Cardiovascular System Intro
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The molecular process necessary to keeps cells alive is called
diffusion
diffusion
allows oxygen and nutrients to enter cells and waste to leave
Why is the cardiovascular system necessary for humans?
Diffusion alone is too slow for large organisms. The cardiovascular system moves substances quickly over long distances
Larger surface area =
increase diffusion efficiency
cells get nutrients and remove waste faster
three main functions of the cardiovascular system?
Gas exchange
Energy balance
Osmoregulation & Communication
Gas exchange
delivers oxygen for cellular respiration and removes carbon dioxide
Energy balance
delivers nutrients for digestion and absorption
removes waste products to excretory organs
Osmoregulation & Communication
carries water, ions, and hormones
three main components of the cardiovascular system
Circulatory fluid (blood) - carries gases and nutrients
Tubes. (blood vessels) - arteries→capillaries→veins
Muscular pump (heart) - moves blood
What are the three types of blood vessels ?
arteries
capillaries
veins
Function of arteries
carry blood away from the heart, branching into smaller arterioles and capillaries
Function of capillaries
infiltrate tissues and organs allowing diffusion of molecules into cells
Function of veins
Merge into veins/venules to carry blood towards the heart
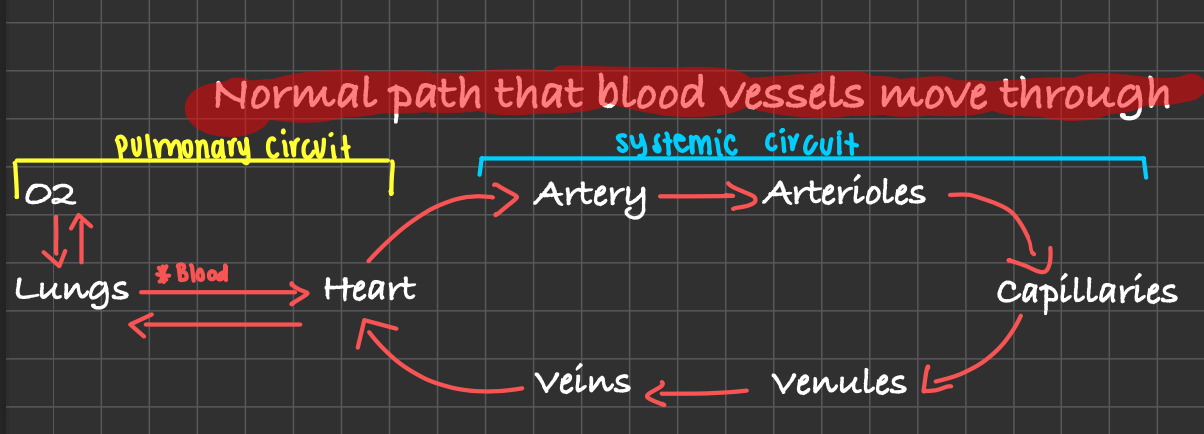
What is the normal path of blood flow through the vessels?
heart→arteries→arterioles→capillaries→venules→veins→heart
Where is the heart located?
thoracic cavity, between the lungs
posterior to the sternum
anterior to the vertebral column
superior of the diaphragm
What are the four chambers of the heart?
Two atria (upper chambers)
Two ventricles (lower chambers)
Atria are upper chambers of the heart that
receive blood returning to the heart
Right atrium
low-oxygen blood returns from systematic circuit
Left atrium
high-oxygen blood returns from pulmonary circuit
Ventricles are lower chambers that
pump blood out of the heart
Right ventricle
sends low-oxygen blood to pulmonary circuit
Left ventricle
sends high-oxygen blood to systemic circuit
Two types of circulatory circuits
pulmonary circuit
systematic circuit
make up the “double circulation”
pulmonary circuit
right heart pumps blood to lungs for oxygenation
chambers involved: right atrium and right ventricle
systemic circuit
left heart pumps oxygenated blood to organs/tissues
chambers involved: left atrium and left ventricle
Pulmonary circuit carries
deoxygenated blood to lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart
Systemic circuit delivers
oxygenated blood to the organs/tissues and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart