ap environmental science unit 4 (earth systems and resources)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 4 APES review with detailed but concise explanations of plate tectonics, ENSO/la niña, coriolis effect, wind patterns, weather, thermohaline circulation, soil, and watersheds. information directly from my APES teacher or mr. smedes :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
earth’s core
it is hot because of radioactive deacy
the most abundant metal at the core is iron
there is a solid inner core and a liquid outer core
order of earth’s layers
solid inner core —> liquid outer core —> mantle —> crust —> lithosphere
subduction zone
a subduction zone is when…
an oceanic plate which is denser, pushes beneath a less dense continental plate
the sinking oceanic plate is melted and magma rises up to the surface through the cracks in the zone. this forms a volcano
earthquakes along subduction zones release a lot energy
if they happens in the ocean…
it will cause a tsunami
the theory of plate tectonics
the lithosphere is divided into plates which are in constant motion
divergent plate boundaries
these occurs when plates move away from each other. these boundaries form rift valleys
common locations of divergent plate boundaries are: east african great rift valley, mid-atlantic ridge
convergent boundaries
occur when plates move towards each other
oceanic & continental
they form a volcano and trench along the subduction zone
common location: between the Nazca Plate and South American Plate
oceanic & oceanic
both of them push up and form trenches alongside, causing an undersea volcano to form and which eventually rises above sea-level and forms an island usually part of an island arc
common location: Pacific Plate south of Alaska (forms Aleutian Islands)
continental & continental
they both push up and form mountains
common location: the Himalayas in India
transform fault
the plates slide past each other
common location: San Andreas Fault (on west coast of California)
impacts of volcanoes
mostly negative:
they cause habitat destruction which disrupts the food web and leads to decreased biodiversity
habitat fragmentation disrupts the gene flow and leads to decreased biodiversity
ash and soot cause decreased visibility and respiratory diseases
sulfur emissions can cause acid rain which can decrease pH and kill low tolerance organisms which disrupts the food web and leads to a decrease in biodiversity
however one positive impacts is:
the weathering of lava leads to fertile soil
convergent earthquakes
plates suddenly collide
divergent earthquakes
plates suddenly move apart
transform earthquakes
plates slide past each other rapidly
how do you read a soil diagram?
you first read clay from the left, then sand from the bottom and lastly, silt from the right
physical weathering
rain, wind, waves
chemical weathering
oxidation, acid rain, lichen
biological weathering
plant roots, bacteria that produce organic acids
o horizon
organic matter or humus made up of mostly dry leaves. it is what is left over after the decomposition process done by worms, fungi, or bacteria.
a horizon
the topsoil or the mineral layer with a defined structure
b horizon
the subsoil with accumulated compounds leached from the a horizon
c horizon
made up of unconsolidated parent material such as weathered bed rock
what are the key functions of soil?
soil provides nutrients (NPK) and anchorage for plants
soil helps transform and decompose certain harmful chemicals and contaminants and filter them out from water
soil forms a habitat. plants depend on soil for water and nutrients and additionally many microorganisms like fungi and worms live in soil
troposphere
the uneven heating of the regions in the troposphere by the sun causes convection currents (hadley cells, ect.) those wind patterns move heat and moisture around the globe. this is the layer we live in.
stratosphere
the stratosphere is where the ozone layer is found which absorbs protects us from the ultraviolet radiation of the sun
thermosphere
auroras occur there because solar particles trapped there interact with oxygen and nitrogen resulting in colored displays of light
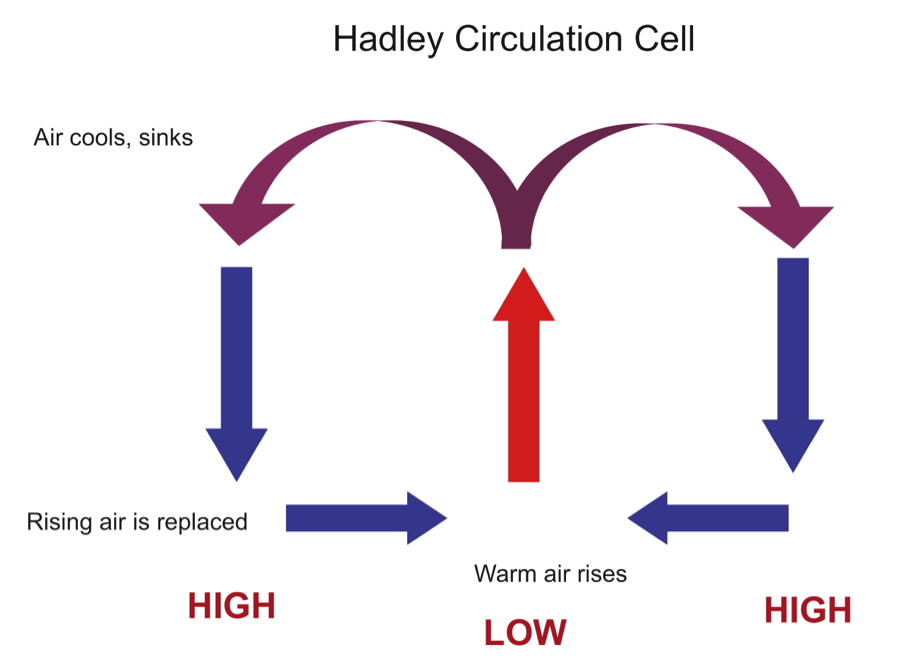
hadley cell
1) warm water evaporates and moves upwards because of its density
2)it undergoes adiabatic cooling and when it moves up it loses energy and slows down to condense which then forms clouds and eventually it rains
3) precipitation/condensation releases energy which results in latent heat release, an exothermic reaction
4) the now cold and dry air moves north and south
5) as the air gets closer to the earth, adiabatic heating occurs because of increases in pressure and the air warms again
because of this 30 degrees is usually dry hot air
coriolis effect
because of the earth’s rotation, circulating air is deflected to the right in the north and the left in the south
rain shadow effect
the cold arid air rises over a mountain it warms and dries when descending on the leeward side causing dry hot air and desert like conditions
the oceans role in weather
coastal weather tends to be more moderate because the ocean warms and cools more slowly than the atmosphere
evaporation
evaporation from the ocean (especially from the tropics) creates the most rain clouds which influences the blocations of wet and dry zones
westerlies and easterlies
westerlies are:
wind moving from west to east
latitude 30-60 north and south
easterlies are:
wind moving from east to west
latitude 0-30 north and south
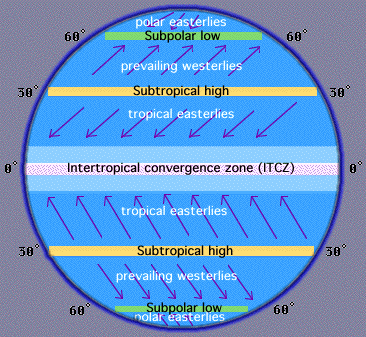
normal conditions
wind is going towards the equator from east to west
cold water along the west coast of South America
the wind blows hot water from the surface allowing upwelling to take place
precipitation is good in Australia and it is decently dry in South America
el niño (el niño souther oscillation, ENSO)
wind is flowing west to east
more hot water is being pushed towards South America which leads to a decrease in upwelling and more pooling of warm water
South America is wet and flooding while Australia is hot and dry usually causing forest/wild fires
la niña
an exaggeration of normal conditions
South america is drier than usual
more precipitation in in Australia which causes flooding
insolation
incoming solar radiation
insolation = solar radiation/area
the surface most perpendicular will have the highest concentration of solar radiation
the angle of incidence decreases moving towards the poles which increases the area of incidence, forcing insolation to decrease
fall equinox
september 22=23

spring equinox
march 20-21
summer solstice
june 20-22

winter solstice
december 21-22
thermohaline circulation
how differences in temperature and salt concentration push water down
thermohaline circulation helps spread heat from equator resulting in only a 30 degree difference from the poles
meridional overturning circulation
ocean currents that bring warm water north and cold water south
watersheds
the area of land water flows through
human impacts on watersheds
impacts:
building dams and rerouting rivers
land decomposition exacerbated by deforestation and its debris ends up in bodies of water
urbanization makes it so there are less pervious surfaces which means an increase in flooding and also unfiltered runoff which redirects polluted and contaminated water in the the watersheds
solutions to human impacts
solutions:
more pervious surfaces (pervious pavers, etc.)
water conservation
proper disposal of chemicals
less use of toxic pesticides and fertilizers
albedo effect
the ability of surfaces to reflect the sun
tree cover helps limit the albedo effect causing less evaporation of water