cognitive approach - social learning theory
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Social learning theory
developed by Bandura
people learn by observing how others behave, including the rewards and punishment they receive. We then imitate the behaviour.
indirect reinforcement
Models in SLT
someone who influences us (the person we observe)
people (especially children) are more likely to imitate the behaviour of people they identify with → role models
role models don’t have to be physically present in the environment
vicarious reinforcement
seeing a model rewarded/punished for doing a behaviour can influence our want to do that behaviour.
Bandura BoBo Doll Aim
whether children learn aggressive behaviors through observing adults, and whether gender impacts imitation.
Bandura BoBo Doll procedure
Children observed either an aggressive adult, a calm adult, or no adult, and were later observed to see if they imitated aggression.
Bandura BoBo Doll results
children in aggressive condition → more aggressive than children in non-agressive condition → children imitate aggressive behaviour
children also showed non imitative aggression - made up new ways of showing aggression e.g with toy gun
Physical aggression was most likely to be imitated by boys observing a male model
no difference between boys and girls in imitation of verbal agression
strengths of Bandura Bobo doll
measurement + causality : lab experiment + standardised procedure → isolates IV (can establish cause and effect) → increases validity + can be replicated
measurement - collected a lot of qualitative + quantitative data → can do statistical comparison between groups + enriches data
limitations of Bandura BoBo doll
lacks ecological validity → lab environment was artificial
low population validity → all pp were children from stanford nursery
researcher bias → Observers were aware of which condition each child was in
ethical issues → children might have imitated long term aggressive behaviour because of this
cognitive processes in SLT
attention : e.g authority, attractiveness of model or desirability of behaviour
retention : observer must remember behaviour
reproduction : observer must be able to carry out the behaviour
motivation : learner must want to replicate behaviour
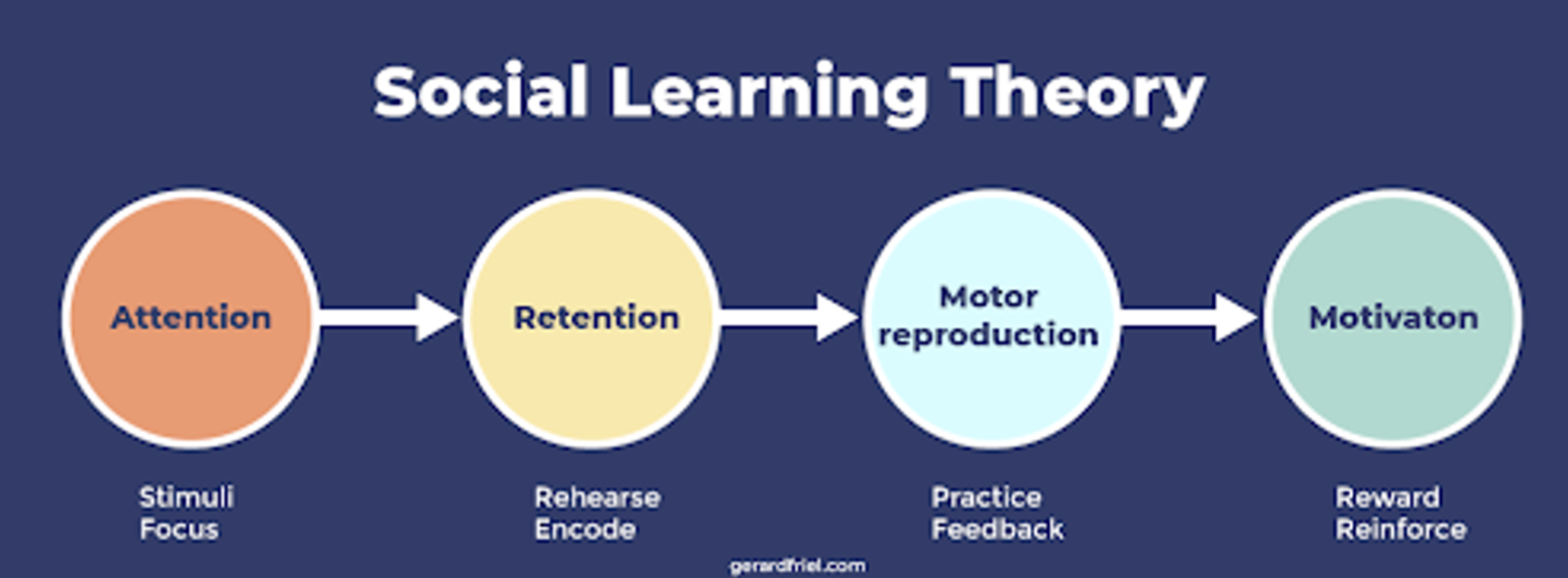
meditational processes
thought prior to imitation
we don’t automatically observe a behaviour and then imitate it
other important factors that affect SLT
consistency : model behaves consistently across situations → more likely to imitate
identification with model : model is like observer → more likely to imitate
liking the model : like → more likely to imitate
self efficacy of observer : high → more likely to imitate behaviour
strengths of SLT
can be used to explain a wide range of behaviours
Bandura showed variables that can increase/decrease likelihood of imitation → increases predictive power
has biological support → modern biological research indicates that mirror neurons play an important role in learning
weaknesses of SLT
difficult to test under naturalistic conditions (difficult to control extraneous variables)
constructs such as motivation, self-effiacy and attention are difficult to measure
strong bias towards nurture side of argument.