Practice Exam Questions for MLS, MT, and MLT
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is the primary function of hemoglobin?
Carry Oxygen to tissues
Hemoglobin serves to carry inspired oxygen from the lungs to tissues, and carbon dioxide from tissues back to the lungs, where it is expired.
Which of the following is responsible for humoral response?
B lymphocytes
In the humoral response, B-lymphocytes are stimulated to when an antigen binds to its surface receptors. This sensitizes or primes the B cell and it undergoes clonal selection, where it reproduces asexually by mitosis. Most of the family of clones become plasma cells. These cells produce antibodies while other B cells become long-lived memory cells
Which of the following can help prevent fires?
Good housekeeping
Keeping your work place neat and orderly
Not permitting trash and combustible material to pile up
The ADA recommends performing an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) on all individuals who are at increased risk for diabetes
False
The ADA recommends regular screening for individuals who are at increased risk for diabetes. OGTT use is discouraged for these individuals unless blood glucose and HbA1c concentrations remain below diagnostic ranges for diabetes but patient displays symptoms of diabetes.
If the antigen frequencies for K = 0.09 and Fy^a = 0.66, what percent of type-specific units would be compatible for a patient with anti-K and anti-Fy^a?
31
The negative antigen frequencies are used in the formula below to determine the percent of type-specific units that would be compatible for the patient. Negative antigen frequencies are determined by subtracting the percent antigen frequency from 100%. The negative antigen frequency for K in this case is .91 (1.00-.09) and the negative antigen frequency for FY^a is 0.34 (1.00-.66).
% compatible units available = 100 x (Neg frequency #1 x Neg frequency #2…)
For this case, the calculation is: % compatible units available = 100 x (0.91 × 0.34) = 30.94 or 31%
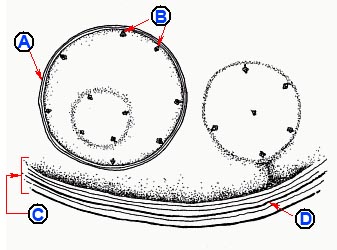
Label the morphologic structures on this parasite form
B - Immature scolices
D - Cyst wall
C - Germinal tissue layers
A - Daughter cyst
Pictured here is an Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst. Humans are accidental hosts in the life cycle of this parasite. Even though each immature scolex has the ability to form an adult worm when developed, there is no mechanism for them to complete their life cycle in the outside environment when humans become involved. Hydatid cysts form in human tissue where they may cause intense pain. Rupture of such a cyst may result in serious complications including death
The term TITER (as it applies to the measurement of antibodies) is best defined as:
Reciprocal of maximum reactive dilution
A specimen with a last reacting tube containing a 1:100 dilution, would be said to have a titer of 100
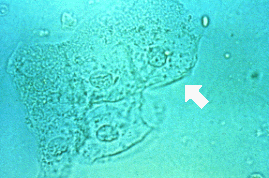
The cell indicated by the arrow is a:
Squamous epithelial cell
Large flat irregular squamous epithelial cells with a low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio are generally found in the urine of females as a result of vaginal contamination
A 40-year-old female receives two units of Red Blood Cells during a surgical procedure. The patient has no prior history of transfusions. Seven days later, she presents with extensive bruising of the extremities and bleeding of the gums, with no additional symptoms. Her platelet count is 5 × 10^9/L (reference interval 150 - 400 × 10^9/L) What is the most likely diagnosis?
Post transfusion purpura (PTP)
Her symptoms, including severe thrombocytopenia one week after transfusion, are most consistent with post-transfusion purpura (PTP). PTP results as an anamnestic response to a platelet antigen
PTP is caused by platelet-specific antibodies in a patient who has been previously exposed to platelet antigens through pregnancy or transfusion. The most frequently identifies antibody is Anti-PLA1, which reacts with platelet antigen HPA-1a. The platelet antibody binds to the platelet surface, which allows for extravascular removal through the liver or the spleen. The patient’s own platelets are destroyed as well, thus aggravating the thrombocytopenia
Heparin interacts with______________, which subsequently inhibits thrombin
antithrombin III
Antithrombin serves as a coagulation inhibitor. When it binds with heparin, coagulation inhibition is made much stronger. This interaction is the reason why heparins are utilized as medications to produce anticoagulation (prevent coagulation)