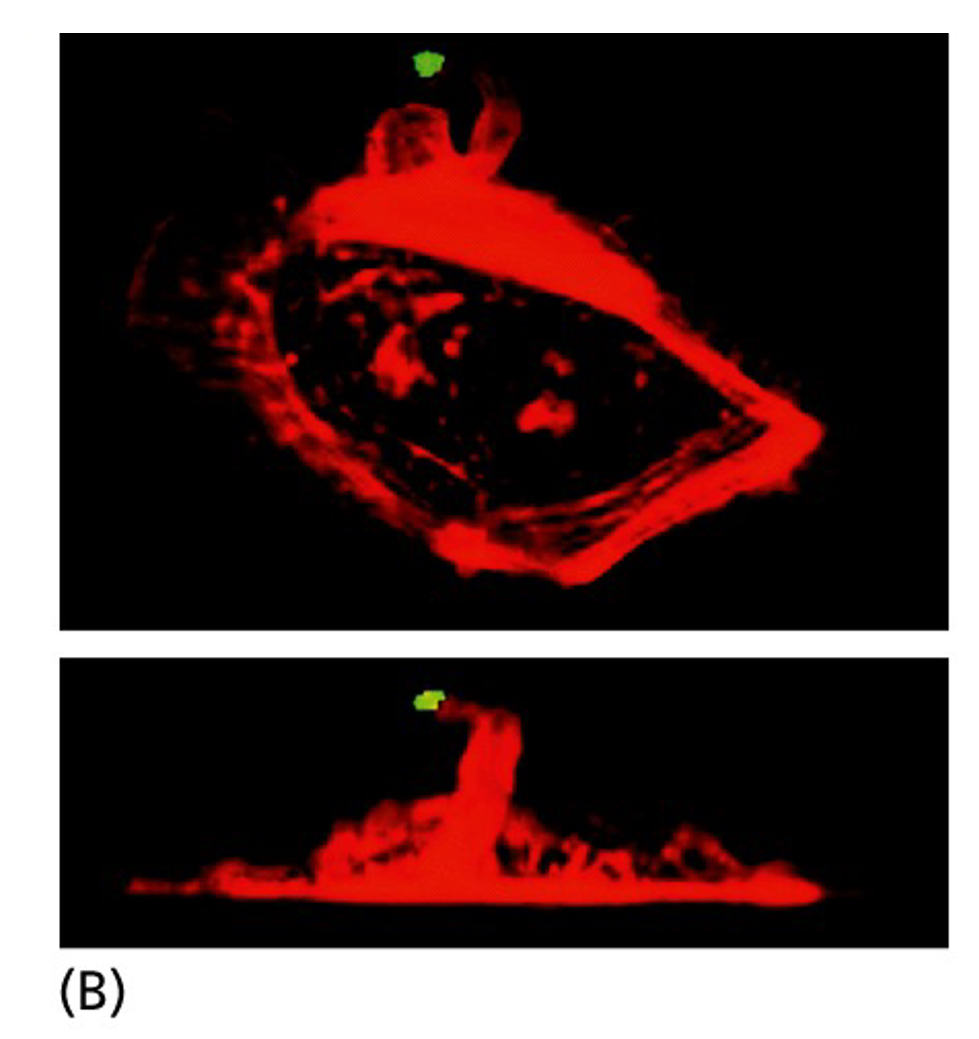
Which growth factor was this cell exposed to?
EGF (epidermal growth factor)
17
New cards
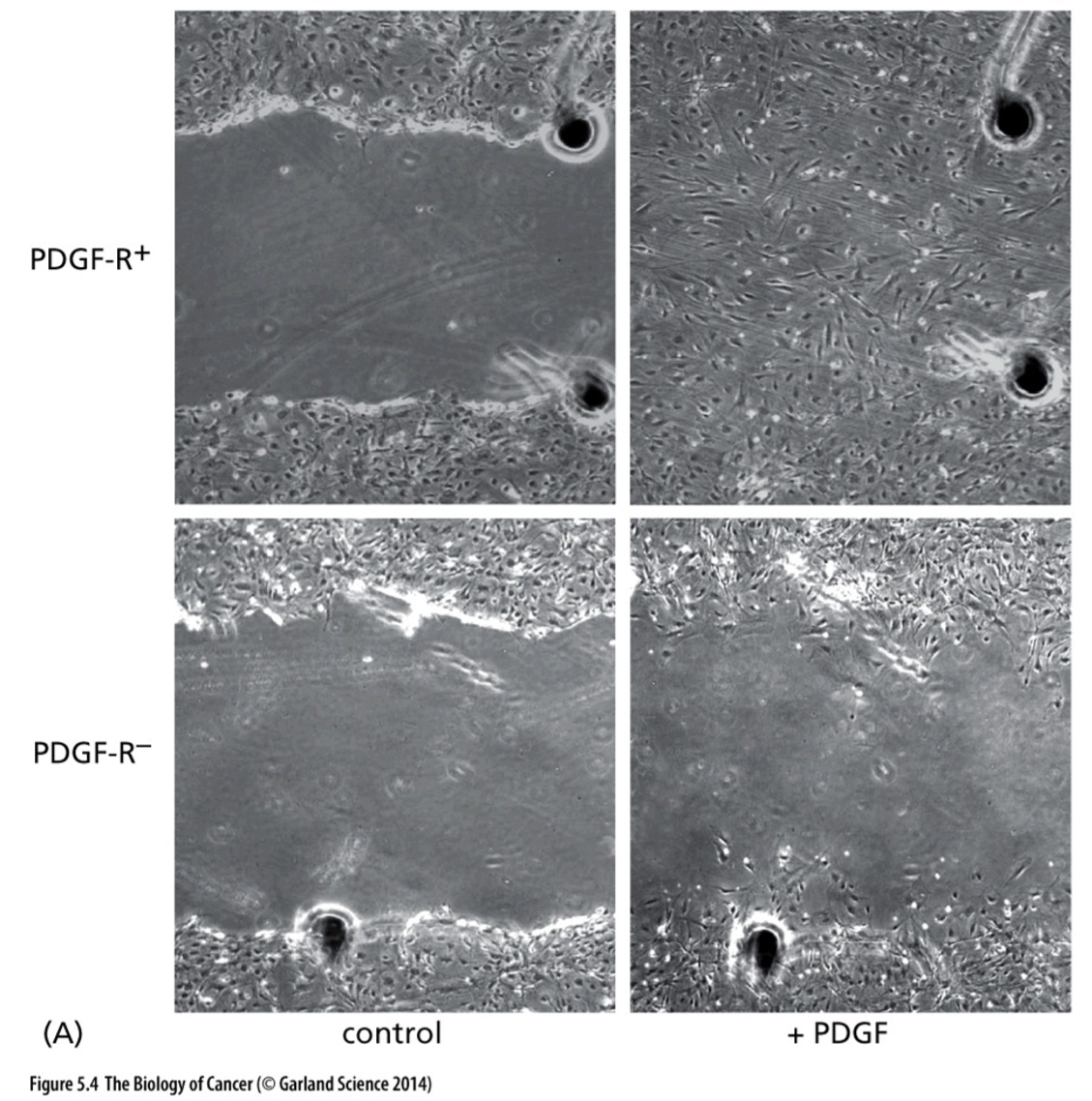
Which growth factor affected the top right picture?
PDGF
18
New cards
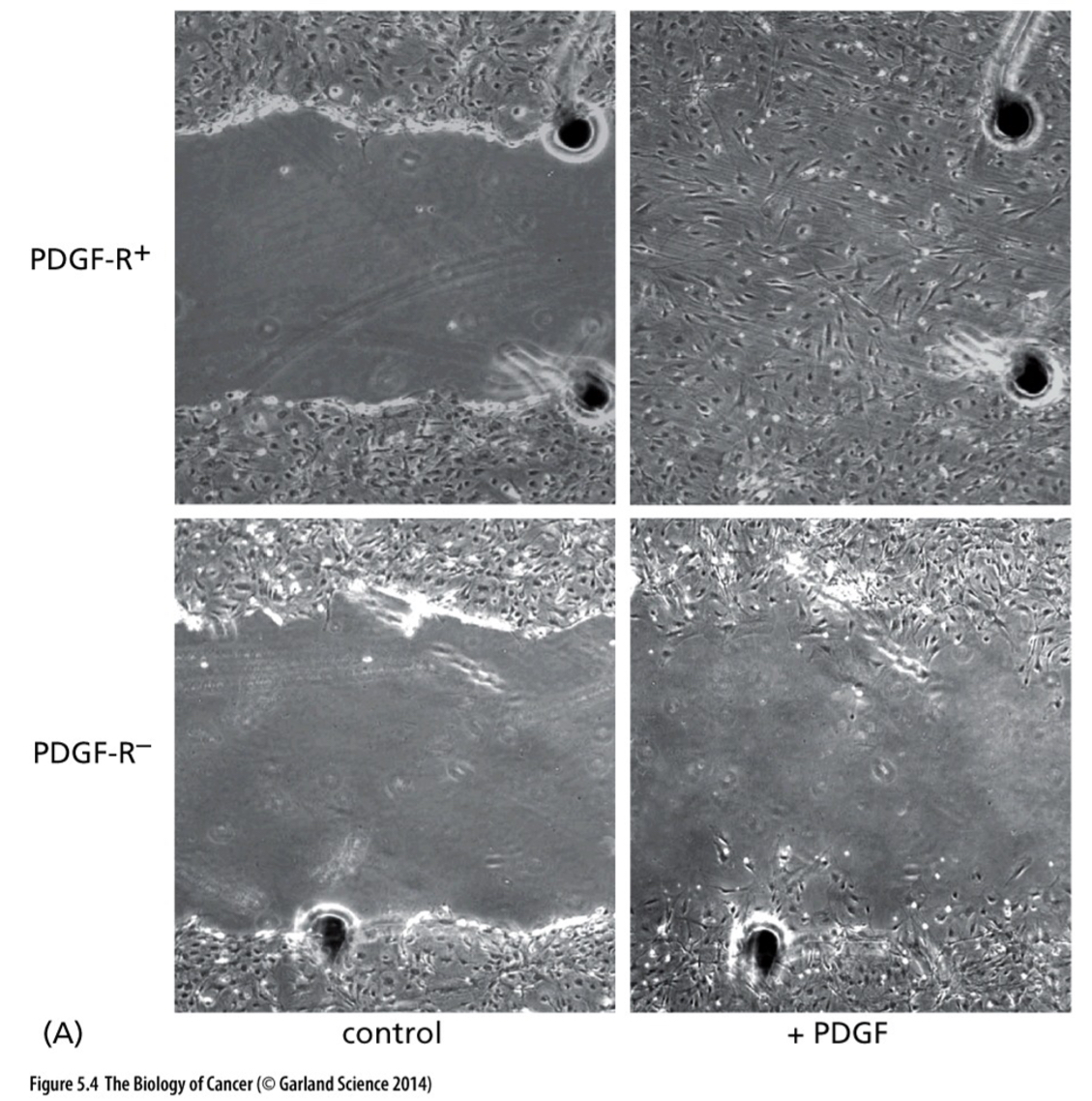
Explain this picture
1. **Top left**: has PDGF receptor, but no PDGF added
2. **Top right**: has PDGF receptors and PDGF added. Look at the fibroblast cells in the middle—> lots of proliferation
3. **Bottom left**: no PDGF receptors and no PDGF added
4. **Bottom right**: no PDGF receptors and PDGF added.There was no change because there were no receptors
19
New cards
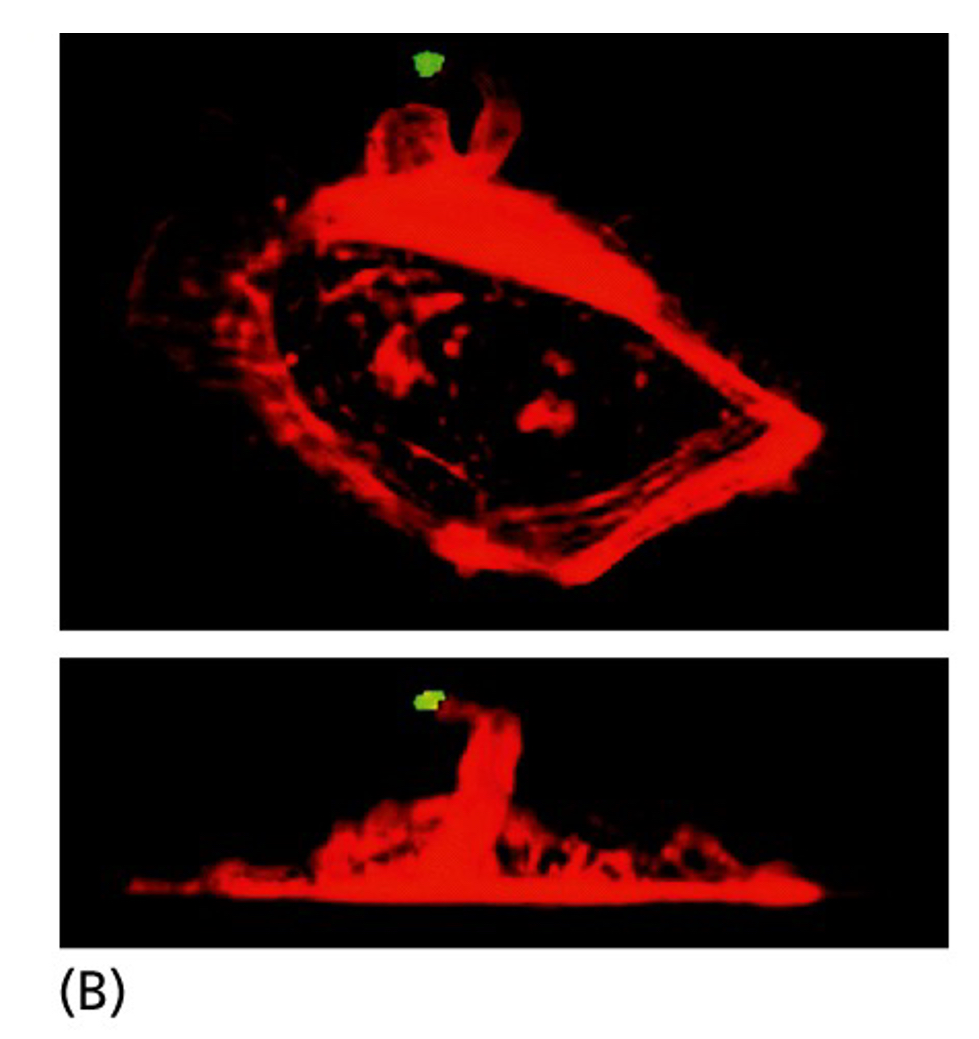
How does EGF affect a cell?
5 min after EGF that has been immobilized on a bead (green) is applied to a mouse mammary carcinoma cell, the cell has reorganized its actin cytoskeleton (red) and extended an arm of cytoplasm toward the growth factor
20
New cards
What does the src phosphorylate?
tyrosine residues
21
New cards
Why are previously discovered kinases different from src proteins?
* Previously discovered kinases attach phosphate groups to serine and threonine amino acid residues
* Src phosphorylates tyrosine residues
* Src phosphorylates tyrosine residues
22
New cards
What type of signaling largely uses tyrosine phosphorylation?
* Signaling through tyrosine phosphorylation is largely used by mitogenic signaling pathways in mammalian cells
23
New cards
What do other kinases rely on to convey their messages?
other kinases rely on serine and threonine phosphorylation to convey their messages
24
New cards
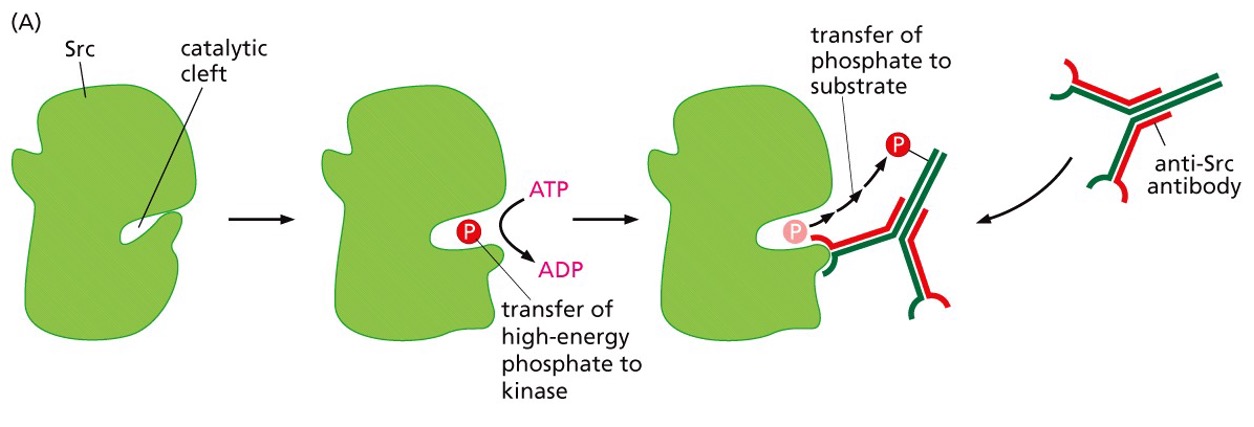
What does the picture show?
* Proof that src is a kinase
* The Src phosphorylated the antibody that they used in the experiment
* The Src phosphorylated the antibody that they used in the experiment
25
New cards
What receptor functions as a tyrosine kinase?
the EGF receptor
26
New cards
What does EGF do?
•EGF binds to receptors on the cell surface – mitogenic effect
•Cells which EGF unable to bind – unresponsive
•Cells which EGF unable to bind – unresponsive
27
New cards
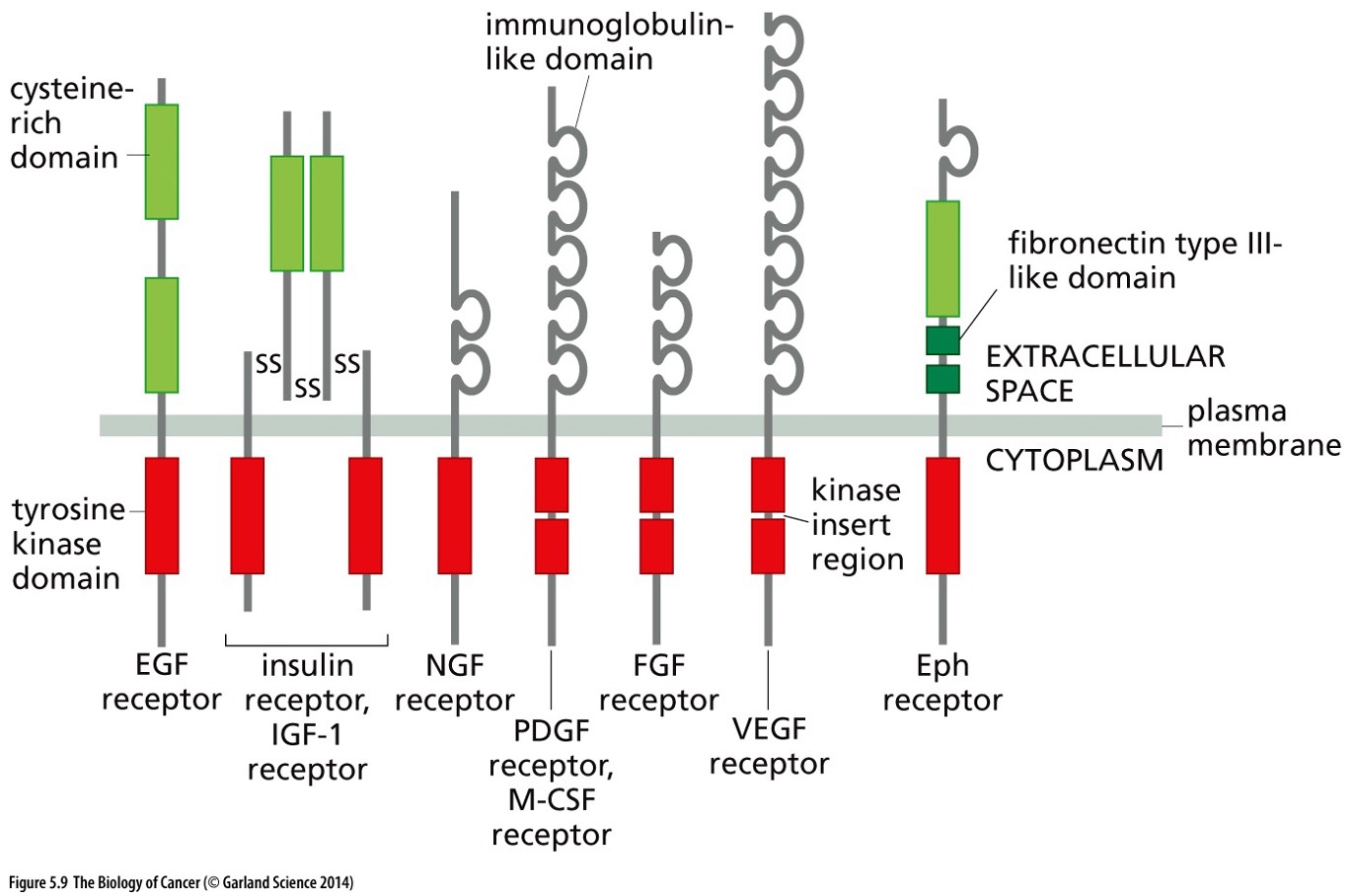
what does this picture show?
Structure of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors
28
New cards
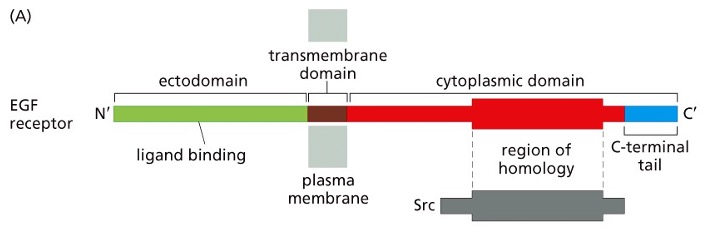
What is the EGF receptor sequence?
* Ectodomain
* Transmembrane domain
* Cytoplasmic domain
* Ectodomain binds EGF, a signal is transmitted
* to the cytoplasmic domain
* Once the cytoplasmic domain is activated- cell
induced to grow and divide
* Transmembrane domain
* Cytoplasmic domain
* Ectodomain binds EGF, a signal is transmitted
* to the cytoplasmic domain
* Once the cytoplasmic domain is activated- cell
induced to grow and divide
29
New cards
True or False: *raf and mos* oncogenes function as serine/threonine kinases
True
30
New cards
True or false: All growth factor receptors have the same ligands
* False
* **Each growth factor receptor has** **its own ligand** or set of ligands
* **Each growth factor receptor has** **its own ligand** or set of ligands
31
New cards
What does the stimulation of growth factor receptors lead to?
•Stimulation of these receptors can also induce changes in cell shape, cell survival and cell motility, in addition to stimulating growth and cell division
32
New cards
True or false: An altered growth factor receptor can function as an oncogene
True
33
New cards
Where was V-ErbB discovered?
•*V-ErbB was* discovered in the genome of avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV) which induces leukemia of red blood cell precursors (erythroleukemia)
34
New cards
What did the viral version of the growth factor receptor lack?
It lacked the ectodomain and therefore is unable to bind EGF
35
New cards
Truncated receptors _______ sends growth stimulating signals
\
a) always
b) never
c) sometimes
\
\
a) always
b) never
c) sometimes
\
a) Always
36
New cards
truncated EGF receptors were discovered to be present in 1/3 of human ________
\
a) breast cancer cells
b) osteocytes
c) glioblastomas
d)melanomas
\
a) breast cancer cells
b) osteocytes
c) glioblastomas
d)melanomas
\
c) glioblastomas
c) glioblastomas
37
New cards
Paracrine signaling
This type of signaling, in which cells communicate over relatively short distances
38
New cards
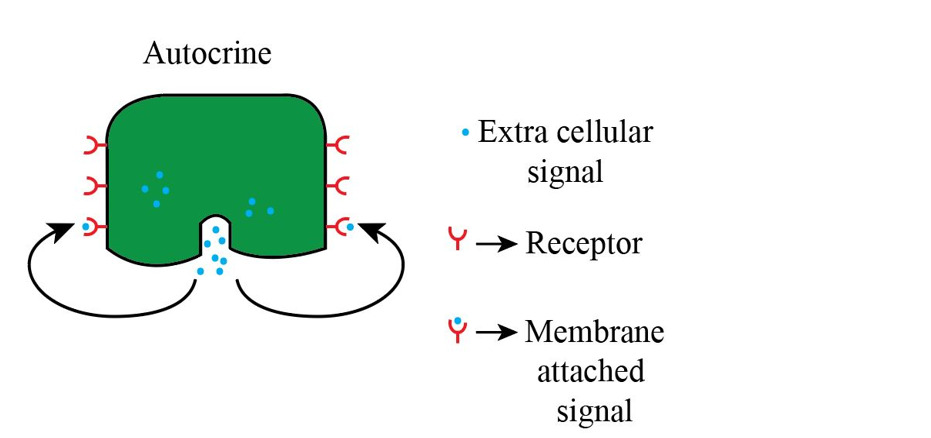
Autocrine signaling
\
\
**Autocrine signaling** is a type of cell signaling where a cell signal released from the cell binds to the same cell
\
**Autocrine signaling** is a type of cell signaling where a cell signal released from the cell binds to the same cell
39
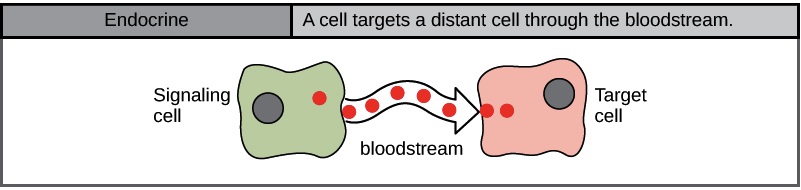
New cards
Endocrine Signaling
Long Distance signaling, signals travel through the bloodstream
40
New cards
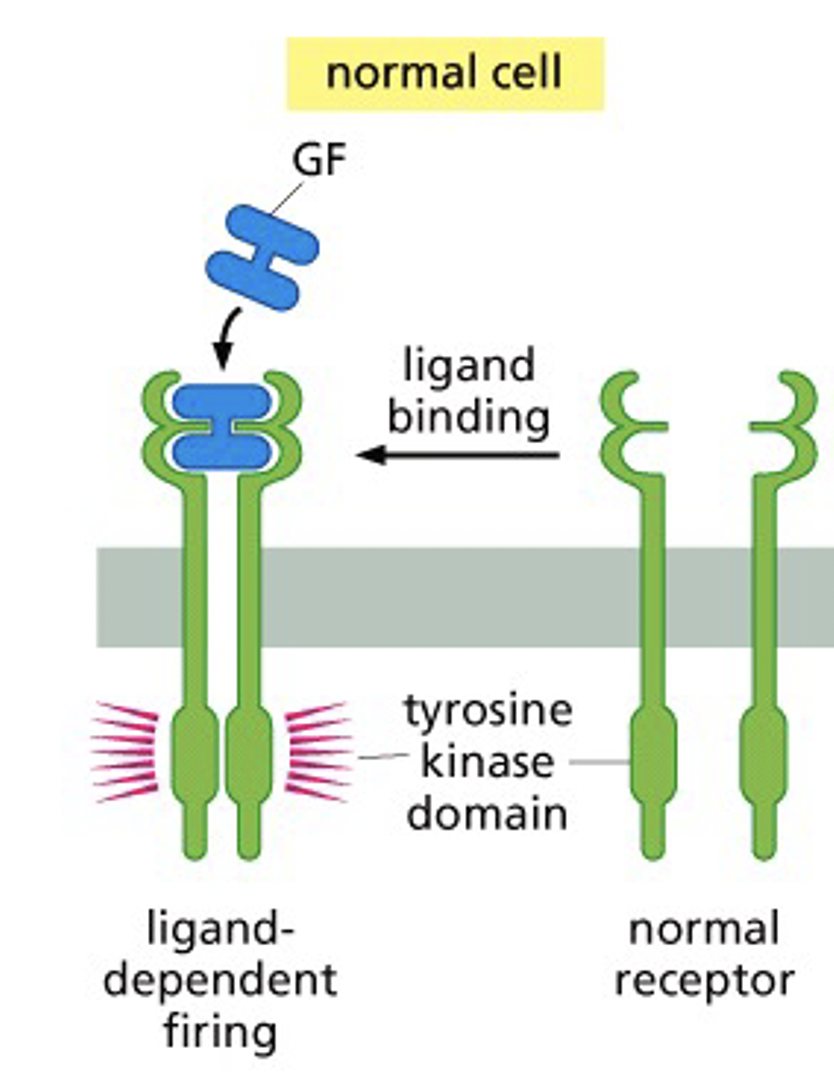
How do normal growth factors and growth factor receptors work?
* ligand-dependent firing
* Growth factor binding leads to phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on a number of intracellular signaling molecules, and these molecules transmit the signal to the inside of the cell. then it goes into the nucleus and usually increases transcription
* Growth factor binding leads to phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on a number of intracellular signaling molecules, and these molecules transmit the signal to the inside of the cell. then it goes into the nucleus and usually increases transcription
41
New cards
What are 2 different ways cancer cells come to be from growth factors and growth factor receptors?
\
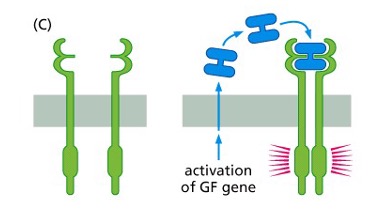
Ligand-Independent Firing
1. mutations affecting structure can keep the receptors firing signals even without a ligand
1. can have no ectodomain (top part) or somewhere in it
2. Overexpression can occur when there are multiple receptors, there’s an increased response
\
Ligand-Independent Firing
1. mutations affecting structure can keep the receptors firing signals even without a ligand
1. can have no ectodomain (top part) or somewhere in it
2. Overexpression can occur when there are multiple receptors, there’s an increased response
\
42
New cards
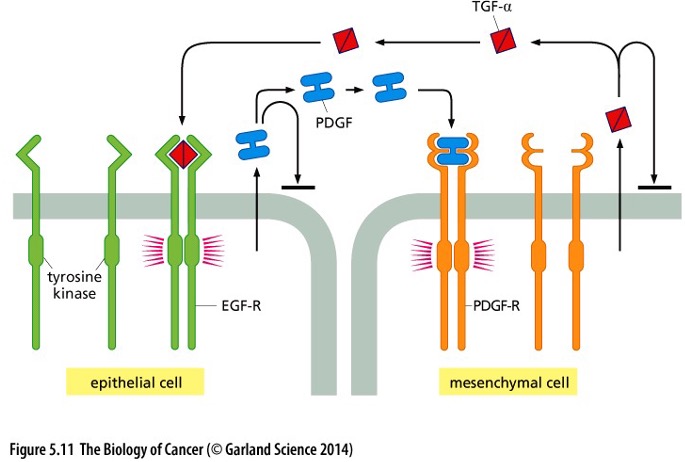
What type of signaling does this picture show?
Paracrine Signaling
43
New cards
What type of signaling is seen in this pic?
autocrine signaling in cancer cell
44
New cards
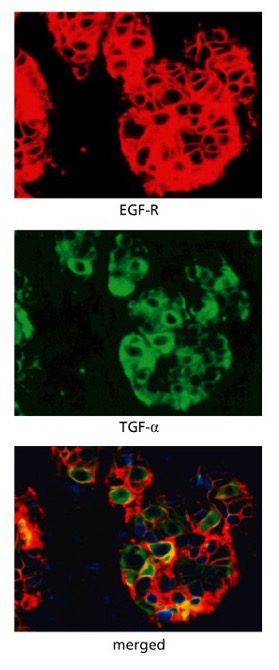
What is this picture an example of?
Example of autocrine signaling in breast cancer carcinoma
45
New cards
True or False: Growth factor receptors similar to the EGF receptor have been found to be overexpressed in human tumors or synthesized in a structurally altered form
True
46
New cards
Transphosphorylation underlies the operations of receptor_____
\
serine/threonine kinases
or
tyrosine kinases
\
serine/threonine kinases
or
tyrosine kinases
\
tyrosine kinases
tyrosine kinases
47
New cards
Transphorphorylation
Each kinase domain phosphorylates the the tyrosine residues of the other receptor
48
New cards
True or False:
Some receptors can heterodimerize with other receptors; i.e. *HER2* can heterodimerize with *EGF-R*
49
New cards
What was seen in tyrosine kinase receptors in many cancers?
•Alterations and over expression in tyrosine kinase receptors (RTKs) have been found in many cancer
50
New cards
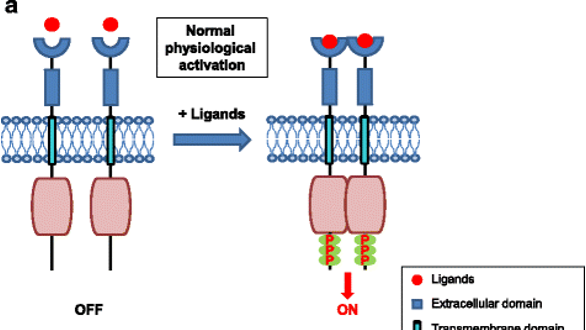
What does this picture show?
Normal
RTKs are activated through formation of inter-molecular dimerization in the presence of ligands, resulting in kinase activation and phosphorylation of the receptor C-terminal tail
\
RTKs are activated through formation of inter-molecular dimerization in the presence of ligands, resulting in kinase activation and phosphorylation of the receptor C-terminal tail
\
51
New cards
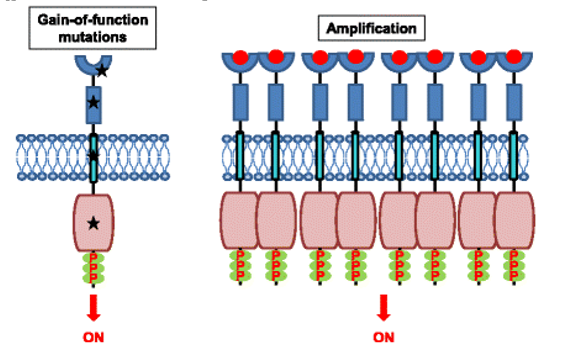
What does this picture show?
Left: The mutations lead to constitutive activation of the RTK, typically in the absence of a ligand.
Right: Overexpression of RTKs (receptor tyrosine kinases) – often as a result of genomic amplification of the RTK gene - leads to the increased local concentration of receptors
Right: Overexpression of RTKs (receptor tyrosine kinases) – often as a result of genomic amplification of the RTK gene - leads to the increased local concentration of receptors
52
New cards
Erythropoietin (EPO) receptor
Regulates the development of red blood cells
53
New cards
Thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor
Controls the development of megakaryocytes (platelet precursors)
54
New cards
Cytokine receptors
regulate diverse immune responses
•Interferon
•Interleukins
•Interferon
•Interleukins
55
New cards
TGF-β (transforming growth factor) receptor
Central role in cancer pathogenesis – suppress proliferation of normal epithelial cells while promoting invasive properties of transformed cells
56
New cards
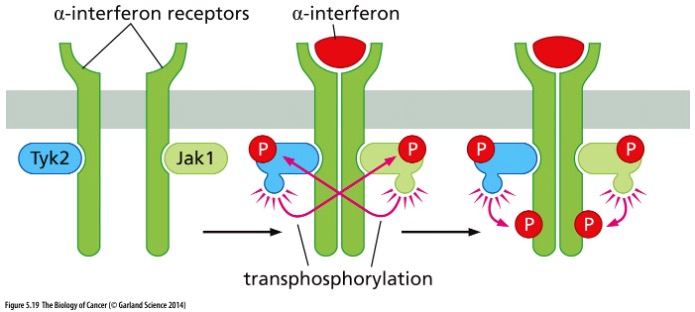
Describe the pic
\-Diff type of receptor
\-does same thing as tyrosine kinase, but diff family
Structure of cytokine receptors: Tyrosine kinases of the *Jak* family
\-does same thing as tyrosine kinase, but diff family
Structure of cytokine receptors: Tyrosine kinases of the *Jak* family
57
New cards
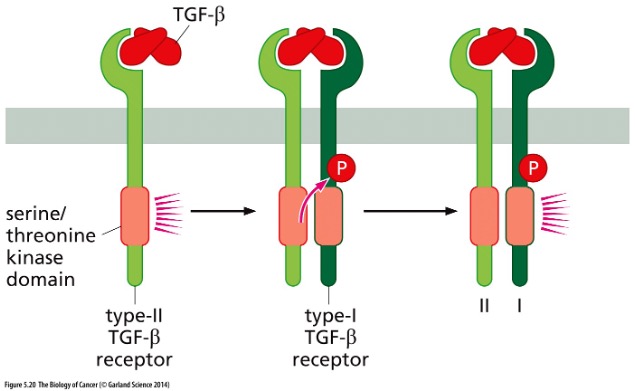
Describe the pic
\
Structure of TGF- β Receptor: Kinase domains specifically phosphorylate serine and threonine
\-Only one side activated
Structure of TGF- β Receptor: Kinase domains specifically phosphorylate serine and threonine
\-Only one side activated
58
New cards
What type of signaling does notch receptor use?
**Juxtracrine signaling**
59
New cards
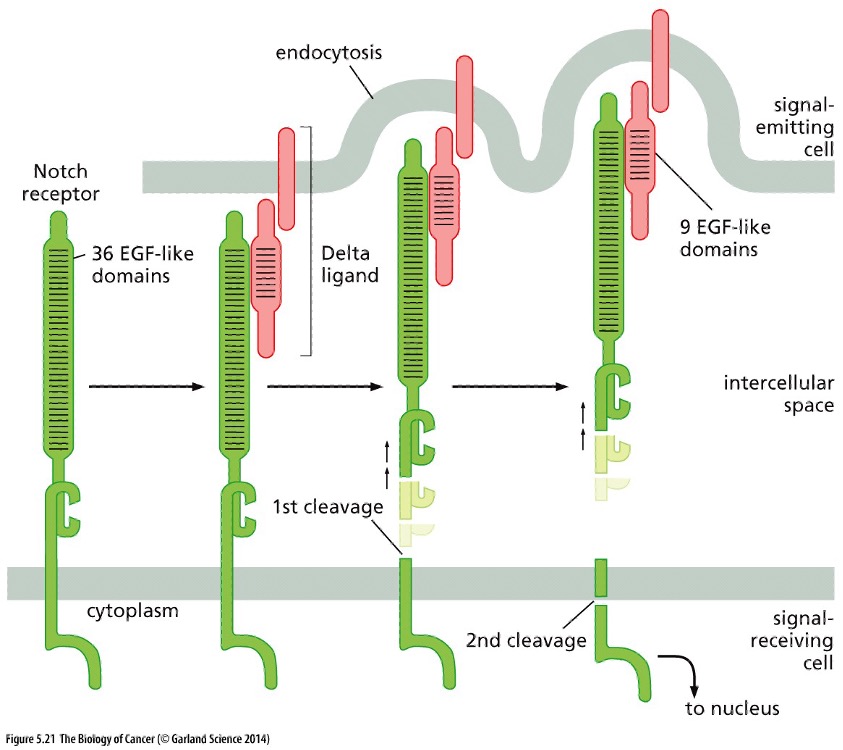
What type of signaling and receptor are seen in the pic?
* **Juxtracrine signaling**
* Notch Receptor
* Notch Receptor
60
New cards
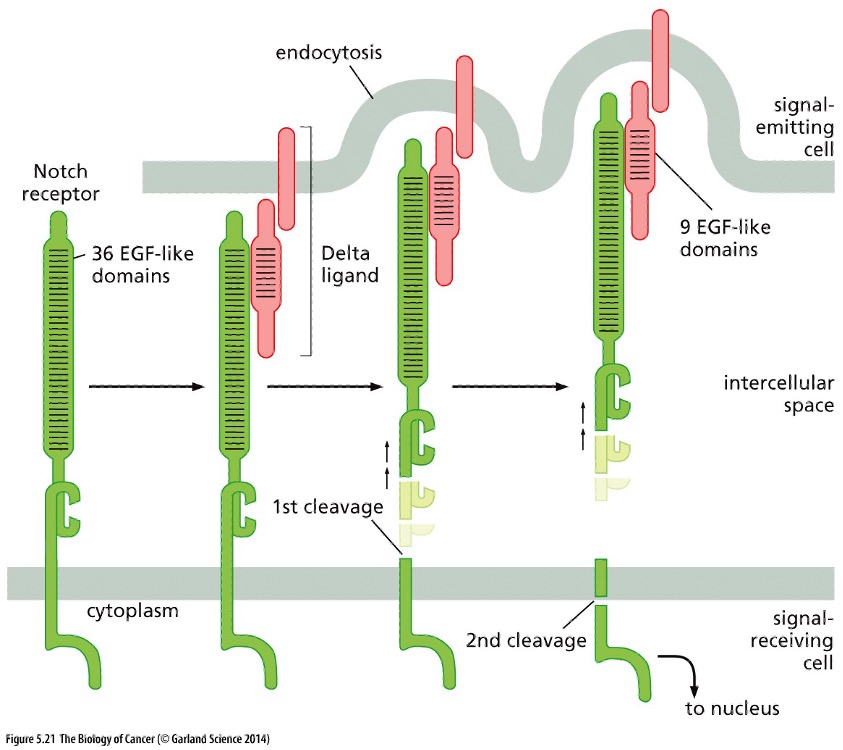
**Juxtacrine** Signaling
* The cells sending the signal have membrane-bound ligands which bind to and activate cell-surface **Notch receptors** on the receiving cell
* Ligand attaches and uses mechanical force to tear the Notch ectodomain away
* Generated by endocytosis of the ligand
* Proteolytic cleavage occurs as a result
* Fragment of Notch is now able to enter the nucleus and activate gene expression
* Ligand attaches and uses mechanical force to tear the Notch ectodomain away
* Generated by endocytosis of the ligand
* Proteolytic cleavage occurs as a result
* Fragment of Notch is now able to enter the nucleus and activate gene expression
61
New cards
True or False: The ligands juxtacrine signaling utilizes are secreted
False
* The cells sending the signal have membrane-bound ligands which bind to and activate cell-surface **Notch receptors** on the receiving cell
* The cells sending the signal have membrane-bound ligands which bind to and activate cell-surface **Notch receptors** on the receiving cell
62
New cards
In juxtacrine signaling what does the cut piece of notch receptor act as?
Transcription Factor
* Fragment of Notch is now able to enter the nucleus and activate gene expression
\
* Fragment of Notch is now able to enter the nucleus and activate gene expression
\
63
New cards
What forms of Notch receptors have been found in half adult T-cell leukemias?
•***Mutant forms of Notch (constitutively active)*** have been found in half adult T-cell leukemias
64
New cards
Which type of signaling does the notch receptor use?
**Juxtracrine signaling**
65
New cards
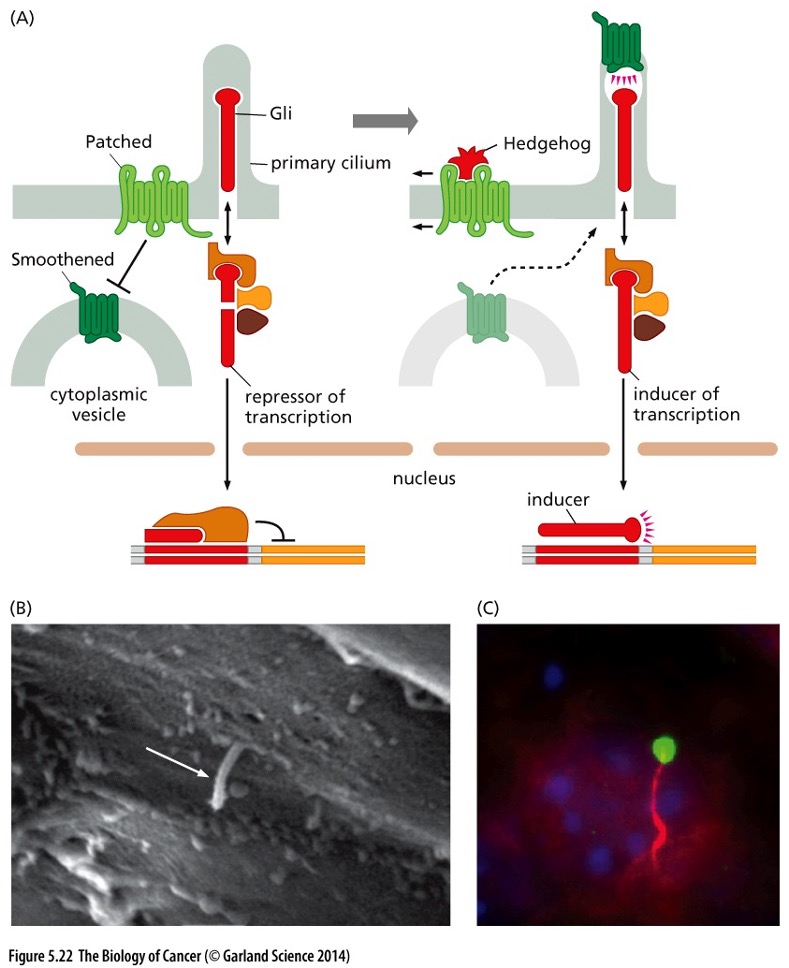
What type of signaling system does this pic show?
The Patched-Smoothened signaling system
66
New cards
What is the substrate of the Patched-Smoothened signaling system?
Hedgehog
67
New cards
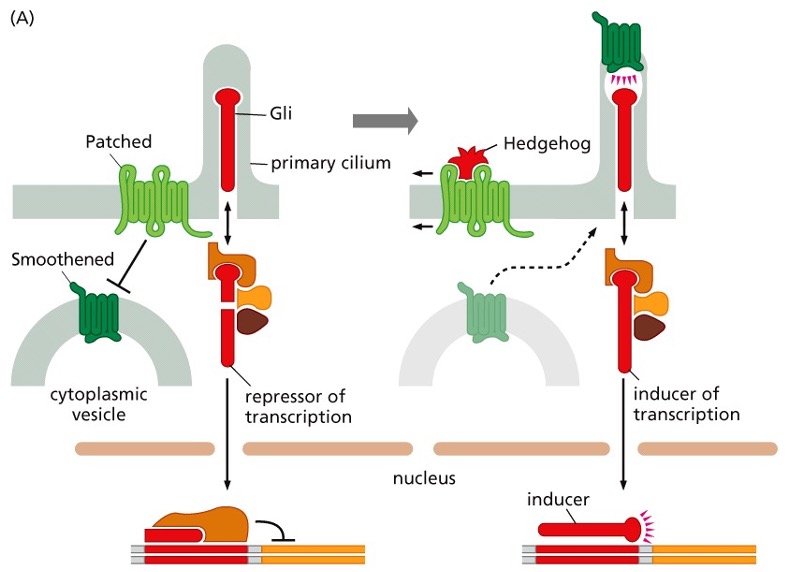
How does this signaling system work?
•When bound by Hedgehog (Hh), Smo and Gli accumulate in the primary cilium
•Gli is converted from a repressor into an inducer of transcription
•Gli is converted from a repressor into an inducer of transcription
68
New cards
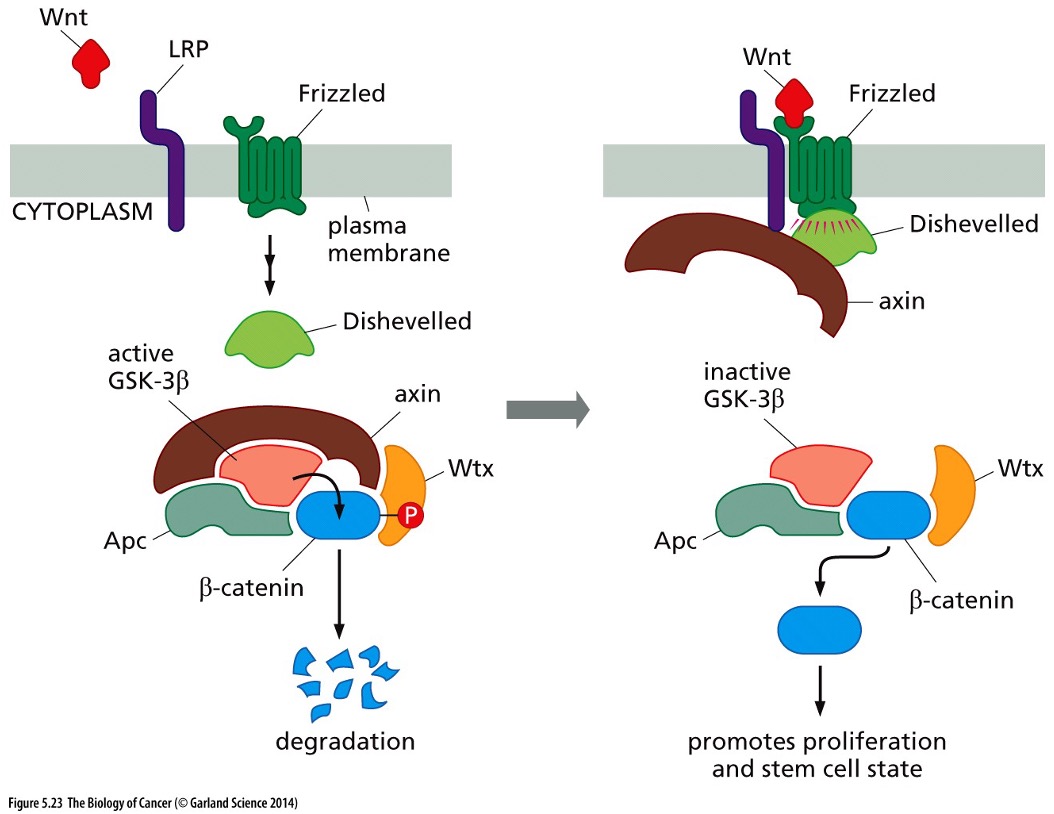
What signaling is is this?
Canonical Wnt signaling via Frizzled receptors
69
New cards
Why does Canonical Wnt signaling via Frizzled receptors play a critical role in cancer pathogenesis?
When this pathway is active, B-catenin stays active and it promotes proliferation and stem cell state which cancers like
70
New cards
**Chemokine receptors** (subset of GPCRs)
play an important role of recruiting cells into the tumor associated stroma, which provides essential physiological support for a variety of cancer cells.
71
New cards
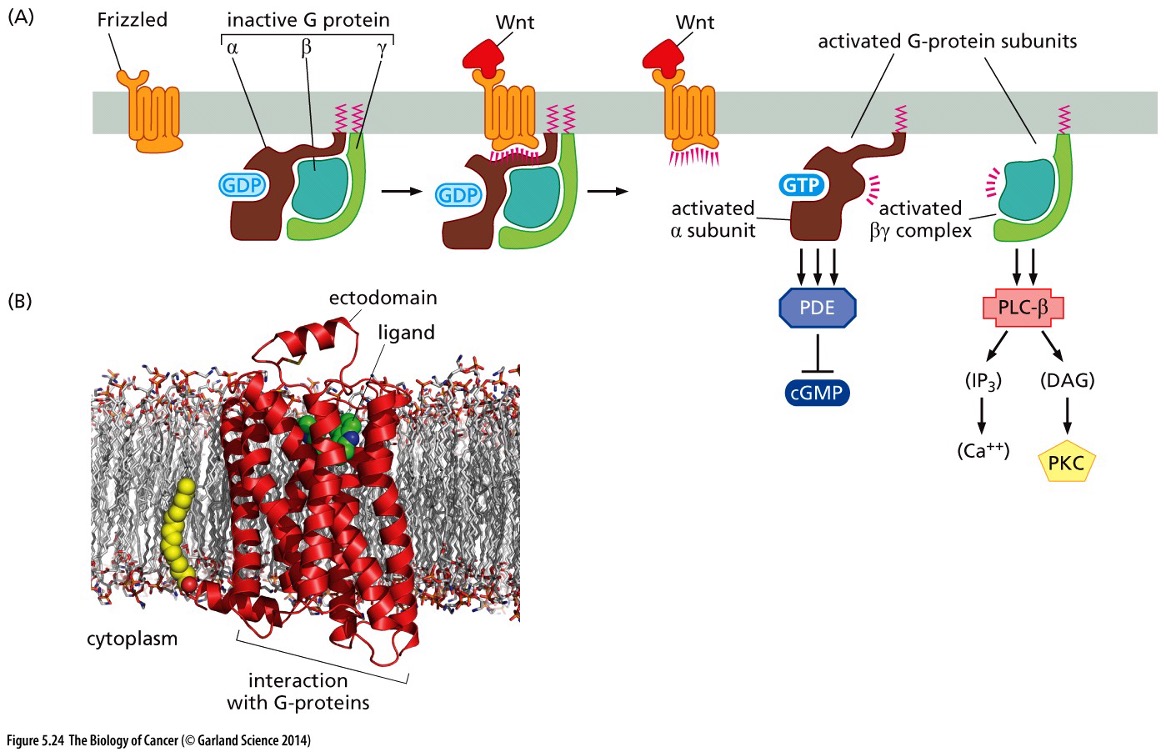
Does this picture show Non-Canonical or Canical Wnt signaling via Frizzled receptors
Non-Canonical Wnt signaling via Frizzled receptors
72
New cards
Is Wnt secreted?
No, it’s Tethered tightly to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and through a lipid tail to the cell membrane
73
New cards
True or False: In the thousands of GPCR-encoding genes in the mammalian genome, a large number of these genes contribute directly to cancer
False,
Only a small number of these genes contribute directly to cancer
Only a small number of these genes contribute directly to cancer
74
New cards
Which of the following is a nuclear receptor?
a) estrogen
b) gli
c) growth factor receptors
d) none of the above
a) estrogen
b) gli
c) growth factor receptors
d) none of the above
a) estrogen
75
New cards
Which receptors play a role in breast, ovarian and prostate carcinomas?
Estrogen, progesterone and androgen receptors
76
New cards
What are some signaling molecules that can cross the plasma membrane on their own and enter the nucleus?
•Steroid sex hormones
•Vitamin D
•Retinoids
•Vitamin D
•Retinoids
77
New cards
True or False: Nuclear receptors can directly alter gene transcription
True
•Contain a DNA binding domain
•Contain a DNA binding domain
78
New cards
Tamoxifen (4-OHT)
selective **estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)**
79
New cards
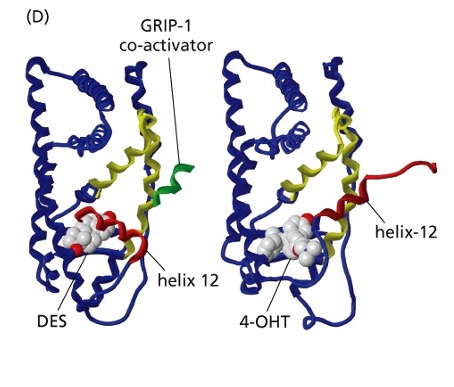
What does Tamoxifen (4-OHT) (selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) ) do?
Block E2 signaling so that the co-activator is unable to bind blocking transcriptional activation
•Clinical benefit for patients with ER-positive breast carcinomas
•Clinical benefit for patients with ER-positive breast carcinomas
80
New cards
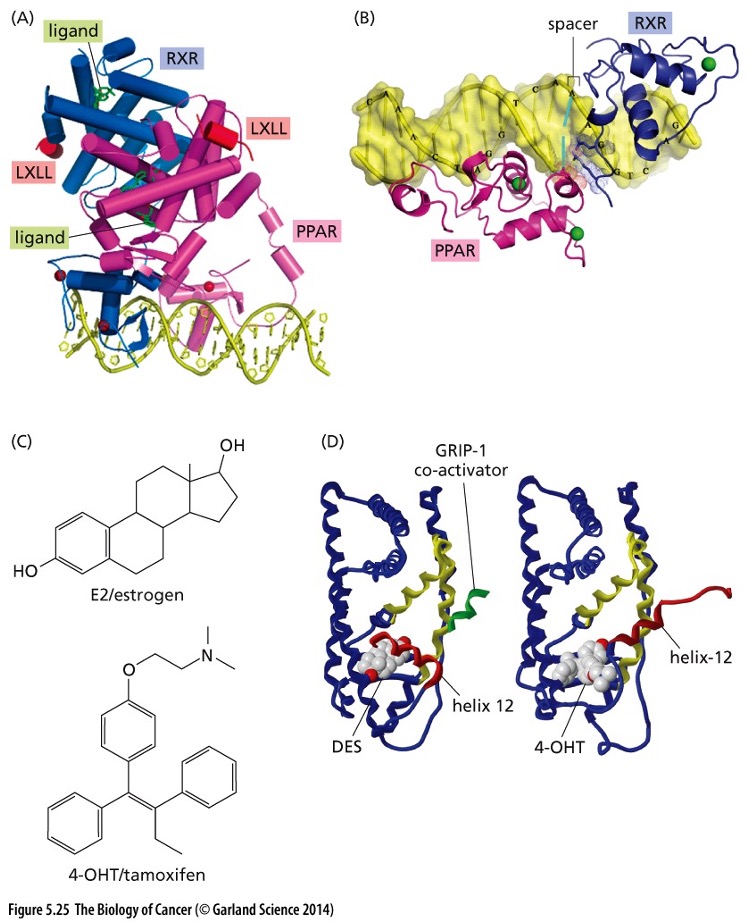
What type of receptors are shown?
Nuclear Receptors
81
New cards
What do integrin receptors sense the association between?
Integrin Receptors sense association between t**he cell and the ECM**
82
New cards
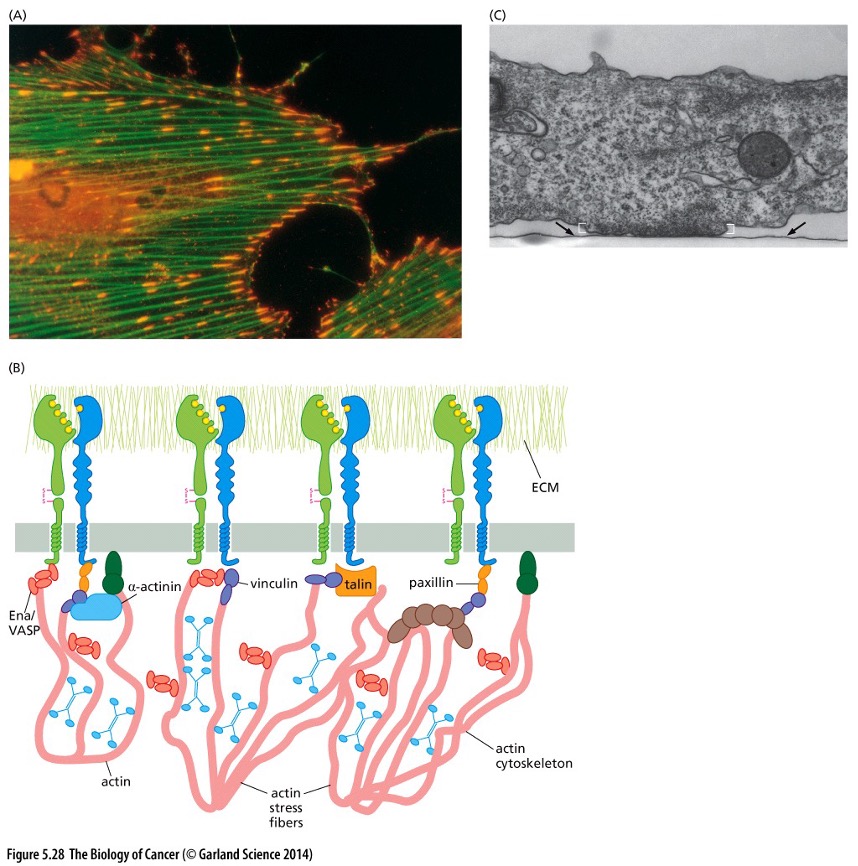
What does this pic show?
**Integrin Receptors**
This schematic figure of the organization of integrins (green, blue) indicates their association with the ECM (green fibers, above) through their ectodomains and their association with the actin cytoskeleton (pink chains) through their cytoplasmic domains via the B subunit of each heterodimer. A series of intermediary proteins, such as actinin, vinculin, and talin, allows these linkages to be formed
This schematic figure of the organization of integrins (green, blue) indicates their association with the ECM (green fibers, above) through their ectodomains and their association with the actin cytoskeleton (pink chains) through their cytoplasmic domains via the B subunit of each heterodimer. A series of intermediary proteins, such as actinin, vinculin, and talin, allows these linkages to be formed
83
New cards
True or False: The ECM and the actin cytoskeleton allow for anchorage, cancer cells do not need anchorage to grow
True
84
New cards
**All of the following are alterations of a growth factor receptor that would likely lead to the transformation of a normal cell into a cancer cell except ____**
A.A truncated receptor missing the ectodomain that is constitutively active
B.A receptor whose ligand binding site is altered resulting in the inability to bind the ligand and active the receptor
C.A mutation in the cytoplasmic domain that leads to constant activation of the receptor
D.A mutation that does not lead to an alteration of the function of the receptor.
E.Both B and D
\
A.A truncated receptor missing the ectodomain that is constitutively active
B.A receptor whose ligand binding site is altered resulting in the inability to bind the ligand and active the receptor
C.A mutation in the cytoplasmic domain that leads to constant activation of the receptor
D.A mutation that does not lead to an alteration of the function of the receptor.
E.Both B and D
\
E. Both B and D