Week 5 - Blood brain barrier
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts related to the central nervous system including the blood-brain barrier, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), meningeal structures, and their respective functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
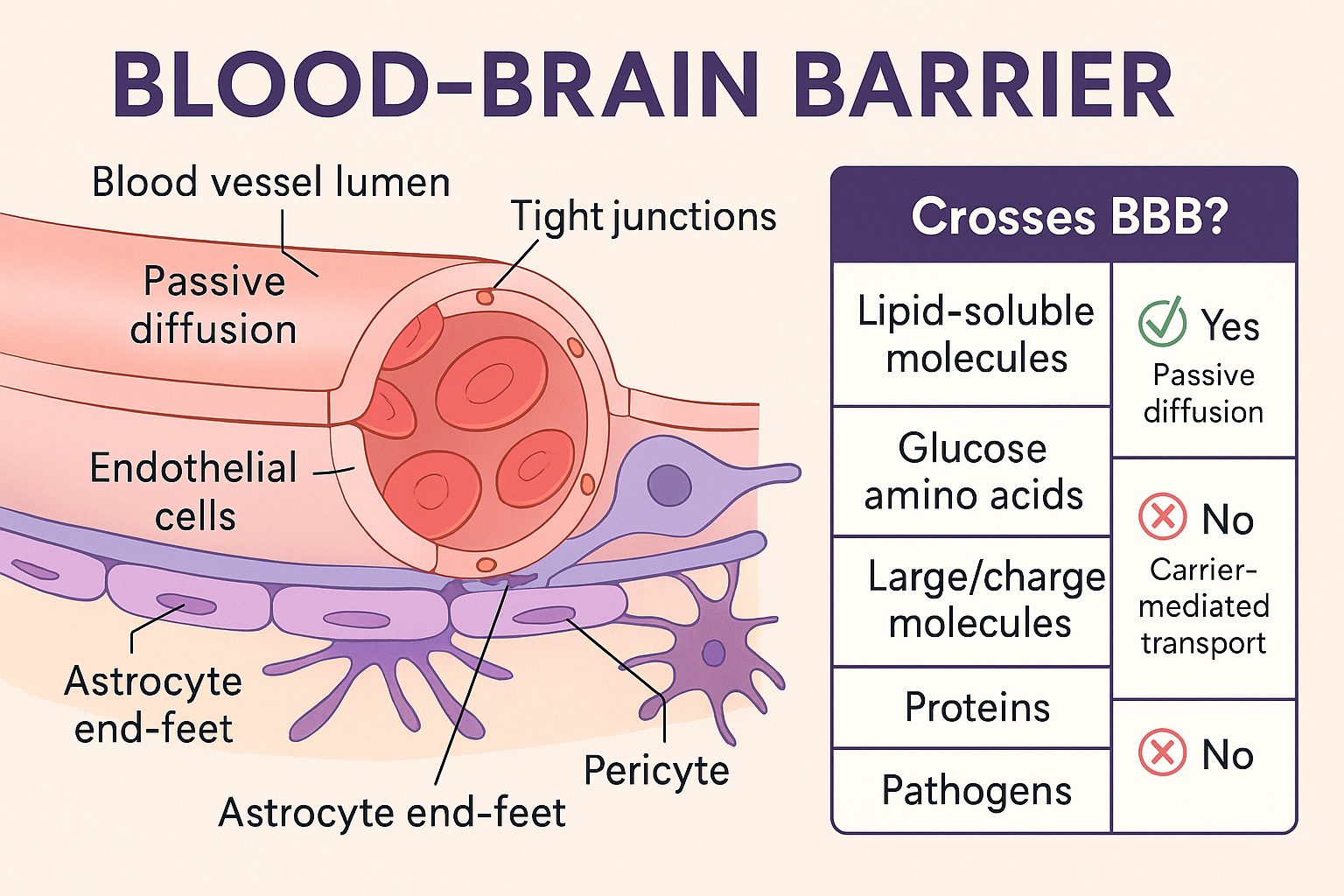
What forms the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)?
Continuous endothelial cells with tight junctions and astrocytes.
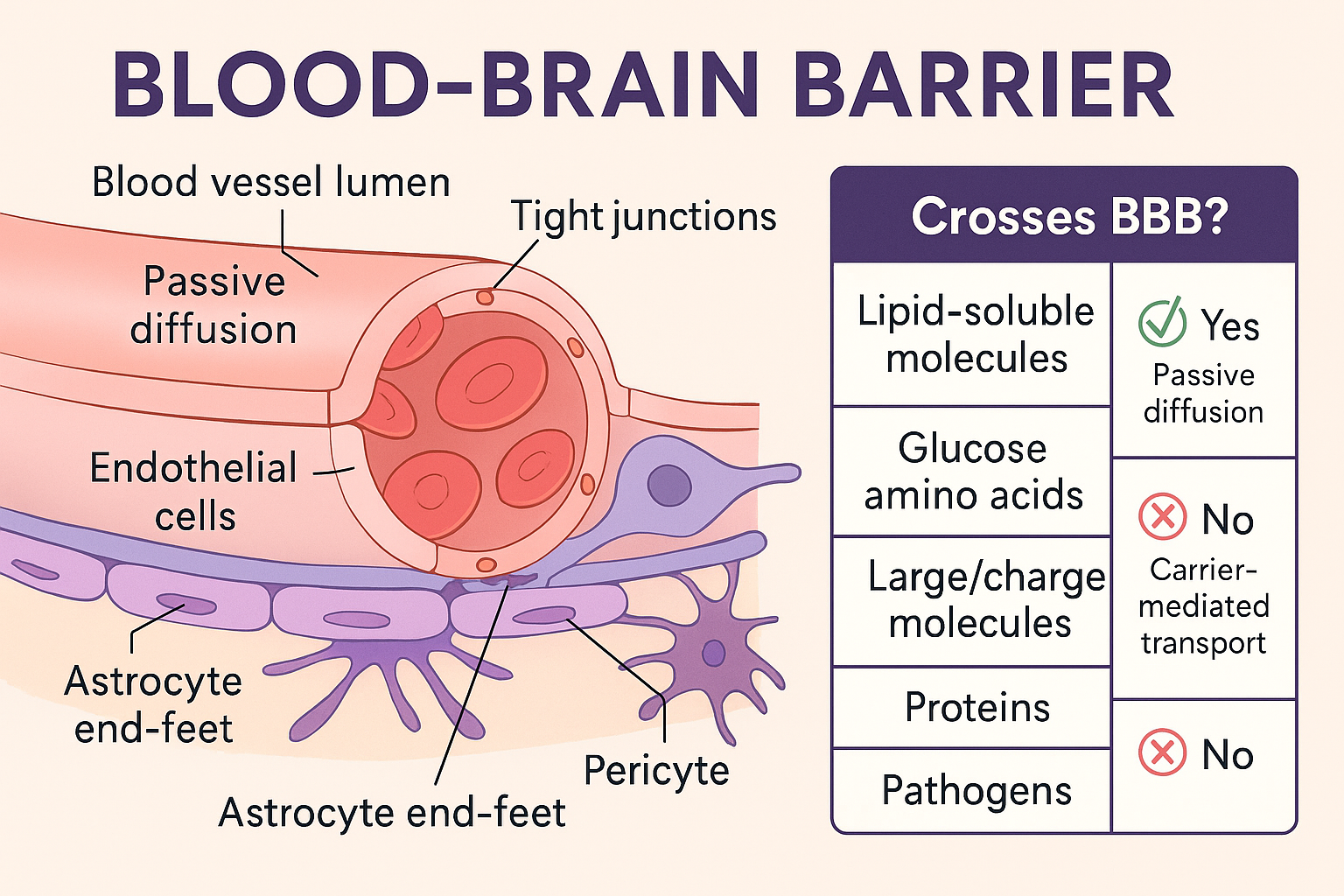
What substances cross the BBB easily?
Water, CO₂, O₂, and hydrophobic substances.
How do glucose and amino acids cross the BBB?
Via membrane transport mechanisms.
What substances cannot cross the BBB?
Large proteins and peptides without special transport.
Which cells line capillaries in the choroid plexus?
Ependymal cells.
How much CSF is present at any time?
Approximately 150 mL.
How much CSF is produced daily?
Approximately 500 mL.
Where is CSF returned?
Into systemic circulation via arachnoid villi.
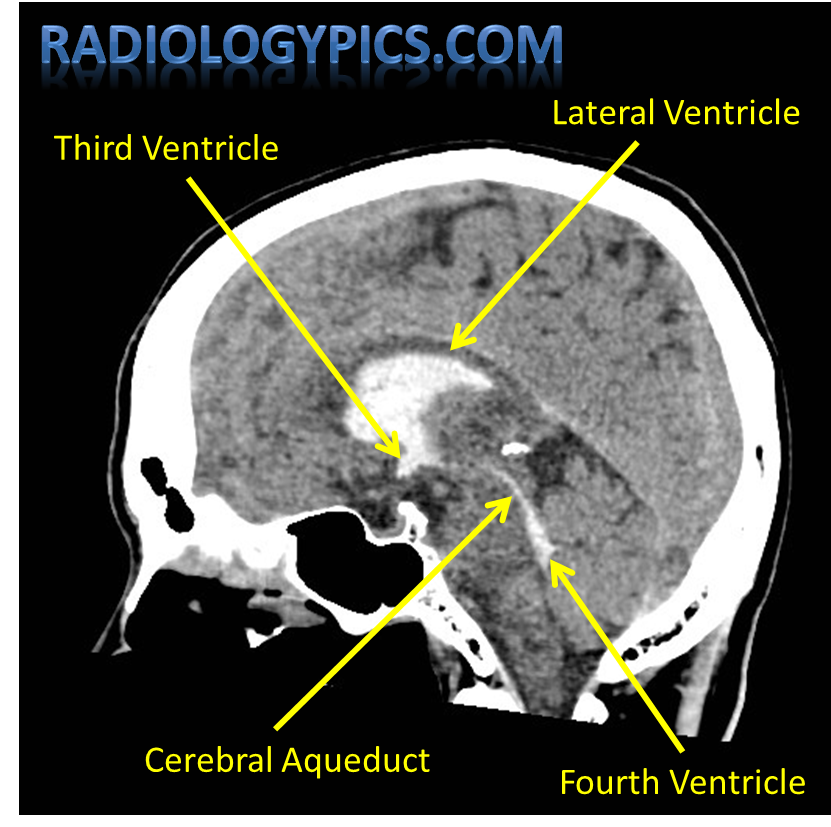
Where are the lateral ventricles located?
In the cerebral hemispheres.
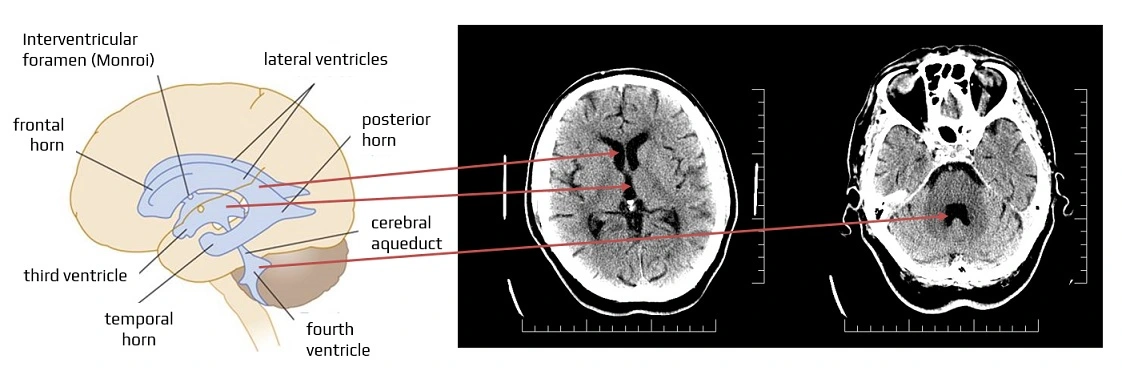
What connects the lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricle?
Interventricular foramen of Monro.
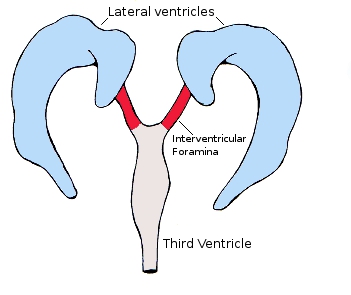
Where is the 3rd ventricle located?
Between the thalamus
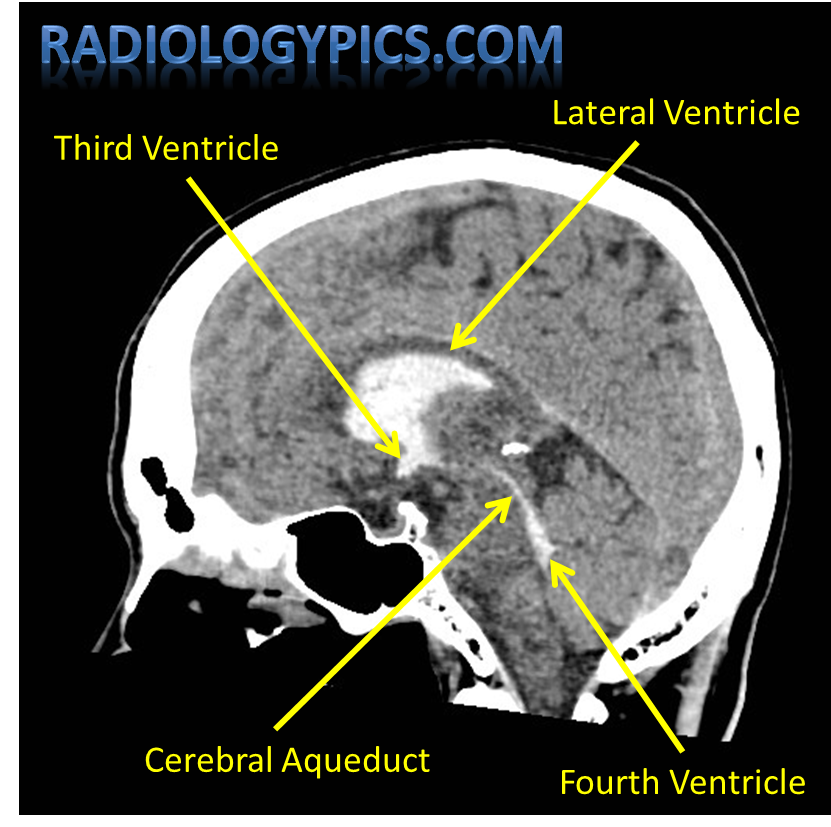
Which structure connects the 3rd to the 4th ventricle?
Cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius.
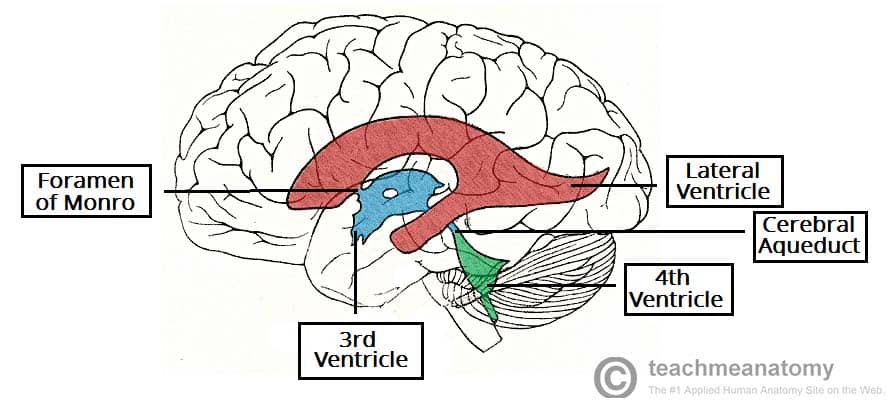
Where is the 4th ventricle located?
Between the pons and cerebellum.
How does CSF exit the 4th ventricle?
Via lateral and median apertures.
The 4th ventricle continues into what structure?
Central canal of the spinal cord.
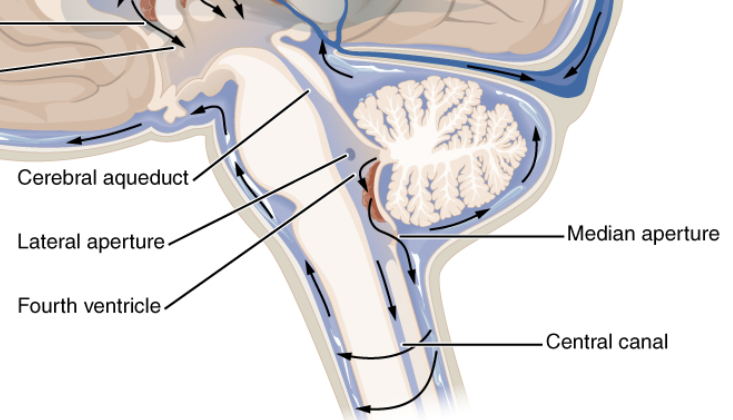
Name one metabolic role of CSF.
Facilitates exchange of nutrients and wastes.
How does CSF protect the brain?
Provides shock absorption.
Why is CSF important for neurons?
Maintains optimal chemical environment.
What are the three meningeal layers?
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater.
Which dura mater layer attaches to the skull?
Periosteal layer.
Which meningeal layer clings to the brain?
Pia mater.
What space contains CSF?
Subarachnoid space.
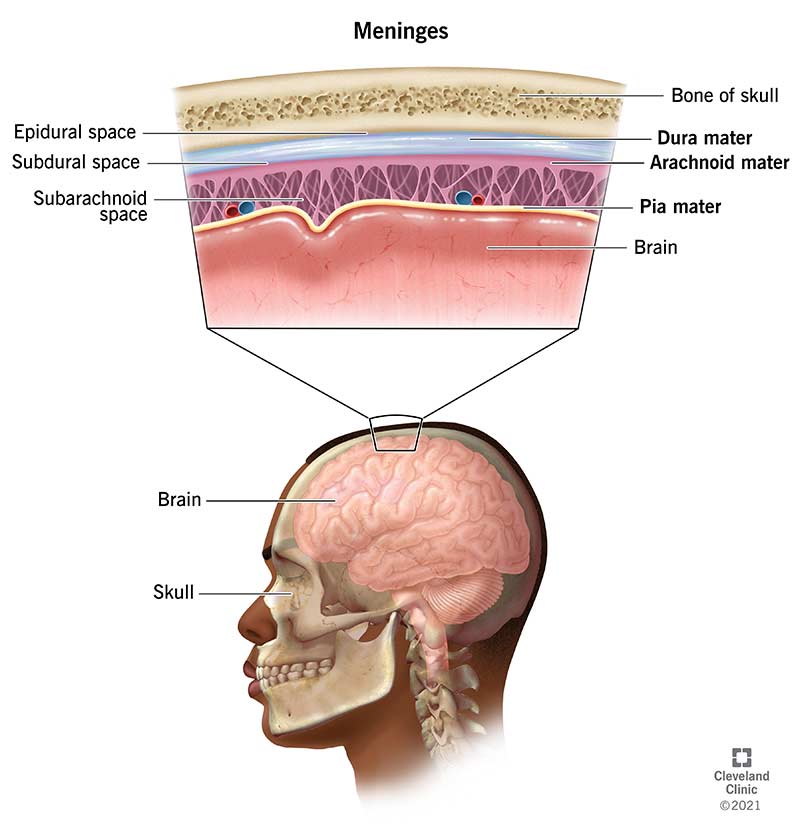
What is found in the epidural space in the spine?
Fat and venous plexus.
Where is a lumbar puncture performed?
L3/L4 into the subarachnoid space.
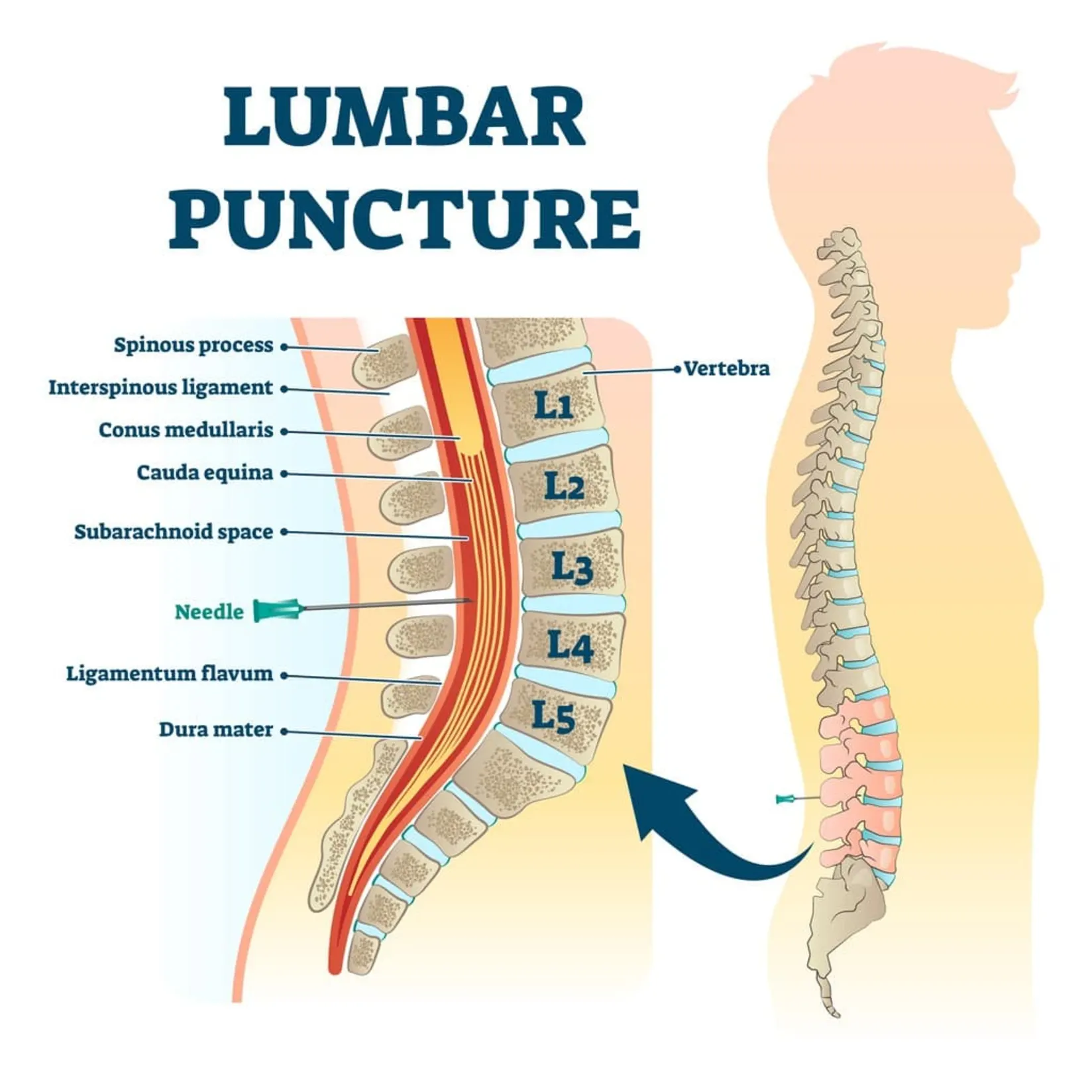
Why not higher than L2 for lumbar puncture?
The spinal cord ends at L2.
What are uses of lumbar puncture?
Test CSF, administer drugs, measure pressure.
What is the purpose of an epidural injection?
Regional anesthesia.
What does the falx cerebri separate?
Cerebral hemispheres.
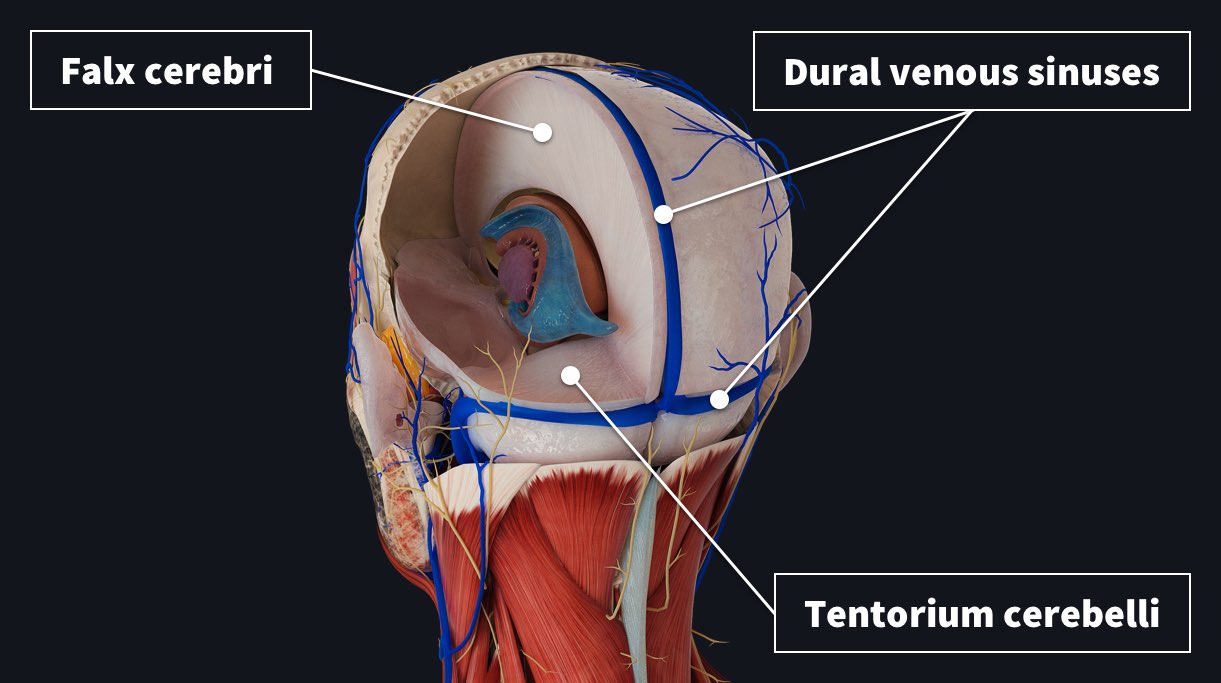
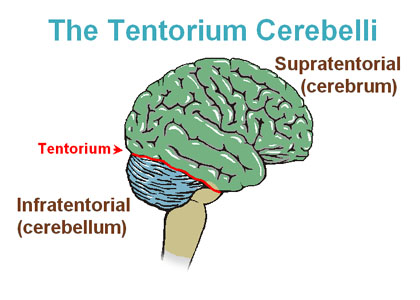
What does the tentorium cerebelli separate?
Cerebrum from cerebellum.
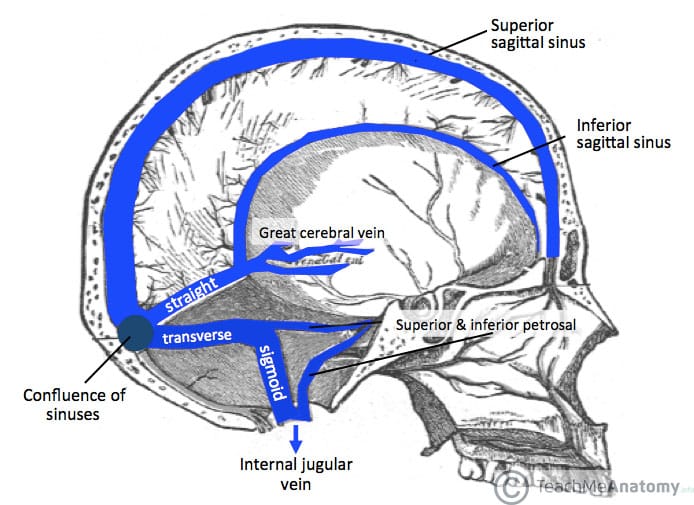
What do dural venous sinuses collect?
Venous blood and CSF.
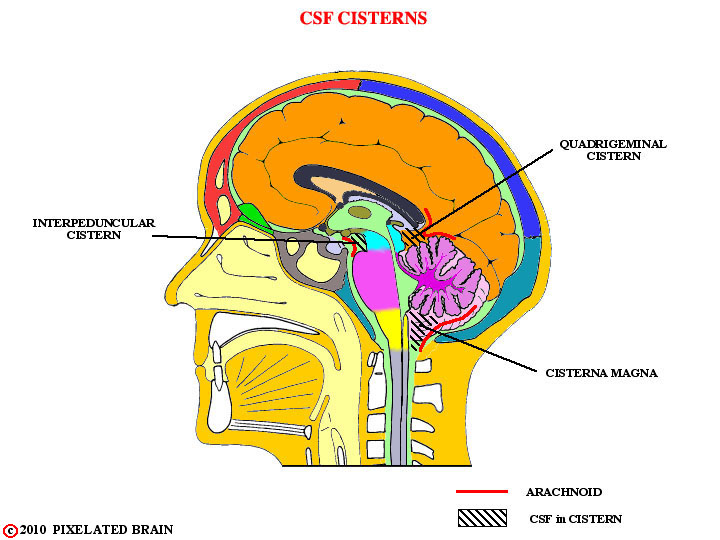
What are subarachnoid cisterns?
Enlarged CSF-filled cavities.
Which cistern contains the pineal gland and the vein of Galen?
Quadrigeminal cistern.
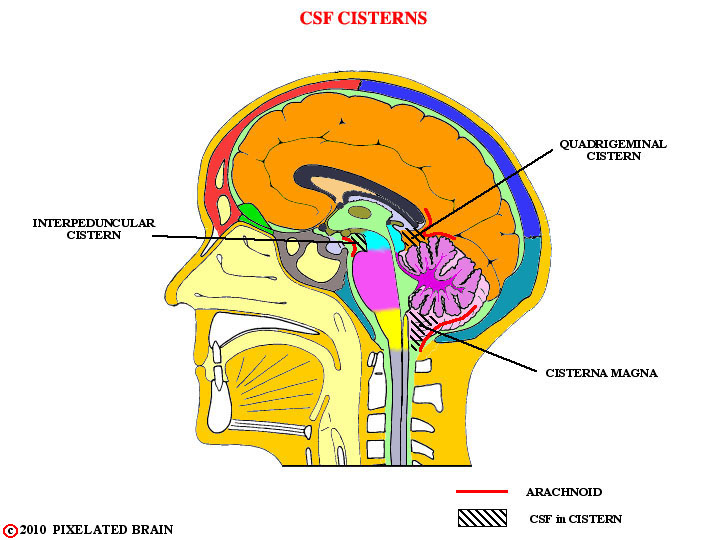
Which cistern is the largest?
Cisterna magna.
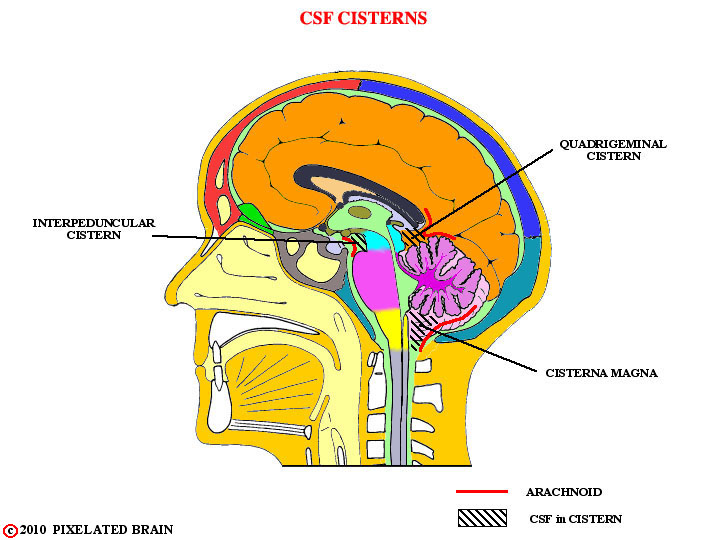
Which cistern contains the Circle of Willis?
Interpeduncular cistern.
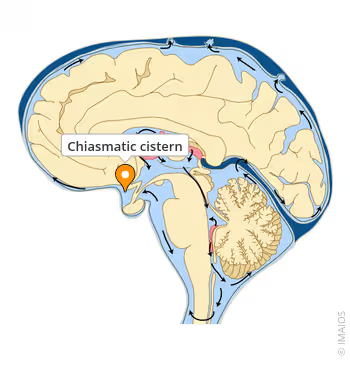
Which cistern contains the optic chiasm?
Chiasmatic cistern.
Which cistern contains the basilar artery?
Prepontine cistern.
Where do dural venous sinuses ultimately drain?
Internal jugular vein.
Which sinus surrounds the pituitary?
Cavernous sinus.
Why is the cavernous sinus clinically important?
It connects to facial veins, increasing infection risk.
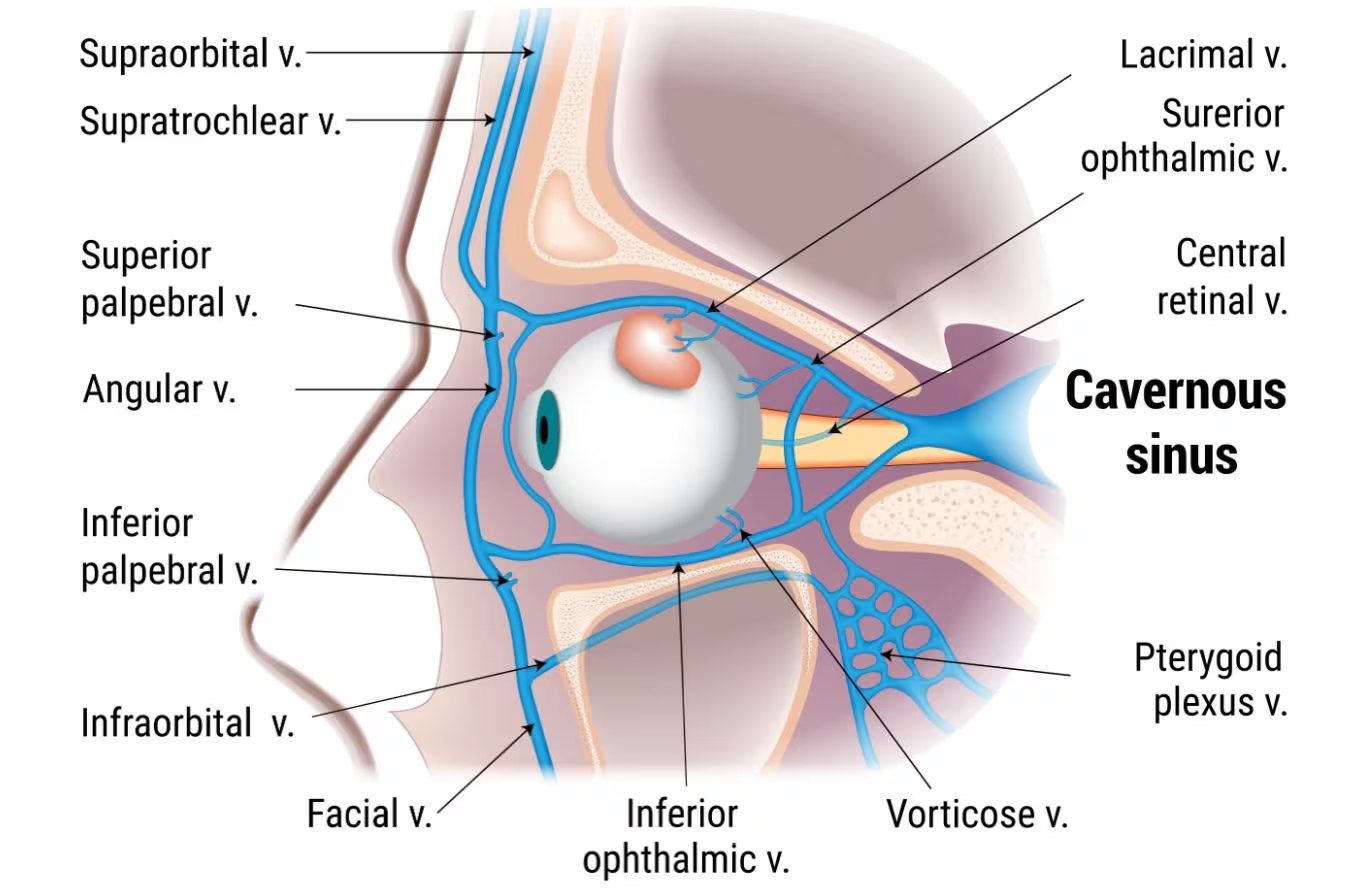
What is the 'danger area' of the face?
Region where the facial vein drains into the cavernous sinus, risking meningitis.