Biopsychology 2- neurons and synaptic transmission
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the three different types of neurons?
Motor, sensory, relay
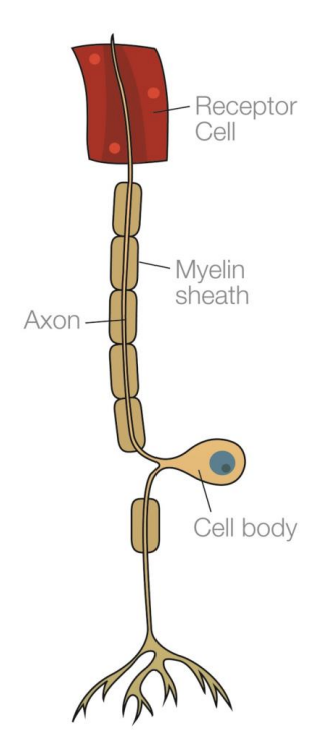
Where are sensory neurons found?
Receptor cells
What do sensory neurons do?
Carry nerve impulses to the spinal cord and brain.
What are the nerve impulses from sensory neurons translated into?
Sensations e.g. vision and touch.
Where do some sensory neurons stop and why?
Spinal cord as it allows for quick reflex actions.
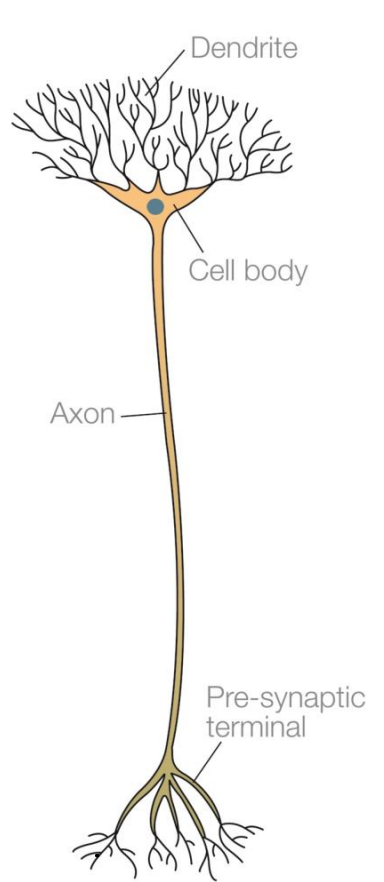
Where are relay neurons found?
Between sensory input and motor output/ response.
Where do relay neurons travel to?
The brain and spinal cord.
What do relay neurons do?
Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate.
Where are motor neurons found?
In the central nervous system (CNS).
What do motor neurons do?
Control muscle movements.
What happens when motor neurons are stimulated?
They release neurotransmitters that bind to the receptors on muscles to trigger a response.
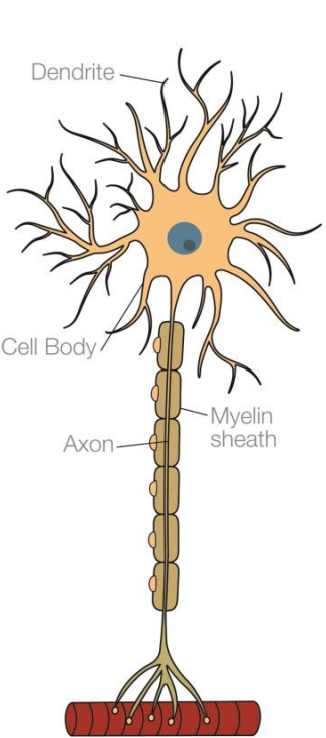
What does a motor neuron look like?
What does a sensory neuron look like?
What does a relay neuron look like?
What do the dendrites in a neuron do?
Receive signals from other neurons or from sensory receptor cells.
Where are dendrites usually connected?
To the cell body.
What is the axon in a neuron and what does it do?
It is a long slender fibre that carries nerve impulses, in the form of an electrical signal known as action potential.
What is the myelin sheath in a neuron and what does it do?
It is a fatty layer which surrounds the axon and acts as an insulator so the electrical impulses can travel faster along the axon.
What does the axon terminal in a neuron do?
Connects the neuron to other neurons (or directly to organs), using a process called synaptic transmission.
Define synaptic transmission.
The process by which one neuron communicates with another across a synapse using chemical neurotransmitters.
What is a synaptic cleft/ gap?
The tiny gap between the presynaptic neuron and the postsynaptic neuron where neurotransmitters are released.
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical substance that transmits signals across the synaptic cleft (e.g., serotonin, dopamine).
What are vesicles?
Small sacs in the presynaptic terminal that store neurotransmitters until released.
What are excitatory neurotransmitters?
A neurotransmitter that increases the likelihood of the postsynaptic neuron firing (e.g., glutamate).
What are inhibitory neurotransmitters?
A neurotransmitter that decreases the likelihood of the postsynaptic neuron firing (e.g., GABA).
What is summation?
The combination of excitatory and inhibitory inputs that determines whether the postsynaptic neuron will fire.
What are the strengths of the theory of neurons and synaptic transmission?
Scientific & Objective Evidence
Neuronal processes studied with EEGs, fMRI, single-neuron recordings → high validity.
Real-World Application
Explanation of neurotransmission underpins drug treatments (e.g., SSRIs increase serotonin availability).
What are the limitations of the theory of neurons and synaptic transmission?
Biological Reductionism
Behaviour explained solely through neurons/NTs oversimplifies disorders with social or cognitive influences.
Overreliance on Animal Research
Much synaptic research comes from animals → issues with generalisability.
Correlational Evidence
Neurotransmitter imbalance research often correlational (e.g., serotonin & depression) → cannot establish cause-effect.